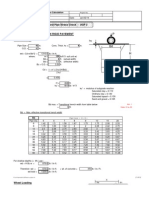
Stress Relaxation Notes Procedure Model Rohr2
Diunggah oleh
Sakshi AgrawalDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Stress Relaxation Notes Procedure Model Rohr2
Diunggah oleh
Sakshi AgrawalHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
The analysis of stress relaxation due to internal creep
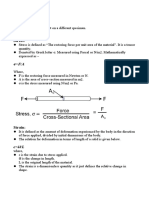
Usually, the analysis of stress relaxation is performed only to estimate the effects on the supports and nozzle connections. Note that at elevated temperatures if the deformation is constant, the stress resisting that deformation will decrease with time. Creep is permanent deformation over time; fatigue is crack propagation over time. Both occur due to applied loads and both can lead to failure. Creep is characterized by looking at the elongation of the sample; fatigue, by elongation of the crack.
Creep is a constant stress situation that is below yield. It is extremely prevalent in higher temperature conditions. Creep is usually tested with a wire of a given size that has a constant load and the elongation is measured over time. Be careful not to mistake creep with stress relaxation. Fatigue is due to cyclic/alternating loading that can be at any stress level. The loading is repeated until the number of cycles imparted causes failure. This is expressed in S-N curves for particular materials. A material is usually said to have an infinite fatigue endurance limit if it can withstand 10^6 cycles at the particular alternating stress level.
Modeling Relaxation in Rohr2
Since creep relaxation is a very slow process, the analysis can be limited to one hot load case in which the system will remain for most of the operation time.
To generate only the thermal load case, the dead load contribution should be removed. For this reason the factor of -1 is given for the load case Dead load (refer to the snapshot) on the following page. In case of a non-linear calculation of the thermal expansion one would usually create a load case Operating which includes thermal expansion but also gravity so that the friction on the supports can be determined correctly. Therefore, one first needs to remove the gravity effect from the combined load
case Operating to create the temperature effect alone, i.e., the load case Thermal.
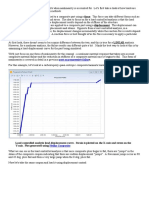
Snapshot showing the generation of the load case Relaxation Note that the operation with RELX changes the sign of the loads but does not operate on the anchor movements.
Thus, it is assumed that stress relaxation does not affect the anchor movements only that the loads have their sign changed.
Now one needs to create a new load case StressRelease having the combination between Relaxation and Dead load which corresponds to the system after the long hot operation and then cooling down including the weight.
Finally, the existing superposition load case Operation is modified so that it also includes (takes into account) the relaxed state (StressRelease). This is done by first moving the load cases Relaxation and StressRelease in the position above Operation. Then, the load case Operation is selected and the key Edit is pressed to open the window with the assigned load cases. Afterwards, the load case StressRelease is added in the list.
The load case StressRelease can also be include in the output table. This can be achieved by selecting the option Output table. Then, select New and specify the load case (StressRelease) to be added in the table.
The above snapshot shows the load case StressRelease included in the output table.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- LAGRANGIAN RELAXATION WITH GAMSDokumen5 halamanLAGRANGIAN RELAXATION WITH GAMSCESARPINEDABelum ada peringkat
- OKE HDPE DesignConsiderationsDokumen24 halamanOKE HDPE DesignConsiderationsparbu kayanganBelum ada peringkat
- Stress Relief and Relaxation ScriptDokumen3 halamanStress Relief and Relaxation Scriptimtheobscure2Belum ada peringkat
- Texto Guía Del Curso Integraph Cadworx 2016Dokumen20 halamanTexto Guía Del Curso Integraph Cadworx 2016adolfocles100% (1)
- Pipe 36pulg Stress Analysis ReportDokumen3 halamanPipe 36pulg Stress Analysis ReportJhony MedranoBelum ada peringkat
- New Why To Use A Spring SupportDokumen9 halamanNew Why To Use A Spring SupportAmarKumarBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorialcaesarsii 130318231300 Phpapp01Dokumen400 halamanTutorialcaesarsii 130318231300 Phpapp01Nayeem UddinBelum ada peringkat
- Power Pint - MPPE-AdvancedDokumen72 halamanPower Pint - MPPE-AdvancedDFW2030Belum ada peringkat
- Calculation of Brine PropertiesDokumen26 halamanCalculation of Brine PropertiesacfernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Pipe Flow ExpertDokumen7 halamanPipe Flow ExpertDesnantaGandhaBelum ada peringkat
- Stress Analysis of Piping Systems with Caesar II ProgramDokumen22 halamanStress Analysis of Piping Systems with Caesar II ProgramDaniel FullerBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid MechDokumen205 halamanFluid MechMahesh Ramteke100% (1)
- Process Measurement and Control InstrumentDokumen121 halamanProcess Measurement and Control InstrumentEvans HopeBelum ada peringkat
- Surya Namaskar BenefitsDokumen3 halamanSurya Namaskar BenefitsHemanth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- 5.00 A Conundrum The Difficulties of Pipe Stress Analysis For Cold PipesDokumen17 halaman5.00 A Conundrum The Difficulties of Pipe Stress Analysis For Cold Pipesprabu2001Belum ada peringkat
- Section 13915-SpecDokumen25 halamanSection 13915-SpecMrbudakbaekBelum ada peringkat
- Determining The Pressure Drop To Be Used in A Control Valve Sizing CalculationDokumen2 halamanDetermining The Pressure Drop To Be Used in A Control Valve Sizing CalculationzhangamecBelum ada peringkat
- Design CalculationDokumen3 halamanDesign CalculationRavi AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Bettis Service Instructions For Hd732-s HydraulicDokumen27 halamanBettis Service Instructions For Hd732-s Hydraulicrangga advBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Refrigeration &gas LawsDokumen12 halamanPrinciples of Refrigeration &gas LawshoahongtrangBelum ada peringkat
- CAESAR II Shortcut KeyDokumen3 halamanCAESAR II Shortcut KeyTamil SelvanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5-Basic ThermodynamicDokumen19 halamanChapter 5-Basic ThermodynamicjaechaosBelum ada peringkat
- Relief Valve - TypesDokumen2 halamanRelief Valve - Typesyushveer002Belum ada peringkat
- 5.plant Layout - Relief SystemDokumen7 halaman5.plant Layout - Relief Systemhalder_kalyan9216Belum ada peringkat
- Easy Guide 14Dokumen37 halamanEasy Guide 14Trilobite3000Belum ada peringkat
- Surge Analysis: What Is Pressure Surge?Dokumen2 halamanSurge Analysis: What Is Pressure Surge?Yang Gul Lee100% (1)
- ThicknessDokumen2 halamanThicknessmohmecirdiBelum ada peringkat
- NPSH - Net Positive Suction HeadDokumen9 halamanNPSH - Net Positive Suction Headlokeshjaddu6Belum ada peringkat
- 9.line Size & Wall ThicknessDokumen48 halaman9.line Size & Wall ThicknessClark PlúaBelum ada peringkat
- Table of Contents and Design BasisDokumen17 halamanTable of Contents and Design BasisEbby OnyekweBelum ada peringkat
- Steel Plate Shear WallDokumen43 halamanSteel Plate Shear WallMark Magadia IpaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 2+3 Pipeway EnggDokumen61 halamanLecture 2+3 Pipeway EnggJaveria SheikhBelum ada peringkat
- Avoid Pressure-Relief System PitfallsDokumen8 halamanAvoid Pressure-Relief System PitfallschublackBelum ada peringkat
- Ansys FluidsDokumen232 halamanAnsys Fluidscapitan55Belum ada peringkat
- Webinar Relief Valves 1Dokumen20 halamanWebinar Relief Valves 1einsten777Belum ada peringkat
- Pro II 8.0 User GuideDokumen390 halamanPro II 8.0 User GuideAngel Quijano ArmengolBelum ada peringkat
- Drawing Extraction Within Framework PlusDokumen6 halamanDrawing Extraction Within Framework PlusShahfaraz AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Paldex Seminar-2 - Stress AnalysisDokumen75 halamanPaldex Seminar-2 - Stress AnalysisKumar Kote100% (1)
- Crude Oil Pipeline Calculation PDFDokumen104 halamanCrude Oil Pipeline Calculation PDFYaserBelum ada peringkat
- Cadworx PidDokumen341 halamanCadworx Pidghallky2011Belum ada peringkat
- SV Pilot Crosby Type-93Dokumen22 halamanSV Pilot Crosby Type-93MarcelocrossBelum ada peringkat
- GCM Guided Relaxation Peaceful Retreat PDFDokumen1 halamanGCM Guided Relaxation Peaceful Retreat PDFanuBelum ada peringkat
- In Line MixingDokumen4 halamanIn Line MixingKemas Ganesha MahendraBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Topic 2 2020 RevisedDokumen3 halamanTutorial Topic 2 2020 RevisedTara PillayBelum ada peringkat
- Siphon Purge SystemDokumen29 halamanSiphon Purge SystemMuhammad SaadullahBelum ada peringkat
- Ki BreathingDokumen66 halamanKi BreathingArief AminBelum ada peringkat
- SolidPlant P&ID Training ManualDokumen116 halamanSolidPlant P&ID Training ManualAli MasterBelum ada peringkat
- Liquid Recirculation System-2Dokumen7 halamanLiquid Recirculation System-2Behnam AshouriBelum ada peringkat
- 08a PDFDokumen36 halaman08a PDFProcess EngineerBelum ada peringkat
- Joule Thomson Expansion J TDokumen6 halamanJoule Thomson Expansion J TISLAM I. Fekry100% (2)
- 521taaai 2Dokumen7 halaman521taaai 2Erwin FerdianBelum ada peringkat
- How Do Things Get Colder?Dokumen4 halamanHow Do Things Get Colder?Zbair100% (2)
- AspenDokumen156 halamanAspenapi-3750488Belum ada peringkat
- Buckling Analysis: Concept & ProcedureDokumen20 halamanBuckling Analysis: Concept & ProcedureDeepak ChachraBelum ada peringkat
- Analyzing Sustained Pipe Stress with COADE's Hot Sustained SolutionDokumen6 halamanAnalyzing Sustained Pipe Stress with COADE's Hot Sustained SolutionshaffetiBelum ada peringkat
- Theories of Elastic FailureDokumen15 halamanTheories of Elastic FailurejaishowBelum ada peringkat
- Different Type of StressDokumen12 halamanDifferent Type of Stressreach_arindom100% (1)
- Autodesk Simulation CommunityDokumen2 halamanAutodesk Simulation CommunityRanvier SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Richmond Stress NotesDokumen110 halamanRichmond Stress Notesmsaad2100% (2)
- Lab MMTDokumen30 halamanLab MMTSaad khanBelum ada peringkat
- Strength-of-Materials-by-James E. Boyd PDFDokumen315 halamanStrength-of-Materials-by-James E. Boyd PDFKolawolejt100% (1)
- Shift Printer On Right Side Shelf: Studyelevation06062015-Comments PDFDokumen1 halamanShift Printer On Right Side Shelf: Studyelevation06062015-Comments PDFSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Livingroomelevations 3 CommentsDokumen1 halamanLivingroomelevations 3 CommentsSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Provide Glass Doors As Before.: Crockeryunit06062015-Comments PDFDokumen1 halamanProvide Glass Doors As Before.: Crockeryunit06062015-Comments PDFSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Water Hammer ThesisDokumen117 halamanWater Hammer Thesishobbsie91Belum ada peringkat
- Pressure Vessel Design ASME GuideDokumen137 halamanPressure Vessel Design ASME Guidesmasudbd100% (15)
- April 182007 FfspresentationDokumen20 halamanApril 182007 FfspresentationSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Masterbedroomelevation06062015 CommentsDokumen1 halamanMasterbedroomelevation06062015 CommentsSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Livingroomelevations 2 VOIDDokumen1 halamanLivingroomelevations 2 VOIDSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- April 182007 FfspresentationDokumen20 halamanApril 182007 FfspresentationSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Trans Basic ConceptsDokumen13 halamanTrans Basic ConceptsSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal Stresses - Advanced Theory and Applications: Printed BookDokumen1 halamanThermal Stresses - Advanced Theory and Applications: Printed BookSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- April 182007 FfspresentationDokumen20 halamanApril 182007 FfspresentationSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- EPC Project Execution PDFDokumen206 halamanEPC Project Execution PDFSakshi Agrawal94% (33)
- Pressure Vessel Design ASME GuideDokumen137 halamanPressure Vessel Design ASME Guidesmasudbd100% (15)
- Plan July 2014 HolidayDokumen1 halamanPlan July 2014 HolidaySakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Proc 1Dokumen3 halamanProc 1Sakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Design Envelope For GRP Pipe As Per ISO 14692Dokumen5 halamanDesign Envelope For GRP Pipe As Per ISO 14692Ashitava Sen100% (1)
- StartupDokumen1 halamanStartupSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- AcknowledgementsDokumen1 halamanAcknowledgementsindigenaforeverBelum ada peringkat
- DisclaimerDokumen1 halamanDisclaimerSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Gask 7Dokumen1 halamanGask 7indigenaforeverBelum ada peringkat
- Inspection Manual For PipingDokumen183 halamanInspection Manual For PipingMartin Zaballa100% (3)
- Flap Co1Dokumen1 halamanFlap Co1Sakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Stress Analysis ManualDokumen39 halamanStress Analysis ManualSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- FKT NiehII Statik GRP StressDokumen98 halamanFKT NiehII Statik GRP StressSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Steam TableDokumen256 halamanSteam TableSakshi Agrawal100% (4)
- Design of Steam Piping System Including Stress AnalysisDokumen128 halamanDesign of Steam Piping System Including Stress Analysissaravootj100% (4)
- UserManualForSupportMTOProgram From PDMSDokumen13 halamanUserManualForSupportMTOProgram From PDMSSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Underground Pipe Stress CheckDokumen6 halamanUnderground Pipe Stress CheckSakshi AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Composites Intro To AerospaceDokumen40 halamanComposites Intro To AerospacegnitinBelum ada peringkat
- Staad Pro-Series 11-Wind Load AnalysisDokumen35 halamanStaad Pro-Series 11-Wind Load AnalysisV.m. Rajan100% (3)
- Design of A Simple Building Using NBCC - IBCDokumen21 halamanDesign of A Simple Building Using NBCC - IBCCuong Ho83% (6)
- Federal Highway AdministrationDokumen13 halamanFederal Highway AdministrationAlfredo A LopezBelum ada peringkat
- 2 A Performance-Based Approach To Security and Blast-Mitigating Building DesignDokumen22 halaman2 A Performance-Based Approach To Security and Blast-Mitigating Building DesignVulebg VukoicBelum ada peringkat
- JHJBJDokumen5 halamanJHJBJarvindBelum ada peringkat
- Scaffold EnglishDokumen11 halamanScaffold Englishbanigx0xBelum ada peringkat
- Static Load Test Service DetailsDokumen2 halamanStatic Load Test Service DetailsMarcelo MotaBelum ada peringkat
- Structural Reliability (Complete)Dokumen101 halamanStructural Reliability (Complete)sofia_kotsiriBelum ada peringkat
- Design For Cyclic LoadingDokumen16 halamanDesign For Cyclic Loadingbanno fakeBelum ada peringkat
- Installation Manual Sartorius Load Cell Type PR6201Dokumen157 halamanInstallation Manual Sartorius Load Cell Type PR6201Denny19900% (1)
- Floating Structures ResearchDokumen37 halamanFloating Structures ResearchAbrar MohiuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Midas Civil2013v3Dokumen18 halamanMidas Civil2013v3silvereyes18Belum ada peringkat
- Design Reports SlabDokumen26 halamanDesign Reports Slabarjun 2008Belum ada peringkat
- Design LoadDokumen20 halamanDesign LoadJeffrey Carlo Viduya AgliamBelum ada peringkat
- SEO Pile Foundation DesignDokumen9 halamanSEO Pile Foundation DesignSudeep JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Wall Footing DesignDokumen102 halamanWall Footing DesignAUNGPSBelum ada peringkat
- Staad Analysis For StackDokumen39 halamanStaad Analysis For StackABIDEEN BAMNEBelum ada peringkat
- Pile Design To BS EN 1997-1:2004 (EC7) and The National AnnexDokumen63 halamanPile Design To BS EN 1997-1:2004 (EC7) and The National AnnexPanchadcharam PushparubanBelum ada peringkat
- Code of Practice BS 7072 1989Dokumen16 halamanCode of Practice BS 7072 1989Adel Jeddi100% (1)
- Fatigue TestingDokumen7 halamanFatigue Testingjazille22100% (1)
- C-857-14 Minimum Design Loading PDFDokumen6 halamanC-857-14 Minimum Design Loading PDFMichael VanWagenenBelum ada peringkat
- Ncma Tek: Empirical Design of Concrete Masonry Walls TEK 14-8ADokumen6 halamanNcma Tek: Empirical Design of Concrete Masonry Walls TEK 14-8Ashamimzubery1969Belum ada peringkat
- Understanding Why Balcony Drainage Often FailsDokumen4 halamanUnderstanding Why Balcony Drainage Often Failsabdul khaderBelum ada peringkat
- Aveng INFRASTRUCTURE Brochure 11-14 - Technical DataDokumen2 halamanAveng INFRASTRUCTURE Brochure 11-14 - Technical DataChristineNyambeBelum ada peringkat
- Structural Design of Box CulvertsDokumen24 halamanStructural Design of Box Culvertsdanilo m.sampagaBelum ada peringkat
- Design CriteriaDokumen4 halamanDesign CriteriaEdmond Dellomas TulipanBelum ada peringkat
- Sabp L 006 PDFDokumen8 halamanSabp L 006 PDFWBelum ada peringkat
- Tackles and Sheave AssemblyDokumen10 halamanTackles and Sheave AssemblyCashew PandaramBelum ada peringkat
- Structural Analysis and Design of Steel TrussDokumen22 halamanStructural Analysis and Design of Steel TrussSandip BudhathokiBelum ada peringkat