Limit Es
Diunggah oleh
rrvvHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Limit Es
Diunggah oleh
rrvvHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
LMITES Y CONTINUIDAD Lic. Anglica E.
Choqueluque Romn
1
LIMITES
Teorema (unicidad del Lmite): Si el lmite de una funcin real en a existe, entonces este
lmite es nico.
Propiedades de los Lmites
Si ) x ( g Lim y ) x ( f Lim
a x a x
existen, entonces
IR k , a x Lim y k k Lim ) i
a x a x
e = =
| | ) x ( g Lim ) x ( f Lim ) x ( g ) x ( f Lim ) ii
a x a x
a x
=
| | IR k ), x ( f Lim k ) x ( f k Lim ) iii
a x
a x
e =
| | ) x ( g Lim * ) x ( f Lim ) x ( g * ) x ( f Lim ) iv
a x a x
a x
=
v)
) x ( g Lim
) x ( f Lim
) x ( g
) x ( f
Lim
a x
a x
a x
= ; 0 ) x ( g Lim
a x
=
vi) | | | | IR p ; ) x ( f Lim ) x ( f Lim
p
a x
p
a x
e =
Limites laterales. Lmites Infinitos:
) x ( f Lim ) x ( f Lim ) x ( f Lim
a x a x a x
+
= -
= + =
+
x
1
Lim ;
x
1
Lim
0 x 0 x
Limites al Infinito: 0
x
1
Lim
x
=
Ejemplos:
1)
2 x
2 x
lim
2 x
2)
x 2
x x
lim
0 x
3)
x 4 x
x 3 x 2 x
lim
3
2 3
0 x
4)
( )
2 2
2
a x
a x
a x 1 a x
lim
+ +
5)
1 x 2 x
2 x x
lim
2
2
1 x
+
+
6)
9 x 15 x 7 x
9 x 3 x 5 x
lim
2 3
2 3
3 x
+ + +
+ +
7)
1 x 2 x
2 x x
lim
2
2
1 x
+
+
8)
2 x 11 x 4 x
2 x x 2 x
lim
2 3
3 4
2 x
+
+
9)
1 1 x 2 x
1 x
lim
2
2
1 x
+
10)
2
2
0 x
x
9 x 6 x
lim
+
11)
x 5 x
25 x
lim
2
2
5 x
12)
x 2
x x
lim
1 x
13)
( )
( )
4
3
3 x
3 x
1 x
lim
+
+
14)
1 x x x
x 5 x 6 x
lim
3 4
2 3
1 x
+
+
15)
a x
a x
lim
a x
LMITES Y CONTINUIDAD Lic. Anglica E. Choqueluque Romn
2
16)
x
3 x 3
lim
0 x
+
17)
1 x 2 x 2 x
3 x 8 x 6 x
lim
3 4
2 4
1 x
+
+
18)
2 3 4
2 3 4
2 x
x 4 x 4 x
4 x 4 x 5 x 4 x
lim
+ +
+ + + +
19)
(
(
1 x
1
1 x
1
lim
1 x
20)
1 3 x
2 x
lim
3 x
+
+
+
21)
1 1 x 2 x
1 x
lim
2
2
1 x
22)
|
|
.
|
\
|
2 x
4 x
4 x
2 x
lim
2
2
2 x
23)
1 x
1 x 2 x 5
lim
2
2
2 x
+
24)
1 3 x
2 x
lim
2 x
+
+
25)
1 3 x
2 x
lim
0 x
+
+
26)
<
> +
=
1 x si x 7
1 x si 5 x
) x ( f
2
2
26)
1 3 x
2 x
lim
x
+
+
CONTINUIDAD DE FUNCIONES
Definicin: Diremos que una funcin de expresin analtica ) x ( f y = es continua en un
punto de su dominio a x = si se verifican estas condiciones:
i) ) existe ( IR ) a ( f e
ii) ) existe ( IR C ) x ( f lim
a x
e =
iii) ) x ( f lim ) a ( f
a x
=
Cuando una funcin no es continua en un punto se dice discontinua
PROPIEDADES DE LAS FUNCIONES CONTINUAS.
Sean ) x ( f y ) x ( g dos funciones continuas en a x = se tiene entonces que:
1. ) x ( g ) x ( f es continua en a x =
2. ) x ( g ). x ( f es continua en a x =
3.
) x ( g
) x ( f
es continua en a x =
TIPOS DE DISCONTINUIDAD DE LAS FUNCIONES
Ya hemos sealado anteriormente que una funcin es Discontinua en un punto a x =
cuando no cumple alguna de las tres condiciones de continuidad en ese punto.
De ah que podamos establecer distintos tipos de Discontinuidad:
LMITES Y CONTINUIDAD Lic. Anglica E. Choqueluque Romn
3
D. EVITABLE en x=a:
i) f(a) puede existir o no
ii) ) existe ( IR l ) x ( f lim
a x
e =
iii) ) x ( f lim ) a ( f
a x
=
- Si el valor de la funcin en x=a, f(a) tomara el valor de l evitaramos la discontinuidad y
sera su valor verdadero.
Ejemplo 1:
En x=2 es discontinua
evitable.
i) existe no ) 2 ( f
ii) ) existe ( IR 4 ) x ( f lim
2 x
e =
Valor verdadero en x=2 es 4
Ejemplo 2:
En x=2 es discontinua
evitable.
i) 1 ) 2 ( f =
ii) ) existe ( IR 4 ) x ( f lim
2 x
e =
iii) 4 1 =
Valor verdadero en x=2 es 4
D. NO EVITABLE:
De salto en x=a
i) La funcin en x=a, f(a) puede existir o no.
ii) existe no ) x ( f lim
a x
, pero existen sus lmites laterales
2 1
2
a x
1
a x
l l
existe ( IR l ) x ( f lim
) existe ( IR l ) x ( f lim
=
e =
e =
- Salto : ) x ( f lim ) x ( f lim
a x a x
+
Ejemplo 1:
En x=2 discontinua de salto.
i) 1 ) 2 ( f =
ii) existe no ) x ( f lim
2 x
; 4 1 ;
) existe ( IR 4 ) x ( f lim
) existe ( IR 1 ) x ( f lim
2 x
2 x
=
e =
e =
LMITES Y CONTINUIDAD Lic. Anglica E. Choqueluque Romn
4
Ejemplo 2:
En x=x
o
discontinua de salto.
i) existe no ) x ( f
o
ii) existe no ) x ( f lim
o
x x
;
1 2
1
x x
2
x x
l l ;
) existe ( IR l ) x ( f lim
) existe ( IR l ) x ( f lim
o
o
=
e =
e =
Asinttica (lmites laterales infinitos o de salto infinito)
i) f(a) puede existir o no.
ii) existe no ) x ( f lim
a x
. Cuando alguno de los lmites laterales (o ambos) no es finito. Puede
ser asinttica por la derecha, por la izquierda o por ambos lados.
Ejemplo 1:
En x=2 discontinua asinttica (lmites laterales infinitos).
i) 4 ) 2 ( f =
ii) existe no ) x ( f lim
2 x
,
e =
+ =
IR 4 ) x ( f lim
) x ( f lim
2 x
2 x
Ejemplo 2:
En x=3 discontinua asinttica (lmites laterales infinitos).
i) existe no ) 3 ( f
ii) existe no ) x ( f lim
3 x
;
+ =
=
+
) x ( f lim
) x ( f lim
3 x
3 x
LMITES Y CONTINUIDAD Lic. Anglica E. Choqueluque Romn
5
EJERCICIOS:
1.- Para que valores de x, la funcin es continua?
a)
3 x 3) (x
7 2x
f(x)
+
+
= b)
3) 1)(x (x x
3
g(x)
+
= c)
5) 3)(x x(x
3
f(x)
+
=
d)
7) 3)(x 1)(x (x
4
f(x)
+
= e) 2) 3)(x (x g(x) + = f)
1 x
5
g(x)
4
=
g)
1 x
1 x
) x ( f
2
= h)
2 x
6 x 5 x
) x ( f
2
+
= i)
8 x 7 x
1 x
) x ( f
3
2
+
=
2.- Estudiar la continuidad y/o indicar el tipo de discontinuidad y representar las funciones
a)
> +
< +
=
1 x ; 1 x
1 x ; 1 x
) x ( f
2
b)
>
< +
=
1 x ; x 3
1 x ; 1 x 2
) x ( f
c)
s
>
=
2 x ; 1 x 2
2 x ; x 4 11
) x ( f
d)
> +
s
=
0 x ; x 1
0 x ; x 1
) x ( f
2
2
e)
> +
<
=
0 x ; 1 x
0 x ; 1 x
) x ( f f)
>
s
=
2 x ; 6 x 2
2 x ; x 2
) x ( f
2
g)
| |
| |
| |
e
e +
e
=
5 , 1 x ; x
1 , 2 x ; x 3 1
2 , 4 x ; 1 x 2
) x ( f
2
h)
>
=
<
=
1 x ; 2 x 2
1 x ; 2
1 x ; x
) x ( f
i)
> +
s s +
<
=
1 x ; 1 x
1 x 0 ; 1 x
0 x ; x
) x ( f
2
j)
>
s s
<
=
0 x ; 4 x
4 x 0 ; 2 x
0 x ; 2
) x ( f
2
k)
>
s
s
=
2 x ; x
2 x < 1 ; 1 x
1 x ; 1 x
) x ( f
2
2
l)
>
s
< +
=
4 x ; 0
4 < x 3 ; x
3 x ; 1 x
) x ( f
2
m)
s
< s
<
=
x 1 , x
1 x 2 - 3,
-2 x ,
x
1
g(x) n)
s s
s s
s s
=
16 x 10 x,
2
1
10 x 3 3,
3 x 0 x,
g(x) o)
> +
<
=
1 x ; 1 x
1 x ;
x
1
) x ( f
p)
>
< <
s +
=
2 x ; 1 - 2x
2 x 2 - ; x - 2
2 x ; x 1
) x ( f q)
>
=
<
=
2 x ; 4
2 x ; 1
2 x ; x
) x ( f
2
r)
>
<
=
2 x ; 4
2 x ; x
) x ( f
2
LMITES Y CONTINUIDAD Lic. Anglica E. Choqueluque Romn
6
s)
=
>
< +
=
1 x ; 1
2 x ; x 2
2 x ; 1 x
) x ( f
2
t)
=
=
=
2 x 3,
2 x ,
2 - x
4 x
g(x)
2
u) ( )
>
=
s
=
2 x ;
2
1
2 x ; 2
1 x ; 2 x 5
x h
v) ( )
>
=
<
=
1 x ; 1 x 2
1 x ; 2
1 x ; x
x h
3.- Estudiar la continuidad y/o discontinuidad de las funciones:
a)
2
x
si 4 x 0
2
f (x) x si 0 x 2
x 6
si 2 x 4
2
s <
= < <
+
s s
b)
>
=
<
=
3 x ;
8 x 1
6 - 2x
3 x ; 5
3 x ;
3 x
9 x
) x ( f
2
2
c) ( ) | |
2
2
x 1 si x 0
f x x 1 si x 0, 2
x 4x 2 si x 2
+ <
= + e
+ >
d)
x si x 2
f (x) 1 si 2 x 5
x 6 si x 5
s
= < s
>
e)
3 si x 1
f (x) 1 2x si 1 x 1
3x 1 si x 1
<
= s <
>
f) ( )
2
1 x
si x 1
f x
1 x
x 3 si x 1
<
=
+
+ >
g)
5x 2 si x 1
f (x) 2 si x 2
1
x si x 2
2
= =
>
h)
2
x 4
si x 2
f (x)
x 2
3 si x 2
=
i)
x 2 si x 3
f (x) x 2
si x 3
x 2
>
= +
j)
2
2
3 si x 2
3x 3 si 2 x 0
f (x)
x 2x 3 si 0 x 3
x 9x 18 si x 3
<
+ s <
=
+ + s <
+ >
4.- Determinar las constantes para que la funcin sea continua
LMITES Y CONTINUIDAD Lic. Anglica E. Choqueluque Romn
7
a)
=
=
=
3 x ; k
3 x ;
3 x
) 9 x (
) x ( f
2
b)
>
s
=
1 x ; x
1 x ; kx
) x ( f
2
c)
<
s s +
< +
=
1 x ; k 2 - 3x
1 x 2 - ; k 3cx
2 - x ; 2c x
) x ( f d)
>
s +
=
2 x ; x a
2 x ; ax x
) x ( f
2
2
e)
>
s +
=
2 x ; ax 3
2 x ; 1 x
) x ( f
2
f)
>
<
=
2 x ; 2 - kx
2 x ;
x 2
8 2x
) x ( f
2
2
g)
>
< s +
< + +
=
1 x ; 2
1 x 0 ; b ax
0 x ; 1 x 2 x
) x ( f
2
h)
>
+
< < +
s
=
4 x ;
x 5
2x -
4 x 1 ; k cx
1 x ; x
) x ( f
i) ( )
( )
2
2
x 1 si x 1
f x a x si 1 x 1
b x si x 1
+ s
= + s s
>
j) ( )
2
x 1 si x 0
f x ax b si 0 x 3
x 5 si x 1
+ <
= + s s
>
k) ( ) ( )
2
x a si x 1
f x x 1 si x 1,1
2 b si x 1
+ s
= + e
>
l)
>
< s +
< + +
=
1 x si 2
1 x 0 si b ax
0 x si 1 x 2 x
) x ( f
2
m)
< +
> +
=
1 x ; a bx
1 x ; b ax
) x ( f
2
2
n)
> +
< < +
< +
=
2 x ; 6 mx
2 x 1 ; 1 x
1 x ; 5 ax
) x ( f
2
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Práctica N3 ElectrodinamicaDokumen1 halamanPráctica N3 ElectrodinamicarrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Examen de Subsanación TerceroDokumen2 halamanExamen de Subsanación Tercerorrvv100% (1)
- Semana 2: Egiptología (Egyptology)Dokumen182 halamanSemana 2: Egiptología (Egyptology)jeycy1002Belum ada peringkat
- Práctica N4 ElectrostaticaDokumen1 halamanPráctica N4 Electrostaticarrvv100% (1)
- Examen Final de Física Quinto ElectrostaticaDokumen2 halamanExamen Final de Física Quinto ElectrostaticarrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Practica 1 ElectrostaticaDokumen1 halamanPractica 1 ElectrostaticarrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Practica 2 ElectrostaticaDokumen2 halamanPractica 2 ElectrostaticarrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Prueba AnalogiasDokumen1 halamanPrueba AnalogiasrrvvBelum ada peringkat
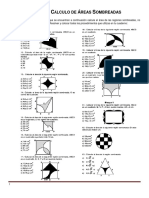
- Taller de Areas SombreadasDokumen1 halamanTaller de Areas SombreadasrrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Práctica N3 ElectrostaticaDokumen1 halamanPráctica N3 ElectrostaticarrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Prueba 1 ElectrostaticaDokumen2 halamanPrueba 1 ElectrostaticarrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Practica Escrita N1 Sistemas3x3 CuartoDokumen1 halamanPractica Escrita N1 Sistemas3x3 CuartorrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Práctica n2 Electrodinamica PubDokumen1 halamanPráctica n2 Electrodinamica PubrrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Prueba Conteo FigurasDokumen1 halamanPrueba Conteo FigurasrrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Practica 1 Areas CuartoDokumen1 halamanPractica 1 Areas CuartorrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Practica CircuitosDokumen1 halamanPractica CircuitosrrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Prueba 1 ElectrodinamicaDokumen2 halamanPrueba 1 ElectrodinamicarrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Prueba 2 ElectrodinamicaDokumen2 halamanPrueba 2 ElectrodinamicarrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Prueba Escrita N1 Unidad4 Sistemas CuartoDokumen2 halamanPrueba Escrita N1 Unidad4 Sistemas CuartorrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Prueba Razonam InductivoDokumen1 halamanPrueba Razonam InductivorrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Práctica N1 ElectrodinamicaDokumen1 halamanPráctica N1 ElectrodinamicarrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Practica Raz Mat - 4 OperacionesDokumen2 halamanPractica Raz Mat - 4 OperacionesrrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Práctica Leyes de KirchoffDokumen1 halamanPráctica Leyes de KirchoffrrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Practica Escrita RM FraccionesDokumen2 halamanPractica Escrita RM FraccionesrrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Practica 2 Raz Mat - 4 OperacionesDokumen1 halamanPractica 2 Raz Mat - 4 Operacionesrrvv0% (1)
- Prueba ProbabilidadDokumen1 halamanPrueba ProbabilidadrrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Examen Final IV Bimestre Mat TerceroDokumen2 halamanExamen Final IV Bimestre Mat TercerorrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Prueba Escrita RM FraccionesDokumen1 halamanPrueba Escrita RM FraccionesrrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Examen Final IV Bimestre Mat QuintoDokumen1 halamanExamen Final IV Bimestre Mat QuintorrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Formulario GADokumen1 halamanFormulario GArrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Temario Subsanación TerceroDokumen1 halamanTemario Subsanación TercerorrvvBelum ada peringkat
- Capítulo 2. Marco Teórico y Estado Del Arte: Fisura Piel de CocodriloDokumen1 halamanCapítulo 2. Marco Teórico y Estado Del Arte: Fisura Piel de CocodriloJhovany Quispe BustincioBelum ada peringkat
- Autónomo N2 Enfermedades de La PielDokumen5 halamanAutónomo N2 Enfermedades de La PielMarjhorie CaraguayBelum ada peringkat
- Huella de CarbonoDokumen3 halamanHuella de CarbonoJimmy Arone SotoBelum ada peringkat
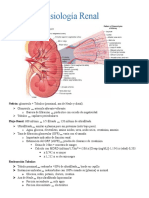
- Fisiología renal: nefrón, flujo renal, ultrafiltrado, reabsorción tubular y regulación hormonalDokumen5 halamanFisiología renal: nefrón, flujo renal, ultrafiltrado, reabsorción tubular y regulación hormonalJean Claudio Miranda ParraBelum ada peringkat
- Hge3 U6 Sesion 03Dokumen5 halamanHge3 U6 Sesion 03Nayely MamaniBelum ada peringkat
- Analisis de Falla de Una Brida de Acero Al CarnonoDokumen10 halamanAnalisis de Falla de Una Brida de Acero Al CarnonoSBelum ada peringkat
- UP6 MaintenanceDokumen32 halamanUP6 MaintenanceEmilio AlBelum ada peringkat
- Soteriología 1Dokumen5 halamanSoteriología 1Elias PonteBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Limpieza y Desinfeccion de Planta Fisica y Personal.Dokumen10 halamanManual Limpieza y Desinfeccion de Planta Fisica y Personal.beatriz cecilia maldonado vBelum ada peringkat
- Hoja de Seguridad DC 6149UDokumen3 halamanHoja de Seguridad DC 6149UCarlos Fredy EcheverríaBelum ada peringkat
- 16 - Apola OfunDokumen92 halaman16 - Apola Ofunrota204100% (1)
- America Del Sur en Un Mapamundi de 1489 PDFDokumen31 halamanAmerica Del Sur en Un Mapamundi de 1489 PDFLeonardo Santoyo AlonsoBelum ada peringkat
- La liturgia religiosa de nuestros antepasadosDokumen5 halamanLa liturgia religiosa de nuestros antepasadosDarien DelgadoBelum ada peringkat
- D - Clase 01Dokumen35 halamanD - Clase 01Edgardo Asencio SevillanoBelum ada peringkat
- Portafolio de ServiciosDokumen5 halamanPortafolio de ServiciosJuan ChaparroBelum ada peringkat
- Anexo 1. Instrumento Autoevaluación PAPE (v1)Dokumen64 halamanAnexo 1. Instrumento Autoevaluación PAPE (v1)Norelis Herrera CassianiBelum ada peringkat
- La CiguapaDokumen5 halamanLa CiguapaYoel Del RosarioBelum ada peringkat
- Calentador de Vapor DirectoDokumen7 halamanCalentador de Vapor DirectoJORDYBelum ada peringkat
- Gestión Responsable de La Innovación (Mapa Conceptual) - JLDokumen1 halamanGestión Responsable de La Innovación (Mapa Conceptual) - JLJorge Eduardo Loayza Pérez100% (2)
- Boga Mar AdentroDokumen7 halamanBoga Mar AdentroYuri BanegasBelum ada peringkat
- Hamburguesa EspiritualDokumen4 halamanHamburguesa EspiritualJosue Alanoca PomaBelum ada peringkat
- Tipos de micrófonos según su construcción y captaciónDokumen4 halamanTipos de micrófonos según su construcción y captaciónKatherine HerreraBelum ada peringkat
- Armaduras - Resistencia de Materiales PDFDokumen12 halamanArmaduras - Resistencia de Materiales PDFMarco Antonio Gutierrez TorresBelum ada peringkat
- Automatización Industrial: Circuitos Eléctricos y AutomatismosDokumen23 halamanAutomatización Industrial: Circuitos Eléctricos y AutomatismosRonalAlcantaraHuaripataBelum ada peringkat
- Transito HidrogramasDokumen10 halamanTransito HidrogramasLuis Cueva PeralesBelum ada peringkat
- La Estrategia Ateisante de Antonio Gramsci - Alfredo Sáenz, S. J.Dokumen14 halamanLa Estrategia Ateisante de Antonio Gramsci - Alfredo Sáenz, S. J.moltenpaper100% (1)
- El Mago Es La Fuerza Creativa InteriorDokumen27 halamanEl Mago Es La Fuerza Creativa InteriorDamaris OkseniukBelum ada peringkat
- Producto AcademicoDokumen31 halamanProducto AcademicoAnto PMontoyaBelum ada peringkat
- Paisaje Con Papel de Volantin. Clase 2Dokumen2 halamanPaisaje Con Papel de Volantin. Clase 2Cynthia AndreaBelum ada peringkat