Defense Mechanism
Diunggah oleh
Katrina PonceHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Defense Mechanism
Diunggah oleh
Katrina PonceHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Defense Mechanism
When people experience difficulties, they have different ways of handling their pain. These different ways of dealing with pain are called defense mechanisms. Originally conceived by Sigmund Freud, much of the development of defense mechanisms was done by his daughter, Anna Freud. Defense mechanisms can be healthy or unhealthy depending on the circumstances and how much a person uses them. If you slam down your briefcase because you are mad at your wife one time, that's not a big deal. But if you frequently take your anger out by throwing or breaking things, there might be a better way of dealing with your anger
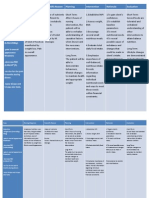
1. Repression-burying a painful feeling or thought from your awareness though it may resurface in symbolic form. Sometimes considered a basis of other defense mechanisms. Ex: You can't remember your father's funeral. 2. Denial-not accepting reality because it is too painful Ex. You are arrested for drunk driving several times but don't believe you have a problem with alcohol. 3. Regression-reverting to an older, less mature way of handling stresses and feelings Ex. You and your roommate have get into an argument so you stomp off into another room and pout 4. Projection-attributing your own unacceptable thoughts or feelings to someone or something else Ex. You get really mad at your husband but scream that he's the one mad at you. 5. Splitting-everything in the world is seen as all good or all bad with nothing in between. Ex. You think your best friend is absolutely worthless because he forgot a lunch date with you. 6. Isolation of affect-attempting to avoid a painful thought or feeling by objectifying and emotionally detaching oneself from the feeling Ex. Acting aloof and indifferent toward someone when you really dislike that person 7. Displacement-channeling a feeling or thought from its actual source to something or someone else. Ex. When you get mad at your sister, you break your drinking glass by throwing it against the wall. 8. Reaction Formation-adopting beliefs, attitudes, and feelings contrary to what you really believe
Ex. When you say you're not angry when you really are. 9. Rationalization-justifying one's behaviors and motivations by substituting "good", acceptable reasons for these real motivations Ex. I always study hard for tests and I know a lot of people who cheat so it's not a big deal I cheated this time. 10. Altruism-handling your own pain by helping others. Ex. After your wife dies, you keep yourself busy by volunteering at your church.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Defense MechanismsDokumen3 halamanDefense MechanismsAlfadz AsakilBelum ada peringkat
- Common Defense MechanismsDokumen6 halamanCommon Defense MechanismsDave Jayraj100% (1)
- Anger Management & CBT: Overcome Anxiety, Depression, and Anger with The Ultimate Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Guide for Men & Women to Take Control of Your Emotions and Build Happier Relationships.Dari EverandAnger Management & CBT: Overcome Anxiety, Depression, and Anger with The Ultimate Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Guide for Men & Women to Take Control of Your Emotions and Build Happier Relationships.Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (28)
- Embrace Your Emotions: A Comprehensive Guide to Unlocking Your Emotional Intelligence, Developing Self-Awareness, and Building Resilience in the Face of Life's ChallengesDari EverandEmbrace Your Emotions: A Comprehensive Guide to Unlocking Your Emotional Intelligence, Developing Self-Awareness, and Building Resilience in the Face of Life's ChallengesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (8)
- Taking Control of Your Life: Achieving Emotional MasteryDari EverandTaking Control of Your Life: Achieving Emotional MasteryBelum ada peringkat
- General Psychology:: Personality (Part I)Dokumen10 halamanGeneral Psychology:: Personality (Part I)Rency RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Addressing Anger - The Ultimate Guide to Anger ManagementDari EverandAddressing Anger - The Ultimate Guide to Anger ManagementBelum ada peringkat
- Controlling Our Anger Before It Controls UsDokumen3 halamanControlling Our Anger Before It Controls UsVivek Reddy100% (1)
- 10 Top Tips For Assertiveness: 1. Listen To Yourself and Others - RespectDokumen3 halaman10 Top Tips For Assertiveness: 1. Listen To Yourself and Others - RespectDipeshBelum ada peringkat
- Communication TechniquesDokumen10 halamanCommunication TechniquesNur Aleah MedtimbangBelum ada peringkat
- Defense Mechanism HandoutDokumen2 halamanDefense Mechanism HandoutJia Ladroma100% (1)
- Defense MechanismsDokumen4 halamanDefense Mechanismssuresh patilBelum ada peringkat
- 15 Common Defense MechanismsDokumen5 halaman15 Common Defense MechanismsVNcomerBelum ada peringkat
- Anger Management: Take Control of Your Emotions - The Ultimate Guide for Men & Women to Achieve Freedom from Anger, Stress, and Anxiety to Build Happier Relationships and Obtain a Better Life.Dari EverandAnger Management: Take Control of Your Emotions - The Ultimate Guide for Men & Women to Achieve Freedom from Anger, Stress, and Anxiety to Build Happier Relationships and Obtain a Better Life.Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (43)
- Defense MechanismsDokumen6 halamanDefense MechanismsVũ Hằng GiangBelum ada peringkat
- Anger Management: A Simple Guide To Achieving Calmness And Getting Rid Of Anger From Your Life For Good!Dari EverandAnger Management: A Simple Guide To Achieving Calmness And Getting Rid Of Anger From Your Life For Good!Belum ada peringkat
- Stop Absorbing Other People's EmotionsDokumen5 halamanStop Absorbing Other People's EmotionsMarielle MaikBelum ada peringkat
- Anger ManagementDokumen4 halamanAnger ManagementSanket ShindeBelum ada peringkat
- Defense Mechanisms OutlineDokumen4 halamanDefense Mechanisms OutlineOnkwani DavidBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of Leslie Becker-Phelps's Bouncing Back from RejectionDari EverandSummary of Leslie Becker-Phelps's Bouncing Back from RejectionBelum ada peringkat
- Overcome Social Anxiety: Cure Shyness and Talk to Anyone with ConfidenceDari EverandOvercome Social Anxiety: Cure Shyness and Talk to Anyone with ConfidencePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5)
- Defense MechanismDokumen5 halamanDefense Mechanismjfgnzls1828Belum ada peringkat
- Ego Defense MechanismDokumen19 halamanEgo Defense MechanismAngel Elizabeth PusungBelum ada peringkat
- Self-Esteem Solution: Boost Self-Esteem, Eliminate Worrying & Insecurity, Find Your Passion & Attract HappinessDari EverandSelf-Esteem Solution: Boost Self-Esteem, Eliminate Worrying & Insecurity, Find Your Passion & Attract HappinessBelum ada peringkat
- Codependency Workbook: 7 Steps to Break Free from People Pleasing, Fear of Abandonment, Jealousy, and Anxiety in Relationships: Healthy Relationships, #1Dari EverandCodependency Workbook: 7 Steps to Break Free from People Pleasing, Fear of Abandonment, Jealousy, and Anxiety in Relationships: Healthy Relationships, #1Belum ada peringkat
- Tiny Tales: Fire Orange Version [A Collection of Short-Short Stories on Soft Skills]Dari EverandTiny Tales: Fire Orange Version [A Collection of Short-Short Stories on Soft Skills]Belum ada peringkat
- Defense Mechanisms: Submitted by Pir Dedar Shah F2019141084Dokumen3 halamanDefense Mechanisms: Submitted by Pir Dedar Shah F2019141084Qasim Ali ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Reconfigure Your Mindset in 2 Weeks The Brain’s Top Secret to Emotional BalanceDari EverandReconfigure Your Mindset in 2 Weeks The Brain’s Top Secret to Emotional BalanceBelum ada peringkat
- Anger Management: 21 Ways To Go From Mad To Glad And Find Peace In Your LifeDari EverandAnger Management: 21 Ways To Go From Mad To Glad And Find Peace In Your LifeBelum ada peringkat
- Defense MechanismsDokumen21 halamanDefense MechanismsJolinaBanawaBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of John Tsilimparis & Daylle Deanna Schwartz's Retrain Your Anxious BrainDari EverandSummary of John Tsilimparis & Daylle Deanna Schwartz's Retrain Your Anxious BrainBelum ada peringkat
- Toddler Discipline: 5 Things You Must Know To Have A Well-Behaved Toddler In No Time!Dari EverandToddler Discipline: 5 Things You Must Know To Have A Well-Behaved Toddler In No Time!Penilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- Anger Management. A Practical Guide to Overcoming Rage and Anxiety. Break the Anger Circle, Control Negative Emotions, Give Peace to Your Mind and Free YourselfDari EverandAnger Management. A Practical Guide to Overcoming Rage and Anxiety. Break the Anger Circle, Control Negative Emotions, Give Peace to Your Mind and Free YourselfBelum ada peringkat
- How to Become a Stronger Person: Increase Self-Discipline, Defeat Depression & Stress, Find Life Purpose & Become a Better YouDari EverandHow to Become a Stronger Person: Increase Self-Discipline, Defeat Depression & Stress, Find Life Purpose & Become a Better YouBelum ada peringkat
- Meditation: Develop Self-Control, Eliminate Worrying & Panic Attacks, Find Life Purpose & Change Your LifeDari EverandMeditation: Develop Self-Control, Eliminate Worrying & Panic Attacks, Find Life Purpose & Change Your LifeBelum ada peringkat
- Marcus Aurelius Complete Works – World’s Best Collection: All Works – Meditations, Teachings, Stoic Philosophy Plus Biography, Bonus Interpretation & Stoicism AnalysisDari EverandMarcus Aurelius Complete Works – World’s Best Collection: All Works – Meditations, Teachings, Stoic Philosophy Plus Biography, Bonus Interpretation & Stoicism AnalysisBelum ada peringkat
- Nursereview Org Therapeutic Communication TechniquesDokumen6 halamanNursereview Org Therapeutic Communication TechniquesPatricia VasquezBelum ada peringkat
- IP CEREA #07: Defense Mechanisms A. Defense MechanismDokumen5 halamanIP CEREA #07: Defense Mechanisms A. Defense MechanismMorzee ExclusivoBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Ways Anxiety Might Be Slowly Eating Away Your LifeDari Everand7 Ways Anxiety Might Be Slowly Eating Away Your LifeBelum ada peringkat
- Anger Management Simplicity: Short Simplicity to Keep Your Anger in CheckDari EverandAnger Management Simplicity: Short Simplicity to Keep Your Anger in CheckBelum ada peringkat
- Defense Mechanism With ExampleDokumen1 halamanDefense Mechanism With ExamplepaorovedilloBelum ada peringkat
- Anger Management for Parents: How to Empathize, Resolve Tantrums Calmly, and Achieve a Peaceful Household through Effective Anger ManagementDari EverandAnger Management for Parents: How to Empathize, Resolve Tantrums Calmly, and Achieve a Peaceful Household through Effective Anger ManagementBelum ada peringkat
- Sensitive Is The New Strong: Secrets OF The Sensitive - Don't Be Afraid To Be Highly SensitiveDari EverandSensitive Is The New Strong: Secrets OF The Sensitive - Don't Be Afraid To Be Highly SensitiveBelum ada peringkat
- ANGER MANAGEMENT FOR PARENTS: Tips and Tricks to Master Your Emotions and be a Loving ParentDari EverandANGER MANAGEMENT FOR PARENTS: Tips and Tricks to Master Your Emotions and be a Loving ParentBelum ada peringkat
- 26.07.10.life Style Management Series-Avoiding Conflicts & ArgumentsDokumen4 halaman26.07.10.life Style Management Series-Avoiding Conflicts & Argumentsmaheshwari prasad shuklaBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of Matthew McKay, Jeffrey C. Wood & Jeffrey Brantley's The Dialectical Behavior Therapy Skills WorkbookDari EverandSummary of Matthew McKay, Jeffrey C. Wood & Jeffrey Brantley's The Dialectical Behavior Therapy Skills WorkbookBelum ada peringkat
- AnxietyDokumen30 halamanAnxietyjulieyauder624Belum ada peringkat
- 15 Common Defense MechanismsDokumen2 halaman15 Common Defense MechanismsDonnah Vie MagtortolBelum ada peringkat
- COGNITIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY MADE SIMPLE: Overcoming Depression, Anxiety, Anger, and Negative Thoughts in Just 21 Days. A Step-by-Step Guide (2022 Crash Course for Beginners)Dari EverandCOGNITIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY MADE SIMPLE: Overcoming Depression, Anxiety, Anger, and Negative Thoughts in Just 21 Days. A Step-by-Step Guide (2022 Crash Course for Beginners)Belum ada peringkat
- Anger Management: Tame The Lion Inside of You for Good - Discover How to Improve Your Emotional Self-Control, Make Your Relationships Thrive, and Completely Take Back Your LifeDari EverandAnger Management: Tame The Lion Inside of You for Good - Discover How to Improve Your Emotional Self-Control, Make Your Relationships Thrive, and Completely Take Back Your LifeBelum ada peringkat
- Anger Management Strategies Controlling HostilityDokumen3 halamanAnger Management Strategies Controlling HostilitySam EmekaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Management of The Perioperative PatientDokumen19 halamanNursing Management of The Perioperative PatientKatrina Ponce100% (4)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen6 halamanCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- Patient S AssignmentDokumen1 halamanPatient S AssignmentKatrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- Safe SuctioningDokumen31 halamanSafe SuctioningKatrina Ponce100% (2)
- Different Types of Oxygen MasksDokumen2 halamanDifferent Types of Oxygen MasksKatrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- Caldwell LucDokumen1 halamanCaldwell LucKatrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- GIT DisordersDokumen171 halamanGIT DisordersKatrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Patient Skin PreparationDokumen26 halamanPrinciples of Patient Skin PreparationKatrina Ponce100% (1)
- DwarfismDokumen2 halamanDwarfismKatrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- Prepared By: Hernandez, Dionne Cedric P. BSN4B Group 8Dokumen24 halamanPrepared By: Hernandez, Dionne Cedric P. BSN4B Group 8Katrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- NE2.1 Ward RoutinesDokumen3 halamanNE2.1 Ward RoutinesKatrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- Operating Room Equipments and Machineries: By: RICACHO, Ma. Norilyn BSN4B - Group8Dokumen38 halamanOperating Room Equipments and Machineries: By: RICACHO, Ma. Norilyn BSN4B - Group8Katrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- Operating Room TeamDokumen18 halamanOperating Room TeamKatrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- Different Types of Oxygen MasksDokumen2 halamanDifferent Types of Oxygen MasksKatrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Community AcquiredDokumen21 halaman"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Community AcquiredKatrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Epidural HemDokumen32 halamanNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- 2.balance Skeletal TractionDokumen18 halaman2.balance Skeletal TractionKatrina Ponce75% (4)
- Pathophysiology of Closed Displacement Segmental FemurDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Closed Displacement Segmental FemurKatrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- 5.casts and MoldsDokumen30 halaman5.casts and MoldsKatrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- Gestalt TherapyDokumen6 halamanGestalt TherapynathalieBelum ada peringkat
- PARTIALDokumen22 halamanPARTIALJeremiah NoconBelum ada peringkat
- Cultural and Global DiversityDokumen5 halamanCultural and Global DiversityDr Linda Mary SimonBelum ada peringkat
- Relationship Between Emotional Intelligence and Psychological Capital With Life Satisfaction in ElderlyDokumen8 halamanRelationship Between Emotional Intelligence and Psychological Capital With Life Satisfaction in ElderlyxbachtiarrBelum ada peringkat
- LeadershipDokumen6 halamanLeadershipUmer farooqBelum ada peringkat
- Janina Fisher DISSOCIATIVE PHENOMENA IN THE EVERYDAY LIVES OF TRAUMA SURVIVORSDokumen38 halamanJanina Fisher DISSOCIATIVE PHENOMENA IN THE EVERYDAY LIVES OF TRAUMA SURVIVORSMargaret KelomeesBelum ada peringkat
- Stress TheoryDokumen16 halamanStress TheoryLeviBelum ada peringkat
- PCMDokumen38 halamanPCMdiop195980% (5)
- Reinforcement TheoryDokumen3 halamanReinforcement TheoryFenil PanchalBelum ada peringkat
- 4 15Dokumen3 halaman4 15Dean ReadBelum ada peringkat
- Teachers Personality and AdjustmentDokumen16 halamanTeachers Personality and AdjustmentsainudheenBelum ada peringkat
- The Light Workers IdentityDokumen4 halamanThe Light Workers IdentityAndy Kolarik100% (1)
- A Sample Format of Questionnaires On Career Planning and DevelopmentDokumen2 halamanA Sample Format of Questionnaires On Career Planning and DevelopmentSameer OmlesBelum ada peringkat
- Methods of Data Collection RM Chapter 6Dokumen9 halamanMethods of Data Collection RM Chapter 6Cheppu MolBelum ada peringkat
- Job Interview QuestionsDokumen1 halamanJob Interview QuestionsYrrech LaneBelum ada peringkat
- 3.02 Learning and Memory: ExamplesDokumen2 halaman3.02 Learning and Memory: ExamplesMarkayla HinesBelum ada peringkat
- Society For The Study of Peace, Conflict, and ViolenceDokumen14 halamanSociety For The Study of Peace, Conflict, and ViolenceJournal of International Relations DUBelum ada peringkat
- The Use of Therapeutic Stories in Counseling Children and Adolescent Sexual Abuse SurvivorsDokumen18 halamanThe Use of Therapeutic Stories in Counseling Children and Adolescent Sexual Abuse Survivorsapi-417140487Belum ada peringkat
- Aera, Apa & Ncme, 2014 PDFDokumen241 halamanAera, Apa & Ncme, 2014 PDFMacarena Yunge100% (2)
- What Is 360 Degree FeedbackDokumen2 halamanWhat Is 360 Degree Feedbackanagha_wankar2548Belum ada peringkat
- EY Written Test SyllabusDokumen4 halamanEY Written Test SyllabusAishwarya KarthikeyanBelum ada peringkat
- IX. Maslow Holistic Dynamic Theory PPT (Acquire)Dokumen39 halamanIX. Maslow Holistic Dynamic Theory PPT (Acquire)Maikah Sabrina CalubBelum ada peringkat
- Parents On Your Side:: by Faiza Rais and Bisma UroojDokumen11 halamanParents On Your Side:: by Faiza Rais and Bisma UroojBismaUroojBelum ada peringkat
- Case 5.1: Marathon Runners at Different LevelsDokumen3 halamanCase 5.1: Marathon Runners at Different LevelsTest Mock50% (2)
- Chapter 13Dokumen28 halamanChapter 13Kayelita Wu100% (2)
- Goldstein 2015 PDFDokumen22 halamanGoldstein 2015 PDFEduardo GuadalupeBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson04 Barriers To Intercultural CommunicationDokumen4 halamanLesson04 Barriers To Intercultural CommunicationPatricia Catherine UrbiztondoBelum ada peringkat
- Blank's Levels of QuestioningDokumen5 halamanBlank's Levels of QuestioningRoman -100% (1)
- Factors Affecting Employee Performance During Restricting Process in Corporate Companies of UgandaDokumen4 halamanFactors Affecting Employee Performance During Restricting Process in Corporate Companies of Ugandadis2011Belum ada peringkat
- Ian E. Pagaran: Teacher 1Dokumen11 halamanIan E. Pagaran: Teacher 1Yanyan EducBelum ada peringkat































![Tiny Tales: Fire Orange Version [A Collection of Short-Short Stories on Soft Skills]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/725049074/149x198/8f2588fd91/1713655727?v=1)