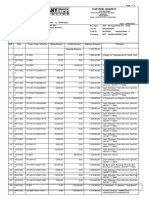
Banking Info
Diunggah oleh
rahul.dandeboinaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Banking Info
Diunggah oleh
rahul.dandeboinaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Some banking information for use
Banking information: 1 Who is Reserve bank governor: Dr Duvvuri subbarao 2 What is CRR : The Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) refers to this liquid cash that banks have to maintain with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) as a certain percentage of their demand and time liabilities 3 How much is CRR at present: 4.50 % of net demand and time liabilities 4 What is SLR: Statutory liquidity ratio the amount banks have to invest in specified government securities approved by RBI 5 What is the purpose of SLR: To control the ability of banks to give loans. If SLR is increased banks can lend less amount 6 How much is SLR at present 23.00% 7 What is repo rate: Repo rate means repurchase rate : the rate at which banks can borrow from reserve bank of India whenever they want by keeping Govt securities as security 8 How much is repo rate now 8.00% 9 What is reverse repo rate: Is the rate at which RBI borrows from commercial banks to control money supply 10 How much is reveres repo rate at present 7.00% 11 What is bank rate Is the rate at commercial banks borrow from RBI by re discounting the commercial bills of exchange (when they need money) 12 How much is bank rate 9.00% 13 Who is the central finance Minister Mr. P. Chindambaram 14 Who issues currency notes in India RBI 15 What is money market : It is a market Where short term(less than one year) debt instruments like Certificate of deposit, commercial papers, treasury bills are traded. 16 Who controls money market: RBI 17 What is capital market Market where long term debt /equity instruments like shares and debentures are traded 18 Who controls capital market SEBI 19 What is priority sector Important sectors of economy which provide large employment like agriculture ,SSI, small business 20 How much banks have to lend to priority sector 40% of their advances. foreign banks with less than 20 branches 32 % of their advances 21 How much they have to lend to agriculture 18 % remaining. 22 % they have to lend to SSI, small business, exports, housing loans below Rs 15 lakhs, education loans etc 22 How many govt banks are there?: 6 SBI and associates,18 nationalized banks, and IDBI ( other PSU) Total 25 23 What are RRBs: Regional rural banks promoted by Nationalized banks to lend in rural areas there are 82 RRBs in India
24 How many RRBs are in AP 5( Hanmkonda, Chittoor,,Kadapa ,Hyderabad (Deccan gramina bank),Guntur 25 How many scheduled coop banks are in Ap: Total 51 in India (majority in Maharashtra) out of which two are in India- Mahesh Coop Urban bank and Vasavi coop urban bank in Hyd 26 What is a scheduled commercial bank : Scheduled Banks in India constitute those banks which have been included in the Second Schedule of Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Act, 1934. RBI in turn includes only those banks in this schedule which satisfy the criteria laid down vide section 42 (6) (a) of the Act. As on 30th June, 1999, there were 300 scheduled banks in India having a total network of 64,918 branches. The scheduled commercial banks in India comprise of State bank of India and its associates (8), nationalized banks (19), foreign banks (45), private sector banks (32), co-operative banks and regional rural banks. 27 What are nationalized banks: Private banks which were nationalized in 1969 (14) and 1980(6) 28 How much business they control: Approximately 80 % 29 Who controls foreign exchange markets: RBI 30 What is CASA: Current account and savings account they are low cost deposits and are also called demand deposits 31 What are coop banks: Co-operative banks are small-sized units organized in the co-operative sector which operate both in urban and non-urban centers. These banks are traditionally centered around communities, localities and work place groups and they essentially lend to small borrowers and businesses. 32 What are urban coop banks: The term Urban Co-operative Banks (UCBs), though not formally defined, refers to primary cooperative banks located in urban and semi-urban areas. These banks, until 1996, could only lend for non-agricultural purposes 33 How coop banks are registered: Co operative Banks in India are registered under the Co-operative Societies Act. The cooperative bank is also regulated by the RBI. They are governed by the Banking Regulations Act 1949 and Banking Laws (Co-operative Societies) Act, 1965. 34 What is the structure of coop banks: Primary Urban Co-op Banks Primary Agricultural Credit Societies District Central Co-op Banks State Co-operative Banks Land Development Banks 35 What are the strengths of coop banks: A Personalized service and competitive rates 36 What is monetary policy & who announces that: Monetary policy is a policy issued by RBI to control money supply(inflation) by controlling credit and interest rates 37 What is fiscal policy: Fiscal policy is governments income expenditure announced by central govt as budget every year collecting money as taxes and spending. 38 What is inflation: It is increase in general price level due to excess money supply ( can be controlled by monetary policy and fiscal policy)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- PDFDokumen8 halamanPDFHellene Lindsay100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- State Bank of India Strategy AnalysisDokumen25 halamanState Bank of India Strategy AnalysisVineet Raj Goel85% (20)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Proforma Invoice: Jose Andres Casanova Segovia Post Code:CHF57 Bolivia Cochabamba CityDokumen1 halamanProforma Invoice: Jose Andres Casanova Segovia Post Code:CHF57 Bolivia Cochabamba CityJosé AndrésCasanovaSegoviaBelum ada peringkat
- The Mystery of Money by Allyn YoungDokumen57 halamanThe Mystery of Money by Allyn YoungLDaggersonBelum ada peringkat
- Histori TransaksiDokumen3 halamanHistori TransaksiHari SusantoBelum ada peringkat
- Bank Management Summary - Chapter OneDokumen6 halamanBank Management Summary - Chapter Oneabshir sugoowBelum ada peringkat
- RBA APU PPT - OJK 16 April 2018Dokumen46 halamanRBA APU PPT - OJK 16 April 2018BunnyBelum ada peringkat
- Session Readings (Euro Issues)Dokumen8 halamanSession Readings (Euro Issues)Arathi SundarramBelum ada peringkat
- El Banco Español-Filipino V. James PetersonDokumen1 halamanEl Banco Español-Filipino V. James PetersonRia Evita RevitaBelum ada peringkat
- 7'P S of Banking in MarketingDokumen15 halaman7'P S of Banking in MarketingAvdhesh ChauhanBelum ada peringkat
- Masters in FinanceDokumen80 halamanMasters in Financemage99Belum ada peringkat
- History of Philippine PesoDokumen5 halamanHistory of Philippine PesoShaira PangilinanBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 05 Classification of ServicesDokumen6 halamanLecture 05 Classification of ServicesMari SenthilBelum ada peringkat
- Statement: Hermann Aflenzer Hermann AflenzerDokumen2 halamanStatement: Hermann Aflenzer Hermann Aflenzerpaiment flechetteBelum ada peringkat
- Cipla-I 4/4/2018 13:45 565.55 NEUTRAL 567.34 Cnxit-I 4/4/2018 12:30 12620 SELL MODE 12634.93Dokumen8 halamanCipla-I 4/4/2018 13:45 565.55 NEUTRAL 567.34 Cnxit-I 4/4/2018 12:30 12620 SELL MODE 12634.93dewanibipinBelum ada peringkat
- Private Equity Investment Banking Hedge Funds Venture CapitalDokumen26 halamanPrivate Equity Investment Banking Hedge Funds Venture Capitalpankaj_xaviersBelum ada peringkat
- Our Classroom EconomyDokumen14 halamanOur Classroom Economyapi-279807682Belum ada peringkat
- Requirements Based TestingDokumen4 halamanRequirements Based TestingVick'y A'AdemiBelum ada peringkat
- Bank Asia StatementDokumen4 halamanBank Asia StatementBD MahamudBelum ada peringkat
- Intern JanataDokumen59 halamanIntern JanataKhairul IslamBelum ada peringkat
- A Case Study of Acquisition of Spice Communications by Isaasdaddea Cellular LimitedDokumen13 halamanA Case Study of Acquisition of Spice Communications by Isaasdaddea Cellular Limitedsarge1986Belum ada peringkat
- GIRO FormDokumen1 halamanGIRO FormBrian EllisBelum ada peringkat
- Bbob Current AffairsDokumen28 halamanBbob Current AffairsGangwar AnkitBelum ada peringkat
- Alternate PetaDokumen2 halamanAlternate PetaAngel Ann AgaoBelum ada peringkat
- Partial Withdrawal FormDokumen1 halamanPartial Withdrawal Formmohd uzaini mat jusohBelum ada peringkat
- Study On The Banking Services Provided by Uttarakhand Gramin BankDokumen12 halamanStudy On The Banking Services Provided by Uttarakhand Gramin BankDivyansh KaushikBelum ada peringkat
- A Critical Review of NPA in Indian Banking IndustryDokumen12 halamanA Critical Review of NPA in Indian Banking IndustryNavneet NandaBelum ada peringkat
- RiskDokumen2 halamanRiskrakesh_danduBelum ada peringkat
- I. Convertible Currencies With Bangko Sentral:: Run Date/timeDokumen1 halamanI. Convertible Currencies With Bangko Sentral:: Run Date/timeLucito FalloriaBelum ada peringkat
- Insular Savings Bank Vs CA June 15, 2005Dokumen2 halamanInsular Savings Bank Vs CA June 15, 2005Sam FajardoBelum ada peringkat