Passive Voice
Diunggah oleh
catandryDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Passive Voice
Diunggah oleh
catandryHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
LECP an 1, sem.
PASSIVE VOICE
We use passive forms for reasons of style and clarity, as well as of meaning. Mostly the rules of passive formation are straightforward, but it needs to be noted that certain words and structures cannot be used in the passive. A number of changes undergo when turning an active sentence into a passive one. Thus, the subject of an active verb becomes the agent in the passive; the object of the active verb becomes the subject of the passive verb (note that verbs that do not have direct object can not be used in the passive); the passive form of verbs can be made in all tenses by using be in the appropriate tense plus the past participle of the main verb. e.g. active voice: The judge will read the names of the winners. passive voice: The names of the winners will be read by the judge.
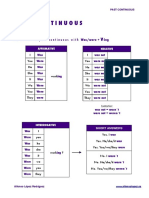
Here are more examples with all the changes an active sentence undergoes when turned into passive. TENSES ACTIVE VOICE PASSIVE VOICE
Simple Present Simple Past Present Continuous Past Continuous. Pres. Perfect Past Perfect Future Future Perfect Conditional Condit. Perfect Present Infinitive Perfect Infinitive
He repairs cars. He repaired the car. Hes repairing the car. He was repairing a car. He has repaired the car. He had repaired the car. He will repair the car. He will have repaired the car. He would repair the car. He would have repaired the car. He ought to repair the car. He ought to have repaired the car.
Cars are repaired here. The car was repaired. The car is being repaired. The car was being repaired. The car has been repaired. The car had been repaired. The car will be repaired. The car will have been repaired. The car would be been repaired. The car would have been repaired. The car ought to be repaired. The car ought to have been repaired.
Notes 1. In colloquial English be can be replaced by get in the passive voice in some expressions. e.g. Hell get (= be) fired if he continues to be late for work. 2. have + object + past participle can be used colloquially to replace a passive verb when we want to talk about an accident or misfortune. e.g. She had her arm broken. (= Her arm was broken) 3. The agent is omitted when it is: a) a pronoun, b) words like one, someone, people, etc. or c) can be easily understood. e.g. Someone destroyed the evidence. The evidence was destroyed. The passive voice is used: 1. when the person who performs the action (agent) can easily be understood. e.g. He has been arrested. (The police have arrested him.) 2. when the subject of the active verb is people, he, she, they, one, somebody, etc. e.g. They say she is smart. It is said that she is smart. /She is said to be smart. 3. when we are interested in the action itself rather than the person who performs it. e.g. The new shopping centre will be opened tomorrow (by the Mayor of the city). 4. when we mean to be tactful by not naming the agent.
e.g. All my perfume has been used. (instead of Youve used all my perfume!) Further points on the passive voice: 1. make, hear, see, help are followed by to + infinitive in the passive. e.g. He helped her cross the street. She was helped to cross the street. 2. let becomes was/were allowed to in the passive. When the subject of let and the object of the infinitive that follows let are the same, then let, when used in the passive voice, is followed by a reflexive pronoun + bare/short passive infinitive. e.g. Mother let me go to the party. I was allowed to go to the party. Dont let them laugh at you. Dont let yourself be laughed at. 3. The passive with verbs such as assume, believe, consider, feel, know, report, say, think, understand, etc. is formed in two ways. a) it + passive + that-clause e.g. They believe she is a spy. It is believed that she is a spy. b) subject + passive + to-infinitive e.g. They believe she is a spy. She is believed to be a spy. 4. Verbs which take two objects as allow, ask, give, lend, send, etc. have two passive forms. e.g. He showed me his latest novel. I was shown his latest novel. and He showed me his latest novel. His latest novel was shown to me. 5. Passive voice with by or with. a) by + agent e.g. Penicillin was discovered by Fleming. b) with/by +instrument e.g. She was killed with a hammer. c) with + material e.g. Irish coffee is made with whisky. d) past participles (such as filled, packed, etc.) + with/by e.g. The theatre was filled with hundreds of spectators. 6. Verbs followed by a certain preposition take the preposition immediately after them when put in the passive. e.g. They accused him of drug running. He was accused of drug running.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- This That These Those Demonstrative Pronouns 2Dokumen6 halamanThis That These Those Demonstrative Pronouns 2jeanBelum ada peringkat
- Exercises On Irregular Verbs For Ms4 LevelDokumen6 halamanExercises On Irregular Verbs For Ms4 LevelmirageBelum ada peringkat
- What Is The Futur Proche?: 1. To Talk About An Action That Will Take Place ShortlyDokumen2 halamanWhat Is The Futur Proche?: 1. To Talk About An Action That Will Take Place ShortlyMadhur ChopraBelum ada peringkat
- (13446) GR 5 Personal Pronoun CASEDokumen2 halaman(13446) GR 5 Personal Pronoun CASEnairsanBelum ada peringkat
- Les Verbes PronominauxDokumen3 halamanLes Verbes PronominauxlettyBelum ada peringkat
- Nivel 5 Past Simple & Past ContinuousDokumen50 halamanNivel 5 Past Simple & Past ContinuousJuly HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- T L 9481 Simple Present Tense Warmup Powerpoint - Ver - 2Dokumen16 halamanT L 9481 Simple Present Tense Warmup Powerpoint - Ver - 2Mirela AnghelinaBelum ada peringkat
- Some Any No GrammarDokumen2 halamanSome Any No GrammarEileen PerezBelum ada peringkat
- English Tenses Past Simple and Past ContinuousDokumen15 halamanEnglish Tenses Past Simple and Past ContinuousLucas FariasBelum ada peringkat
- Past Simple and Past ContinuousDokumen4 halamanPast Simple and Past ContinuousАлекс ГриненкоBelum ada peringkat
- Articles ExercisesDokumen3 halamanArticles ExercisesEllia45Belum ada peringkat
- French Reading Comprehension TestDokumen10 halamanFrench Reading Comprehension Testglen4uBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Past TenseDokumen1 halamanSimple Past TenseLylian Ching Manjan0% (2)
- Adverbs of FrequencyDokumen3 halamanAdverbs of FrequencyMilagritos Culqui AlvaradoBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Forms Progressive Forms Perfect Forms Perfect Progressive FormsDokumen4 halamanSimple Forms Progressive Forms Perfect Forms Perfect Progressive FormsYolanda RuizBelum ada peringkat
- Cooking Verbs CrosswordDokumen1 halamanCooking Verbs CrosswordChiew N PangBelum ada peringkat
- (HTTPS://WWW - Lawlessfrench.c: QuestionsDokumen9 halaman(HTTPS://WWW - Lawlessfrench.c: Questionsnoel8938lucianoBelum ada peringkat
- EXERCISE Past Simple vs. Past ContinuousDokumen4 halamanEXERCISE Past Simple vs. Past ContinuousnejlaBelum ada peringkat
- Verb TenseDokumen16 halamanVerb TenseRose Bt MustafhaBelum ada peringkat
- Chez Moi UnitDokumen38 halamanChez Moi UnitElla ElleBelum ada peringkat
- The Perfect Crime U3 New Headway Pre IntDokumen5 halamanThe Perfect Crime U3 New Headway Pre Intinas khalil100% (1)
- Punctuation MaterialDokumen3 halamanPunctuation MaterialEko RaharjoBelum ada peringkat
- Present Simple RulesDokumen2 halamanPresent Simple RulesLeonid2009 gaming 2ndBelum ada peringkat
- Passe Compose PDFDokumen9 halamanPasse Compose PDFAnjali JainBelum ada peringkat
- Hobbies Present Simple PDFDokumen18 halamanHobbies Present Simple PDFEC Pisano RiggioBelum ada peringkat
- Verb To Be Present WorksheetDokumen1 halamanVerb To Be Present WorksheetStiwar MenaBelum ada peringkat
- MODALSDokumen1 halamanMODALSAna Maria Armero100% (1)
- Past Simple - All FormsDokumen1 halamanPast Simple - All FormsrenataBelum ada peringkat
- 2.1. Noun Possessive CaseDokumen10 halaman2.1. Noun Possessive CaseAna DerilBelum ada peringkat
- Summer Tutorial VerbsDokumen3 halamanSummer Tutorial VerbsPeterAndrewRegenciaBelum ada peringkat
- Direct and Indirect Object PronounsDokumen11 halamanDirect and Indirect Object PronounsHamish HaldaneBelum ada peringkat
- Direct and Indirect Objects ReviewDokumen3 halamanDirect and Indirect Objects Reviewrsargent2665Belum ada peringkat
- MOdals AuxilaryDokumen25 halamanMOdals Auxilarymeymirah100% (1)
- Conditional-Sentences All TypesDokumen3 halamanConditional-Sentences All TypesTedj GhomriBelum ada peringkat
- IRREGULAR VERBS ExerciseDokumen1 halamanIRREGULAR VERBS Exercisegrzincic7623Belum ada peringkat
- Verbs With 2 Objects ExercisesDokumen2 halamanVerbs With 2 Objects ExercisesZsuzsa StuparBelum ada peringkat
- Collective Nouns ExerciseDokumen1 halamanCollective Nouns ExerciseAhmad Izhar Amiruddin100% (1)
- CLOZESDokumen3 halamanCLOZESCarlosBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet On The Verb TO BE (Present Simple)Dokumen1 halamanWorksheet On The Verb TO BE (Present Simple)maryruteBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz Exercises 11 Modal Verbs 9Dokumen2 halamanQuiz Exercises 11 Modal Verbs 9Hicham RajawiBelum ada peringkat
- Used ToDokumen20 halamanUsed ToMile Pino EastBelum ada peringkat
- Conditionals Upper Secondary ExercisesDokumen6 halamanConditionals Upper Secondary ExercisespilaruquiBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Present 2Dokumen2 halamanSimple Present 2jorher502Belum ada peringkat
- Future SimpleDokumen2 halamanFuture SimpleJelena Ostojic100% (1)
- Present TensesDokumen1 halamanPresent TensesDumitrita UrsuBelum ada peringkat
- Ompound Ords: Diagramming A SentenceDokumen4 halamanOmpound Ords: Diagramming A SentenceMis IrissBelum ada peringkat
- We Form The Past Continuous WithDokumen3 halamanWe Form The Past Continuous WithFernando OyuelaBelum ada peringkat
- Getting To Know You 1Dokumen6 halamanGetting To Know You 1Aomme Jogthong100% (1)
- Simple Present TenseDokumen6 halamanSimple Present TenseYanina FerrerBelum ada peringkat
- Singular and Plural NounDokumen35 halamanSingular and Plural NounDiana Alejo100% (1)
- Possessive Pronoun Practice: Worksheet #1: Identifying Possessive PronounsDokumen1 halamanPossessive Pronoun Practice: Worksheet #1: Identifying Possessive PronounsGuru FatahBelum ada peringkat
- Past Perfect Printable WorksheetDokumen2 halamanPast Perfect Printable Worksheetwww.getenglishlessons.comBelum ada peringkat
- Passive Voice: Tense TranformationsDokumen6 halamanPassive Voice: Tense TranformationsStephy PunctBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Class Notes-HU 101 - (Module 1-Grammar)Dokumen15 halaman1 - Class Notes-HU 101 - (Module 1-Grammar)Sukhwinder SinghBelum ada peringkat
- TensesDokumen28 halamanTensesKalai ShanBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Passive VoiceDokumen12 halamanMakalah Passive VoiceaqibBelum ada peringkat
- E1 - The Passive Voice - CDokumen13 halamanE1 - The Passive Voice - CDarcy DeeaBelum ada peringkat
- 1.categories of The VerbDokumen7 halaman1.categories of The Verbabril iñon rukavinaBelum ada peringkat
- E1 - The Passive Voice - CDokumen13 halamanE1 - The Passive Voice - CDarcy DeeaBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT V. Passive VoiceDokumen4 halamanUNIT V. Passive VoiceCESAR MIERBelum ada peringkat
- LLR - Lec RezolvataDokumen40 halamanLLR - Lec RezolvatacatandryBelum ada peringkat
- Preview Assessment: LLR - Limba Engleza ContemporanaDokumen31 halamanPreview Assessment: LLR - Limba Engleza ContemporanacatandryBelum ada peringkat
- Preview Assessment: LLR - Limba Engleza Curs Practic: Question Completion Status: Întrebarea Nr. 1Dokumen19 halamanPreview Assessment: LLR - Limba Engleza Curs Practic: Question Completion Status: Întrebarea Nr. 1catandryBelum ada peringkat
- LB Engleza Contemporana MorfologieDokumen94 halamanLB Engleza Contemporana MorfologieNicoleta-Mariana GoiaBelum ada peringkat
- Engleza de Afaceri-Grila WordDokumen28 halamanEngleza de Afaceri-Grila WordcatandryBelum ada peringkat
- Direct Reported SpeechDokumen1 halamanDirect Reported SpeechcatandryBelum ada peringkat
- Limba Engleza Curs Practic - An 1 - Sem 2 - Grile RezolvateDokumen23 halamanLimba Engleza Curs Practic - An 1 - Sem 2 - Grile RezolvatecatandryBelum ada peringkat
- LB Engleza - Sintaxa FrazeiDokumen34 halamanLB Engleza - Sintaxa FrazeicatandryBelum ada peringkat
- English Practical CourseDokumen46 halamanEnglish Practical CoursecatandryBelum ada peringkat
- Limba Engleza ContemporanaDokumen40 halamanLimba Engleza ContemporanacatandryBelum ada peringkat
- Engleza CPDokumen45 halamanEngleza CPcatandryBelum ada peringkat
- Uwamungu Et Al 2022 - Contaminacion de Suelos Por MicroplasticosDokumen14 halamanUwamungu Et Al 2022 - Contaminacion de Suelos Por MicroplasticosXXUHAJBelum ada peringkat
- 504 Loan Refinancing ProgramDokumen5 halaman504 Loan Refinancing ProgramPropertywizzBelum ada peringkat
- General Nursing Council of Zambia: Summary of Results For Each School December 2019 Qualifying Examinations SessionDokumen15 halamanGeneral Nursing Council of Zambia: Summary of Results For Each School December 2019 Qualifying Examinations SessionAndrew LukupwaBelum ada peringkat
- Us and China Trade WarDokumen2 halamanUs and China Trade WarMifta Dian Pratiwi100% (1)
- Aradau Security Materiality SDDokumen22 halamanAradau Security Materiality SDTalleres NómadaBelum ada peringkat
- Utilitarianism Bentham: PPT 6 Hedonic Act UtilitarianismDokumen9 halamanUtilitarianism Bentham: PPT 6 Hedonic Act UtilitarianismPepedBelum ada peringkat
- Noodles Illinois LocationDokumen2 halamanNoodles Illinois LocationWardah AuliaBelum ada peringkat
- Winning From Within - SummaryDokumen4 halamanWinning From Within - SummaryShraddha Surendra100% (3)
- Special Penal LawsDokumen14 halamanSpecial Penal LawsBrenna ColinaBelum ada peringkat
- Expense ReportDokumen8 halamanExpense ReportAshvinkumar H Chaudhari100% (1)
- Level 2 TocDokumen5 halamanLevel 2 TocStephanie FonsecaBelum ada peringkat
- Mun Experience ProposalDokumen2 halamanMun Experience Proposalapi-296978053Belum ada peringkat
- Year 1 Homework ToysDokumen7 halamanYear 1 Homework Toyscyqczyzod100% (1)
- Adidas Case StudyDokumen5 halamanAdidas Case StudyToSeeTobeSeenBelum ada peringkat
- Lectio Decima Septima: de Ablativo AbsoluteDokumen10 halamanLectio Decima Septima: de Ablativo AbsoluteDomina Nostra FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Chaucer HumourDokumen1 halamanChaucer HumouranjumdkBelum ada peringkat
- Henry IV Part 1 Study GuideDokumen21 halamanHenry IV Part 1 Study GuideawtshfhdBelum ada peringkat
- Proposed Food Truck LawDokumen4 halamanProposed Food Truck LawAlan BedenkoBelum ada peringkat
- The Body of The Atman in The Katha UpanishadDokumen4 halamanThe Body of The Atman in The Katha UpanishadmikikiBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report On "Buying Behaviour: of Gold With Regards ToDokumen77 halamanProject Report On "Buying Behaviour: of Gold With Regards ToAbhishek MittalBelum ada peringkat
- Macquarie Equity Lever Adviser PresentationDokumen18 halamanMacquarie Equity Lever Adviser PresentationOmkar BibikarBelum ada peringkat
- Sikfil ReviewerDokumen6 halamanSikfil ReviewerBarrientos Lhea ShaineBelum ada peringkat
- WN On LTC Rules 2023 SBDokumen4 halamanWN On LTC Rules 2023 SBpankajpandey1Belum ada peringkat
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDokumen7 halamanBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledYanna ManuelBelum ada peringkat
- Text and Meaning in Stanley FishDokumen5 halamanText and Meaning in Stanley FishparthBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Rodney Britton v. Apple Inc. Job Descrimination, Sexual HarrassmentDokumen8 halaman1 Rodney Britton v. Apple Inc. Job Descrimination, Sexual HarrassmentJack PurcherBelum ada peringkat
- Ocampo - v. - Arcaya-ChuaDokumen42 halamanOcampo - v. - Arcaya-ChuaChristie Joy BuctonBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S0141391023000721 MainDokumen28 halaman1 s2.0 S0141391023000721 MainYemey Quispe ParedesBelum ada peringkat
- 755 1 Air India Commits Over US$400m To Fully Refurbish Existing Widebody Aircraft Cabin InteriorsDokumen3 halaman755 1 Air India Commits Over US$400m To Fully Refurbish Existing Widebody Aircraft Cabin InteriorsuhjdrftBelum ada peringkat
- Roof Structure Collapse Report - HongkongDokumen11 halamanRoof Structure Collapse Report - HongkongEmdad YusufBelum ada peringkat
- English Vocabulary Master for Intermediate Learners - Listen & Learn (Proficiency Level B1-B2)Dari EverandEnglish Vocabulary Master for Intermediate Learners - Listen & Learn (Proficiency Level B1-B2)Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (18)
- Learn English: Ultimate Guide to Speaking Business English for Beginners (Deluxe Edition)Dari EverandLearn English: Ultimate Guide to Speaking Business English for Beginners (Deluxe Edition)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (26)
- How to Improve English Speaking: How to Become a Confident and Fluent English SpeakerDari EverandHow to Improve English Speaking: How to Become a Confident and Fluent English SpeakerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (56)
- English Vocabulary Master: 150 Phrasal Verbs (Proficiency Level: Intermediate / Advanced B2-C1 – Listen & Learn)Dari EverandEnglish Vocabulary Master: 150 Phrasal Verbs (Proficiency Level: Intermediate / Advanced B2-C1 – Listen & Learn)Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (56)
- Learn English: Must-Know American English Slang Words & Phrases (Extended Version)Dari EverandLearn English: Must-Know American English Slang Words & Phrases (Extended Version)Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (30)
- English Pronunciation: Pronounce It Perfectly in 4 months Fun & EasyDari EverandEnglish Pronunciation: Pronounce It Perfectly in 4 months Fun & EasyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (24)
- English. Speaking Master (Proficiency level: Intermediate / Advanced B1-C1 – Listen & Learn)Dari EverandEnglish. Speaking Master (Proficiency level: Intermediate / Advanced B1-C1 – Listen & Learn)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (47)
- 7 Shared Skills for Academic IELTS Speaking-WritingDari Everand7 Shared Skills for Academic IELTS Speaking-WritingPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- ESL Role Plays: 50 Engaging Role Plays for ESL and EFL ClassesDari EverandESL Role Plays: 50 Engaging Role Plays for ESL and EFL ClassesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (10)
- English Made Easy Volume One: Learning English through PicturesDari EverandEnglish Made Easy Volume One: Learning English through PicturesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (15)
- English in Situations: Business English – New Edition (16 Topics – Proficiency level: B2 – Listen & Learn)Dari EverandEnglish in Situations: Business English – New Edition (16 Topics – Proficiency level: B2 – Listen & Learn)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (41)
- English Vocabulary Master: Phrasal Verbs in situations (Proficiency Level: Intermediate / Advanced B2-C1 – Listen & Learn)Dari EverandEnglish Vocabulary Master: Phrasal Verbs in situations (Proficiency Level: Intermediate / Advanced B2-C1 – Listen & Learn)Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (43)
- Learn English - Level 4: Intermediate English, Volume 1: Lessons 1-25Dari EverandLearn English - Level 4: Intermediate English, Volume 1: Lessons 1-25Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (8)
- Learn British English - Level 1: Introduction to British English, Volume 1: Volume 1: Lessons 1-25Dari EverandLearn British English - Level 1: Introduction to British English, Volume 1: Volume 1: Lessons 1-25Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- English Vocabulary ExercisesDari EverandEnglish Vocabulary ExercisesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (47)
- Learn English - Level 1: Introduction to English, Volume 1: Volume 1: Lessons 1-25Dari EverandLearn English - Level 1: Introduction to English, Volume 1: Volume 1: Lessons 1-25Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (6)
- English Vocabulary Master for Advanced Learners - Listen & Learn (Proficiency Level B2-C1)Dari EverandEnglish Vocabulary Master for Advanced Learners - Listen & Learn (Proficiency Level B2-C1)Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (7)
- Spanish Short Stories For Beginners (Vol 1): Use short stories to learn Spanish the fun way with the bilingual reading natural methodDari EverandSpanish Short Stories For Beginners (Vol 1): Use short stories to learn Spanish the fun way with the bilingual reading natural methodPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (18)
- The Picture of Dorian Gray (The Original 1890 Uncensored Edition + The Expanded and Revised 1891 Edition)Dari EverandThe Picture of Dorian Gray (The Original 1890 Uncensored Edition + The Expanded and Revised 1891 Edition)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (9054)
- Teaching Vocabulary, Revised EditionDari EverandTeaching Vocabulary, Revised EditionPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect: English Conversation, Premium Second EditionDari EverandPractice Makes Perfect: English Conversation, Premium Second EditionPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (3)
- ESL Reading Activities For Kids (6-13): Practical Ideas for the ClassroomDari EverandESL Reading Activities For Kids (6-13): Practical Ideas for the ClassroomPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Simple English Fluency System: How To Be Fluent In English Even If You Think It's Impossible!Dari EverandSimple English Fluency System: How To Be Fluent In English Even If You Think It's Impossible!Penilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (4)
- English Grammar Guide: 23 Grammar Rules You Must Know To Speak and Write English Like A NativeDari EverandEnglish Grammar Guide: 23 Grammar Rules You Must Know To Speak and Write English Like A NativePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (32)
- The Three Musketeers: Bilingual Edition (English – French)Dari EverandThe Three Musketeers: Bilingual Edition (English – French)Belum ada peringkat