5.2 Refraction and 5.3 Total Internal Reflection (Exercise)
Diunggah oleh
mydadawalfnDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
5.2 Refraction and 5.3 Total Internal Reflection (Exercise)
Diunggah oleh
mydadawalfnHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Refraction and total internal reflection 1) Using Snells law, determine the constant when the angle of incidence
and the angle of refraction are: a) 50 and 30 b) 30 and 18 c) 60 and 38 2) a) What is the angle of refraction in a medium if the angle of incidence in air is 48 and the index of refraction of the medium is 1.58? b) What is the angle of incidence in a medium in the case where the angle of refraction in air is 40 and the index of refraction of the medium is 1.58?
1) Using Snells law, determine the constant when the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction are: a) 50 and 30 b) 30 and 18 c) 60 and 38 2) a) What is the angle of refraction in a medium if the angle of incidence in air is 48 and the index of refraction of the medium is 1.58? b) What is the angle of incidence in a medium in the case where the angle of refraction in air is 40 and the index of refraction of the medium is 1.58?
3) A ray of light passes from air into water at an angle of incidence of 50. What is the angle of refraction? (HINT: You will need to use the sin-1 function on your calculator). 4) Light travels from air into water. If the angle of refraction is 30, what is the angle of incidence? 5) A ray of light in air strikes a block of quartz at an angle of incidence of 30. The angle of refraction is 20. What is the index of refraction in quartz? 6) One ray of light in air strikes a diamond and another strikes a piece of fused quartz. In each case the angle of incidence is 40. What is the difference in the angles of refraction? 7) An underwater swimmer looks up toward the surface of the water on a line of sight that makes an angle of 25 with a normal to the surface of the water. What is the angle of incidence in air for the light rays that enter the swimmers eye? 8) What is the critical angle for light rays passing from: a) glass into air b) glass into water 9) In each of the following questions, the second medium is air. a) What is the critical angle if the index of refraction for a medium is 1.68? b) What is the index of refraction of a medium if the critical angle is 40?
Indices of Refraction for Various Media: Medium Index of Refraction (n) Air/vacuum 1.00 Ice 1.31 Water 1.33 Ethyl alcohol 1.36 Vegetable oil 1.47 Acrylic 1.49 Glass 1.52 Diamond 2.42
3) A ray of light passes from air into water at an angle of incidence of 50. What is the angle of refraction? (HINT: You will need to use the sin-1 function on your calculator). 4) Light travels from air into water. If the angle of refraction is 30, what is the angle of incidence? 5) A ray of light in air strikes a block of quartz at an angle of incidence of 30. The angle of refraction is 20. What is the index of refraction in quartz? 6) One ray of light in air strikes a diamond and another strikes a piece of fused quartz. In each case the angle of incidence is 40. What is the difference in the angles of refraction? 7) An underwater swimmer looks up toward the surface of the water on a line of sight that makes an angle of 25 with a normal to the surface of the water. What is the angle of incidence in air for the light rays that enter the swimmers eye? 8) What is the critical angle for light rays passing from: a) glass into air b) glass into water 9) In each of the following questions, the second medium is air. a) What is the critical angle if the index of refraction for a medium is 1.68? b) What is the index of refraction of a medium if the critical angle is 40?
Indices of Refraction for Various Media: Medium Index of Refraction (n) Air/vacuum 1.00 Ice 1.31 Water 1.33 Ethyl alcohol 1.36 Vegetable oil 1.47 Acrylic 1.49 Glass 1.52 Diamond 2.42
Answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. a) 1.53 a) 28 35 42 1.46 11 34 a) 41 a) 37 b) 1.62 b) 24 c) 1.41
Answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. a) 1.53 a) 28 35 42 1.46 11 34 a) 41 a) 37 b) 1.62 b) 24 c) 1.41
b) 61 b) 1.56
b) 61 b) 1.56
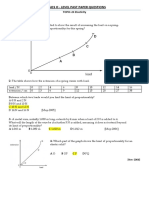
Lenses 1) Find the power: (a) convex lens, f = 20 cm, (b) convex lens, f = 5 cm.
Refraction and total internal reflection
2) An object is placed in front of a convex lens with focal length of 10 cm. Find the nature, position and magnification of the image formed when the object distance is 15 cm. 3) An object is placed 20 cm from a concave lens of focal length 15 cm. a) Calculate the image distance. b) State the characteristics of the image formed. A convex lens with focus length of 15 cm formed an image which is real, inverted and same size with the object. What is the object distance from the lens? When an object of height 3.0 cm is placed 20 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm, what is the height of the image formed? Starting with the lens formula, ,
4)
5)
6)
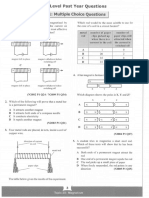
a) derive an equation that gives the relationship between liner magnification, m and the image distance, v. Hence sketch the graph of m against v. b) State the value of m at the point of intersection of the graph with the vertical axis. c) Describe how you would determine the focal length of the lens using the graph. 7) The figure on the right shows the structure of a slide projector. a) Why is the light source placed at the centre of curvature of the concave mirror and the focus of the condenser lens? b) State the characteristics of the image formed on the screen. c) Why the slide has to be placed inverted in the projector?
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- W44 5.3 Total Internal ReflectionDokumen6 halamanW44 5.3 Total Internal ReflectionBid HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Form 4 Physics RevisionDokumen5 halamanForm 4 Physics RevisionannmarieBelum ada peringkat
- Sec 1E Revision Quiz Chapter 2 AnsDokumen4 halamanSec 1E Revision Quiz Chapter 2 Ansscribduser0811972100% (1)
- Form 5 ProbabilityDokumen11 halamanForm 5 ProbabilityThanaletchumy ChandrasegarBelum ada peringkat
- Task 1: Group 1 - The Alkali MetalsDokumen4 halamanTask 1: Group 1 - The Alkali MetalsNeen NaazBelum ada peringkat
- Level Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-24 Elasticity PAPER-1 Multiple ChoiceDokumen4 halamanLevel Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-24 Elasticity PAPER-1 Multiple Choiceelty TanBelum ada peringkat
- Test: Waves: Section A: CoreDokumen14 halamanTest: Waves: Section A: Coreapi-3705610Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 4Dokumen33 halamanPhysics Form 4 Chapter 4Eric LengBelum ada peringkat
- Homeworks 1 eDokumen8 halamanHomeworks 1 eSumi VjBelum ada peringkat
- Class 10 p1 Thermal PhysicsDokumen10 halamanClass 10 p1 Thermal PhysicsSameer Abu MunsharBelum ada peringkat
- Form 2 Science Chapter 7Dokumen32 halamanForm 2 Science Chapter 7qq23582% (11)
- WorkEnergy P2Dokumen26 halamanWorkEnergy P2dhairya gandhi100% (1)
- O Level Nuclear Physics and RadioactivityDokumen16 halamanO Level Nuclear Physics and RadioactivityMd SafwatBelum ada peringkat
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 4 - Teacher'sDokumen9 halamanForm 4 Physics Chapter 4 - Teacher'sPavithiran50% (2)
- Biology Class 9 Revised Syllabus Break Up 2020-21-23Dokumen7 halamanBiology Class 9 Revised Syllabus Break Up 2020-21-23MohammadBelum ada peringkat
- Rates Practice Exam QuestionsDokumen18 halamanRates Practice Exam QuestionsisheanesuBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 3 Chapter 4Dokumen95 halamanScience Form 3 Chapter 4Eric Chew100% (1)
- Integrated Science Form 2 June 2010Dokumen9 halamanIntegrated Science Form 2 June 2010asjawolverine0% (2)
- 4 Work, Energy and PowerDokumen1 halaman4 Work, Energy and PowerGajendraBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Science Notes Ch8 ElectricDokumen3 halamanIntegrated Science Notes Ch8 ElectricAngel LiBelum ada peringkat
- 8.1-Transport - in - Plants - Igcse-Cie-Biology - Solved OLIDokumen13 halaman8.1-Transport - in - Plants - Igcse-Cie-Biology - Solved OLIAmber TeacherBelum ada peringkat
- Year 9 Physics Pressure WorksheetDokumen5 halamanYear 9 Physics Pressure Worksheetaswata NarayanBelum ada peringkat
- O Level Pure Physics Topic by Topic 3 109 112Dokumen4 halamanO Level Pure Physics Topic by Topic 3 109 112Kugan KishurBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Form 4 PreliminariesDokumen6 halamanPhysics Form 4 PreliminariesMejo Joy0% (1)
- P6 Science SA1 2017 Henry Park Exam PapersDokumen48 halamanP6 Science SA1 2017 Henry Park Exam PapersrishitBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Worksheet For Grade - 10 (Part - 2) Ebenezer School (From K-G Up To Preparatory)Dokumen6 halamanPhysics Worksheet For Grade - 10 (Part - 2) Ebenezer School (From K-G Up To Preparatory)YishakBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1-Introduction To ScienceDokumen53 halamanChapter 1-Introduction To ScienceSumi VjBelum ada peringkat
- Combined PhysicsDokumen361 halamanCombined PhysicsBaumkuchBelum ada peringkat
- S 3 Physics Notes For O' LevelDokumen96 halamanS 3 Physics Notes For O' Levelmemeaw100% (1)
- Radioactive Worksheet IGCSEDokumen2 halamanRadioactive Worksheet IGCSESyakti PerdanaBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet States of Matter ks3Dokumen2 halamanWorksheet States of Matter ks3Edward edwardBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Reflection of Light: Practice 1.1 (P. 5)Dokumen24 halaman1 Reflection of Light: Practice 1.1 (P. 5)Kwok Chi HoBelum ada peringkat
- 2019 JC1 H2 Math (Promotion Exam) Anglo Chinese Junior College AnswerDokumen16 halaman2019 JC1 H2 Math (Promotion Exam) Anglo Chinese Junior College AnswerSalman ShethBelum ada peringkat
- FORM 2, Chap 03-BiodiversityDokumen15 halamanFORM 2, Chap 03-BiodiversitySyahrul100% (11)
- 12 SACE Start of Year Revision SOLUTIONSDokumen6 halaman12 SACE Start of Year Revision SOLUTIONSLydia LamBelum ada peringkat
- Notes - Topic 5 Forces, Density and Pressure - CAIE Physics A-LevelDokumen5 halamanNotes - Topic 5 Forces, Density and Pressure - CAIE Physics A-LevelMahamIsmailBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 1 ExcerciseDokumen8 halamanChap 1 ExcerciseGreen Signal100% (2)
- Form 2 Chapter 2Dokumen2 halamanForm 2 Chapter 2Ng Imm Khuan100% (1)
- 2019 Sec 4 Science Chemistry SA2 Singapore Sports SchoolDokumen30 halaman2019 Sec 4 Science Chemistry SA2 Singapore Sports School19Y1H GAO CHENZHANGBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 2 November 1999Dokumen5 halamanPaper 2 November 1999MSHBelum ada peringkat
- 1 How Plants Grow and Chapt1 of Book3 PhotosynDokumen15 halaman1 How Plants Grow and Chapt1 of Book3 Photosynrashmi_harryBelum ada peringkat
- Waves and Interference Worksheet 2Dokumen14 halamanWaves and Interference Worksheet 2Freya SawBelum ada peringkat
- Revision Form 5 Chapter 3 PDFDokumen18 halamanRevision Form 5 Chapter 3 PDFYz PohBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 6th Fun With Magnets ScienceDokumen5 halamanGrade 6th Fun With Magnets Scienceredjasemk100% (1)
- 2012 OLevel Science Physics Paper 2 Questions and AnswersDokumen10 halaman2012 OLevel Science Physics Paper 2 Questions and AnswersMethodology OfStudiesBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Grade 7Dokumen6 halamanMaths Grade 7Anonymous 3E1GVEBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1 Quantitative SLHL Test ADokumen9 halamanTopic 1 Quantitative SLHL Test APak Hei Marcus CHOWBelum ada peringkat
- Sec4 2019 Science Physics PapersDokumen427 halamanSec4 2019 Science Physics PapersChristine Gan Tze TingBelum ada peringkat
- MID-TERM EXAMINATION (Chapter 1 To Chapter 4)Dokumen8 halamanMID-TERM EXAMINATION (Chapter 1 To Chapter 4)Shakilla HamzahBelum ada peringkat
- Chem Insights Chapter 7 WSDokumen3 halamanChem Insights Chapter 7 WSwakakkaBelum ada peringkat
- F2 Science C8 Force and Motion TextDokumen15 halamanF2 Science C8 Force and Motion TextAlex LowBelum ada peringkat
- 2012 Physics 5058 O-Level AnswersDokumen7 halaman2012 Physics 5058 O-Level AnswersheyitsvanBelum ada peringkat
- Famine Lesson Worksheet PDFDokumen83 halamanFamine Lesson Worksheet PDFTong LawrenceBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 2 Microscopic World IDokumen15 halamanTopic 2 Microscopic World IBelladonna LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Question Bank (Chapters 31-33)Dokumen45 halamanPhysics Question Bank (Chapters 31-33)Young KimBelum ada peringkat
- Reflection and RefractionDokumen1 halamanReflection and RefractionAnderson KandaiBelum ada peringkat
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch30 Test BankDokumen8 halamanWolfson Eup3 Ch30 Test BankifghelpdeskBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1 Phy250Dokumen9 halamanTutorial 1 Phy250Muhammad AziziBelum ada peringkat
- Review Sheet 2426 Final ExamDokumen19 halamanReview Sheet 2426 Final ExamperezromBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment Refraction of Light (Refractive Index)Dokumen2 halamanExperiment Refraction of Light (Refractive Index)mydadawalfn100% (1)
- Experiment Reflection of Light (Optical Pin)Dokumen2 halamanExperiment Reflection of Light (Optical Pin)mydadawalfn100% (1)
- Linear Motion Equation EXERCISEDokumen1 halamanLinear Motion Equation EXERCISEmydadawalfnBelum ada peringkat
- Inovasi PBS Eng Y3 47Dokumen1 halamanInovasi PBS Eng Y3 47mydadawalfnBelum ada peringkat
- 0625 Y14 SQ 191114Dokumen114 halaman0625 Y14 SQ 191114mydadawalfnBelum ada peringkat
- 1.8 Tension and UpthrustDokumen9 halaman1.8 Tension and Upthrustmydadawalfn80% (5)
- Physics Paper 2Dokumen2 halamanPhysics Paper 2mydadawalfn100% (2)
- 1 The Nucleus of An AtomDokumen10 halaman1 The Nucleus of An AtommydadawalfnBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding The Uses of C.R.O.Dokumen24 halamanUnderstanding The Uses of C.R.O.mydadawalfnBelum ada peringkat
- Answering Techniques For Physics Paper 3Dokumen2 halamanAnswering Techniques For Physics Paper 3jajabeansBelum ada peringkat
- 2.10 ExerciseDokumen2 halaman2.10 ExercisemydadawalfnBelum ada peringkat
- Prefixes: How To Remember The Prefixes?Dokumen3 halamanPrefixes: How To Remember The Prefixes?mydadawalfnBelum ada peringkat
- f4 c4 Heat SumDokumen9 halamanf4 c4 Heat SummydadawalfnBelum ada peringkat
- Linear Motion and GraphDokumen1 halamanLinear Motion and GraphmydadawalfnBelum ada peringkat
- Calipers and MicrometersDokumen56 halamanCalipers and MicrometersUTHISHBelum ada peringkat
- Troysperse CD1Dokumen4 halamanTroysperse CD1Fajar Ismanto Part IIBelum ada peringkat
- Luisa 1Dokumen20 halamanLuisa 1Walenty JanowiczBelum ada peringkat
- Worzakowska2016 Article ThermalBehaviorDecompositionMeDokumen10 halamanWorzakowska2016 Article ThermalBehaviorDecompositionMeJavier Andres Munoz ChavesBelum ada peringkat
- Control System Engineering EC6405 Unit I-Cont Rol Syste M Mod Elin G Part ADokumen12 halamanControl System Engineering EC6405 Unit I-Cont Rol Syste M Mod Elin G Part ASivaprakasam KarthikeyanBelum ada peringkat
- A Guidebook To Mechanism in Organic ChemistryDokumen280 halamanA Guidebook To Mechanism in Organic Chemistryarpit100% (1)
- ISO/TS 12913-2:2018 Soundscape - Part 2: Data Collection and Reporting Requirements - What's It All About?Dokumen3 halamanISO/TS 12913-2:2018 Soundscape - Part 2: Data Collection and Reporting Requirements - What's It All About?jrlr65100% (1)
- SurveyiingDokumen11 halamanSurveyiingELEVATED KnowledgeBelum ada peringkat
- Adaptive Control PDFDokumen2 halamanAdaptive Control PDFArjun PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Sheldon S File 3Dokumen7 halamanSheldon S File 3NATHANIEL YACASBelum ada peringkat
- Radiation QuestionsDokumen27 halamanRadiation QuestionsSteve BishopBelum ada peringkat
- GeomaticaDokumen5 halamanGeomaticaAlcantaraSusyBelum ada peringkat
- 4Dokumen13 halaman4Aruna KumarasiriBelum ada peringkat
- PIPA BV Eflex - p015 - e PDFDokumen8 halamanPIPA BV Eflex - p015 - e PDFNur Cholis HadiBelum ada peringkat
- Astm D3078 94Dokumen1 halamanAstm D3078 94Jusuf Hasan100% (1)
- Ce2253 Applied Hydraulic Engg Qus Bank PDFDokumen13 halamanCe2253 Applied Hydraulic Engg Qus Bank PDFthamilarasuBelum ada peringkat
- First Push 2024 Grade 12 Marking Guide March 2024Dokumen12 halamanFirst Push 2024 Grade 12 Marking Guide March 2024lemonlululu1Belum ada peringkat
- Brackish WaterDokumen35 halamanBrackish WaterChemsys SunnyBelum ada peringkat
- Potential Difference WorksheetDokumen2 halamanPotential Difference WorksheetDigCity DiggBelum ada peringkat
- Pengaruh Kecepatan Pemotongan Dan Ketebalan Bahan Terhadap Kekerasan Dan Kekasaran Permukaan Baja Aisi 1045 Menggunakan CNC Plasma Arc CuttingDokumen6 halamanPengaruh Kecepatan Pemotongan Dan Ketebalan Bahan Terhadap Kekerasan Dan Kekasaran Permukaan Baja Aisi 1045 Menggunakan CNC Plasma Arc CuttingRamjay BudiartoBelum ada peringkat
- Semiconductor Memories Semiconductor Memories Semiconductor Memories Semiconductor MemoriesDokumen37 halamanSemiconductor Memories Semiconductor Memories Semiconductor Memories Semiconductor MemoriesPriyank DevpuraBelum ada peringkat
- Rock Proof: Liquid Water Integral WaterproofDokumen2 halamanRock Proof: Liquid Water Integral Waterproofimran jamalBelum ada peringkat
- HW1 Phys3041Dokumen3 halamanHW1 Phys3041Sam TseBelum ada peringkat
- MIT6 003F11 hw04 PDFDokumen14 halamanMIT6 003F11 hw04 PDFSudheer KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Test Physics Rotational Motion NEETDokumen9 halamanTest Physics Rotational Motion NEETAnwaar MalviBelum ada peringkat
- Method Development and Validation For Estimation of Dosulepin in Pure and Dosage Form by Using HPLCDokumen8 halamanMethod Development and Validation For Estimation of Dosulepin in Pure and Dosage Form by Using HPLCBaru Chandrasekhar RaoBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Pinch TechnologyDokumen46 halamanIntroduction To Pinch TechnologyM Scott GreenBelum ada peringkat
- Cromax 4140 PDFDokumen2 halamanCromax 4140 PDFDidik PrihantoroBelum ada peringkat
- St. Joseph'S College of EngineeringDokumen2 halamanSt. Joseph'S College of Engineeringfaizu35Belum ada peringkat
- Water Stagnant of Solar ModulesDokumen6 halamanWater Stagnant of Solar ModulesNITIN MISHRABelum ada peringkat
- Week 5 - Random Variables, CDF, PDFDokumen16 halamanWeek 5 - Random Variables, CDF, PDFHaris GhafoorBelum ada peringkat