Yearly Plan 2011 Biology Form 4: Week Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Notes
Diunggah oleh
Yeexin HoongJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Yearly Plan 2011 Biology Form 4: Week Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Notes
Diunggah oleh
Yeexin HoongHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
YEARLY PLAN 2011 BIOLOGY FORM 4
WEEK
LEARNING AREA
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
LEARNING OUTCOMES
NOTES
FORM 4 ORIENTATION WEEK ( 4 7 JANUARY 2011)
th th
1.0 Introduction to Biology
1.1 Understanding the study of Biology
State what the study of Biology is Explain the importance of Biology List the different fields of study in Biology List the careers related to Biology State various ways of studying Biology
Discussion
1.2 Applying scientific investigation
Identify the variables in a given situation Identify the relationship between two variables to form a hypothesis Design and carry out a simple experiment to test the hypothesis Record and present data in a suitable form Interpret data to draw conclusions Write a report on an experiment Practice scientific attitudes and noble values
Discussion
2.0 Cell Structure and Cell Organization
2.1 Understanding cell structure and function
Draw and label an animal cell Draw and label a plant cell Identify the cellular components of an animal cell Identify the cellular components of a plant cell State the functions of the cellular components in an animal cell
Sketching
State the functions of the cellular components in a plant cell Compare and contrast an animal cell and a plant cell Relate the density of certain organelles with the functions of specific cells
Discussion
CHINESE NEW YEAR BREAK (29 JANUARY 6 FEBRUARY 2011)
th
th
2.2 Understanding cell organization
State the necessity for cell specialization in multicellular organism as compared to unicellular organism Describe cell specialization in multicellular organisms Describe cell organization in the formation of tissues, organs and systems in multicellular organisms State the meaning of internal environment Identify factors affecting the internal environment Describe the involvement of various systems in maintaining optimal internal environment.
Role play
2.3 Appreciating the uniqueness of the cell
Predict the state of certain cells without a particular cellular component Illustrate that most cells are specialized for the job that they perform
3.0 Movement of Substances Across the Plasma Membrane
3.1 Analyzing the movement of substances across the plasma membrane
State the substances required by living cells State the substances that have to be eliminated from cells Explain the necessity for movement of substances across the plasma membrane Describe the structure of plasma membrane
Discussion Interpreting diagrams
Describe the permeability of the plasma membrane Explain the movement of soluble substances across the plasma membrane through the process of passive transport Explain the movement of water molecules across the plasma membrane by osmosis Explain the movement of substances across the plasma membrane through active transport Explain the process of passive transport in living organisms using examples
3.2 Understanding the movement of substances across the plasma membrane in everyday life
Explain what hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic solutions are Explain the effects of hypotonic and hypertonic solutions on plant cell and animal cell Explain plasmolysis, deplasmolysis, haemolysis and crenation Design an experiment to determine the concentration of external solution which is isotonic to cell sap Make an inference on the concentration of cell sap in plant tissues Replace the movement of substances across the plasma membrane with the concentration gradient Explain the phenomenon of wilting plants using the examples Explain the preservation of food using examples
Discussion Experiment
3.3 Appreciating the movement of substances across the plasma membrane
Explain the necessity of movement of substances across the plasma membrane which occurs in a continuous and controlled manner for survival of the cell
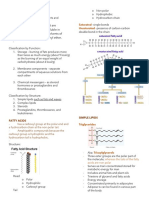
4.0 Chemical Composition of the Cell
4.1 Understanding the chemical composition of the cell
State the elements in the cell List the chemical compounds in the cell Explain the importance of organic compounds in the cell Explain the importance of water in the cell
Discussion Brain storming
4.2 Understanding carbohydrates
State the elements in carbohydrates State the types of carbohydrate Explain the formation and breakdown of disaccharides and polysaccharides
4.3 Understanding proteins
State the elements in proteins State the various structures of proteins Explain the formation and breakdown of dipeptides and polypeptides Explain the meaning of essential amino acids and non-essential amino acids
Illustrating
4.4 Understanding lipids
State the elements in lipids State the main types of lipid State the components of fats and oils Explain the formation and breakdown of fats and oils Compare and contrast saturated fats and unsaturated fats
10
4.5 Understanding enzymes
State what enzymes are Explain why enzymes are needed in life processes List the general characteristics of enzymes Relate the name of enzyme to substrate State sites where the enzymes are synthesized
State the meaning of intracellular enzymes and extracellular enzymes Explain the movement of specific organelles in the production of extracellular enzymes
11
FIRST SEMESTER BREAK (SOMETHING LIKE THAT)
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 25 26 27 28 4.0 Heat 29
30
31 32 5.0 Light
33 34
35
36
37
38
39
40
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- BiologyDokumen7 halamanBiologyLuis VasquezBelum ada peringkat
- SMJK Phor Tay Biology Form 4 (Yearly Plan 2015)Dokumen8 halamanSMJK Phor Tay Biology Form 4 (Yearly Plan 2015)pooyenpengBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm Study Guide CP BiologyDokumen1 halamanMidterm Study Guide CP BiologyCrystalBelum ada peringkat
- GCE - O Level BiologyDokumen25 halamanGCE - O Level BiologyWayne WeeBelum ada peringkat
- Form One Biology: by The End of Form One Work, The Learner Should Be Able ToDokumen54 halamanForm One Biology: by The End of Form One Work, The Learner Should Be Able TooyooBelum ada peringkat
- Name: - Date: - Biology F4 Rev. - Chapter 2 - Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDokumen2 halamanName: - Date: - Biology F4 Rev. - Chapter 2 - Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationCasuarina NiraimathiBelum ada peringkat
- 2015 Fall Semester Test Biology Study Guide: Fromunit 1 (Answer On Your Own Paper)Dokumen8 halaman2015 Fall Semester Test Biology Study Guide: Fromunit 1 (Answer On Your Own Paper)beckid75Belum ada peringkat
- Revision BIODokumen12 halamanRevision BIOPreyhunter ?Belum ada peringkat
- Cells and Heredity: Unit OneDokumen4 halamanCells and Heredity: Unit Oneapi-287848315Belum ada peringkat
- Science Chapter 2: Cell-The Basic Unit of LifeDokumen2 halamanScience Chapter 2: Cell-The Basic Unit of LifeWan RoziahBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus Cambridge o Level BiologyDokumen12 halamanSyllabus Cambridge o Level BiologyNisha AliyaBelum ada peringkat
- BIO 101 Course Objectives Sp23Dokumen6 halamanBIO 101 Course Objectives Sp23begush015Belum ada peringkat
- Grade 9 / Year 10 Biology Course Syllabus 2020-2021course Outline Term 1Dokumen8 halamanGrade 9 / Year 10 Biology Course Syllabus 2020-2021course Outline Term 1CanioBelum ada peringkat
- Cluster/Subject/Competency: 1. Biological Science 1-Plant and Animal Biology 1Dokumen3 halamanCluster/Subject/Competency: 1. Biological Science 1-Plant and Animal Biology 1Baby Jane AnayBelum ada peringkat
- Obe Chem 103L 2015-2016Dokumen11 halamanObe Chem 103L 2015-2016Joseph AndaganBelum ada peringkat
- Year 11 Jan Mock Revision ListDokumen9 halamanYear 11 Jan Mock Revision Listbseddon6969Belum ada peringkat
- Yearly Teaching Plan 2012 - Biology Form FourDokumen13 halamanYearly Teaching Plan 2012 - Biology Form FourChe Mahani HussainBelum ada peringkat
- ANPH-M1-CU2. The Cell & Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction (Mitosis and Meiosis)Dokumen26 halamanANPH-M1-CU2. The Cell & Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction (Mitosis and Meiosis)ajdBelum ada peringkat
- Themes in The Study of LifeDokumen4 halamanThemes in The Study of Lifeapi-233187566Belum ada peringkat
- Biology IntroductionDokumen122 halamanBiology Introductioncpantsula0% (1)
- Biology B1 Characteristics of Living OrganismsDokumen28 halamanBiology B1 Characteristics of Living OrganismsShamini Segari GunasakaranBelum ada peringkat
- BIO 101 Exit Exam Study GuideDokumen3 halamanBIO 101 Exit Exam Study GuideOlaide Seun Akintade100% (1)
- Scheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4, 2013Dokumen27 halamanScheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4, 2013Haslinda SheikhBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy Physiology Course InfoDokumen5 halamanAnatomy Physiology Course InfoJessa ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Myp Biology Student ChecklistsDokumen12 halamanMyp Biology Student CheckliststeddyenBelum ada peringkat
- Study Questions For Test 1 BioDokumen4 halamanStudy Questions For Test 1 BiokadooieBelum ada peringkat
- AllChapterQuestions PDFDokumen23 halamanAllChapterQuestions PDFKim Na NaBelum ada peringkat
- Biological Science Ncbts-Based Let 2009 TosDokumen8 halamanBiological Science Ncbts-Based Let 2009 TosEngineerEducator0% (1)
- Tutorial Sheet BIO 101 - MSFPDokumen11 halamanTutorial Sheet BIO 101 - MSFPhopekingbwalya23Belum ada peringkat
- Homework Assignment #2 (Chapters 2, 3-4.1)Dokumen5 halamanHomework Assignment #2 (Chapters 2, 3-4.1)joseBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Notes Form 2 - Form Two Biology by The End of Form Two Work, The Learner Should Be Able ToDokumen71 halamanBiology Notes Form 2 - Form Two Biology by The End of Form Two Work, The Learner Should Be Able ToKehmoka TimothyBelum ada peringkat
- Honor Biology Midterm Exam Review Questions The Science of BiologyDokumen2 halamanHonor Biology Midterm Exam Review Questions The Science of BiologybobopowerBelum ada peringkat
- ANPH-M1-CU2. The Cell & Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction (Mitosis and Meiosis) PDFDokumen26 halamanANPH-M1-CU2. The Cell & Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction (Mitosis and Meiosis) PDFJamaica M DanguecanBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology Course SyllabusDokumen5 halamanAnatomy and Physiology Course SyllabusDanna ManaloBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Notes Form One Syllabus by The End of Form One Work, The Learner Should Be Able ToDokumen77 halamanBiology Notes Form One Syllabus by The End of Form One Work, The Learner Should Be Able ToKehmoka TimothyBelum ada peringkat
- Mid Term Study Guide For 2022 Without EcologyDokumen8 halamanMid Term Study Guide For 2022 Without EcologyAniya HarriottBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Division: Origin of CellsDokumen9 halamanCell Division: Origin of CellselizabethBelum ada peringkat
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Sultan Badlishah Annual Lesson Plan Biology Form 4 (2016)Dokumen30 halamanSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Sultan Badlishah Annual Lesson Plan Biology Form 4 (2016)wienna1987Belum ada peringkat
- Studyguide AnswerkeyDokumen23 halamanStudyguide Answerkeyapi-237676607Belum ada peringkat
- Course InformationDokumen7 halamanCourse InformationSani IsmailBelum ada peringkat
- Science Competencies in 5th and 6th Grade With Table of SpecificationsDokumen25 halamanScience Competencies in 5th and 6th Grade With Table of SpecificationsTerence Pelingon89% (18)
- Chapter 3 Lecture 7thDokumen48 halamanChapter 3 Lecture 7thapi-208617789Belum ada peringkat
- Cluster/Subject/Competency: 1. Biological Science 1-Plant and Animal Biology 1Dokumen3 halamanCluster/Subject/Competency: 1. Biological Science 1-Plant and Animal Biology 1Baby Jane AnayBelum ada peringkat
- Quarter2 Syllabus StudentDokumen3 halamanQuarter2 Syllabus Studentapi-232311174Belum ada peringkat
- Science Form 3 2016 Year Plan: SMK (L) Methodist Kuala LumpurDokumen13 halamanScience Form 3 2016 Year Plan: SMK (L) Methodist Kuala LumpurkriizBelum ada peringkat
- ANPH-M1-CU2. The Cell & Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction (Mitosis and Meiosis)Dokumen25 halamanANPH-M1-CU2. The Cell & Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction (Mitosis and Meiosis)Angelo SoteroBelum ada peringkat
- RPH Biologi TG4Dokumen28 halamanRPH Biologi TG4lilyraj100% (1)
- Module 7Dokumen38 halamanModule 7LeighBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan Biology Form 4 2011Dokumen8 halamanLesson Plan Biology Form 4 2011FidaBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1 Living Cells On-LineDokumen46 halamanTopic 1 Living Cells On-Lineadkin142119Belum ada peringkat
- AP Biology Free Response Questions Through 2010Dokumen44 halamanAP Biology Free Response Questions Through 2010Bob100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Bio Test Study Guide BDokumen4 halamanChapter 7 Bio Test Study Guide BRachel FrankenfieldBelum ada peringkat
- Biomolecules Exam RevisionDokumen3 halamanBiomolecules Exam RevisionCarmen CheahBelum ada peringkat
- Course ObjectivesDokumen4 halamanCourse ObjectivesAdam NicholsBelum ada peringkat
- Review GuideDokumen5 halamanReview Guidefacob95876Belum ada peringkat
- Ib Biology List of ObjectivesDokumen6 halamanIb Biology List of Objectivespaulo05132Belum ada peringkat
- Week Date Topic/Sub Topic Descriptions Learning OutcomesDokumen8 halamanWeek Date Topic/Sub Topic Descriptions Learning OutcomesAndrea JoeBelum ada peringkat
- AP BioDokumen4 halamanAP BioAlisha MasonBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2Dokumen11 halamanChapter 2Tang Szu ChingBelum ada peringkat
- Reply Speech: What Has Been The Government/ Opposition's Stand?Dokumen2 halamanReply Speech: What Has Been The Government/ Opposition's Stand?Yeexin HoongBelum ada peringkat
- Clothes and Accessories Vocabulary Esl Crossword Puzzle Worksheets For KidsDokumen6 halamanClothes and Accessories Vocabulary Esl Crossword Puzzle Worksheets For KidsYeexin HoongBelum ada peringkat
- Mad About EnglishDokumen1 halamanMad About EnglishYeexin HoongBelum ada peringkat
- Question 35Dokumen2 halamanQuestion 35Yeexin HoongBelum ada peringkat
- Section CDokumen1 halamanSection CYeexin HoongBelum ada peringkat
- Action Verbs Pictionary 1 Handactiout PDFDokumen2 halamanAction Verbs Pictionary 1 Handactiout PDFYeexin Hoong33% (3)
- LyricsDokumen2 halamanLyricsYeexin HoongBelum ada peringkat
- Beserah Fishing VillageDokumen1 halamanBeserah Fishing VillageYeexin HoongBelum ada peringkat
- Edible Cell Biology Project RubricDokumen1 halamanEdible Cell Biology Project Rubricalathena alathenaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure Function Review PresentationDokumen8 halamanCell Structure Function Review PresentationCharles IppolitoBelum ada peringkat
- AnatomyDokumen23 halamanAnatomyMiracle For NursesBelum ada peringkat
- UltraDokumen6 halamanUltrabasana siamremareBelum ada peringkat
- Essay Prokaryotic vs. EukaryoticDokumen2 halamanEssay Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryoticctramel001Belum ada peringkat
- Biol 1700 2019Dokumen21 halamanBiol 1700 2019api-434583946Belum ada peringkat
- Cellular Transport Notes (7.4) - ScreenDokumen28 halamanCellular Transport Notes (7.4) - ScreenBomber 9012Belum ada peringkat
- 1 - BGB 201aDokumen81 halaman1 - BGB 201aAnkush YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry - A Short CourseDokumen1.026 halamanBiochemistry - A Short CourseFelicita Urzi100% (3)
- Dialysis ExperimentDokumen2 halamanDialysis ExperimentAbhishek GadhwalBelum ada peringkat
- Past Questions Cells N Biomolecules A Level BiologyDokumen32 halamanPast Questions Cells N Biomolecules A Level BiologyZak berry100% (1)
- Scientific MethodDokumen10 halamanScientific MethodHannaj May De GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- STBP 1023 Cell BiologyDokumen73 halamanSTBP 1023 Cell BiologyAzman YaacubBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Paper 2Dokumen15 halamanBiology Paper 2gothBelum ada peringkat
- Active Transport MechanismDokumen3 halamanActive Transport MechanismDaren jay GeneraleBelum ada peringkat
- Lipids - ReviewerDokumen7 halamanLipids - ReviewerIYA LABAOBelum ada peringkat
- The Cell (Cytology) : Dr. Moono SilitongoDokumen60 halamanThe Cell (Cytology) : Dr. Moono SilitongoOsman M JubaBelum ada peringkat
- 1920 H2 Bio JC1 MYE Revision Package (QNS) (For Students) PDFDokumen80 halaman1920 H2 Bio JC1 MYE Revision Package (QNS) (For Students) PDFHlaing HlaingBelum ada peringkat
- A Review of Water Treatment Membrane Nano Technologies 2011 Eric HoekDokumen26 halamanA Review of Water Treatment Membrane Nano Technologies 2011 Eric Hoekrancak100% (1)
- Cell Biology PYQs Solution - 19189642 - 2023 - 06 - 05 - 12 - 38Dokumen12 halamanCell Biology PYQs Solution - 19189642 - 2023 - 06 - 05 - 12 - 38Arsh DhawanBelum ada peringkat
- Costanzo Physiology 7Th Edition Costanzo PHD Full ChapterDokumen67 halamanCostanzo Physiology 7Th Edition Costanzo PHD Full Chapterkristine.dixon271100% (6)
- Environmental Applications of Immobilized Microbial Cells A PDFDokumen23 halamanEnvironmental Applications of Immobilized Microbial Cells A PDFCamelia TincuBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure, Function Practice Test With AnswersDokumen16 halamanCell Structure, Function Practice Test With AnswersDJ ISAACSBelum ada peringkat
- Cell and MicrobesDokumen12 halamanCell and MicrobesSUBHABelum ada peringkat
- Cell WallDokumen4 halamanCell WallSamia KhandkerBelum ada peringkat
- English For Academics and Professional Purposes: General To SpecificDokumen10 halamanEnglish For Academics and Professional Purposes: General To SpecificChristine Joy CagatinBelum ada peringkat
- Cells 4THDokumen70 halamanCells 4THKyng GamariBelum ada peringkat
- 4 - Physiology Main Handout Oct 2023Dokumen99 halaman4 - Physiology Main Handout Oct 2023Trisha Anne WacasBelum ada peringkat
- Toxicokinetics DynamicsDokumen76 halamanToxicokinetics DynamicsSunil100% (1)
- Cells and Organelles Coloring PagesDokumen5 halamanCells and Organelles Coloring Pagescarsontk421Belum ada peringkat