Inverter Design
Diunggah oleh
Kirthika Vinoth KumarDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Inverter Design
Diunggah oleh
Kirthika Vinoth KumarHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EXP NO:2 DATE: CMOS INVERTER LAYOUT DESIGN
AIM: To design cmos inverter layout and from schematic entry to post layout simulation using mentor graphics EDA tools.
TOOLS REQUIRED: Mentor Graphics.
CMOS INVERTER THEORY: An inverter circuit outputs a voltage representing the opposite logic level to its input.inverters can be constructed using a single nmos transistor or a single pmos transistor coupled with a resistor.since this resistive drain approach uses only a single type of transistor it can be fabricated at low cost.However because current flows through the resistor in one of the two states ,the resistive drain configuration is disadvantaged for power consumption and processing speed.
CMOS inverter consists of a pull-up transistor and a pull-down transistor. Pull-up transistor is made up of p-type transistor and pull-down is of n-type. These pull-down and pull-up transistors are connected in series. When we are applying a low voltage (0v) n-type transistor will be off and p-type transistor will be conducting. Thus we will have vdd as the output (5V). When the input voltage is high the n-type transistor will conduct and p-type transistor will be in off state. Now we will get 0V as the output.
CMOS INVERTER SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM:
CMOS INVERTER SIMULATION:
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM OF CMOS INVERTER: For drawing a schematic diagram enter into pyxis schematic window and open a new schematic file. Pick and place 4-pin nmos , 4-pin pmos ,vdd and gnd from the library. Wire all the compound and connect input output ports. After check and save generate a symbol for the schematic and again apply check and save. Close all the windows. For drawing a schematic diagram enter into pyxis schematic window and open a new schematic file.
1.In the schematic_edit palette, select Library. Click on Device Lib to place the transistors - an
NMOS(4-pin) and a PMOS(4-pin) 2.Click on Generic Lib to place Portin, Portout, VDD. 3. In the schematic_edit palette, select WIRE (or press F3). For adding a wire between two points click once at the starting point and at all intermediate points to define the net route and double click at the end point to complete the routing. D, and Ground. 4.Change the instance name of the component 5.To change the reference number (INST), select the component, click right mouse button, and then select Properties > Modify Multiple. In the box of Instance, change the ASIM_MODEL, INST, L, and W values . To change the reference number automatically highlight all components, click the right mouse button, Instance > Alter Click on Check & Save in the schematic edit palette 6.After schematic is completed, want to create a block symbol to represent this circuit. This symbol can be used in other schematics to perform the same function as this circuit. Open add -> Generate Symbol.Again apply check and save. Close all the windows.
SIMULATION: The electrical performance and the functionality of the circuit must be verified using a Simulation tool. The simulation phase also serves in detecting possible design errors that may have been created during the schematic entry step. Open a new file and add the symbol which
is generated previously. From the library add pattern, dc source, vdd and gnd. Place and wire the input and output ports. Enter into the simulation mode. Include the rule file and go to analysis. Select transient analysis and set the transient analysis times. In probes add the input output ports for analysis. Select run eldo and view the waves.
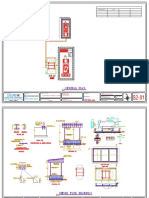
CMOS INVERTER LAYOUT DIAGRAM:
DRC FOR CMOS INVERTER:
LAYOUT OF CMOS INVERTER: The creation of the mask layout is one of the most important steps in the full-custom (bottom-up) design flow. This is where the designer describes the detailed geometries and the relative positioning of each mask layer to be used in actual fabrication, using a Layout Editor. Physical layout design is very tightly linked to overall circuit performance (area, speed and power dissipation) since the physical structure determines the transconductances of the transistors, the parasitic capacitances and resistances, and obviously, the silicon area which is used to realize a certain function. On the other hand, the detailed mask layout of logic gates requires a very intensive and time-consuming design effort. The physical design of cmos logic gates is an iterative process which starts with the circuit topology and the initial sizing of the transistors. Enter into the IC station and open the simulation file of the inverter in new layout file. Both schematic and layout window will open. Select metal1. Instantiate nmos ,pmos ,input and output ports, vdd and gnd. Draw polysilicon to join the gates. Draw a 5*5 polysilicon and a 2*2 polycontact . Place polycontact in side the 5*5 polysilicon and attach to the gates. Use metal for wire the input , output , vdd and gnd. Place the p-well and n-well contacts and save the layout.
DESIGN RULE CHECK: ASIC designers perform two major checks before fabrication. The first check is a designrule check ( DRC ) to ensure that nothing has gone wrong in the process of assembling the logic cells and routing. For the DRC ,from the tools go to calibre and select DRC. Select the rule file and run DRC. The checking result will be the layout passed all checking. If error exists check the design rule violations. And repeat DRC.
The created mask layout must conform to a complex set of design rules, in order to ensure a lower probability of fabrication defects. A tool built into the Layout Editor, called Design Rule Checker, is used to detect any design rule violations during and after the mask layout design. The designer must perform DRC, and make sure that all errors are eventually removed from the mask layout, before the final design is saved. Layout is constructed based on lambda based design rule and the technology .DRC is used to check the layout whether that any violation have occurred with respect to rule file.
CMOS INVERTER LVS CHECKING:
CMOS INVERTER PEX RESULT:
LVS CHECKING:
Layout versus schematic ( LVS ) check to ensure that what is about to be committed to silicon is what is really wanted. After the mask layout design of the circuit is completed, the design should be checked against the schematic circuit description created earlier. By comparing the original network with the one extracted from the mask layout the designer can check that the two networks are indeed equivalent. The LVS step provides an additional level of confidence for the integrity of the design, and ensures that the mask layout is a correct realization of the intended circuit topology. Note that the LVS check only guarantees a topological match. In other words, a successful LVS will not guarantee that the extracted circuit will actually satisfy the performance requirements. Any errors that may show up during LVS such as unintended connections between transistors, or missing connections/devices, etc should be corrected in the mask layout - before proceeding to post-layout simulation.
An electrical schematic is extracted from the physical layout and compared to the netlist. This closes a loop between the logical and physical design processes and ensures that both are the same. From file go to GDSII and text on ports. Go to tools and form calibre select LVS. Add the rule file and .spi file for the input. Apply run LVS and check the result.
PARASITIC EXTRACTION AND POST LAYOUT SIMULATION: Parasitic extraction is performed after the mask layout design is completed in order to create a detailed net-list for the simulation tool. The circuit extractor is capable of identifying the individual transistors and their interconnections as well as the parasitic resistances and capacitances that are inevitably present between these layers. The extracted net-list can provide a very accurate estimation of the actual device dimensions and device parasitics that ultimately determine circuit performance. The extracted net-list file and parameters are subsequently used in Layout-versus-Schematic comparison and in detailed transistor-level simulations (post-layout simulation). From calibre select PEX. Select the rule file. In input select the .spi file and in output select the parameters to be analyzed. The run RVE and check the results. Reenter into the simulation mode and view waves and compare the results.
SIMULATION DIAGRAM AFTER PEX:
WAVE FORM:
RESULT: Thus designed cmos inverter layout and from schematic entry to post layout simulation using mentor graphics EDA tools is done.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 1000w Inverter 2Dokumen20 halaman1000w Inverter 2meerhamzaBelum ada peringkat
- Grid Connected Inverter Design GuideDokumen52 halamanGrid Connected Inverter Design GuideRakesh SandarativjuBelum ada peringkat
- Inverter Design in CadenceDokumen6 halamanInverter Design in CadenceEr Sourav NathBelum ada peringkat
- Power ElectronicsDokumen83 halamanPower ElectronicsSreekanth SurendrenBelum ada peringkat
- All About Inverter Design FundamentalsDokumen36 halamanAll About Inverter Design Fundamentalsbiya saraBelum ada peringkat
- Inverters - ANTECHDokumen21 halamanInverters - ANTECHOG100% (2)
- ABSTRACT of InverterDokumen5 halamanABSTRACT of InverterNarsim Mudiraj75% (4)
- Z Source Inverter DesignDokumen84 halamanZ Source Inverter Designakkarapakaananda100% (1)
- Pulse-Width-Modulated (PWM) Inverter : Chapter 10 (Or 6) PDokumen35 halamanPulse-Width-Modulated (PWM) Inverter : Chapter 10 (Or 6) PM.h. SawonBelum ada peringkat
- High-Efficiency Pure Sine Wave Inverter PDFDokumen123 halamanHigh-Efficiency Pure Sine Wave Inverter PDFMaximilian SylvesterBelum ada peringkat
- DTMF Encoding and DecodingDokumen6 halamanDTMF Encoding and DecodingmastelecentroBelum ada peringkat
- Working Sinewave InverterDokumen10 halamanWorking Sinewave InverterxenotargetBelum ada peringkat
- Switch Mode InvertersDokumen22 halamanSwitch Mode InvertersVivek SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Inverter Filter DesignDokumen7 halamanInverter Filter DesignChAmirShokatGujjarBelum ada peringkat
- Free Download: David Bell Electronic Devices and CircuitsDokumen4 halamanFree Download: David Bell Electronic Devices and CircuitsAbhishek ChaurasiaBelum ada peringkat
- Power Presentation On Design of InverterDokumen18 halamanPower Presentation On Design of Inverteraa bbBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Phase Inverter ProposalDokumen4 halaman3 Phase Inverter ProposalAlan Walker100% (1)
- Sample 7436Dokumen11 halamanSample 7436Ram BalajiBelum ada peringkat
- Latest-Solar Inverter Design 1Dokumen1 halamanLatest-Solar Inverter Design 1Jike RaphealBelum ada peringkat
- Semicounductors & Pn-Junction (Complete)Dokumen47 halamanSemicounductors & Pn-Junction (Complete)Khalid AliBelum ada peringkat
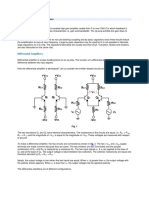
- Basics of Differential AmplifierDokumen6 halamanBasics of Differential AmplifierveeranjaneyulugopuBelum ada peringkat
- DC Ac Pure Sine Wave Inverter With MinimDokumen66 halamanDC Ac Pure Sine Wave Inverter With MinimKang Aryo100% (1)
- Malacious SoftwareDokumen54 halamanMalacious SoftwareNarender KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On Signal GeneratorsDokumen3 halamanNotes On Signal GeneratorsAdrian PostavaruBelum ada peringkat
- Module - 5: Power AmplifiersDokumen58 halamanModule - 5: Power AmplifiersSILPA AJITH100% (2)
- TIDA - 10KW 3 - Level Grid Tied Inverter Refrence Design TI PDFDokumen38 halamanTIDA - 10KW 3 - Level Grid Tied Inverter Refrence Design TI PDFSandeep Kumar SahooBelum ada peringkat
- Tempsens Handbook PDFDokumen180 halamanTempsens Handbook PDFKristijan CudarBelum ada peringkat
- PWM Power Inverter 250 To 5000 WattDokumen17 halamanPWM Power Inverter 250 To 5000 WattMolay Karmakar100% (1)
- Wien Bridge Oscillator DocumentationDokumen6 halamanWien Bridge Oscillator DocumentationZahidur Ovi Rahman100% (1)
- EE201 Semiconductor Devices PDFDokumen284 halamanEE201 Semiconductor Devices PDFAnonymous AyCl4LBelum ada peringkat
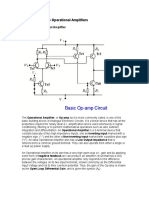
- Opamp Lecture PDFDokumen163 halamanOpamp Lecture PDFPriyatham KattaBelum ada peringkat
- Circuit Simulation Lab 3rd SemDokumen41 halamanCircuit Simulation Lab 3rd SemSUNIL MAURYABelum ada peringkat
- شرح الكترونيات 1 AmplifiersDokumen43 halamanشرح الكترونيات 1 AmplifiersAboodA.KhraishiBelum ada peringkat
- IR Transmitter and Receiver Circuit DiagramDokumen21 halamanIR Transmitter and Receiver Circuit DiagramAndy ZhuBelum ada peringkat
- Circuits For The HobbyistDokumen298 halamanCircuits For The HobbyisttuzruhiBelum ada peringkat
- DOMINO PPT FINAL AnkitDokumen32 halamanDOMINO PPT FINAL Ankitsurbhi98Belum ada peringkat
- Electronics Circuit Design LabDokumen34 halamanElectronics Circuit Design Labsrvdhar100% (1)
- PowerBeam PBE-M5-400 QSGDokumen24 halamanPowerBeam PBE-M5-400 QSGMaogageoffreyBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 5 Digital CommunicationDokumen14 halamanUNIT 5 Digital CommunicationSunithaBelum ada peringkat
- ESE 570 Cadence Lab Assignment 2: Introduction To Spectre, Manual Layout Drawing and Post Layout Simulation (PLS)Dokumen7 halamanESE 570 Cadence Lab Assignment 2: Introduction To Spectre, Manual Layout Drawing and Post Layout Simulation (PLS)Parul TrivediBelum ada peringkat
- IC Layout Design-SaadDokumen51 halamanIC Layout Design-SaadMuhammad SaadBelum ada peringkat
- Labs-VLSI Lab ManualDokumen56 halamanLabs-VLSI Lab ManualAbdul Basit Awan50% (2)
- Layout Manual - CMOS Inverter - Exp 3Dokumen22 halamanLayout Manual - CMOS Inverter - Exp 3ApoorvaBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment Using Capture CMOS & NMOSDokumen14 halamanExperiment Using Capture CMOS & NMOSS.DharanipathyBelum ada peringkat
- VLSI Backend Lab ManualDokumen56 halamanVLSI Backend Lab ManualAllanki Sanyasi Rao100% (1)
- Vlsi Unit-VDokumen41 halamanVlsi Unit-VJay SubbareddyBelum ada peringkat
- M.Tech Lab Manual-FInal-4.8.2021Dokumen28 halamanM.Tech Lab Manual-FInal-4.8.2021RAMYA VATHSALYA PBelum ada peringkat
- Nirma University Institute of Technology: B. Tech. in Electronics and Communication Engineering Semester - VDokumen15 halamanNirma University Institute of Technology: B. Tech. in Electronics and Communication Engineering Semester - VPragya jhalaBelum ada peringkat
- ResultDokumen7 halamanResultZulli KhairiBelum ada peringkat
- Ec1401 Vlsi DesignDokumen18 halamanEc1401 Vlsi DesignSurya PrakashBelum ada peringkat
- C C C C CC C: C C C CDokumen4 halamanC C C C CC C: C C C CRishav HarshBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Physical Design AN: Unit 3Dokumen17 halamanBasic Physical Design AN: Unit 3Shrey MalikBelum ada peringkat
- Analog Lab 2Dokumen13 halamanAnalog Lab 2Ajay NaikBelum ada peringkat
- Stick Diagrams and LayoutsDokumen17 halamanStick Diagrams and LayoutsPraneetha InumarthiBelum ada peringkat
- Vlsi NotesDokumen5 halamanVlsi NotesDiwakar TiwaryBelum ada peringkat
- VLSI Answer KeyDokumen15 halamanVLSI Answer Keyrendezvous2k23Belum ada peringkat
- Cadence Tutorial - Analog Design FlowDokumen57 halamanCadence Tutorial - Analog Design FlownarashimarajaBelum ada peringkat
- Vlsi Lab Manual - Draft-10ecl77Dokumen159 halamanVlsi Lab Manual - Draft-10ecl77GaganRs100% (2)
- EEE458 VLSI II Laboratory Laboratory Module 3: Schematic Driven Layout Design With Virtuoso Layout Suite XL (VXL) EditorDokumen8 halamanEEE458 VLSI II Laboratory Laboratory Module 3: Schematic Driven Layout Design With Virtuoso Layout Suite XL (VXL) EditorIrfanKhanBelum ada peringkat
- TV Course OutcomesDokumen1 halamanTV Course OutcomesKirthika Vinoth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Ashok Sharma Semiconductor Memories Technology Testing and ReliabilityDokumen473 halamanAshok Sharma Semiconductor Memories Technology Testing and ReliabilityJayashri Zambre90% (21)
- VHDL Code For ALUDokumen26 halamanVHDL Code For ALUKirthika Vinoth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Emi, EmcDokumen13 halamanEmi, EmcKirthika Vinoth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- A Packed Cultural Calendar - The Indian Music and Dance Festivals You Shouldn't Miss - The HinduDokumen6 halamanA Packed Cultural Calendar - The Indian Music and Dance Festivals You Shouldn't Miss - The HindufisaBelum ada peringkat
- A 150.xx Service Black/ITU Cartridge Motor Error On A Lexmark C54x and X54x Series PrinterDokumen4 halamanA 150.xx Service Black/ITU Cartridge Motor Error On A Lexmark C54x and X54x Series Printerahmed salemBelum ada peringkat
- J 2022 SCC OnLine SC 864 Tushardubey Symlaweduin 20221015 214803 1 23Dokumen23 halamanJ 2022 SCC OnLine SC 864 Tushardubey Symlaweduin 20221015 214803 1 23Tushar DubeyBelum ada peringkat
- VMC Ballscrew 32mm Horizontal Plane ReplacementDokumen11 halamanVMC Ballscrew 32mm Horizontal Plane ReplacementMarlon GeronimoBelum ada peringkat
- Bangalore University: Regulations, Scheme and SyllabusDokumen40 halamanBangalore University: Regulations, Scheme and SyllabusYashaswiniPrashanthBelum ada peringkat
- X25Dokumen10 halamanX25RajBelum ada peringkat
- PolisiDokumen16 halamanPolisiResh 0000Belum ada peringkat
- HDMI CABLES PERFORMANCE EVALUATION & TESTING REPORT #1 - 50FT 15M+ LENGTH CABLES v3 SMLDokumen11 halamanHDMI CABLES PERFORMANCE EVALUATION & TESTING REPORT #1 - 50FT 15M+ LENGTH CABLES v3 SMLxojerax814Belum ada peringkat
- Nitotile LM : Constructive SolutionsDokumen2 halamanNitotile LM : Constructive SolutionsmilanbrasinaBelum ada peringkat
- Khrone 5 Beam Flow Meter DatasheetDokumen16 halamanKhrone 5 Beam Flow Meter DatasheetAnoop ChulliyanBelum ada peringkat
- Object Based and Unified StorageDokumen12 halamanObject Based and Unified Storageashu narayanBelum ada peringkat
- ISA 265 Standalone 2009 HandbookDokumen16 halamanISA 265 Standalone 2009 HandbookAbraham ChinBelum ada peringkat
- Uncertainty-Based Production Scheduling in Open Pit Mining: R. Dimitrakopoulos and S. RamazanDokumen7 halamanUncertainty-Based Production Scheduling in Open Pit Mining: R. Dimitrakopoulos and S. RamazanClaudio AballayBelum ada peringkat
- CPCDokumen6 halamanCPCpranjalBelum ada peringkat
- Paper - 1: Principles & Practice of Accounting Questions True and FalseDokumen29 halamanPaper - 1: Principles & Practice of Accounting Questions True and FalsePiyush GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Moeller Vol07 - Tab02 Signal Tower PDFDokumen46 halamanMoeller Vol07 - Tab02 Signal Tower PDFArga WahyumiantoBelum ada peringkat
- Feeding Pipe 2'' L 20m: General Plan Al-Sabaeen Pv-Diesel SystemDokumen3 halamanFeeding Pipe 2'' L 20m: General Plan Al-Sabaeen Pv-Diesel Systemمحمد الحديBelum ada peringkat
- HACCP Coconuts 2019Dokumen83 halamanHACCP Coconuts 2019Phạm Hồng Ngân100% (4)
- Slope Stability Analysis Using FlacDokumen17 halamanSlope Stability Analysis Using FlacSudarshan Barole100% (1)
- BS351: Financial Reporting: Learning ObjectivesDokumen3 halamanBS351: Financial Reporting: Learning ObjectivesMajeed Ullah KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970Dokumen2 halamanComprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970Bryan AbestaBelum ada peringkat
- Governance of Cyber Security Research ProposalDokumen1 halamanGovernance of Cyber Security Research ProposalAleksandar MaričićBelum ada peringkat
- Report - Fostering The Railway Sector Through The European Green Deal PDFDokumen43 halamanReport - Fostering The Railway Sector Through The European Green Deal PDFÁdámHegyiBelum ada peringkat
- UnderstandingcpucoresDokumen5 halamanUnderstandingcpucoresAbdul NabiBelum ada peringkat
- Business en Pre Above S+T ReadingDokumen3 halamanBusiness en Pre Above S+T Readingsvetlana939Belum ada peringkat
- Thermal Hybrids R5Dokumen9 halamanThermal Hybrids R5amir.kalantariBelum ada peringkat
- 9MFY18 MylanDokumen94 halaman9MFY18 MylanRahul GautamBelum ada peringkat
- Orange Stripe # 57 EnglishDokumen2 halamanOrange Stripe # 57 EnglishShahid RazaBelum ada peringkat
- Goal of The Firm PDFDokumen4 halamanGoal of The Firm PDFSandyBelum ada peringkat
- Latest Eassy Writing Topics For PracticeDokumen18 halamanLatest Eassy Writing Topics For PracticeAnjani Kumar RaiBelum ada peringkat