MM207midsem
Diunggah oleh
Anand LalwaniJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
MM207midsem
Diunggah oleh
Anand LalwaniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
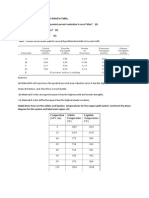
True or false 1.Direction of mixed dislocation is parallel to burger vector. False. it is neither parallel nor perpendicular.
2.Tilt boundary is associated with edge dislocation. True. When edge dislocation align in same direction tilt boundary exits.
3.Resolved shear stress is zero when applied stress is parallel to given slip system. True. Hall-Patch equation.
4.Solid- solution is metal strengthening process. True. It decreases lattice strain.
5.Every metal strain hardens at room temperature. False. Metals such as lead and tin do not strain harden at room temperature because their re-crystallization temperatures lie below room temperature.
6.FCC metals are more brittle than HCP metals. False. HCP metals are typically more brittle than FCC metals because there are fewer slip systems in HCP.
7. Tcrss increases with increasing the impurity. True. Because as impurity increases strength of metal increases.
8. Burger vector changes direction when dislocation change its direction and nature(e.g. screw to mixed to edge dislocation). False.
9.The magnitude of the strain fields decreases as we move away from the dislocation. True.
10.Surface energy decreases with increase in planar density. True. As the planar density increases, the number of nearest atoms in the plane increases, which results in an increase in the number of satisfied atomic bonds in the plane, and a decrease in the number of unsatisfied bonds. Since the number of unsatisfied bonds diminishes, so also does the surface energy decrease. Q. State and explain Hume Rothery Rules. Ans: 4 factors are a)Size of solute-If atomic diameter of the solute atoms differ by more than 15% from the solvent then extent of primary solid solution formation is small. In such cases, size factor is unfavourable for extensive solid solution formation. b)Crystal structure of solute and solvent-Same cystal structures of solvent and solute promotes formation of solid solution. c)Electrochemical effect between solute and solvent-The more electropositive one is and the more electronegative the other, greater tendency exists for compound formation. Less tendency exists for solid solution formation. d)Relative Valency Effect-A metal of higher valency is more likely to dissolve to a large extent in a lower valency one than vice versa.
Numerical Q. Calculate the volume of an BCC unit cell in terms of the atomic radius R. A1. the atoms touch one another across a body-diagonal the length of which is 4R. Since the unit cell is a cube, its volume is a2 where a is the cell edge length. From the right triangle, 2a2 + a2 = (16R2) so a = 4R/ (3) 1/2 The BCC unit cell volume Vc may be computed from VC = a3 = 64R3 * 27-3/2 .
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Swiggy 20novDokumen1 halamanSwiggy 20novAnand LalwaniBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Lecture MSW and BMW ManagementDokumen114 halamanLecture MSW and BMW ManagementAnand Lalwani100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- Numerical Analysis of Auto Ignition and Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition Engine by Using Elementary ReactionsDokumen14 halamanNumerical Analysis of Auto Ignition and Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition Engine by Using Elementary ReactionsAnand LalwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- MA 205 Complex Analysis: Shripad M. Garge. IIT BombayDokumen16 halamanMA 205 Complex Analysis: Shripad M. Garge. IIT BombayAnand LalwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Question (1) : of Those Metals Listed in TableDokumen4 halamanQuestion (1) : of Those Metals Listed in TableAnand LalwaniBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Student Support ServicesDokumen7 halamanStudent Support ServicesAnand LalwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grading Stats: Minor Couses CPI 8Dokumen10 halamanGrading Stats: Minor Couses CPI 8Anand LalwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Singapore Airlines Consumer SatisfactionDokumen24 halamanSingapore Airlines Consumer SatisfactionAnand LalwaniBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Wassenaar ArrangementDokumen230 halamanThe Wassenaar ArrangementJeanne J. NunezBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Overview of Fretting Corrosion in Electrical ConnectorsDokumen8 halamanOverview of Fretting Corrosion in Electrical ConnectorsSergio SoriaBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Oralium ROI Brochure - Al Roof SheetDokumen16 halamanOralium ROI Brochure - Al Roof Sheet1pallabBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Biological Corrosion FailuresDokumen10 halamanBiological Corrosion FailuresJose QuiinteroBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- ADVANCED Inoganic BookDokumen490 halamanADVANCED Inoganic BookHassan Haider100% (1)
- RRL Weathering On RoofingDokumen11 halamanRRL Weathering On RoofingPonsyo PonsiBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Syllabus EnglishDokumen2 halamanChemistry Syllabus EnglishGeetika SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Loctite CAT Part Numbers PDFDokumen48 halamanLoctite CAT Part Numbers PDFpanchoBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Bangladesh International School, Dammam The Periodic Table An Overview of The Periodic TableDokumen4 halamanBangladesh International School, Dammam The Periodic Table An Overview of The Periodic TableSIAM PLAZ YTBelum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Chapter 6 - Chang Test BankDokumen22 halamanChapter 6 - Chang Test BankDariusz MilewskiBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Metallurgy Vol. 1 2 y 3Dokumen55 halamanPhysical Metallurgy Vol. 1 2 y 3veronicaBelum ada peringkat
- 24 SAJET NEC-watermarkDokumen6 halaman24 SAJET NEC-watermarkraviteja036Belum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Chapter 3 - Metals and Non-Metals (Part 1)Dokumen12 halamanChapter 3 - Metals and Non-Metals (Part 1)VarunBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1091)
- Armstrong Metal CeilingDokumen28 halamanArmstrong Metal CeilingVishalSinghBelum ada peringkat
- The Handbook Rubber BondingDokumen70 halamanThe Handbook Rubber BondingNano Max100% (2)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- PCM CoolingDokumen27 halamanPCM CoolingInquiry XEEPLBelum ada peringkat
- Def Stan 970 PDFDokumen2.087 halamanDef Stan 970 PDFSergeBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 7 MEDokumen2 halamanGrade 7 MEEhr WinBelum ada peringkat
- Instant Download Practical Approach To Electroencephalography e Book Ebook PDF Version PDF FREEDokumen33 halamanInstant Download Practical Approach To Electroencephalography e Book Ebook PDF Version PDF FREEsteven.frerichs424100% (49)
- Metallic CoatingDokumen14 halamanMetallic CoatingJOSEPH HERBERT MABELBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- AMPCO 18 SandDokumen1 halamanAMPCO 18 SandS BHATTACHARYYABelum ada peringkat
- On The Art of Cutting MetalsDokumen247 halamanOn The Art of Cutting MetalsKasey ColeBelum ada peringkat
- Corrosion Control For Buried Water MainsDokumen43 halamanCorrosion Control For Buried Water Mainsdelta_scopeBelum ada peringkat
- Heavy Metals in SoilsDokumen615 halamanHeavy Metals in SoilsMiroslav Cici Pavelkic100% (1)
- At Room Temperature, Is Stiffer Than .: Alumina AluminumDokumen7 halamanAt Room Temperature, Is Stiffer Than .: Alumina AluminumLourdes Marie Rosalejos OrtegaBelum ada peringkat
- SSPC PAINTING MANUAL Vol 1 PDFDokumen551 halamanSSPC PAINTING MANUAL Vol 1 PDFLeuman Teran100% (17)
- Fortress Xray VS MDDokumen5 halamanFortress Xray VS MDJolafancyBelum ada peringkat
- Metals and Metallurgical PrinciplesDokumen13 halamanMetals and Metallurgical PrinciplesManoj KhanalBelum ada peringkat
- Free Mastic G 316Dokumen5 halamanFree Mastic G 316Kelly RobertsBelum ada peringkat
- C. L. Lewis, W. L. Ott, N. M. Sine, R. Belcher and L. Gordon (Auth.) - The Analysis of Nickel-Elsevier (1966)Dokumen219 halamanC. L. Lewis, W. L. Ott, N. M. Sine, R. Belcher and L. Gordon (Auth.) - The Analysis of Nickel-Elsevier (1966)Mudavath Babu RamBelum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)