Lab ID and Common Virulence Factors of Staph, Strep, Neisseria, Moraxella
Diunggah oleh
TinyJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Lab ID and Common Virulence Factors of Staph, Strep, Neisseria, Moraxella
Diunggah oleh
TinyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
LKCR 3BMT 13
Bacteriology - Preliminary Coverage
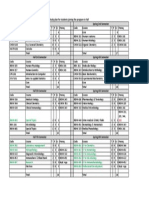
Points of genera differentiation Micrococci Microscopic appearance Staphylococci Gram (+) cocci singly, in pairs and in clusters Nonmotile Non spore forming Aerobic/Facultati ve anaerobic *except S. saccharolyticus = obligate anaerobe + depends on organism
*S. aureus, S.
Streptococci Gram (+) cocci in pairs or chains Nonmotile Non spore forming Facultative anaerobic / aerotolerant anaerobes -
Enterococci
Neisseria Gram (-) diplococci
*N.elongata and N. weaveri = rod shaped
Gram (+) cocci
Gram (+) cocci
Motility Spore-Forming
Nonmotile Non spore forming
depends on specie Non spore forming Facultative anaerobic Pseudocatalase (Weak bubbling)
Nonmotile Non spore forming
Atmospheric Requirement
Strict aerobic
Aerobic
+
*N. elongata = catalase negative
Catalase Test
Coagulase Test
intermedius, S. schleiferi, S. lugdunensis = (+) contains Staphylocoagulase
Colony appearance
With yellow pigment in BAP
Round, Medium sized, cream-colored, white or rarely light gold and "buttery-looking"
Oxidase/ Bacitracin Susceptibility
+ (Sensitive)
(Resistant)
Small and somewhat transparent *Hemolysis depends on organism + (susceptible) : S.pyogenes and S. pneomoniae only
Usually non-hemolytic
Depends on organism
(Resistant)
Oxidase (+)
LKCR 3BMT 13
Bacteriology - Preliminary Coverage
Laboratory Diagnosis of Staphylococcus sp. S. aureus Pinhead, white, creamy, -hemolytic Yellow colonies in MSA (fermenta tion of mannitol) + S. epidermidis S. saprophyticus S. haemolyticus S. ludgunensis S. schleiferi
Cultural Characteristics in BAP
Pinhead, non-hemolytic white to gray colonies
Slightly larger colonies with about 50% of the strains producing yellow pigmentation
Medium sized with moderate or weak hemolysis and variable pigmentation
Medium sized and hemolytic
No description found
Coagulase test Clumping factor Pyrrolidonyl Arylamidase Voge-Proska uer (VP) test
Novobiocin susceptibility
+ + +
(Susceptible)
+ +
+ on slide test - on tube test Some strains (+) + + +
(Susceptible)
+ on slide test - on tube test Some strains (+) + + +
(Susceptible)
+ (Susceptible)
(Resistant)
+ (Susceptible)
Virulence Factors of Staphylococcus sp. Organism Virulence Factor Enterotoxin A, B, D Enterotoxin B,C > G,I Enterotoxin B Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 / Enterotoxin F Exfoliative Toxin / Epidermolytic toxin -Hemolysin -Hemolysin (sphingomyelinase C) Pathogenicity Food poisoning Toxic Shock Syndrome Staphylococcal pseudomembranous enterocolitis Menstruating-associated TSS Staphylococcal Skin Scalded Syndrome / Ritter disease Damage to platelets and macrophages and cause severe tissue damage Hot-cold lysin ; enhances hemolytic activity at 37C & 4C
Staphylococcus aureus
LKCR 3BMT 13
Bacteriology - Preliminary Coverage
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Staphylococcus lugdunensis
Suppresses phagocytosis and associated with severe cutaneous - Hemolysin associated with infections and necrotizing Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) / pneumonia Staphylococcal leukocidin Associated with community acquired staphylococcal infections Hydrolyzes hyaluronic acid in Hyaluronidase connective tissues, permitting spread of bacteria Ability to bind the Fc portion of Protein A immunoglobulin G (IgG) -lactamase Resistance to penicillin Nosocomial/Hospital-acquired UTIs Poly-gamma-DL-glutamic acid and (indwelling catheters, prosthetic Biofilm production devices) Slime Infective endomielitis UTIs in young women (adheres more effectively to the lining of the epithelial cells in UG tract) Oxacillin Resistance Gene mecA More virulent and mimics S. aureus infections
Infections caused by S. aureus Folliculitis- relatively mild infection of a hair follicle or oil gland Furuncles- boils; large, raised superficial abscesses Carbuncles- larger, more invasive lesions develop from multiple furuncles, which may progress into deeper tissues Bullous impetigo- larger and surrounded by a small zone of erythema; highly contagious Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSS)/Ritter Disease- extensive exfoliative dermatitis Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)- associated with highly absorbent tampon use; two types (menstruatingand non-menstruating-associated) Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)- most commonly drug-induced due to hypersensitivity reaction Food poisoning- ingestion of contaminated food (enterotoxins do not cause any detectable odor or change in the appearance or taste of the food) Pneumonia- contagious, lower respiratory tract infection; multiple abscesses and focal lesions in the pulmonary parenchyma Osteomyelitis- bacteria gains entrance into the blood and may lodge in the diaphysis of the long bones MRSA- Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus MRSE- Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Epidermidis Vancomycin- drug of choice for serious staphylococcal infections VISA- Vancomycin-Intermediate S. Aureus
LKCR 3BMT 13
Bacteriology - Preliminary Coverage
VRSA- Vancomycin-Resistant S. Aureus D-test- Double Disk Diffusion test (Macrolide resistance: erythromycin and clindamycin) Classification of Streptococcus and Enterococcus Species Lancefield Group Antigen Hemolysis Type(s) Common Terms Disease Association(s)
Rheumatic fever, scarlet fever, pharyngitis, glomerulonephritis, pyogenic infections
S. pyogenes
Group A Strep
S. agalactiae
Group B Strep
S. dysgalactiae, S. equi
Group C Strep Non-enterococcus (cannot grow on 6.5% NaCl), member of viridans strep Enterococcus
Neonatal Sepsis, meningitis, puerperal fever, pyogenic infections Pharyngitis, impetigo, pyogenic infections Endocarditis, UTIs, pyogenic infections UTIs, pyogenic infections Pneumonia, meningitis, pyogenic infections Pyogenic infections, endocarditis, dental caries, abscesses in various tissues
S. Bovis
, none
E. faecalis, E. faecium S. pneumoniae
, , none
--
Pneumococcus
Anginosus group, mutans group, mitis group, salivarus group
A, C, F, G, N
, , none
Viridans Strep
LKCR 3BMT 13
Bacteriology - Preliminary Coverage
Types of Hemolysis Hemolysis Alpha () Beta () Non hemolytic Alpha-prime () or wide zone Description Partial lysis of RBCs around colony Greenish discoloration of area around colony Complete lysis of RBCs around colony Clear area around colony No lysis of RBCs around the colony No change in agar Small area of intact RBCs around colony surrounded by a wider zone of complete hemolysis
Laboratory Diagnosis of Streptococcus sp. S. pyogenes Lancefield Antigen Hemolysis A S. agalactiae B
Grayish, white, mucoid colonies surrounded by a small zone of -hemolysis S. dysgalactiae Non-entero cocci Enterococci
S. pneumoniae
Viridans Strep A,C,F,G,N , , none
D , none
D , , none
, none
Colonial characteristics on BAP
Small, transparent & smooth with a welldefined area of -hemolysis
Small Pyogenic colonies, streptococci usually large colony non-hemol ytic
Small colonies with occasional , hemolysis
Large zone of -hemolysis Young colonies hemolysis have a w/ green round, discoloratio glistening, n, fastidious wet, mucoid, domeshape
PYR hydrolysis Hippurate hydrolysis CAMP hydrolysis
LAP (Leucine aminopeptidase) hydrolysis
+ +
+ + +
+ +
+ +
VP test
-D-Glucuronidase
+/S
-/R
+ -/R
-/R
-/R
+/S
Mitis group= (-)
-/R
Bacitracin Susceptibility
LKCR 3BMT 13
Bacteriology - Preliminary Coverage
Vancomycin Susceptibility Optochin Susceptibility Bile Esculin Growth in 6.5% NaCl Bile Solubility
+/S -/R -
+/S -/R -
+/S -/R -
+/S -/R + -
S>R -/R + + -
+/S +/S +
+/S -/R -
Antigenic Structure and Virulence Factors of Streptococcus sp. Organism Antigenic structure Virulence factor M protein encoded by emm genes Fibronectin-binding protein (protein F) and Lipoteichoic acid Hyaluronic acid capsule Streptococcus pyogenes M protein Streptolysin O (SLO) Pathogenicity Resistance to phagocytosis and adherence to mucosal cells Adhesion molecules that secure attachment Prevents opsonized phagocytosis and masks its antigen to remain undetected Oxygen-labile; highly immunogenic, lyses leukocytes, platelets, etc. Oxygen-stable; lyses leukocytes and non-immunogenic Lysis of fibrin clots Separates tissue and spreads infection Scarlet fever Prevents phagocytosis but is ineffective after opsonization; most significant component: Sialic acid Inhibits activation of the alternative pathway of complement system Protection
Streptolysin S Streptokinase Hyaluronidase (Spreading factor) Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins (Spes)
Streptococcus agalactiae
Group B-specific antigen (acid-stable polysaccharide)
Capsule
Sialic Acid Streptococcus C-substance that reacts Capsular polyssaccharide
LKCR 3BMT 13
Bacteriology - Preliminary Coverage
pneumoniae
with C-reactive protein Extracellular dextran and adhesins Adherence and colonization in endocarditis Similar to group A
Viridans Streptococci
Polysaccharide capsule and cytolysin
Enterococcus
Not stated
Protein M, streptolysin O, hyaluronidase, DNAse, Streptokinase Extracellular surface protein, extracellular serine protease, gelatinase Cytolysin
Colonization and adherence to heart valves Two-subunit toxin similar to bacteriocins
Clinical Infections of Streptococci sp. Organism Clinical Infection Pharyngitis Strep throat Impetigo Pathology/Definition Most common clinical manifestation of group A strep infection Most common in children (5-15 yo); sore throat, malaise, fever Localized skin disease, from small vesicles to weeping lesions Acute spreading skin lesion that is intensely erythematous with a plainly demarcated but irregular edge Deeper invasion of streptococci Diffuse red rash that appears on upper chest and spreads to trunk and upper extremities, followed by desquamation Invasive infection; rapidly progressing inflammation and necrosis of the skin, subcutaneous fat and fascia; flesh-eating disease Entire organ system shuts down, leading to death Rheumatic fever and acute glomerulonephritis (AGN) MOT: Vertical transmission of the organism from the mother to
Erysipelas Cellulitis S. pyogenes Scarlet fever
Necrotizing fasciitis
Streptococcal Toxic shock syndrome Post-streptococcal sequelae S. agalactiae Invasive disease of the newborn
LKCR 3BMT 13
Bacteriology - Preliminary Coverage
Bacterial pneumonia S. pneumoniae Pneumococcal pneumonia Empyema Subacute bacterial endocarditis Oral infections (since they are oropharyngeal commensals) UTIs and bacteremia
newborn Infections often presents as Pneumonia or meningitis with bacteria Number one cause of pneumonia in elderly patients and patients with underlying diseases Sudden onset of chills, dyspnea and cough Pleural effusion Most common infection Gingivitis and dental caries Most common
Viridans Streptococci (Opportunistic pathogens) Enterococcus
Laboratory Diagnosis of Pathogenic Neisseria sp. and Moraxella catarrhalis N. gonorrhoeae Small, grayish-white, translucent, raised with entire edge Urethra (Male) Endocervix (Female) porB + + + (immediate, vigorous bubbling) + + N. meningitidis Slightly larger than N. gonorrhoeae, bluish-gray in BAP or small, tan, sometimes mucoid, convex colonies on CAP Nasopharynx, oropharynx, urogenital and rectal sites porA and porB + + (weak, delayed bubbling) + + + M. catarrhalis Smooth, opaque, gray to white, hockey puck colonies
Colonial Morphology
Primary Isolation Sites Presence of Por Catalase (3% H2O2) test Oxidase test Superoxol (30% H2O2) test Growth on Modified Thayer Martin, Martin Lewis, NY City agar Growth on Nutrient medium (BAP, CAP) at RT Acid production from Glucose Acid production from Maltose
Upper respiratory tract None + + -
Some are (+), some are (-) + -
LKCR 3BMT 13
Bacteriology - Preliminary Coverage
Acid production from DNase Reduction of Nitrate & Nitrite
Production of Hydroxyprolylaminopeptidase
+ + -
Virulence Factors of N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis Organism Virulence factor Receptors for human transferrin Capsule, cell membrane proteins I, II, and III, and Lipooligosaccharide (LOS) endotoxin Pili (fimbriae) Pathogenicity Compete with the human hosts for Iron Protection and antigenic variation Initial attachment to host tissues *T1, T2= Possess pili, virulent forms *T3-T5= devoid of pili, avirulent, found in subcultures Forms channels for nutrients to pass into and waste products to exit the cell Facilitate adherence Blocks host serum bactericidal (IgG) against the organism Same pathogenicity Pandemic United States (B= community-acquired disease) Meningococcal pneumonia Invasive diseases
N. gonorrhoeae
Porin protein (Por) or protein I Protein II (Opa/Opacity) Protein III (Rmp / Reduction modified protein) Same virulence factors as N. gonorrhoeae Group A strains N. meningitidis Serogroup B and C Serogroup Y Serogroup W-135
Clinical infections of N. gonorrhoeae, N. menigitidis, M. catarrhalis Organism Clinical Infection Acute urethritis, purulent discharge, dysuria, AHU strains isolated Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), sterility, ectopic pregnancy, perihepatitis (Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome) Pathology/Diagnosis Found in men
N. gonorrhoeae
Found in women
LKCR 3BMT 13
Bacteriology - Preliminary Coverage
10
Ophthalmia neonatorum
Epidemic meningitis
Fulminant meningococcemia or sepsis N. meningitidis Hemorrhage Bacteremia Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome Upper respiratory tract infection Lower respiratory infections
Gonococcal eye infection in newborns MOT: Infected birth canal in vaginal delivery *erythromycin= antimicrobial eyedrop Onset of frontal headache, stiff neck, sometimes fever May occur with or without meningitis once N. meningitidis enters bloodstream; with DIC, septic shock and Waterhouse-friedrichsen syndrome Pupura with petechial skin rash Tachycardia and hypotension may develop Hemorrhage in the adrenal glands In healthy children and elderly In adults with Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
M.catarrhalis
Laboratory Diagnosis of Non-pathogenic Neisseria sp.
N. flavescens
N.cinerea
N. lactamica
N. mucosa
N. polysacc -harea +
N. sicca
N. subflava
N. elongata
N. weaveri
Growth on selective media Growth in BAP, CAP Carbohy drate metaboli sm Catalase test Oxidase test
Reduction of Nitrate
+ + -
+ + -
+ + -
+ + +
+ + -
+ + -
+ + -
+ -
+ + -
LKCR 3BMT 13
Bacteriology - Preliminary Coverage
11
Reduction of Nitrite
+ Small, grayish, white, translusc ent
*Point of differentiati on w/ N.
gonorrhoeae = N.cinerea
varied Small, grayish white with yellow ring (only one to use lactose)
varied
Varied
+
Rod-shaped in miscrope Large, grayish white with yellowish tinge
Colonial morphology
Golden yellow colonies in BAP or CAP
Large, often adherent to the agar and very mucoid
Small, gray (sometms yellowish), translusce nt, raised
Dry, wrinkled adherent, and breadcrumb like *sicca= dry
*subflava = less yellow
Small, semi-op aque with a smooth appeara nce
is +/S with Colistin
Selective Media for the Isolation of N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis Selective Medium Thayer-Martin Inhibitory Agents Vancomycin Colistin Nystatin Vancomycin Colistin Nystatin Trimethoprim Vancomycin Colistin Anisomycin Trimethoprim Vancomycin Colistin Amphotericin B Trimethoprim Vancomycin Lincomycin Colistin Amphotericin B Trimethoprim Suppressed Organisms Gram (+) Gram (-) Yeast Gram (+) Gram (-) Yeast Swarming Proteus spp. Gram (+) Gram (-) Yeast Swarming Proteus spp. Gram (+) Gram (-) Yeast Swarming Proteus spp. Gram (+) Gram (+) Gram (-) Yeast Swarming Proteus spp. Capnocytophaga sp.
Modified Thayer-Martin
Martin-Lewis
New York City
GC-LECT
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Study Plan Fall AdmissionDokumen1 halamanStudy Plan Fall AdmissionTinyBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment No. 8: Specific Heat of MetalsDokumen2 halamanExperiment No. 8: Specific Heat of MetalsTiny100% (1)
- Synthesis of Soap DetergentDokumen4 halamanSynthesis of Soap DetergentTiny100% (5)
- Comparative Investigation of Organic Compounds: CH CLDokumen5 halamanComparative Investigation of Organic Compounds: CH CLTinyBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1091)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Etiology of MalocclusionDokumen72 halamanEtiology of MalocclusionPavan PreethamBelum ada peringkat
- 4th Semester SyllabusDokumen4 halaman4th Semester SyllabusBHU tBelum ada peringkat
- Control of Sleep and WakefulnessDokumen101 halamanControl of Sleep and WakefulnessLevente BalázsBelum ada peringkat
- American Journal of Nanotechnology & NanomedicineDokumen9 halamanAmerican Journal of Nanotechnology & NanomedicineSciresBelum ada peringkat
- Biotech ReviewerDokumen1 halamanBiotech Reviewerdenmarkde22Belum ada peringkat
- Chromosomal AberrationDokumen7 halamanChromosomal AberrationANSA PRIYADARSHINI0% (1)
- Biology Prelims 2023Dokumen6 halamanBiology Prelims 2023SwethanaBelum ada peringkat
- Ecological Genomics Ecology and The Evolution of Genes and GenomesDokumen358 halamanEcological Genomics Ecology and The Evolution of Genes and Genomesmax100% (1)
- Eating Disorders: The Cause and Effect of MedicalizationDokumen6 halamanEating Disorders: The Cause and Effect of MedicalizationhaleeboppBelum ada peringkat
- Muscular DystoniaDokumen20 halamanMuscular Dystoniarudresh singhBelum ada peringkat
- Sci 10Dokumen3 halamanSci 10Jairus TanBelum ada peringkat
- Slides Turner SyndromeDokumen32 halamanSlides Turner SyndromeAsunción AncoBelum ada peringkat
- BJS 16-3 PDFDokumen59 halamanBJS 16-3 PDFJhonatan Paredes VásquezBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Repurposing - DUPHAT - 23Dokumen32 halamanDrug Repurposing - DUPHAT - 23Maha Saber AyadBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 2 PAPER 2 Biology 2021Dokumen17 halamanUNIT 2 PAPER 2 Biology 2021Shamena Hosein100% (1)
- Dna Replication Lecture Notes 2011Dokumen70 halamanDna Replication Lecture Notes 2011براءة أحمد السلامات100% (1)
- Herpes Simplex I and IIDokumen50 halamanHerpes Simplex I and IItummalapalli venkateswara raoBelum ada peringkat
- Preliminary Study of C. (Morphocarabus) Zawadzkii SeriatissimusDokumen1 halamanPreliminary Study of C. (Morphocarabus) Zawadzkii SeriatissimusPrunar FlorinBelum ada peringkat
- Symptoms of Diabetes: Losing Weight and Keeping It OffDokumen10 halamanSymptoms of Diabetes: Losing Weight and Keeping It OffGohar imranBelum ada peringkat
- Paediatrics MCQDokumen4 halamanPaediatrics MCQVineeta ChittoriaBelum ada peringkat
- Biology A (Salters Nuffield) : Pearson Edexcel GCE Level 3 GCEDokumen28 halamanBiology A (Salters Nuffield) : Pearson Edexcel GCE Level 3 GCEjBelum ada peringkat
- Lactic AcidosisDokumen1 halamanLactic AcidosisLee June LyngBelum ada peringkat
- True False NG Questions Strategy PracticeDokumen5 halamanTrue False NG Questions Strategy PracticeSabzali NavruzovBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines Sams Principles On Xenotransplantation 2000Dokumen10 halamanGuidelines Sams Principles On Xenotransplantation 2000jojdoBelum ada peringkat
- Pedigree Analysis: (Cf. Chapters 4.4, 5.2, 6.2 of Textbook)Dokumen11 halamanPedigree Analysis: (Cf. Chapters 4.4, 5.2, 6.2 of Textbook)Kristyne OliciaBelum ada peringkat
- CEN02 2019 Paramedical CategoriesDokumen51 halamanCEN02 2019 Paramedical CategoriesAnonymous tgveMIeRBelum ada peringkat
- Ca OvaryDokumen27 halamanCa OvaryMuhammad AbeeshBelum ada peringkat
- IFU - BM6010 e FE 2Dokumen3 halamanIFU - BM6010 e FE 2Imas NurhayatiBelum ada peringkat
- Research PaperDokumen7 halamanResearch Paperapi-242499715Belum ada peringkat
- NONLINEAR (NLS) DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS (Basic Physics and Principles of Equipment)Dokumen13 halamanNONLINEAR (NLS) DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS (Basic Physics and Principles of Equipment)testnation100% (1)