Forensic Science MS New Syllabus (2010-2012)
Diunggah oleh
Ae BanpongDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Forensic Science MS New Syllabus (2010-2012)
Diunggah oleh
Ae BanpongHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Question Number 6.
(a)(i)
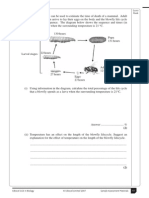
Question Using information in the diagram, calculate the total percentage of the life cycle that a blowfly spends as a larva when the surrounding temperature is 21 C. Correct Answer Correct answer (with or without working) = 2 marks Answer: 51.9% (accept 52% or 51.88%) Correct working with incorrect answer = 1 mark Accept any working that would give correct answer eg 179 / 345 x 100 = 52% Mark 2
Question Number 6.(a)(ii)
Question Temperature has an effect on the length of the blowfly lifecycle. Suggest an explanation for the effect of temperature on the length of the blowfly lifecycle. Correct Answer Award one mark for each of the following points in context to a maximum of two marks. 1. 2. 3. 4. idea that length of life cycle is dependant on metabolic rate of blow fly; metabolic rate is determined by enzyme activity/eq; as temperature increases (up to an optimum) enzyme activity increases; idea that as a result of temperature increase (to a max) length of lifecycle decreases; Mark 2
134
Sample Assessment Materials
Edexcel Limited 2007
Edexcel GCE in Biology
Question Number 6.(a)(iii)
Question Suggest two factors, other than temperature, that may affect the timing of the blowfly life cycle and lead to an incorrect estimate of the time of death. Answer Award one mark for each of the following points in context to a maximum of two marks. 1. humidity; 2. drugs; 3. oxygen; 4. ref. to genetic differences; Mark 2
Question Number Q6(b)
Question Describe how rigor mortis in muscles occurs. Answer Award three marks for the following in context. 1. Muscle cells deprived of oxygen 2. Respiration becomes anaerobic/reference to lactic acid 3. Fall in pH 4. Inhibits enzymes 5. ATP no longer produced 6. Bonds between muscle proteins become fixed Mark 3
Edexcel GCE in Biology
Edexcel Limited 2007
Sample Assessment Materials
135
Question Number 6.(c)
Question The process of succession occurs in plant communities as well as in a dead body. Compare these two forms of succession. Answer Award one mark for each of the following points in context to a maximum of three marks. 1. as each organism feeds it changes the body / environment 2. this allows conditions suitable for colonisation/growth of other species 3. ref to other organisms eg microbes 4. in plant succession many early species are replaced over time 5. in this case most of the early insects remain as others colonise 6. suitable reference to climax community in plants 7. {longer timescale / larger area} in plants Mark 3
136
Sample Assessment Materials
Edexcel Limited 2007
Edexcel GCE in Biology
Question Number 4(a)(i)
Answer Statement This sequence of bases could be used as a template during translation TRUE FALSE 6 6
Mark
A strand of mRNA could be synthesised using this sequence
This sequence codes for 7 amino acids during protein synthesis
6
(3)
1 mark each correct box ;;; [crosses in both boxes for a statement = 0]
Question Number 4(a)(ii)
Answer 1. ribosomes / RER / rough endoplasmic reticulum / poly(ribo)some ; 2. descriptive feature e.g. (for ribosome or polysome) {ribosomal RNA / rRNA} / protein component / {two sub-units / large and small sub-unit} (for RER) ribosome attached to membrane ;
Mark
(2)
Question Number 4(b)(i)
Answer 1. {change / eq} in DNA ; 2. ref to {change / deletion / addition / duplication / substitution / eq} of {bases / nucleotides} ;
Mark
(2)
1001 6BI0
Question Number 4(b)(ii)
Answer 1. correct reference to change in frequency of either allele e.g. mutant increases / normal decreases ; 2. idea of reproductive success of the {mutant / non-photosynthetic} individuals ; 3. (as trees develop) pond will be (more) shaded / eq ; 4. (less light means) less photosynthesis possible / eq ; 5. ref to photosynthetic individuals die / {nonphotosynthetic / mutant} individuals survive ; 6. ref to pass on the {mutation / allele} (for using organic compounds) / eq ; 7. ref to more organic nutrients in pond ;
Mark
maximum (4)
1001 6BI0
Question Number 5(a)(i)
Answer C;
Mark (1)
Question Number 5(a)(ii)
Answer B;
Mark (1)
Question Number 5(a)(iii)
Answer 1. (S/ suspect) 3 ; 2. (S3) matches {all / 9 / eq} of the bands in the sample ; 3. DNA profiling assumes every individuals DNA is {unique / different} / eq ; 4. apart from identical twins / eq ; 5. ref to DNA profiling analyses the {introns / noncoding blocks / STR / short tandem repeats / eq} ; 6. non-coding DNA {very variable / hypervariable / eq} ; 7. large number of {introns / non-coding blocks / eq} ; 8. idea of many {combinations / eq} (at each locus) ;
Mark
maximum (5)
1001 6BI0
Question Number 5(b)
Answer 1. ref to DNA profiling has several stages ; 2. ref to {artefacts / contamination / eq} can arise at any stage ; 3. only {a few sequences / small portion } of DNA analysed / eq ; 4. ref to possibility of two identical profiles from unrelated individuals ; 5. {identical twins / closely-related individuals / eq} may show same profile / eq ;
Mark
maximum (2)
Question Number 5(c)
Answer 1. comparisons made between DNA from fossils and other organisms ; 2. to find genetic relationships / how closely related / eq ; 3. ref to used in {taxonomy / classification / eq} ; 4. to understand evolutionary lines / to determine common ancestor / eq ;
Mark
maximum (2)
1001 6BI0
Question Number 1(a)
Answer cross next to degree of muscle concentration ;
Mark (2)
cross next to signs of decomposition ; Question Number 1(b) Answer 1. idea of SD {measures / shows} {spread / range / eq} of data ; 2. Idea of most readings are within {+ 1 x SD / + 2 x SD} e.g. approx 60% readings within (+ )1 x SD / approx 90% readings within (+) 2 x SD ; 3. idea that as length of time increases, SD increase / eq ; 4. idea of more variability (in temperature) as time increases / eq ; 5. comment on change in reliability of time of death with time / eq ; 6. estimate (of time of death) can only be within a {4 / 5 / 6 / 7} hour period ; 7. use of manipulated data ; Question Number 1(c) Answer three from the following: {(body) mass/ BMI / weight / eq} {(subcutaneous) fat /eq} surface area, {ambient / eq } temperature immersion in water age (of person at death) skin colour thickness of hair gender clothing blood loss humidity air movement {core / body} temperature at time of death ;;; Mark max (4) Mark
(3)
6BI04_01 1006
Question Number 5(a)
Answer
Mark
Description Polymer formed from a single strand of nucleotides Pentose present in the nucleotides Adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine present Nucleotides linked by phosphodiester bonds
DNA only
RNA only 9
Both DNA and RNA
9 9 9
all rows correct 2 marks two or three rows correct 1 mark Question Number 5(b)(i) 1. DNA strands {separate / unzip / eq} ; 2. idea that one DNA {strand / eq} used as template (to form mRNA) / eq ; 3. from free nucleotides / eq ; 4. reference to complementary base pairing ; 5. reference to hydrogen bonding ; 6. correct reference to {RNA-polymerase / DNA helicase} ; 7. credit correct sequence of bases on {mRNA / DNA} ; Answer
(2) Mark
max (3)
6BI04_01 1006
Question Number 5(b)(ii)
Answer
Mark
1. reference to specific amino acid attachment to tRNA ; 2. idea that anticodon (on tRNA) {attaches / binds / lines up / eq} to the {codon / triplet} on mRNA ; 3. example quoted using the information in the diagram e.g. tRNA with alanine has CGA anticodon which binds to GCU on mRNA ; 4. idea that two tRNA held in ribosome (at any one time) ; 5. reference to formation of peptide {bonds / links} (between adjacent amino acids) ; 6. reference to peptidyl transferase ; Question Number 5(c) 1. stop codon ; 2. used to end the {sequencing / further attachment of tRNA / eq} ; 3. release of the {polypeptide / ribosome} /eq ; max (2) Answer max (3) Mark
6BI04_01 1006
Question Number 6(a)(i)
Answer C;
Mark
(1) Question Number 6(a)(ii) Answer B; (1) Question Number 6(a) (iii) Question Number 6(b) Answer A; Answer 1. idea of sequence of {bases / nucleotides} on DNA determines sequence on (pre-) mRNA ; 2. reference to complementary base pairing / stated example e.g. AU / CG / GC / TA (DNA: mRNA) ; 3. reference to formation of bonds by condensation reaction ; 4. phosphodiester {bonds / links} ; 5. reference to RNA-polymerase ; Question Number 6(c)(i) Answer 1. reference to {start / stop / nonsense} (codon) ; 2. start (codon) needed to begin {polypeptide synthesis / eq} / {stop / nonsense} (codon) needed to end {polypeptide synthesis /eq } / eq ; max (3) Mark Mark (1) Mark Mark
(2)
6BI04_01 1101
Question Number 6(c)(ii)
Answer 1. reference to {difference / variations / eq } of {exons / mRNA} ; 2. reference to different {primary structure / sequence of amino acids} ; 3. reference to {secondary / tertiary } structure of proteins depends on primary {structure / sequence} / eq ; 4. due to {change in / different} bonds ; 5. {hydrogen / ionic / disulphide} bonds ; 6. reference to different 3D shape / eq ;
Mark
max (3)
6BI04_01 1101
Question Number 4(a)
Answer 1. fibrous long / linear / straight (chains), globular compact / spherical / eq ; 2. globular are folded and fibrous are not / eq ;
Mark
3. globular are soluble and fibrous are not / eq ; 4. fibrous involved in {structural / eq} and globular are not ; 5. globular involved in {catalysis / metabolism / eq} and fibrous are not ; (2)
Question Number 4(b)(i)
Answer C;
Mark (1)
Question Number 4(b)(ii)
Answer Any two from: 1. physical damage / eq ; 2. immersion in water / eq ; 3. (external) temperature / eq ; 4. burning / eq ; 5. electrocution / eq ; 6. reference to {clothing / eq} ; 7. wind / air movements / eq ;
Mark
(2)
Question Number 4(c)
Answer 1. reference to not {all / both / eq} muscles {contract / relax / reach (full) rigor / eq} at same {time / rate / eq} ; 2. idea of jaw muscle contracting before leg muscle / eq ; 3. idea of jaw muscle reaches {full contraction / rigor} before leg muscle / eq ; 4. jaw starts contraction {0.5 / 0.8 / 0.9} hours before leg OR jaw reaches (full) rigor 2.5 hours before leg ; 5. reference to {full contraction / rigor} in muscle does not last very long ; 6. idea of leg is still contracting while jaw is relaxing / eq ;
Mark
(4)
Question Number 6(a)(i)
Answer C;
Mark
(1)
Question Number 6(a)(ii)
Answer D;
Mark
(1)
Question Number 6(a)(iii)
Answer D;
Mark (1)
Question Number 6(b)(i)
Answer 1. humans more closely related to chimp (than to orang utan and gorilla) / eq ; 2. reference to humans and chimps more closely related to orang utan than gorilla ; 3. reference to similarity of sequence indicates closeness of ancestral relationship / eq ; 4. human and chimp sequence identical / eq ; 5. orang utan has one difference, gorilla has two differences / eq ; 6. reference to {number 19 for orang utan / number 9 and 19 for gorilla} different ;
Mark
(4)
Question Number 6(b)(ii)
Answer 1. reference to similarity (of DNA) indicates closeness of relationship ; 2. because genes are sections of DNA / eq ; 3. genes are the codes for protein / eq ;
Mark
(2)
Question Number 6(b)(iii)
Answer 1. reference to source of DNA sample, e.g. blood, saliva, semen ; 2. reference to small samples of DNA can be amplified by PCR ; 3. reference to use of (restriction / eq) enzymes to {break / eq} DNA ; 4. reference to use of {electro potential / potential difference / eq} ; 5. reference to {treatment / staining / eq} ; 6. show up as {bands / bars / eq} ; 7. reference to the {number of bands / eq} that match indicates similarity of the DNA ;
Mark
(3)
Question Number 1(a)
Answer Substance X = (DNA)primer(s) ; Substance Y = (mono)nucleotide(s) ; Substance Z = DNA strand(s) ;
Mark
(3) Question Number 1(b)(i) Answer A; (1) Mark
Question Answer Number 1(b)(ii) C;
Mark (1) Mark (1)
Question Number 1(b)(iii)
Answer B;
Question Number 1(c)(i)
Answer 1. Idea that human enzymes will not work at {high / these/ above 37oC eq} ; 2. reference to {denaturation /change in shape of active site}(at temperatures in PCR) ;
Mark
(2)
Question Number 1(c)(ii)
Answer 1. (xylem / wood) made of dead material / has no {living material / cytoplasm / cell contents / nuclei / mitochondria} / eq ; 2. no {DNA / nucleic acid} present / eq ;
Mark
(2)
6BI04_01 1201
Question Number 5(a)
Answer B forensic entomology ;
Mark (1)
Question Number 5(b)(i)
Answer D temperature ;
Mark (1)
Question Number 5(b)(ii)
Answer 1. idea that the body has been dead for a while ; 2. (because) more than one species of insect present / eq ; 3. reference to succession (of insect species) ; 4. idea that life cycle {times / stages} of the insects are {known / used / eq} ; 5. idea that life cycle times depend on (environmental) temperature ; 6. credit specific ref to information in table e.g. blowfly cycle complete ;
Mark
(3)
Question Number 5(c)(i)
Answer 1. idea that a drop in body temperature is linked to time after death e.g. algor mortis ; 2. idea that factors affect temperature drop e.g. environmental temperature, body size, clothing ; 3. (useful because ) time of death can be calculated if (ambient) temperature known / eq ; 4. only useful for short period of time following death e.g. 24 hours, a day ;
Mark
(2)
Question Number 5(c)(ii)
Answer 1. idea that body decomposes in a specific sequence (with time) ; 2. idea that factors affect decomposition e.g. environmental temperature, wounds ; 3. (not useful) if all the body has decomposed / eq ;
Mark
(2)
Question Number 8(a)
Answer 1. (Double-stranded because made of) two strands ; 2. (strands joined) by hydrogen bonds (between bases ) ; 3. (polynucleotide) of {many / eq} nucleotides ; 4. (nucleotides) linked by phospho(di)ester bonds / eq ;
Mark
(3)
Question Number *8(b) QWC
Answer Take into account quality of written communication when awarding the following points. 1. idea of sequence of bases {forming the genetic code / determines the amino acid sequence} ; 2. idea that one triplet codes for an amino acid; 3. ref to (DNA) acting as a template ; 4. reference to transcription OR detail of transcription e.g. DNA unzips, mRNA synthesis ; 5. idea that mRNA moves from nucleus to cytoplasm / eq ; 6. reference to translation OR detail of translation e.g. role of ribosome, codonanticodon interaction ; 7. idea that tRNA carries an amino acid ; 8. ref to formation of peptide bonds between amino acids ; 9. idea that primary structure is the {sequence /order / eq} of amino acids ; 10.comment on post-transcriptional modification of mRNA (between transcription and translation)e.g. removal of introns, splicing ;
Mark
(5)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Cell StructureDokumen2 halamanCell StructureAe BanpongBelum ada peringkat
- Core skeletal muscles mashupDokumen5 halamanCore skeletal muscles mashupAe BanpongBelum ada peringkat
- Lab #11: Respiratory Physiology: BackgroundDokumen12 halamanLab #11: Respiratory Physiology: BackgroundAe BanpongBelum ada peringkat
- Questions Section B 1993-2003Dokumen29 halamanQuestions Section B 1993-2003Ae BanpongBelum ada peringkat
- Vaping Is Far From HarmlessDokumen3 halamanVaping Is Far From HarmlessAe BanpongBelum ada peringkat
- Bmat 2017Dokumen13 halamanBmat 2017Ae BanpongBelum ada peringkat
- QP Option H (2007-2013)Dokumen70 halamanQP Option H (2007-2013)Ae Banpong100% (1)
- Examiner Tips For IGCSE BiologyDokumen12 halamanExaminer Tips For IGCSE BiologySunSun Hemnilrat42% (12)
- Forensic Science QP New Syllabus (2010-2012)Dokumen25 halamanForensic Science QP New Syllabus (2010-2012)Ae BanpongBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4-Ecology Evolution Ecoystems Global Warming Forensics QuestionsDokumen136 halamanUnit 4-Ecology Evolution Ecoystems Global Warming Forensics Questionsareyouthere92100% (2)
- EDEXCEL: AS BIOLOGY REVISION NOTES: UNIT 1 METABOLISM OVERVIEWDokumen14 halamanEDEXCEL: AS BIOLOGY REVISION NOTES: UNIT 1 METABOLISM OVERVIEWAe Banpong0% (2)
- Immunity MS New Syllabus (2010-2012)Dokumen32 halamanImmunity MS New Syllabus (2010-2012)Ae BanpongBelum ada peringkat
- Ecology Evolution Ecoystems Global Warming QP (2010-2012)Dokumen61 halamanEcology Evolution Ecoystems Global Warming QP (2010-2012)Ae BanpongBelum ada peringkat
- 6BI07 Jan 2013 QP PDFDokumen16 halaman6BI07 Jan 2013 QP PDFAe BanpongBelum ada peringkat
- Immunity QP New Syllabus (2010-2012)Dokumen40 halamanImmunity QP New Syllabus (2010-2012)Ae Banpong100% (1)
- Photosynthesis MS New Syllabus (2010-2012)Dokumen16 halamanPhotosynthesis MS New Syllabus (2010-2012)Ae BanpongBelum ada peringkat
- Sat Subject Tests Practice PDFDokumen72 halamanSat Subject Tests Practice PDFSri KondabattulaBelum ada peringkat
- Aqa Biol1 W MS Jun11Dokumen6 halamanAqa Biol1 W MS Jun11Ae BanpongBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4 Notes Edexcel BiologyDokumen19 halamanUnit 4 Notes Edexcel BiologyAe Banpong69% (13)
- Photosynthesis QP New Syllabus (2010-2012)Dokumen18 halamanPhotosynthesis QP New Syllabus (2010-2012)Ae Banpong100% (1)
- Note By4 By5Dokumen263 halamanNote By4 By5Ae BanpongBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4 Notes Edexcel BiologyDokumen19 halamanUnit 4 Notes Edexcel BiologyAe Banpong69% (13)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Blunt 2010Dokumen73 halamanBlunt 2010Adriana TorrecillasBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Applications of Urinary Organic Acids. Part 1Dokumen11 halamanClinical Applications of Urinary Organic Acids. Part 1farkad rawiBelum ada peringkat
- Importance of Biological MoleculeDokumen3 halamanImportance of Biological MoleculeMary Antonette LucioBelum ada peringkat
- ARCO PP+ BenefitsDokumen38 halamanARCO PP+ BenefitsMuhammad AdninBelum ada peringkat
- BCH MCQs1Dokumen304 halamanBCH MCQs1moxdegr8100% (1)
- Lipid DropletsDokumen2 halamanLipid DropletsAaronmiguel27Belum ada peringkat
- Amino Acid MetabolismDokumen30 halamanAmino Acid MetabolismMeddebateBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry 9Th Edition Campbell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokumen51 halamanBiochemistry 9Th Edition Campbell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFciaramilcahbrpe100% (11)
- 7.012 First Section Self-Quiz SolutionsDokumen2 halaman7.012 First Section Self-Quiz SolutionsGlendonBelum ada peringkat
- Trna Model PDFDokumen3 halamanTrna Model PDFYoga NovalBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 011Dokumen17 halamanChap 011alexa chalhoubBelum ada peringkat
- Mindoro State College of Agriculture and Technology: I. ObjectivesDokumen7 halamanMindoro State College of Agriculture and Technology: I. ObjectivesJunjun CaoliBelum ada peringkat
- Lehninger: Principles of BiochemistryDokumen79 halamanLehninger: Principles of BiochemistryrestreolBelum ada peringkat
- KrushKrokMnemonics 1 1Dokumen23 halamanKrushKrokMnemonics 1 1Fianyo DavidBelum ada peringkat
- Enzymes: Biological Catalysts That Speed Up ReactionsDokumen34 halamanEnzymes: Biological Catalysts That Speed Up ReactionsShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat Ghani100% (1)
- Essay For Protein SynthesisDokumen7 halamanEssay For Protein Synthesisbsr3rf42100% (1)
- 06 Chapter 1Dokumen63 halaman06 Chapter 1Dintakurthi PrasanthBelum ada peringkat
- Encode SequenceDokumen212 halamanEncode SequenceRaj Naithik100% (1)
- From Gene To ProteinDokumen42 halamanFrom Gene To ProteinNathan AdornadoBelum ada peringkat
- Pyrimidine & Biosynthesis of DeoxyribonucleotidesDokumen46 halamanPyrimidine & Biosynthesis of DeoxyribonucleotidesRabia ButoolBelum ada peringkat
- Dna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 1Dokumen4 halamanDna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 1afkogsfea100% (2)
- Natural ProductsDokumen69 halamanNatural Productslalo199Belum ada peringkat
- Metabolism of Purine & Pyrimidine NucleotidesDokumen38 halamanMetabolism of Purine & Pyrimidine NucleotidesShimmering MoonBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report On Amino Acid From Protein Source, Plant Growth PromoterDokumen7 halamanProject Report On Amino Acid From Protein Source, Plant Growth PromoterEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersBelum ada peringkat
- IUMS2014, ProceedingDokumen1.487 halamanIUMS2014, Proceedingamir-scribdBelum ada peringkat
- Nucleotides McqsDokumen8 halamanNucleotides McqsSp Ppv0% (1)
- Secondary-Metabolite Biosynthesis and MetabolismDokumen372 halamanSecondary-Metabolite Biosynthesis and MetabolismMuhammad IlfanBelum ada peringkat
- Sci10 Q3 Module4Dokumen28 halamanSci10 Q3 Module4kaloy domanaisBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry of Hormones 2Dokumen42 halamanBiochemistry of Hormones 2Hazel Grace BellenBelum ada peringkat
- GENETICSDokumen196 halamanGENETICSJulianne PetargueBelum ada peringkat