Mam Dedel
Diunggah oleh
Louise Marie Palamos DamascoJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Mam Dedel
Diunggah oleh
Louise Marie Palamos DamascoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
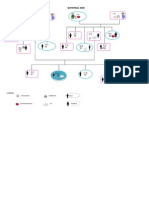
Predispposing factors: Age: 63 Hereditary
Precipitating factors: Diet Lifestyle Hypertension Diabetes
High glucose in blood
Impaired fnxnign of insulin glucose by adipokines
Over Compensatation of pancreas
Enters blood by glucokinase
Adipon ectin
Leptin
Restin
Exhaustion
Form atp
Negative Feedback Inhibit insulin metabolism Decrease insulin production
Close K channel
Impairment
Insulin Resistance
Type 2 diabetes millitus
Intracellular hypoglycemia
Extracellular hyperglycemia
Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
Shunting of glucose polyol pathway or the sorbitol aldose reductase
Glycoprotein cell wall deposit
Sorbitol to fructose
Plaque deposition in lumen of blood
vessels
Accumulation of sorbitol in the basement membrane of the cells and between that uses sorbitol pathway
Accelerated atherosclerosis
Basement membrane thickened
Atherosclerotic Aorta
Cell receives inadequate oxygen and nutrition and retained waste products
Narrowing of blood vessels
Ischemia in the kidney
Decrease blood flow circulation
Tissue injury
Activation of RAAS
ACE
Aldosterone
Diabetic nephropathy
Vasoconstrictio n
Water retention
Increased BP
Hypertension
Thickening hyalinization of vessel walls Narrowing of the arteriols Vascular structure thicken
Decrease perfussion
Damage to nephron
Hypertensive Nephrosclerosis
Tubular damage
Tubular damage
glumerosclerosis
GFR
proteinuria
Renal blood
Stage I DIMINISHED RENAL RESERVE GFR 50%
Increase permeability of glomerular capillaries
Increase NA macula densa
albuminuria
Increase intrarenal tension
hypoalbumininemia Decrease renal blood flow Decrease plasma oncotic pressure Decrease plasma volume
Decrease glomerular filtration rate
Further loss of nephron functioning
Accumulation of solutes
Stage II RENAL INSUFFICIENCY GFR 20-50%
BUN, Creatinine levels begin to rise
Remaining nephrons undergo changes to compensate for those damaged nephrons
Filtration of more concentrated blood by the remaining nephrons
Hypertrophy of nephrons
Intolerance and exhaustion of the remaining nephrons
Further damage of the nephrons
80-90% damage
Stage III RENAL FAILURE GFR 10-20%
Impaired kidney function and Uremia - Reduction in renal capillaries -Scarring of Glomeruli - Atrophy & Fibrosis of Renal tubules > 90 % of kidney damage
Malfunction of RAAS
Nitrogenous wastes impairs platelets
Decreased Erythropoietin Production
Toxins impair immune system
Toxins affect CNS
Na & H2O retention Continuous decline in renal function
Decreased Urine Output Oliguria
Increased blood pressure
Edema
Decreased Immune system
Pulmonary Edema, Peripheral Edema
Risk for superinfection
Hypertension
Bleeding Tendencies
Uremic Encephalopathy
ANEMIA
Stage IV END-STAGE RENAL DISEASE (ESRD) GFR <10% Sepsis -changes in mentation/ psychiatric symptoms -irritability -fatigue -insomnia
Nonspecific injury to Arterial wall
Increase work load
Continuous Multisystem Affectation
Desquamation of endothelial lining Heart pumps forcefully Increased Permeability Lipids and platelets assimilate into the area Oxidized LDL attracts monocytes and the macrophages to the site Plaques begin to form from cells which imbed into the endothelium Enlargement of the muscle
Multiple Organ Failure
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
DEATH
Lipids are engulfed by the cells and smooth muscle cellls develop
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE(formation of atheromas)
Decreased Coronary tissue perfusion
Coronary Ischemia
Anaerobic Metabolism PAIN (Angina Pectoris/ Acute MI)
Production of Lactic Acid
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1091)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Toltec Body Healing EbookDokumen204 halamanToltec Body Healing EbookDanielle Grace100% (3)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- 5 6057345046456304562Dokumen490 halaman5 6057345046456304562DK DeepakBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Child-Pugh Score & MELDDokumen3 halamanChild-Pugh Score & MELDChaterine GraceBelum ada peringkat
- External Ventricular DrainDokumen5 halamanExternal Ventricular DrainSze Ching WanBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding The Stress ResponseDokumen7 halamanUnderstanding The Stress ResponseHermela Ghebremichael100% (1)
- Immunology MCQDokumen51 halamanImmunology MCQLouise Marie Palamos DamascoBelum ada peringkat
- Biology 8 Frog Dissection GuideDokumen10 halamanBiology 8 Frog Dissection GuideRyan SantosBelum ada peringkat
- NeuroDokumen31 halamanNeuroLouise Marie Palamos Damasco100% (3)
- 130 Immunology Questions and AnswersDokumen46 halaman130 Immunology Questions and Answers成失92% (13)
- General Survey GeriaDokumen6 halamanGeneral Survey GeriaLouise Marie Palamos DamascoBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Management Process?Dokumen5 halamanWhat Is Management Process?Louise Marie Palamos DamascoBelum ada peringkat
- Hyper GravidarumDokumen3 halamanHyper GravidarumLouise Marie Palamos DamascoBelum ada peringkat
- Apppendix CDokumen1 halamanApppendix CLouise Marie Palamos DamascoBelum ada peringkat
- Floor PlanDokumen1 halamanFloor PlanLouise Marie Palamos DamascoBelum ada peringkat
- Genogram (Or)Dokumen2 halamanGenogram (Or)Louise Marie Palamos DamascoBelum ada peringkat
- At The End of The Lesson The Student Should Be Able ToDokumen8 halamanAt The End of The Lesson The Student Should Be Able ToIrene IlustrisimoBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar Pustaka 1Dokumen7 halamanDaftar Pustaka 1Teddy Agung SaputraBelum ada peringkat
- DIET in Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen3 halamanDIET in Chronic Kidney Diseaseatul_desai_3Belum ada peringkat
- Early Recurrence of Carcinoma Gall Bladder After R0 Resection of Stage T1B-T3Dokumen6 halamanEarly Recurrence of Carcinoma Gall Bladder After R0 Resection of Stage T1B-T3IJAR JOURNALBelum ada peringkat
- Las Sci 10 Melc 3 Week-1-3-SummativeDokumen5 halamanLas Sci 10 Melc 3 Week-1-3-SummativeSamad Recca T. NatividadBelum ada peringkat
- Alagille Syndrome: A GuideDokumen16 halamanAlagille Syndrome: A GuideKarla Edith Rodriguez NavaBelum ada peringkat
- Rinhs Science 8 4th Catch Up Activity 2 Digestive System Crossword PuzzleDokumen2 halamanRinhs Science 8 4th Catch Up Activity 2 Digestive System Crossword PuzzleRyan BersaminBelum ada peringkat
- Super 20 Ch-7 Control & Coordination Class 10 Science (2) YeahhhhhDokumen2 halamanSuper 20 Ch-7 Control & Coordination Class 10 Science (2) Yeahhhhhkamalkandpal4848Belum ada peringkat
- Defense Mechanisms of The BodyDokumen33 halamanDefense Mechanisms of The Bodymazna khalilBelum ada peringkat
- Class Teaching On Pyloric StenosisDokumen23 halamanClass Teaching On Pyloric StenosisRuchika KaushalBelum ada peringkat
- Human Anatomy KROKDokumen60 halamanHuman Anatomy KROKsushmitaBelum ada peringkat
- Effects of Yoga On Digestive SystemDokumen54 halamanEffects of Yoga On Digestive SystemManish Nahar33% (3)
- Endocrine System Transes PDFDokumen5 halamanEndocrine System Transes PDFShemess ButgorgBelum ada peringkat
- CRRT Role in Sepsis 17122016Dokumen26 halamanCRRT Role in Sepsis 17122016Ogin NigoBelum ada peringkat
- Milia AriaDokumen8 halamanMilia AriaAtsabitFarisBelum ada peringkat
- Miliaria SVDokumen26 halamanMiliaria SVTaufiq Ramadhan100% (1)
- Definingacutekidney Injury: Siddharth Verma,, John A. KellumDokumen16 halamanDefiningacutekidney Injury: Siddharth Verma,, John A. KellumNicolas Peña RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory Quiz: Student Academic Learning ServicesDokumen4 halamanRespiratory Quiz: Student Academic Learning ServicesFREDRICKBelum ada peringkat
- Non Ulcerative Dyspepsia Secondary To Stress DisorderDokumen79 halamanNon Ulcerative Dyspepsia Secondary To Stress Disorderromeo rivera100% (1)
- Marolf2012 US Colangite FelinosDokumen7 halamanMarolf2012 US Colangite FelinosThaís ChouinBelum ada peringkat
- Structure and Function of The Human EyeDokumen10 halamanStructure and Function of The Human EyeSyed MujtabaBelum ada peringkat
- Conductivity (The Ability To Transmit The Impulse To OtherDokumen7 halamanConductivity (The Ability To Transmit The Impulse To OtherLizzie FernandoBelum ada peringkat
- Jaundice-Review of Clinical Features, Differential Diagnosis and RemediesDokumen13 halamanJaundice-Review of Clinical Features, Differential Diagnosis and RemediesDr-Dalya ShakirBelum ada peringkat
- The Integumentary System Powerpoint PresentationDokumen53 halamanThe Integumentary System Powerpoint PresentationGeulia RosalesBelum ada peringkat