Консультации Гастроэнтеролога Advice Gastroenterologist
Diunggah oleh
Abdullah SaleemDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Консультации Гастроэнтеролога Advice Gastroenterologist
Diunggah oleh
Abdullah SaleemHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Topic 156.
"changes in the oral mucosa in diseases of the digestive tract (stomach ulcer, gastritis, enteritis, colitis, chronic hepatitis). Change the color, swelling of the mucous membrane of the mouth. Coated tongue. The tactics of a dentist. " Diseases of the digestive tract SUBJECTIVE EXAMINATION
COMPLAINTS
MEDICAL HISTORY
LIVING HISTORY
OBJECTIVE ASSESSMENT
INSPECTION
PALPATION
PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSIS
ADDITIONAL METHOD
BACTERIOSCOPY
LABORATORY
CYTOLOGICALLY
DIAGNOSTIC SEARCH FINAL DIAGNOSIS
ADVICE GASTROENTEROLOGIST
TREATMENT
LOCAL PREVENTION
GENERAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION
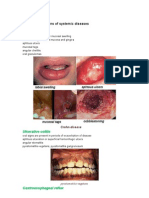
1. Financial and methodological support classes: machinery and equipment dental office, illustrations, methodical practice session for teachers, recording and reporting. 2. Materials for the lab: The receptors of the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue are the sources of reflections that have an impact on the secretory and motor function of the gastrointestinal tract. At the same time, the mouth is the reaction of the effector field of pathological reflexes of the internal organs . If any of the bowel at the same time can be observed lesions of the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue, expressed in the smoothness of the papillae and tongue swelling , sensation of dryness.Defeats language and GPRS in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract usually are nonspecific and occur development raids , swelling , desquamation varying degrees , atrophy of the papillae , etc., in remission , or in the treatment of the underlying disease language to varying degrees cleared of debris and can take a normal appearance . Subjective sensations of touch usually accompanied, however, by the presence of a dense plaque , patients may experience a numbing taste .Appearance of plaque can help in the verification of the underlying disease . For example, in acute gastritis tongue coated , swollen , thick patina , black, covers the entire surface of the tongue , leaving it free to the lateral surface and the tip . Sometimes the whole tongue is covered with mucus. Marked dry tongue and taste bitter, sour , and bad breath.In chronic gastritis raid whitish- gray in color, sometimes dark, does not occupy the entire surface. Gastric ulcer grayish patina . For stomach bleeding observed dry and pale tongue. Dense, white coating , which is located on the entire surface of the tongue , there is a cancer of the stomach. In the raid - pitelialnye cells , mucus , microflora , a large number of white blood cells . When carcinomatous cachexia marked pallor language. Smooth , shiny, sometimes cracked , with abundant bloom language marked with dysentery . Acute inflammation of the peritoneum in all cases accompanied by dry tongue, the appearance of cracks on it , raid. Sometimes there are so- called dyspeptic ulcers are prone to relapse . Feature of many gastrointestinal diseases is also swollen condition of the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue, does not cause any discomfort. Swelling can reach considerable severity , andwhereas patients notice awkwardness of language, increasing its size , sometimes biting tongue and buccal mucosa . When viewed from the tip , the sides of the tongue, buccal mucosa revealed fingerprints teeth tongue increased in size . The mucosa becomes pasty , acquires a whitish appearance. Edematous condition of the oral mucosa in the gastro -intestinal disorders blister test is confirmed positive McClure -Aldrich ( blister resorption time is shortened at a rate of 45-60 minutes). In gastritis mucosal changes hydrophilicity : anatsidny state slowed blister test , hyperacidity - speed. Often blister test is positive in the gastro -intestinal diseases without apparent violations of the relief of the mucous membrane and gives an indication of the presence of latent edema , which is important in the diagnosis of early changes and prognosis of diseases. Swelling of the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue is an important diagnostic sign of chronic colitis and determined in 80 % of cases. This is due to violation of the absorptive capacity of the intestine , its barrier function , are also important as violations of the water balance .Discoloration tongue mucosa is also common manifestation of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. Catarrhal glossitis, stomatitis in the form of appearance of congestion areas bright red color or with a predominance of cyanosis detected ulcers , colitis, enterocolitis and other diseases. Pallor of the mucous membrane was observed in persons suffering from peptic ulcer disease. Often, patients are also concerned about a burning sensation and pain in the language mainly while taking a hot and spicy food.Desquamation of the epithelium of the tongue in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is common. Described the so-called " ulcerative language." In this case, on the back of the tongue were found bright spots of various sizes and shapes that against the background of " overlaid " language created a kind of superficial ulcers. Similar changes occurred as a result of atrophy of the filiform papillae or reinforced their desquamation . Described focal desquamation - limited areas along the midline of the back of his tongue in the third as red spots on the background of a coated tongue . These
changes resemble diamond glossitis, but distinct from, and desquamative , and " geographical " language that appears in acute gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer. Outbreaks desquamation disappear during the treatment of peptic ulcer , missing in remission, no tendency to migrate. Of all the papillae of the tongue most often on the gastro-intestinal disease respond whiskers . Thus, there is atrophy of the filiform papillae in acute and chronic gastritis , hypo-and anatsidny gastritis , dysentery, acute hepatitis , liver cirrhosis , viral hepatitis, chronic pancreatitis. Hyperplasia of them observed in peptic ulcer disease , giperatsidnom gastritis, gastric cancer , acute pancreatitis .Paresthesia of the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue, glossalgia often mucous membrane of the rtaovozhdayut various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Often, burning, tingling may occur without apparent change of language.Significant breach of taste sensitivity in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. To determine it is widely used method of functional mobility of the tongue .Taste buds perform the sensing function and are effector ( end ) link gastro- lingual reflex. It is known that the number of functional receptors language depends ostoyaniya functional digestive tract. Maximum activity is observed in their feeling of hunger .Changes in taste sensitivity were found in almost all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. These disorders are a consequence of changes in the normal reflex connection of the tongue and stomach disorders as a result of the secretory and motor functions of the stomach , typical of peptic ulcer disease. In gastric cancer reported a reduction of taste sensitivity to bitter and sweet . In the epithelium of the phenomenon of para-and hyperkeratosis with desquamation of the surface layers , swelling of the underlying tissues , and sometimes loss of integrity (ulcers ) . More profound morphological change in the language determined in comparison with other departments mouth. Their expression is directly dependent on the severity of the underlying disease. The resulting structural abnormalities lead to partial or complete denervation of individual sections of the mucosa and create preconditions for change and trophic ulcers . Along with the described changes in the mouth saliva Violations of the law : sometimes there is increased salivation ( with acute peptic ulcer, gastritis giperatsidnom ), but more often there is sialoschesis ( in peptic ulcer , gastritis , etc.). Changes in the pathogenesis of oral mucosa (edema , paraesthesia , desquamation of the epithelium , etc.) , along with the reflector , humoral mechanisms are important vitamin deficiencies , particularly the group V, and increased vascular permeability fabric . It is important to note that the treatment of the underlying disease often leads to the disappearance or drastic reduction of the severity of dental manifestations.The main features of oral lesions in dysentery : catarrhal, aphthous stomatitis, glossitis deskvamativny . At 2-3 days from the onset of the disease develops catarrhal stomatitis, which transforms in the future to canker .In patients with chronic colitis and enterocolitis is marked glossitis, aphthous stomatitis, " perleches " developing against deficiency of vitamin E and B2. In chronic colitis diagnostic feature was furred , and with enterocolitis desquamation and atrophic changes of its epithelium. Defeats tongue and lips were probably the result of hypovitaminosis , coming in lesions gastrointestinal tract. In patients with gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer observed morphological and functional changes in the minor salivary glands. Develops hypersalivation , often followed by dry ( the chronic course of peptic ulcer disease ) , the emergence of the AFTS and ulcers of the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue, hypertrophy of the filiform papillae , swelling of the tongue. Acute gastritis. The tongue is coated with a thick gray patina that covers the entire surface, except for the side and the tip, swollen, sometimes covered with mucus. There have dry tongue, taste bitter, sour. Chronic gastritis. The disease is characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Gastritis flowing with secretory failure , pain little pronounced. Increasingly concerned about the heaviness in the epigastrium , belching, dominated by symptoms of intestinal and gastric dyspepsia . In the long joining signs polyhypovitaminosis , protein deficiency , in some cases - a violation of
hematopoiesis . In these patients, the oral mucosa is often a pale pink color , normally hydrated . Complaints about the perversion of taste, " metallic" taste , especially in the morning . On the mucous membrane of the lips - exfoliative cheilitis , cracked . Filiform papillae of the dorsal surface of the tongue flattened , mushroom seems magnified . Often this form of pathology characteristic is the presence of foci of atrophy of the filiform papillae until the appearance of small erosions . On the periphery of the foci of atrophy can be observed whitish rim , composed of hyperplastic epithelium. There is a fixed form of desquamative glossitis . Such changes in the mucous language appear most intense periods of exacerbation of the underlying disease . In chronic gastritis with preserved or increased secretion of the middle and distal thirds of the dorsal surface of the tongue filiform papillae often hypertrophied . In the same area of the most intensely expressed raid whitish- yellow or grayish- yellow. The color and consistency of plaque may vary depending on the intensity and severity of dyspeptic symptoms. Mushroom-shaped papillae back of the tongue is less clearly defined due to the hypertrophy of the filiform papillae and the density of plaque. The leaf buds are embossed , are somewhat bloodshot , which often is the reason for overdiagnosis and unwarranted suspicion of cancer . The phenomenon is more marked paresthesia in the root and tip of the tongue . Joining secondary infection often exacerbates mucosal changes . Here is change the language at different nosological forms of gastritis : hyperacid gastritis - language cyanotic , swollen , overlaid with dense bloom , hypo-and anatsidny gastritis - the language is reduced in volume, thread-like papillae his atrophied raid on the back of the tongue is missing . The surface is smooth and shiny , with its bright red spots and stripes. Peptic ulcer. The main symptom of peptic ulcer disease are late , hungry, night pain , not related to the quality of food and stoped eating or weak alkali solutions . Pain occur in the pit area at the umbilicus and may radiate to the back, behind the breastbone . Clinical symptoms that develop in the mouth, not much different from those in chronic gastritis .Ulcers in the stomach as well as in the states hypoacid , oral mucosa pale pink sialoschesis is most common during periods of exacerbation of the underlying disease. Fur grayish white color is most pronounced at its distal tightly attached to the underlying tissues.Phase physiological desquamation of the filiform papillae inhibited , broken leafshaped relief , mushroom-shaped papillae at the beginning of the disease has changed little , but in the future , depending on the nature of the flow of peptic ulcer may be hyperplastic or, conversely, reduced in size and unobtrusive . With concomitant violation of the biliary tract mucosa of the mouth and tongue more bright, with icteric tint of the curtains of the soft palate . During periods of acute illness can be observed swelling language. Language increased prints are teeth on the lateral surfaces and in the tip . In areas adjoining the tongue to the teeth with visible mikroerozii stomatoskopicheskom study , plots thinned epithelium than at times due to subjective feelings of the patient ( burning sensation , mild tingling , soreness ) , worse at the time of the meal. If duodenal ulcer, often oral mucosa accompanied by dysfunction of the biliary tract, language changes similar to those described above. Patients suffering from chronic relapsing forms of peptic ulcer disease with persistent violation of the secretory function of the most frequentlycomplained of a burning sensation and pain in the tongue and feeling "burned" language, worse in the evening. Pain in the English show a close neuro-reflex connections of different parts of the digestive tract, especially the mucous membranes of the mouth, stomach and intestines. This is indicated by the frequent cases of migrating form of desquamative glossitis in patients with peptic ulcer disease, in which on the dorsal surface of the tongue can be seen from the pockets of epithelial desquamation melkotochechnye to 0.51.5 see their location is constantly changing, which makes the migration of pain. Is spontaneous disappearance of lesions that distinguishes this form of desquamative glossitis from the "geographical" language.
Enterocolitis. The disease is characterized by the simultaneous defeat of the stomach, small and large intestines. In its genesis - various infections ( Salmonella group , Escherichia coli, Proteus , etc.) , food and drug allergy, toxicity of heavy metals , chemicals , etc.In acute enterocolitis oral mucosa swelling, hyperemia , increased salivation . Prints teeth visible on the buccal mucosa through the clamping teeth, the lateral surface of the tongue . Subsequently, there is dryness of the mouth. The dorsal surface of the tongue is covered with dense grayish- yellow. In severe intoxication and dysbiosis observed hyperplasia of the filiform papillae and their coloring in brown or even black. Discoloration filiform papillae most pronounced at their base , the top of the papillae stained less intensely . One of the complications of the disease is candidiasis of the mouth and tongue. Duration of candidiasis is in direct proportion to the main manifestations of the disease.In chronic enterocolitis oral mucosa pale pink. Celebrated its slight swelling on the surface of the tongue - the haze of grayish -yellow color, especially in the morning intensely expressed in the distal parts of the language. Other changes to the oral mucosa , determined visually , due to a combination of chronic enterocolitis with damage to other parts of the digestive system. The most common pathology of the oral mucosa in chronic enterocolitis is a chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis . Frequent occurrences of the afts in the mouth long before the appearance of symptoms of gastro -intestinal tract. The usual places of localization of these elements are the cheeks, the vestibular surface of the lips , retromolar space and language. Rubtsov form of recurrent aphthous stomatitis is more common in people with gastric ulcer , chronic hepatitis , colitis. Among patients with recurrent aphthous stomatitis about 2% are patients with a form of defeat, has a certain originality. Regardless of age, without any clearly identifiable precipitating factors in the mucous membrane of the mouth appear melkotochechnye foci of destruction , in a short time transformed into a deep, sharply painful ulcers . In some cases, the period of their existence to be 6-12 months , due to migration of ulcers on the stretch . At the site of healed elements remain severe scarring , significantly changing the architecture of the mucosa , this form is known as stomatitis Setton . The identity of the flow and morphogenesis , the possibility of its transformation after treatment in a mild form of this type can be regarded as one of the options HRAS ( deforming form). In chronic colitis desquamation language found in 33% of patients (compared with chronic gastritis - in only 17.2 %). Focal epithelial desquamation often oral mucosa accompanied by a burning sensation and mild pain in the tongue, increasing when taking hot food , smoking, but sometimes patients may not be aware of it.Thus, changes in the oral mucosa in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract characterized by discoloration , swelling during exacerbations of the underlying disease , its bloom in the language of focal and diffuse desquamation of the epithelium of the dorsal surface of the tongue , thinning of individual sections of the mucosa. A frequent symptom of the disease are glossalgia and chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis . Changes in the mucous membranes of the oral cavity in diseases of the digestive system should be differentiated from a number of other pathological conditions. Atrophic changes, manifested in the form of desquamative glossitis, should be differentiated from the "geographic" tongue, fixed drug enantemy, secondary recurrent syphilis, lichen planus, candidiasis. CHRAS must be differentiated from a number of specific processes, viral lesions. Deforming the shape of CHRAS should be differentiated from venous ulcers in the endocrine and cardiovascular disease, pre-cancerous conditions.Treatment of diseases of the mouth and tongue in patients suffering from disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, it should be done in conjunction with the gastroenterologist. Rehabilitation of the oral cavity is carried out in periods of remission of the pathological process. Diseases of the liver and gall bladder. Anatomical and physiological characteristics of oral communication with the liver determined by its diverse functions in the body : the participation in digestion , in the regulation of blood volume , blood formation , metabolism, pigment metabolism , etc. A substantial Antitoxic , glycemic role of the liver.Changes in the language of liver diseases clinicians attach
great diagnostic and prognostic value . Pathological manifestations of the language can be in the form of color changes of its mucous membranes, occurrence of areas of desquamation , epithelial proliferation of individual sections of the language, the appearance of furrows on the back of the tongue , described a "smooth , red tongue " with cirrhosis of the liver. Joining portal hypertension oral mucosa was accompanied by the appearance of a bluish- pink color language. Describes the language changes in hepatic impairment : tongue moist , dark red " strawberry " , atrophic , smooth, devoid of plaque. Drinking large amounts of fat (the so -called functional nutritional lipidogennye liver disorder , syndrome Vorenzhe ) appears " assessable " tongue , loss of appetite and food taste ( dysgeusia ) .When liver damage typical changes of language are the catarrhal glossitis , edema , cyanotic color of the side and bottom surfaces of the tongue , atrophy of the filiform papillae . Diffuse staining of the mucous membrane of the soft palate in yellow is a sign of liver damage , jaundice , limited and located on the outer edge of the soft palate - a sign of the defeat of the gall bladder. Often, the disease of the liver and gall bladder mucosa of oral cavity accompanied by the appearance of the characteristic bitter taste and the " liver smell " out of his mouth , decreased taste sensitivity analyzer. Botkin 's disease at the height of the disease there is a decrease of taste sensitivity to sweet and bitter . With the improvement of the general condition of taste sensitivity is restored. In chronic hepatitis marked by a variety of inflammatory and degenerative changes in the nature of : redness , dryness , swelling, and desquamation of the epithelium , the occurrence of hemorrhage , small erosion. There have been bitter , taste perversion (acidic or " metallic" taste ) . The most common symptoms for all liver disease are bleeding gums, as well as various forms of gingivitis.The most common and earliest symptom - itching of the skin , caused by a high content of bile acids in the blood. It is known that histamine in this case plays no important role - this explains the low efficiency in such cases antihistamines . Significant reduction of itching can be achieved by a diet rich in unsaturated fatty acids, and the ingestion of cholestyramine . Icteric coloration , often diffuse - due to hyperbilirubinemia , urticaria ( often observed in predzheltushnogo period of acute hepatitis ) - have immune- nature , occurs in about one-quarter of patients with hepatitis . Epidemic , or viral hepatitis ( Botkin's disease ) . Primarily affects the liver , reticuloendothelial system , the digestive tract. Usually the first symptoms are dyspepsia , oral mucosa accompanied by fever, astenovegetative syndrome. Frequent catarrhal conditions of the upper respiratory tract , arthralgia , rash , itching . Constant symptom is jaundice height of the disease , which develops slowly over a period of two weeks or once reaches its maximum. Icteric coloration consistently appears on the sclera, hard palate , skin and visible mucous membranes. Nausea, vomiting , belching, unstable chair worried sick almost the entire period of the disease . In some cases, there are signs of extrahepatic " liver palms " and " spider veins " on the skin.The mucous membrane of the mouth is always involved in the pathological process . In the prodromal period is marked dryness of mucous membranes, it is often swelling, diffuse congestion hotspots . During the period marked jaundice ascending intense coloration different mucosal sites . Often accompanying symptom of liver disease are vascular disorders . They manifest themselves in the form of hemorrhage , the most pronounced in the area of the soft palate and buccal surface of the lips . At the height of the disease there are sites desquamation of the epithelium back of the tongue , oral mucosa accompanied by atrophy of the filiform papillae . Almost always there is a burning sensation of the tongue is bright red, shiny.An important feature of infectious hepatitis - icteric staining of the excretory ducts of the salivary glands paired , their hyperplasia and maceration . Often - hyperplasia of ducts of minor salivary glands, the " hiatus " of their end sections . In the prodromal period , and in the midst of diseases of the mucous membrane of the mouth can be observed multiple small , often prone to erosion of the group . Fibrinous coating on their surfaces intensely colored in yellow. The elimination of pathological changes in the oral mucosa occurs as the inverse of the underlying disease. Chronic hepatitis. The disease often develops as a continuation of an epidemic of hepatitis, but can also develop under the influence of industrial hepatotropic substances or as a toxic- allergic
reaction to a number of drugs. Proved the effects of alcohol on the development of the endogenous protein and vitamin deficiency of the liver. A frequent symptom of chronic hepatitis are a pain in the right upper quadrant or epigastric region associated with eating or physical stress . Frequent diarrheal manifestations - nausea , bloating , impaired chair. Characterized by decreased performance, muscle weakness . The liver is almost always increased, sealed with a characteristic sharp-edged , often painful. In the mouth - a perversion of taste, bitterness , especially in the morning . It is noted ikterichnost shade of the mucous membrane of the soft palate. Subjective symptom is paresthesia of the mouth and tongue. Patients complain of burning or tingling sensation , not only in language but also in the lips . The burning sensation and pain in the mucosa is often combined with the feeling of itching , especially in the area of the palatina . Cirrhosis of the liver. The mucous membrane of the mouth with cirrhosis of the liver in the early stages of the disease is not very different in hepatitis : burning sensation in the hard and soft palate , buccal surface of the lips and tongue. In the development stages of cirrhosis of the liver , respectively, the general symptoms noted discoloration of the mucous membrane , it becomes a pale pink color with cyanotic hue. Vienna expanded language . Marked focal or diffuse clouding of the epithelium. In some places - it maceration up to the formation mikroerozy . Secondary vitamin A deficiency can lead to a more pronounced hyperkeratosis , particularly in the areas of physiological keratinization of the mucosa of the mouth ( hard palate , gums , tongue back ) . In those areas where the mucosa is injured bite, marked , along with hyperkeratosis , fissures and nonhealing erosion. Periglottis atrophied to the level of epithelial desquamation . Pockets of desquamation can be single or merge to capture the entire surface of the tongue. Language becomes smooth , bloodshot. Often there is an intensification of natural folds language. The red border of lips and mucous membrane thinned . May appear in the median and lateral fractures with delayed epithelialization and propensity to infection. The mucous membrane of the mouth is dry, there may be problems of candidiasis . Weakened patients candidates mycotic lesion is chronic. Plaque is torn away from difficult subject areas of the mucous membranes , which can viewed lihenopodobnye pockets as a result of sprouting strands of mycelium in the epithelium . Signs of secondary giporiboflavinoza are nonhealing cracks in the corners of the mouth. In the case of joining secondary microbial flora impetigopodobnye develop a rash. Gums are pale pink in color, showing signs of atrophy of its marginal edge . In cirrhosis of the liver can be observed aphthous and herpetic eruptions . Swollen tongue , lateral and ventral surface of his cyanotic , thread-like papillae are atrophied . 1. Practical skills on the topic: 1) be able to work in the dental equipment; 2) be able to work with a dental tool , know the rules of sterilization ; 3) be able to make recording and reporting therapist and analyze performance; 4) to be able to plan and carry out a clinical examination of the patient with gastrointestinal disorders , outline a treatment plan ; 5 ) be able to perform and assess the hygienic characteristics of oral cavity; 6) be able to take the material for cytological and microscopy studies , analyze the results ; 7) to be able to carry out irrigation, instillation , applique medications; 8) to be able to write down the recipe , assign physical therapy ; 9) to be able to perform professional oral hygiene ; 10) be able to give advice on the choice of means and objects of oral hygiene, prevention of complications. 2. Terminology : morbus ulcerosa ; gastritis acuta et chronica; enteritis; hepatitis chronica. 3. Questions for Knowledge Control : 1) the reasons for the defeat of the oral mucosa in the pathology of the digestive tract.
2) what are the main complaints of the mouth, characteristic of the digestive tract. 3) what are the changes of the oral mucosa and tongue with hypo-and giperatsidnom gastritis . the concept of a coated tongue and desquamative glossitis . 4 ) what are the dental manifestations of gastric ulcer and 12 duodenal ulcer. 5 ) the main manifestations of colitis and enterocolitis in the mouth. 6 ) clinical manifestations of hras . factors contributing to the severity of the disease . 7) differential diagnosis of chras . 8 ) treatment of chras . 9) what are the main manifestations of liver disease from the mouth. 10 ) the role of the dentist in the early diagnosis of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract . 11) approach to the patient dentist with suspected gastrointestinal pathology . features of the dental treatment of patients with pathology of the gastrointestinal tract . Assignments to control the source of knowledge: 1. Woman '51 complains of a burning sensation and tingling back and side surfaces of the tongue, which disappears during the meal, but is enhanced by the evening , dry mouth , taste perversion . For the first time such feelings emerged a year ago after the trauma , over time these feelings are amplified . Anatsidny suffering from gastritis , diabetes , trouble sleeping . What is the most likely diagnosis ? A. Glossodiniya . B. Glossitis Moeller - Gnter . C. Candida glossitis . D. Ganglionitis sublingual ganglia . E. Desquamative glossitis . 2 . A patient 55 years complains of burning , discomfort in the language. Within five years of suffering hypoacid gastritis. What changes the language most likely to occur in this patient? A. Hypertrophy of the papillae . B. . Erosion on the first side surfaces . C. C. Coated tongue . D. D. Atrophy and flattening of the papillae . E. E. Folding of the language. 3 . The girl is 18 years old, working a chemical plant after hypothermia observed malaise , fever , pain when eating . The patient suffers enterocolitis . Objective: to hyperemia , swelling of the oral mucosa numerous blisters and erosions formed after the opening of bubbles. GI = 3 , multiple cavities. What was the most likely cause of the disease ? A. Hazardous working conditions . B. Virus. C. Pathology of the gastrointestinal tract . D. Oral hygiene . E. Bacterial allergy . 4 . A patient 30 years old complains of pain on swallowing , the presence of plaque and cavities. In history: chronic gastritis . Objectively: the oral mucosa is hyperemic , edematous , abundant greenish patina on the soft palate , tonsils, the tongue , in 46 , 47 cavities of medium depth . Bacteriological examination of plaque Lefler found many diplococci . What is the dentist's tactics in relation to the patient? A. Infectious disease consultation .
B. Treatment of caries, dental health . C. Consultation otolaryngologist . D. Treatment of the oral mucosa , antibiotics . E. Consultation gastroenterologist. 5 . A patient 38 years complains about the presence of painful " sores " on the mucosa of the tongue. From time to time in 4 years like this one single " sores " appeared in different places of the oral mucosa , a history : peptic ulcer , chronic colitis . OBJECTIVE: on the right side of the tip of the tongue - erosion , covered with yellow- gray fibrinous coating, sharply painful to the touch , surrounded by a bright red inflammatory rim. What is the most likely diagnosis ? A. Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis . B. Traumatic erosion . C. Recurrent herpes. D. Erosive stomatitis . E. Pemphigus . 6. Patient 57 years old complains of dryness and burning sensation on the lateral surface of the tongue , which disappear during the meal. Such feelings have appeared three months ago. In history : gastritis with reduced secretion . OBJECTIVE: periglottis and mouth normal. The back of the tongue is covered small number of white bloom . Regional limfouzlyne determined by palpation. Oral cavity sanitized . What is the most likely diagnosis ? A. Glossodiniya B. Neuritis of the lingual nerve C. desquamative glossitis D. Glossitis Moeller Gunter E. candidiasis 7. In a patient with cirrhosis of the liver , numerous subcutaneous hemorrhage. What is the possible cause of their appearance ? A. Excessive destruction of vitamin C B. Disruption of the synthesis of vitamin K C. The lack of factor III in plasma D. hypocalcemia E. Decrease synthesis factor II 8. Sick 68- years took about a year diclofenac about pain in the knee joints . The night before, after a hearty dinner, suddenly there were black liquid stool , severe weakness , vomiting, a onetime , after which he lost consciousness. Ambulance rushed to hospital. Objectively : the patient is conscious, more lethargic , pale, respiration 20/min , Ps- 102/min , blood pressure 110/ 70 mm Hg The abdomen was soft , sensitive epigastric . Specify the most likely diagnosis : A. myocardial infarction B. Gastro- intestinal bleeding C. Mesenteric artery thrombosis D. food poisoning E. Cerebrovascular accident 9. The worker smelter 55ti years suffering from chronic cholecystitis , on the buccal mucosa near the hilly corner of the mouth , the white color , towering above the surrounding mucosa , with painless seal at the bottom. The oral cavity is not sanitized . Which of the following is a priority in the tactics of the dentist ? A. Conducting focus cryoablation B. Referral to a gastroenterologist
C. Dental health D. Purpose ectylotic E. Direction for consultation in Oncology Center 10 . The patient was 18 years of age diagnosed as a folded tongue. A symptom of the syndrome may be what this anomaly of development? A. Grynszpan's syndrome B. Cindrom Stevens Johnson C. Melkersson -Rosenthal syndrome D. Behcet's syndrome E. Sjogren syndrome 11. Female 33 years old disturb sores in the mouth, especially during meals . Of common diseases noted chronic bronchitis , chronic colitis . Objectively: the mucous membrane of the lower lip and the transitional fold unit erosion rounded shape , the size of 5-6 mm in diameter , covered with a yellowish- white fibrinous coating, which is difficult to remove, surrounded by a nimbus bloodshot , painful on palpation. What is the diagnosis put a doctor? A. Chronic recurrent herpes B. Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis C. traumatic erosion D. Behcet's syndrome E. secondary syphilis 12. Patient 30 years old complains of burning and discomfort in the language, change in taste, which appeared six months ago. From history we know that it is over 10 years old is suffering from gastritis hypoacid . OBJECTIVE: oral mucosa anemic , the language of the detected changes characteristic hypoacid gastritis. After the examination was set symptomatic glossitis . What changes are characteristic of the language hypoacid gastritis ? A. Hypertrophy and swelling of the tongue papillae B. Erosion on the first side surfaces C. Hypertrophy of the papillae and the presence of plaque in the language D. Atrophy of the tongue and the smoothness of tongue papillaeE. Hypertrophy of the papillae and focal epithelial desquamation 13. Go to the dentist turned 22 years old patient complaining of constant dry mouth , itching, presence of white patches on the tongue , " perleches " in the corners of the mouth. The described symptoms occurred 3 months ago. During this period, the patient has lost 8 pounds, had two recurrent herpes infections , pneumonia , during the month of suffering persistent diarrhea. Determine the tactics examination of the patient : A. Consultation with a gastroenterologist B. C. consultation dermatologist D. Consultation with an immunologist E. consultation rheumatologist 14. In the treatment of the patient's teeth at 52 years old doctor determined in the back third of the tongue , in the midline in front of circumvallate papillae , oval patch size 2,5 x2, 0 cm, red color, which clearly stands out from the surrounding mucosa. What is the most likely diagnosis ? A. traumatic glossit B. candidiasis C. Pellagroidny glossit D. rhomboid glossitis
E. syphilis 15. The patient complained of a painful existence , " ulcer " formations in the mouth, which appear periodically at intervals of 2-3 months. Objectively: the mucous membrane of the lower lip and tongue erosion rounded, surrounded by a rim of inflammatory hyperemia . Which specialist should refer the patient for examination? A. cardiologist B. surgeon C. infectious diseases D. gastroenterologist E. Haematologist 18. Thick gray coating on the back of the tongue , except for the tip and sides , dry , sometimes mucus , the most typical : A. acute gastritis B. chronic gastritis C. chronic hepatitis D. Gastric ulcer E. enterocolitis 19. Perversion of taste, sometimes "metallic" taste in the mouth, tongue papillae threadlike flatness up to their atrophy and appearance of bright red spots and small erosions on the background color of the normal oral mucosa suggest the diagnosis: A. Peptic ulcer B. Chronic gastritis hypoacid C. acute gastritis D. Hyperacid chronic gastritis E. chronic hepatitis 20. Hypertrophy of the filiform papillae usually in the middle and distal portions of the surface of the back of the tongue , swollen tongue , coated , cyanotic , mushroom-shaped papillae malorelefny indicate : A. chronic hepatitis B. acute gastritis C. Chronic gastritis giperatsidnom D. Gastric ulcer E. Hypoacid chronic gastritis 21. Against the background of pale pink color of the oral mucosa observed patches on the tongue , light gray , focal epithelial desquamation , usually on the cheeks , tongue, buccal surface of the lips , in the retromolar space as the afts , sometimes turning into sores - are observed at : A. Gastric ulcer B. chronic hepatitis C. Hypoacid chronic gastritis D. enterocolitis E. acute gastritis 22. Complaints of burning in the language, the feeling of " baked " language , migrating fociDesquamation of the epithelium, sometimes spontaneously disappear , coated tongue firmly soldered to the underlying tissues , oral mucosa pale pink color - these symptoms are typical for: A. enterocolitis B. chronic hepatitis C. acute gastritis
D. Hyperacid chronic gastritisE. Gastric ulcer 23. Burning, itching, soreness of the oral mucosa , especially in the area of the soft palate , icteric tint, perversion of taste sensitivity , a sense of bitterness in the mouth - are characteristic :A. chronic hepatitisB. Gastric ulcerC. Hypoacid chronic gastritisD. enterocolitisE. acute gastritis
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Oral Manifestation of GIT DiseasesDokumen33 halamanOral Manifestation of GIT DiseasesSura Abdel JabbarBelum ada peringkat
- Vpatho Module 1Dokumen54 halamanVpatho Module 1Lib PalmaresBelum ada peringkat
- ND 2 PathologyDokumen13 halamanND 2 Pathologyadeniransegun820Belum ada peringkat
- Oral Manifestations of Systemic Diseases: A Guide to Common ConditionsDokumen14 halamanOral Manifestations of Systemic Diseases: A Guide to Common Conditionsshygal1981Belum ada peringkat
- Orofacial Manifestation of Git DisordersDokumen74 halamanOrofacial Manifestation of Git DisordersKassim OboghenaBelum ada peringkat
- Taste Disorders: DR - Abdullah Alhayani, MBBSDokumen33 halamanTaste Disorders: DR - Abdullah Alhayani, MBBSalhayaniBelum ada peringkat
- Gitoralmanifestation 180812171655Dokumen74 halamanGitoralmanifestation 180812171655hassonamonaBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Frictional HyperkeratosisDokumen15 halamanOral Frictional HyperkeratosisFajarRahmantiyoBelum ada peringkat
- Halitosis - Etilogy and PathogenesisDokumen26 halamanHalitosis - Etilogy and PathogenesisPrathusha UmakhanthBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Oral Medicine Lecture NotesDokumen3 halamanClinical Oral Medicine Lecture NotesDrMurali G ManoharanBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Complications of Cancer TreatmentDokumen68 halamanOral Complications of Cancer TreatmentFarisha RasheedBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Malodor: by - DR Monisha Kaushik 2Nd Yr MdsDokumen55 halamanOral Malodor: by - DR Monisha Kaushik 2Nd Yr Mdsmonishakaus24Belum ada peringkat
- StomatitisDokumen44 halamanStomatitisNessa Layos Morillo100% (1)
- StomatitisDokumen17 halamanStomatitis4A - Hazel Ann G. EspinolBelum ada peringkat
- Common Oral Lesions: Aphthous Ulceration, Geographic Tongue, Herpetic GingivostomatitisDokumen13 halamanCommon Oral Lesions: Aphthous Ulceration, Geographic Tongue, Herpetic GingivostomatitisFaridaFoulyBelum ada peringkat
- Geographic TongueDokumen5 halamanGeographic Tonguebhawna_aroraBelum ada peringkat
- Drg. Zaiviani Juniani K, MkesDokumen33 halamanDrg. Zaiviani Juniani K, MkesdimasahadiantoBelum ada peringkat
- Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis Linked to Gastric PolypsDokumen3 halamanRecurrent Aphthous Stomatitis Linked to Gastric PolypsdrgozanBelum ada peringkat
- Tongue in Disease and Remedial Diagnosis - Science-Based HomeopathyDokumen7 halamanTongue in Disease and Remedial Diagnosis - Science-Based HomeopathyTakpire DrMadhukar100% (1)
- Oral Submucous FibrosisDokumen5 halamanOral Submucous Fibrosiskunnuve5005100% (1)
- Dental Management of Patients With Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDokumen17 halamanDental Management of Patients With Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseLeonid GroysmanBelum ada peringkat
- Dry Mouth EngDokumen25 halamanDry Mouth EngJelena BlagojevicBelum ada peringkat
- Scalloped Tongue - Treatment Symptoms and Causes - Scalloped TongueDokumen7 halamanScalloped Tongue - Treatment Symptoms and Causes - Scalloped TongueJing CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Tongue Anatomy and FunctionsDokumen37 halamanTongue Anatomy and FunctionsVlad ScutelnicBelum ada peringkat
- Fissured Tongue: A Case Report and Review of Literature: KeywordsDokumen5 halamanFissured Tongue: A Case Report and Review of Literature: Keywordssiti baiq gadishaBelum ada peringkat
- Stomatitis: Overview of The AnatomyDokumen6 halamanStomatitis: Overview of The Anatomyjhing_tajulBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Oral Manifestation of Sustemic DiseaseDokumen43 halamanPediatric Oral Manifestation of Sustemic DiseaseMike SihombingBelum ada peringkat
- The Procedure For Examining Stomatologic PatientsDokumen21 halamanThe Procedure For Examining Stomatologic PatientsOzzie RaynsBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Medicine: (I. Penyakit Mulut)Dokumen178 halamanOral Medicine: (I. Penyakit Mulut)claudiaciwiBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Manifestaions of Systemic DiseasesDokumen116 halamanOral Manifestaions of Systemic DiseaseslikhithaBelum ada peringkat
- Riaz Gul AHN Unit 1Dokumen106 halamanRiaz Gul AHN Unit 1Riaz Gul RindBelum ada peringkat
- Tonguedisorders 150616104030 Lva1 App6892Dokumen34 halamanTonguedisorders 150616104030 Lva1 App6892Mohan VeerabomalaBelum ada peringkat
- Salivary Gland DiseaseDokumen63 halamanSalivary Gland DiseaseAnchal RainaBelum ada peringkat
- Mouth and Esophagus DisordersDokumen47 halamanMouth and Esophagus DisordersSures Amoeba RajBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Manifestations of Systemic DiseasesDokumen11 halamanOral Manifestations of Systemic DiseasesMezo Salah100% (2)
- Pathology of The Alimentary SystemDokumen15 halamanPathology of The Alimentary SystemsatriayanuwardaniBelum ada peringkat
- DR - Punik Mumpuni DIGESTIDokumen38 halamanDR - Punik Mumpuni DIGESTIontakecilBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Exam NotesDokumen3 halamanOral Exam NotesDrumz StaffBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Manifestations of Systemic Diseases A Review, 2014 PDFDokumen9 halamanOral Manifestations of Systemic Diseases A Review, 2014 PDFDwi Indah LestariBelum ada peringkat
- Folliate PappilaeDokumen9 halamanFolliate PappilaeEga Muhamad YusufBelum ada peringkat
- Financial and Methodological Support Classes: Machinery and Equipment Dental Office, AnDokumen11 halamanFinancial and Methodological Support Classes: Machinery and Equipment Dental Office, AnAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Gingival InfectionsDokumen31 halamanAcute Gingival InfectionsPathivada LumbiniBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Dyah Ayu Larasati, S.KedDokumen10 halamanDiagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Dyah Ayu Larasati, S.KedAndhee Whoelank ZiyeangtaecgmhueerymhuerryeBelum ada peringkat
- A Patient With Dry Mouth PDFDokumen6 halamanA Patient With Dry Mouth PDFWahdatBelum ada peringkat
- Tongue Diseases NDokumen46 halamanTongue Diseases NhazeemmegahedBelum ada peringkat
- Ilovepdf MergedDokumen157 halamanIlovepdf MergedSajjad AliBelum ada peringkat
- HalitosisDokumen34 halamanHalitosisVinay KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Oral, Git, Billiary ConditionsDokumen107 halamanOral, Git, Billiary ConditionsNathaniel Mbiu TimBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Manifestations of Systemic DiseaseDokumen10 halamanOral Manifestations of Systemic DiseasedrnainagargBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 22. Diseases of GITDokumen6 halamanTopic 22. Diseases of GITAdeleye John AdebolaBelum ada peringkat
- Diseases of the Oral Cavity: Signs, Symptoms and ManagementDokumen117 halamanDiseases of the Oral Cavity: Signs, Symptoms and ManagementRamanujam SridharBelum ada peringkat
- Challenges in oral care of oral lichen planus in diabetic patientsDokumen10 halamanChallenges in oral care of oral lichen planus in diabetic patientsDanis Diba Sabatillah YaminBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Medicine - Update For The Dental Practitioner.: Dry Mouth and Disorders of SalivationDokumen5 halamanOral Medicine - Update For The Dental Practitioner.: Dry Mouth and Disorders of SalivationGowriBelum ada peringkat
- Oral MedicineDokumen174 halamanOral Medicineindah100% (1)
- Diagnosis and Management of Xerostomia in The Elderly PatientDokumen59 halamanDiagnosis and Management of Xerostomia in The Elderly PatientDMnDLBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroenterology For Dentists 2017Dokumen52 halamanGastroenterology For Dentists 2017David McMahonBelum ada peringkat
- GERD (Heart Burn) : Gastrointestinal DisordersDokumen7 halamanGERD (Heart Burn) : Gastrointestinal DisordersKateBelum ada peringkat
- A Simple Guide to Bad Breath and Mouth DiseasesDari EverandA Simple Guide to Bad Breath and Mouth DiseasesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Managing Geriatric Patients' Oral HealthDokumen50 halamanManaging Geriatric Patients' Oral HealthJen de Luna50% (2)
- Differential Diagnosis of Dental Diseases PDFDokumen529 halamanDifferential Diagnosis of Dental Diseases PDFAbdullah Saleem100% (2)
- Financial and Methodological Support Classes: Machinery and Equipment Dental Office, AnDokumen11 halamanFinancial and Methodological Support Classes: Machinery and Equipment Dental Office, AnAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Drug and Alcohol Use by Dental Healthcare Professionals and StudentsDokumen44 halamanDrug and Alcohol Use by Dental Healthcare Professionals and StudentsAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Dental Management of Medically Compromised PatientsDokumen12 halamanDental Management of Medically Compromised Patientsمحمد ابوالمجدBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 161: Changes in The Mucous Membrane of Oral Cavity in Hypovitaminosis and Avitaminosis A, C. Tactics of Dentists. Questions For Control of KnowledgeDokumen9 halamanTopic 161: Changes in The Mucous Membrane of Oral Cavity in Hypovitaminosis and Avitaminosis A, C. Tactics of Dentists. Questions For Control of KnowledgeAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- MUnich Uni Ad FormDokumen4 halamanMUnich Uni Ad FormAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Cranial Nerves: By: Dr. Pamela Josefina T. FabieDokumen48 halaman12 Cranial Nerves: By: Dr. Pamela Josefina T. FabieAbdullah Saleem100% (3)
- Contact Info for Dr. Malek B. H. AbazaidDokumen119 halamanContact Info for Dr. Malek B. H. Abazaidioana373283% (6)
- Dental Hand InstrumentsDokumen21 halamanDental Hand Instrumentsbrain_man22Belum ada peringkat
- ImplantDokumen7 halamanImplantAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- InternshipApplicationForm 2011Dokumen2 halamanInternshipApplicationForm 2011Abdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 15 Nonodontogenic Benign Tumors of The Jaws PDFDokumen22 halamanChapter 15 Nonodontogenic Benign Tumors of The Jaws PDFAbdullah Saleem100% (1)
- Intern Dentist Dubai InfoDokumen3 halamanIntern Dentist Dubai InfoAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Occlusal TraumaDokumen3 halamanOcclusal TraumaAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Financial and Methodological Support Classes: Machinery and Equipment Dental Office, AnDokumen11 halamanFinancial and Methodological Support Classes: Machinery and Equipment Dental Office, AnAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Khazeena e RehmatDokumen187 halamanKhazeena e RehmatSehra E Madina100% (1)
- DermatoDermatology Case HX R Logy Case HX R - NewDokumen10 halamanDermatoDermatology Case HX R Logy Case HX R - NewAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Content of Classification Examination PDFDokumen1 halamanContent of Classification Examination PDFAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- AnatomyDokumen24 halamanAnatomyAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Risk and Risk and Periodontal Disease ManagementPeriodontal Disease ManagementDokumen14 halamanRisk and Risk and Periodontal Disease ManagementPeriodontal Disease ManagementAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Khazeena e RehmatDokumen187 halamanKhazeena e RehmatSehra E Madina100% (1)
- Local Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDokumen102 halamanLocal Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgerydr_jamal1983Belum ada peringkat
- 010009000003a60e00000000810e000000000400000003010800050000000b0200000000050000000cDokumen29 halaman010009000003a60e00000000810e000000000400000003010800050000000b0200000000050000000cAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Requirements of a Balanced DietDokumen8 halamanRequirements of a Balanced DietAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- New Text DocumentDokumen5 halamanNew Text DocumentAbdullah SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Body SystemsDokumen4 halamanBody SystemsKathryn Schultz29% (14)
- Digestive System BreakdownDokumen3 halamanDigestive System BreakdownSyifa IndanaBelum ada peringkat
- Adani Public School: Nanakapaya, Mundra 2020 - 2021 Science (Class 10)Dokumen44 halamanAdani Public School: Nanakapaya, Mundra 2020 - 2021 Science (Class 10)Siddharth SouravBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 9 Digestive System FunctionsDokumen6 halamanGrade 9 Digestive System FunctionsRamyRamia ElzantBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Science Notes 06 Life Processes 11Dokumen13 halaman10 Science Notes 06 Life Processes 11rajkumar trivedi100% (2)
- Human Digestive SystemDokumen14 halamanHuman Digestive Systemfatimah17Belum ada peringkat
- English Final Semester Test For Grade Xii A. Choose The Best Answer For The Following Questions The Following Text Is For The Questions Number 1 - 4Dokumen9 halamanEnglish Final Semester Test For Grade Xii A. Choose The Best Answer For The Following Questions The Following Text Is For The Questions Number 1 - 4Liza RahmawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank For Medical Language For Modern Health Care 4th Edition by AllanDokumen62 halamanTest Bank For Medical Language For Modern Health Care 4th Edition by Allansophiacarrdabemqozri100% (22)
- Bio RevisionDokumen58 halamanBio RevisionKesithan AnandarashBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Laws Opt OutDokumen39 halamanGas Laws Opt OutTahir HussainBelum ada peringkat
- AAC Activity 1 (Life Process)Dokumen2 halamanAAC Activity 1 (Life Process)JamesBelum ada peringkat
- Case Presentation (October 3)Dokumen54 halamanCase Presentation (October 3)Ayessa Camelle DumileBelum ada peringkat
- Communicable Diseases of The GITDokumen31 halamanCommunicable Diseases of The GITNicole Anne TungolBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomifisiologimanusia Pencernaan 120923110823 Phpapp02Dokumen124 halamanAnatomifisiologimanusia Pencernaan 120923110823 Phpapp02api-268725095Belum ada peringkat
- Case Presentation GastroenteritisDokumen58 halamanCase Presentation GastroenteritisShereen Manabilang100% (3)
- Biochem Reviewer ProteinsDokumen27 halamanBiochem Reviewer Proteinsram castilloBelum ada peringkat
- Master Cleanse INSTRUCTIONSDokumen6 halamanMaster Cleanse INSTRUCTIONSAlexander Rosental100% (2)
- Digestive Organs & Their HistologyDokumen5 halamanDigestive Organs & Their HistologyMall HiBelum ada peringkat
- Digestive System Histology GuideDokumen14 halamanDigestive System Histology GuideFhayee Sulaik HaronBelum ada peringkat
- The General Anatomy of The Teeth Comparative Anatomy of The TeethDokumen9 halamanThe General Anatomy of The Teeth Comparative Anatomy of The Teethsomebody_maBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy & Physiology Digestive System Exam ReviewDokumen13 halamanAnatomy & Physiology Digestive System Exam Reviewhugomiso100% (3)
- Case Study Bactegroup 3Dokumen19 halamanCase Study Bactegroup 3Marjune DimayugaBelum ada peringkat
- General Science Ebook 1 Jagran JoshDokumen136 halamanGeneral Science Ebook 1 Jagran JoshCentral Province Online Publishers50% (2)
- Medical TerminologyDokumen33 halamanMedical TerminologySusanBernardBelum ada peringkat
- Modern Physics ModuleDokumen111 halamanModern Physics ModuleMichael EsmallaBelum ada peringkat
- Anaphy Lec Finals ReviewerDokumen35 halamanAnaphy Lec Finals Reviewermicah cajandabBelum ada peringkat
- Body System ChecklistDokumen8 halamanBody System Checklistapi-421876369Belum ada peringkat
- Soal SoalDokumen3 halamanSoal SoalRengga ZekliBelum ada peringkat
- Handout - Chapter 3 - Digestion - Google Docs - 1665372467933 3Dokumen8 halamanHandout - Chapter 3 - Digestion - Google Docs - 1665372467933 3NC ExistentialBelum ada peringkat
- DigestiveDokumen6 halamanDigestiveanon_783012033Belum ada peringkat