Tissue Spread Sheet
Diunggah oleh
api-239695135Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Tissue Spread Sheet
Diunggah oleh
api-239695135Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
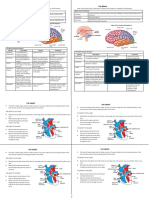
Structural Characteristics
Function of tissue
Organ(s) which contain this tissue type
Simple squamous epithelium
Broad and thin nuclei, single layer of thin, flattened cells
Provides a smooth, friction-reducing interior lining, acts as filtration and site of diffusion
Lines interior of heart, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and body cavities
Stratified squamous epithelium
Many cell layers make it thick, accumulate keratin
Keratinized form provides protective covering that prevents water and other substances from escaping
Forms epidermis; lines the mouth, throat, vagina, and anal canal
Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium
Not layered, only one nucleus, contain cilia
Cilia extending from tissue moves mucus and trapped particles out of the airway; moves sex cells from one region to another Protects underlying tissues, secretes digestive fluids, and absorbs nutrients from digested food
Lines the passages of respiratory and reproductive systems
Simple columnar epithelium
Elongated, single layer of cells
Lines uterus and most digestive tract organs
Osseous
most rigid connective tissue, contains collagen, lamellae form concentric patterns
Forms bone that supports body structures, houses marrow
All bones
Adipose
Specialized form of loose fibrous connective tissue
Cushions joints and some organs, insulates, stores fat and energy
Lies beneath the skin, behind eyes, in certain abdominal membranes, on the surface of the heart, etc.
Areolar
Delicate, thin membranes; cells are located some distance apart
Produces collagenous and elastic fibers, binds Integumentary the skin to underlying system, muscles organs and fills spaces between muscles
Hyaline cartilage
Very fine collagenous fibers
Aids in development of most bones, cushions joints
Ends of joints, soft part of nose, and supporting rings of respiratory passages
Reticular cartilage (fibrocartilage)
Very tough, contains many collagenous fibers
Shock absorber for structures subjected to pressure
Between vertebrae, knee joints, pelvic girdle
Blood
Red and white cells, platelets (cellular fragments), forms in marrow
Transports a variety of substances between interior body cells and those that exchange with the external environment
Blood vessels, heart chambers
Smooth muscle
Lacks striations, shorter than skeletal, spindle-shaped with a single, centrally located nucleus
Involuntary contractions to move food through the digestive tract, constricts blood vessels, and empties urinary bladder
Digestive tract, blood vessels, urinary bladder
Cardiac muscle
Striated, joined end to end, branched, interconnected in complex networks
Involuntary contractions pumps blood through the heart chambers and into blood vessels
Heart
Skeletal muscle
Long, threadlike cell with alternating light and dark striations, many nuclei
Voluntary contractions make facial expressions, write, talk, sing, chew, swallow, and breathe
Respond to stimulus by transmitting electrical impulses to muscles or glands
Muscles that move head, trunk, and limbs
Nervous
Sensitive to changes in their surroundings, nucleus
Brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- FIU - Cervical SpineDokumen42 halamanFIU - Cervical Spineamoon12Belum ada peringkat
- Dolls Eye MovementDokumen3 halamanDolls Eye MovementMamata BeheraBelum ada peringkat
- Braddom Lower Extremity DrillsDokumen4 halamanBraddom Lower Extremity DrillsKennie RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- DapusDokumen4 halamanDapusRiza ZaharaBelum ada peringkat
- Ch. 15 Sensory SystemDokumen23 halamanCh. 15 Sensory SystemJackieFernandezBelum ada peringkat
- FR Training Cert Worksheets 080412 2Dokumen8 halamanFR Training Cert Worksheets 080412 2api-30886506Belum ada peringkat
- Shoulder DysfociaDokumen92 halamanShoulder DysfociaKagomie SaskieBelum ada peringkat
- The Brain The Brain: Major Parts of The Brain Major Parts of The BrainDokumen4 halamanThe Brain The Brain: Major Parts of The Brain Major Parts of The BrainRanulfo MayolBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology Reviewer PDFDokumen10 halamanAnatomy and Physiology Reviewer PDFArnoldBelum ada peringkat
- The Scip Propeller Flap Versatility For R - 2019 - Journal of Plastic ReconstrDokumen8 halamanThe Scip Propeller Flap Versatility For R - 2019 - Journal of Plastic Reconstrydk sinhBelum ada peringkat
- Checklist Neurologic AssessmentDokumen6 halamanChecklist Neurologic AssessmentPaulo Pabito100% (3)
- Cupping PointsDokumen9 halamanCupping PointsAna JacintaBelum ada peringkat
- Aggarwal 1999Dokumen10 halamanAggarwal 1999Khaoula BeddaaBelum ada peringkat
- The Blood Circulatory SystemDokumen3 halamanThe Blood Circulatory SystemListiyani IsmailBelum ada peringkat
- Eng-Fil Parts of The BodyDokumen14 halamanEng-Fil Parts of The BodyJoseth OyardoBelum ada peringkat
- Posterior Teeth ArrangementDokumen1 halamanPosterior Teeth ArrangementVy HuynhBelum ada peringkat
- Group 1 Potd Part 2Dokumen1 halamanGroup 1 Potd Part 2Regina CabelisBelum ada peringkat
- Cow's HeartDokumen10 halamanCow's HeartAllyzha AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- Avian Sensory Systems: Sensory World Similar To Ours, That of Other Primates, Primarily VisualDokumen30 halamanAvian Sensory Systems: Sensory World Similar To Ours, That of Other Primates, Primarily VisualijudoptoBelum ada peringkat
- MPFL Reconstruction ProtocolDokumen8 halamanMPFL Reconstruction ProtocolOana ApostoiuBelum ada peringkat
- SLMCCM Self Study Guide 1 BerDokumen3 halamanSLMCCM Self Study Guide 1 BerPaolo PanlaquiBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Position Where Most Exercises BeginDokumen9 halamanBasic Position Where Most Exercises Beginantonettedgreat67% (3)
- Fisika BioelektrikDokumen50 halamanFisika BioelektrikFachriza EffendiBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen3 halamanWhat Is A Urinary Tract InfectionStepyn SalvadorBelum ada peringkat
- BSC 6 Sem General Mammalian Physiology 2 Zoology Summer 2018Dokumen1 halamanBSC 6 Sem General Mammalian Physiology 2 Zoology Summer 2018Ujjwala KumbhalkarBelum ada peringkat
- NEET PG 2020 Questions: (Memory Based)Dokumen25 halamanNEET PG 2020 Questions: (Memory Based)Anmol KudalBelum ada peringkat
- Hyperthyroidism: Annals of Internal Medicine July 2012Dokumen17 halamanHyperthyroidism: Annals of Internal Medicine July 2012Deepa RajBelum ada peringkat
- Mri of The Shoulder Joint Technique & Normal AppearanceDokumen53 halamanMri of The Shoulder Joint Technique & Normal AppearanceHossam SakrBelum ada peringkat
- Soalan Bio Bab 3 3.1 Ccov20 1Dokumen6 halamanSoalan Bio Bab 3 3.1 Ccov20 1Anas AjmalBelum ada peringkat
- Body by RingsDokumen6 halamanBody by RingsDenis Osmenaj100% (1)