CHOLINERGICS
Diunggah oleh
trentsuggsJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CHOLINERGICS
Diunggah oleh
trentsuggsHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CHOLINERGICS
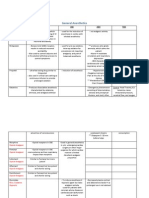
ACh M1, M2, M3 MOA -All choline esters/natural alkaloids activate M1, M2, M3 receptors -postsynaptic receptors alter function of effector organ -presynaptic receptors inhibit release of neurotransmitter MOA
USE
Diarrhea Urination Miosis Bronchicon Bradycardia Excitation o Lacrimation Salivation
Carbachol * insensitive to Ach Esterase
USE
Open Angle Glaucoma o Causes contraction of ciliary muscle resulting in outflow through trabecular meshwork Stimulates both N & M receptors
Diarrhea Urination Miosis Bronchicon Bradycardia Excitation o Lacrimation Salivation
Bethanechol * insensitive to Ach E * No Nicotinic effect Pilocarpine -tertiary amine form from plant genus Pilocarpus Muscarine -quaternary ammonium compound from mushrooms Inocybe and Clitocybe Edrophonium
M1, M2, M3
MOA
USE
Bowel & Bladder Constipation Urinary Retention (post-op/postpartum) Xerostomia Post-op nonobstructive ileus Neurogenic Bladder
Diarrhea Urination Miosis Bronchicon Bradycardia Excitation o Lacrimation Salivation
M1, M2, M3
MOA
USE
Open Angle Glaucoma o Causes contraction of ciliary muscle resulting in outflow through the trabecular meshwork Xerostomia due to Siorgen Syn. or radiation
Diarrhea Urination Miosis Bronchicon Bradycardia Excitation o Lacrimation Salivation
M1, M2, M3
MOA
USE **Poisoning from mushroom is called mycetism
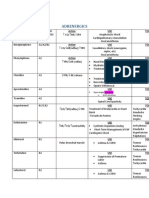
Indirect Cholinergic Agonist Reversible Cholinesterase Inhibitor
MOA -reversibly binds to the active site of enzyme so preventing Ach abscess
USE
Diagnosis of Myasthenia Gravis Differentiate between MG & Cholinergic Crisis o MG Improvement of symptoms
Excessive D
CC symptoms get worse
Physostigmine -carbamate
Indirect Cholinergic Agonist Reversible Cholinesterase Inhibitor Indirect Cholinergic Agonist Reversible Cholinesterase Inhibitor Indirect Cholinergic Agonist Reversible Cholinesterase Inhibitor Indirect Cholinergic Agonist Irreversible Cholinesterase Inhibitor
MOA -undergo two-step hydrolysis similar to Ach, but is more resistant to hydrolysis MOA -undergo two-step hydrolysis similar to Ach, but is more resistant to hydrolysis * can also directly activate nicotinic receptors at neuromus. junction MOA -selective inhibitor of Ach E in the BRAIN
USE
Glaucoma Bowel & Bladder Atonia Overdose of
o o
Convulsion Muscle Par Excessive D
Atropine Phenothiazide Neuroleptics TCAs
Neostigmine -carbamate
USE
Reversible Cholinesterase Inhibitor Myasthenia Gravis treatment Paralytic Ileus Antidote for Polarizing NMJ blockade (tubocurarine)
Excessive D
Donezepil
USE
Treatment of ALZHEIMERS by slowing the deterioration of cognitive function
Parathion
(organophosphate)
MOA -binds to the esteratic site; phosphorylated enzyme is extremely stable Aging loss of alkyl group strengthens complex MOA - Spontaneous hydrolytic regeneration of phosphorylated Ach E -Oximes have high affinity for Phosphorus atom and can rapidly regenerate the enzyme IF it did not AGE
USE
Insecticide
Diarrhea Urination Miosis Bronchicon Bradycardia Excitation o Lacrimation Salivation
Pralidoxime
Ach E reactivator
USE
AChEsterase Reactivator in Organophosphate poisoning
-Muscu he
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- General AnestheticsDokumen4 halamanGeneral AnestheticstrentsuggsBelum ada peringkat
- Anti AdrenergicsDokumen2 halamanAnti AdrenergicstrentsuggsBelum ada peringkat
- Adrenergics: Action USE ToxicityDokumen2 halamanAdrenergics: Action USE ToxicitytrentsuggsBelum ada peringkat
- AMC Questions Sample2 PDFDokumen2 halamanAMC Questions Sample2 PDFtrentsuggsBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Pentravan Scientific BrochureDokumen38 halamanPentravan Scientific BrochureГабриела ГеоргиеваBelum ada peringkat
- Dhanushiya A-P Saravanan (0359079) Classification of NSAIDsDokumen12 halamanDhanushiya A-P Saravanan (0359079) Classification of NSAIDsaurtho sadaaf sharrarBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar Obat Dengan Nama/Ucapan Dan Atau Rupa Mirip (Look Alike Sound Alike/Lasa) Instalasi Farmasi Rsud LawangDokumen1 halamanDaftar Obat Dengan Nama/Ucapan Dan Atau Rupa Mirip (Look Alike Sound Alike/Lasa) Instalasi Farmasi Rsud LawangMiftahkhul KhusnaBelum ada peringkat
- CDM Antibio1 DosageGuidelines Adults enDokumen2 halamanCDM Antibio1 DosageGuidelines Adults endwiBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac Case StudyDokumen3 halamanCardiac Case StudyJessi ParsonsBelum ada peringkat
- Who Expert Committe On Drug DependenceDokumen266 halamanWho Expert Committe On Drug DependenceAlcione Ferreira SáBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Bullet In: Obstetric Analgesia and AnesthesiaDokumen17 halamanPractice Bullet In: Obstetric Analgesia and AnesthesiaKatherine ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- AlembicDokumen4 halamanAlembicNarender OrugantiBelum ada peringkat
- WC ListDokumen42 halamanWC ListyoganaBelum ada peringkat
- Processing The Prescription OrderDokumen9 halamanProcessing The Prescription OrderRose AnnBelum ada peringkat
- Theophylline Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanTheophylline Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (5)
- Clinical Medications WorksheetsDokumen2 halamanClinical Medications WorksheetsMichael Kuzbyt0% (1)
- HIV & TBDokumen51 halamanHIV & TBRhea DerijeBelum ada peringkat
- Glargine Insulin For Veterinary UseDokumen3 halamanGlargine Insulin For Veterinary Use13Belum ada peringkat
- PHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jun2020 05Dokumen2 halamanPHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jun2020 05GAnnBelum ada peringkat
- Rak 4.1Dokumen14 halamanRak 4.1Apotik Karya SehatBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Studii StatineDokumen37 halaman6 Studii Statinejust4uhopeBelum ada peringkat
- Anticholinergic SDokumen22 halamanAnticholinergic SALNAKIBelum ada peringkat
- Yovita - The Role of Clinical Pharmacist On Safe Administration AntibioticDokumen48 halamanYovita - The Role of Clinical Pharmacist On Safe Administration AntibioticRois HasyimBelum ada peringkat
- Bodega - Id Casa - ID Articulo - Id Textbox6 ExistenciaDokumen48 halamanBodega - Id Casa - ID Articulo - Id Textbox6 ExistenciaAshley TerrazaBelum ada peringkat
- AP Agung SerdamDokumen220 halamanAP Agung Serdamjihan.luthfiyahBelum ada peringkat
- Sple 11july 2023Dokumen10 halamanSple 11july 2023Arun SabuBelum ada peringkat
- ShejayLomongo BSN2Dokumen15 halamanShejayLomongo BSN2Shejay LomongoBelum ada peringkat
- Please Admit To Room of Choice Under The Service of DRDokumen2 halamanPlease Admit To Room of Choice Under The Service of DRDave AnchetaBelum ada peringkat
- PNSSDokumen2 halamanPNSSBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Barang Bebas Buat PKPADokumen152 halamanBarang Bebas Buat PKPABrian FoxBelum ada peringkat
- Tablet 1Dokumen24 halamanTablet 1Anis Yahya100% (1)
- LAMPIRAN I Hal51-100 2013 PDFDokumen50 halamanLAMPIRAN I Hal51-100 2013 PDFHotman PermanaBelum ada peringkat
- Spontaneous ReportingDokumen14 halamanSpontaneous Reportingmatin5Belum ada peringkat
- Antibiotics FamiliesDokumen5 halamanAntibiotics FamiliesTiffany SamanthaBelum ada peringkat