9 Science Metals Nonmetals
Diunggah oleh
Ajay AnandDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
9 Science Metals Nonmetals
Diunggah oleh
Ajay AnandHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Finish Line & Beyond
MATERIALS: METALS AND NON—METALS
Physical Properties
Chemical Properties
Reaction of Metals with Oxygen
Reaction of Metals with Water
Reaction of Metals with Acids
www.excellup.com ©2009 send your queries to enquiry@excellup.com
Finish Line & Beyond
A metal is a chemical element whose atoms readily lose electrons to form positive
ions (cations), and form metallic bonds between other metal atoms and ionic bonds
between nonmetal atoms.
Non-Metal is a chemical element lacking typical metallic properties.
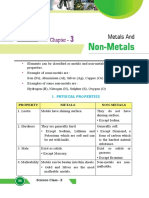
Physical Properties of Metals and Non-metals
Metals Nonmetals
• Good electrical conductors and heat
• Poor conductors of heat and
conductors.
electricity.
• Malleable - can be beaten into thin
• Brittle - if a solid.
sheets.
• Nonductile.
• Ductile - can be stretched into wire.
• Do not possess metallic luster.
• Possess metallic luster.
• Transparent as a thin sheet.
• Opaque as thin sheet.
• Solids, liquids or gases at room
• Solid at room temperature (except
temperature
Hg).
Chemical Properties of Metals and Non-metal
Metals are Electropositive Elements
Metals are very reactive. Metals tend to loose electrons easily and form positively
charged ions; therefore metals are called electropositive elements. Sodium metal
forms sodium ions Na+, Mg forms positively charged Magnesium ions Mg2+and
aluminium forms aluminium ions Al3+. The electropositive nature allows metals to
form compounds with other elements easily.
Reaction of Metals with Oxygen
Metals like sodium (Na) and potassium (K) are some of the most reactive metals.
Potassium, sodium, lithium, calcium and magnesium react with oxygen and burn in
air.
www.excellup.com ©2009 send your queries to enquiry@excellup.com
Finish Line & Beyond
Metals from aluminium to copper in the activity series of metals, react slowly when
heated in air to form the metal oxides. Aluminium is the fastest and copper is the
slowest of them.
• Sodium metal reacts with the oxygen of the air at room temperature to form
sodium oxide. Hence, sodium is stored under kerosene to prevent its reaction
with oxygen, moisture and carbon dioxide.
• Sodium oxide is a basic oxide which reacts with water to form sodium
hydroxide.
• Mg does not react with oxygen at room temperature. On heating, Mg burns in
air with intense light and heat to form MgO.
• Zinc metal burns in air only on strong heating to form zinc oxide.
• Iron metal does not burn in dry air even on strong heating. In moist air, iron
is oxidized to give rust.
www.excellup.com ©2009 send your queries to enquiry@excellup.com
Finish Line & Beyond
• On heating in air it burns with a brilliant flame forming triferric tetroxide.
• Copper is the least reactive metal and does not burn in air even on heating.
However, on prolonged strong heating copper reacts with oxygen and forms
copper (II) oxide (CuO) outside and copper (I) oxide (Cu2O) inside.
• Gold and platinum do not react with oxygen in air.
Reaction of Metals with Water
Potassium, sodium, lithium and calcium react with cold water.
• Sodium reacts vigorously with cold water forming sodium hydroxide and
hydrogen.
• Metals from magnesium to iron in the activity series of metals, react with
steam (but not H2O) to form the metal oxide and hydrogen gas.
www.excellup.com ©2009 send your queries to enquiry@excellup.com
Finish Line & Beyond
• Red hot iron reacts with steam to form Iron (II, III) oxide.
Note: The reaction between iron and steam is irreversible. Tin, lead, copper,
silver, gold and platinum do not react with water or steam.
Reaction of Metals with Acids
• Potassium, sodium, lithium and calcium react violently with dilute H 2SO4 and
dilute HCl, forming the metal salt (either sulphate or chloride) and hydrogen gas.
The reaction is similar to the reaction with water.
• Magnesium, aluminium, zinc, iron, tin and lead react safely with dilute acid.
Magnesium is the fastest and lead is the slowest of the six.
www.excellup.com ©2009 send your queries to enquiry@excellup.com
Finish Line & Beyond
Zinc with dilute sulphuric acid is often used for the laboratory preparation of
hydrogen. The reaction is slow at room temperature, but its rate can be increased by
the addition of a little copper (II) sulphate. Zinc displaces copper metal, which acts
as a catalyst.
In general,
• Hydrochloric acid makes a metal chloride.
• Sulphuric acid makes a metal sulphate.
• Reactions with nitric acid are more complex, the nitrate is formed but the gas
is rarely hydrogen, and more often, an oxide of nitrogen.
Reaction of Metals with Salt Solutions
Reactive metals can displace any metal less reactive than itself, from the oxide,
chloride or sulphate of the less reactive metal in solution or their molten state. If
metal A displaces metal B from its solution, it is more reactive than B.
www.excellup.com ©2009 send your queries to enquiry@excellup.com
Finish Line & Beyond
Copper (II) sulphate solution is blue; iron sulphate solution is almost colourless when
dilute. During the displacement, the blue solution loses its colour and the iron metal
is seen to turn pink-brown as the displaced copper becomes deposited on it.
On heating the mixture of magnesium powder and black copper (II) oxide, white
magnesium oxide is formed with brown bits of copper:
Adding magnesium to blue copper (II) sulphate solution, the blue colour fades as
colourless magnesium sulphate is formed and brown bits of copper metal form a
precipitate:
www.excellup.com ©2009 send your queries to enquiry@excellup.com
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Metals and Non MetalsDokumen28 halamanMetals and Non MetalsALEENABelum ada peringkat
- Metals and Non Metals Notes Class 10 2022-23Dokumen37 halamanMetals and Non Metals Notes Class 10 2022-23ramkumarsingh12406100% (1)
- Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NotesDokumen12 halamanClass 10 Metals and Non Metals NotesShreyash VishwakarmaBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 5: Metals: Main Group Al, Ga, In, SN, TL, PB, Bi, PoDokumen5 halamanCHAPTER 5: Metals: Main Group Al, Ga, In, SN, TL, PB, Bi, Pocory kurdapyaBelum ada peringkat
- Class 8 Chap 4 Metals and Non MetalsDokumen34 halamanClass 8 Chap 4 Metals and Non MetalsAncy davidBelum ada peringkat
- Mainly in Group I, Group II, and The Transition Block - Those The Staircase LineDokumen14 halamanMainly in Group I, Group II, and The Transition Block - Those The Staircase LineOrderPlace AccountBelum ada peringkat
- Metals and Non MetalsDokumen72 halamanMetals and Non MetalssimoneBelum ada peringkat
- Metals and Non Metals N 1Dokumen8 halamanMetals and Non Metals N 1rincyBelum ada peringkat
- Metals & Non-Metals: Topics in The ChapterDokumen7 halamanMetals & Non-Metals: Topics in The ChapterManya SinghviBelum ada peringkat
- The Periodic Table of ElementsDokumen41 halamanThe Periodic Table of ElementsPawan GoswamiBelum ada peringkat
- ChemistryDokumen31 halamanChemistryvisheshsingla411Belum ada peringkat
- Padhle 10th - Metal & Non-Metals Lecture SlidesDokumen25 halamanPadhle 10th - Metal & Non-Metals Lecture SlidesBitan DasBelum ada peringkat
- Science: (Chemistry)Dokumen22 halamanScience: (Chemistry)Isaiah JohnsonBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 3 Metals - and - Non - Metals NewDokumen14 halamanChapter - 3 Metals - and - Non - Metals NewRahul IngleBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4Dokumen16 halamanChapter 4Bhavya JangidBelum ada peringkat
- Metals and Non Metals - NotesDokumen8 halamanMetals and Non Metals - NotesMohita RastogiBelum ada peringkat
- Metal and Non Metal Class VIIIDokumen9 halamanMetal and Non Metal Class VIIIamrendraBelum ada peringkat
- Metal and Non Metal Class VIIIDokumen9 halamanMetal and Non Metal Class VIIIDr. Amrendra JhaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Metallurgy For Welding and Fabricating ProfessionalsDokumen190 halamanBasic Metallurgy For Welding and Fabricating ProfessionalsdaemsalBelum ada peringkat
- Uydz Uw WV USKa N61 MM JC 4Dokumen6 halamanUydz Uw WV USKa N61 MM JC 4varshatagade126Belum ada peringkat
- Metals OlevleDokumen9 halamanMetals OlevleaayannisarBelum ada peringkat
- Metals and Non MetalsDokumen9 halamanMetals and Non MetalsKrishna SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Class X - Science (Chemistry) Metals and Non-Metals: Chapter NotesDokumen14 halamanClass X - Science (Chemistry) Metals and Non-Metals: Chapter NotesSuraj Luwangcha100% (1)
- Silver Hills Public School, Kozhikode: Class NotesDokumen12 halamanSilver Hills Public School, Kozhikode: Class NotesMaria Joe.kBelum ada peringkat
- Revision Notes On Materials Metals and Non-MetalsDokumen9 halamanRevision Notes On Materials Metals and Non-MetalsHoang HaBelum ada peringkat
- Notes - Metals Ad Non-Metals - C-XDokumen8 halamanNotes - Metals Ad Non-Metals - C-Xpratishtha MishraBelum ada peringkat
- 03 General Chemistry Conduction Bonding Acid-Base Compounds P 03Dokumen242 halaman03 General Chemistry Conduction Bonding Acid-Base Compounds P 03shihab shoronBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Notes-Metals and Non MetalsDokumen15 halamanChemistry Notes-Metals and Non MetalsKISHORE ADITYA DHINESH KUMARBelum ada peringkat
- St. John'S School Greater Noida WestDokumen5 halamanSt. John'S School Greater Noida WestIndia Tech with AstitvaBelum ada peringkat
- Metals and Non-Metals Notes Provided by TeacherDokumen7 halamanMetals and Non-Metals Notes Provided by TeacherAdeeba Raheel QureshiBelum ada peringkat
- Metals and Non-MetalsDokumen20 halamanMetals and Non-MetalsDevyansh MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Geography Lesson 2Dokumen5 halamanGeography Lesson 2indaneBelum ada peringkat
- 3 NOV Class 10 Metals and Non-Metals ChemDokumen40 halaman3 NOV Class 10 Metals and Non-Metals Chemgourav kaliaBelum ada peringkat
- Element Classification of Elements: Class-X Chapter - 3 Metals and Non-MetalsDokumen11 halamanElement Classification of Elements: Class-X Chapter - 3 Metals and Non-MetalsInsha Hasan 10DBelum ada peringkat
- Metals and Non MetalsDokumen57 halamanMetals and Non MetalsLOLBOIBelum ada peringkat
- Learn PracticallyDokumen35 halamanLearn Practicallyprincethakan9Belum ada peringkat
- 8th Metal and Non MetalDokumen8 halaman8th Metal and Non MetalsubrotokumarmohantaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Metallurgy Forwelding and Fabricating Professionals-150408060058-Conversion-gate01Dokumen190 halamanBasic Metallurgy Forwelding and Fabricating Professionals-150408060058-Conversion-gate01syarif irwantoBelum ada peringkat
- Properties of Metals Non-Metals MetalloidsDokumen23 halamanProperties of Metals Non-Metals MetalloidsConnie Joy CalawagBelum ada peringkat
- Metal and NonDokumen18 halamanMetal and NonMIN. Dr. Tanaji sawant officeBelum ada peringkat
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 3 2017 PDFDokumen10 halamanStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 3 2017 PDFKaran Pratap67% (3)
- Metal and NonmetalDokumen26 halamanMetal and NonmetalSudhanshu Sekhar PandaBelum ada peringkat
- The Reactivity Series NotesDokumen8 halamanThe Reactivity Series NotesTHEVINESHBelum ada peringkat
- Materials Metals and Non-MetalsDokumen5 halamanMaterials Metals and Non-Metalssidhantm823Belum ada peringkat
- Metals and Their Properties - Physical and ChemicalDokumen5 halamanMetals and Their Properties - Physical and Chemicalcourtz911Belum ada peringkat
- CH 6 Metals and Non MetalsDokumen11 halamanCH 6 Metals and Non MetalsRonnith NandyBelum ada peringkat
- Materials: Metals and Non Metals: Done By: S.LakeishaDokumen34 halamanMaterials: Metals and Non Metals: Done By: S.LakeishalakeishaBelum ada peringkat
- METALSDokumen24 halamanMETALSKillua ZoldyckBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Oxidation & RustingDokumen13 halaman2 Oxidation & RustingSelwah Hj AkipBelum ada peringkat
- Metals NotesDokumen4 halamanMetals NotesDiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Metals and Non-Metals Notes - RemovedDokumen15 halamanMetals and Non-Metals Notes - RemovedCyber Atharv100% (1)
- Chemistry 03 - Metals and Non Metals - Class Notes - (10th Board Booster)Dokumen102 halamanChemistry 03 - Metals and Non Metals - Class Notes - (10th Board Booster)iomkar699Belum ada peringkat
- b4b13229 14 Metals and Their ExtractionDokumen21 halamanb4b13229 14 Metals and Their ExtractionMuhammad UzairBelum ada peringkat
- Metals and Non-Metals NotesDokumen18 halamanMetals and Non-Metals NotesMustafa Khan100% (1)
- Metals and Non-Metals NotesDokumen18 halamanMetals and Non-Metals NotesAzeem IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Metals and NonmetalsDokumen15 halamanMetals and NonmetalsFfffyfBelum ada peringkat
- Reading Material by NVS TeacherDokumen12 halamanReading Material by NVS Teacher10E Yuvan Sarabeshan Thirumeninathan [3383]Belum ada peringkat
- Metals NotesDokumen19 halamanMetals NotesELIJAH MUPETABelum ada peringkat
- Why Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksDari EverandWhy Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksBelum ada peringkat
- Train Journey PreviewDokumen5 halamanTrain Journey PreviewAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Homework 30 NovDokumen2 halamanHomework 30 NovAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes AugDokumen11 halamanLecture Notes AugAjay Anand100% (1)
- TQMAug 21Dokumen9 halamanTQMAug 21Ajay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Definitions & Dimensions Planning Quality Costs TQM History Barriers To TQMDokumen10 halamanDefinitions & Dimensions Planning Quality Costs TQM History Barriers To TQMAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- 6 History Chapter 12 SuhasDokumen7 halaman6 History Chapter 12 SuhasAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Preview of Satires in ShortDokumen2 halamanPreview of Satires in ShortAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes Aug 18Dokumen9 halamanLecture Notes Aug 18Ajay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Finish Line & BeyondDokumen5 halamanFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- 8 SocSc RulingtheCountrysideDokumen6 halaman8 SocSc RulingtheCountrysideBalqis SalamaBelum ada peringkat
- Finish Line & BeyondDokumen2 halamanFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Finish Line & BeyondDokumen7 halamanFinish Line & BeyondAjay Anand100% (1)
- Finish Line & BeyondDokumen4 halamanFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- 8 SocSc JudiciaryDokumen4 halaman8 SocSc JudiciaryAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Social Science ResourcesDokumen3 halaman8 Social Science ResourcesAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Finish Line & Beyond Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation andDokumen5 halamanFinish Line & Beyond Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation andAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Finish Line & BeyondDokumen2 halamanFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Finish Line & BeyondDokumen4 halamanFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Finish Line & BeyondDokumen4 halamanFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Finish Line & BeyondDokumen3 halamanFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Finish Line & BeyondDokumen4 halamanFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Finish Line & BeyondDokumen7 halamanFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Finish Line & BeyondDokumen5 halamanFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Social Science IndustriesDokumen5 halaman8 Social Science IndustriesAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Finish Line & BeyondDokumen5 halamanFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Science SoundDokumen5 halaman8 Science SoundAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Social Science AgricultureDokumen4 halaman8 Social Science AgricultureAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Finish Line & BeyondDokumen4 halamanFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Science Stars&SolarSystemDokumen7 halaman8 Science Stars&SolarSystemAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Science ReproductionDokumen6 halaman8 Science ReproductionAjay AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Iconic Chemistry Classes Mole Concept: Iitian Sushil KumarDokumen2 halamanIconic Chemistry Classes Mole Concept: Iitian Sushil KumarsushanjBelum ada peringkat
- 01 IntroductionDokumen4 halaman01 IntroductionChrispin MachilikaBelum ada peringkat
- S275JR PDFDokumen1 halamanS275JR PDFEmrahCayboylu100% (1)
- Resistivity Conductivity and Temperature CoefficientsDokumen6 halamanResistivity Conductivity and Temperature Coefficients10rodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- Mining of Precious Metals and Minerals - August 2018Dokumen220 halamanMining of Precious Metals and Minerals - August 2018Marcus HowardBelum ada peringkat
- Test Review Topic 13:3 AK PDFDokumen10 halamanTest Review Topic 13:3 AK PDFKeyerria HowardBelum ada peringkat
- Property Chart and Tables-1Dokumen24 halamanProperty Chart and Tables-1Ashutosh GargBelum ada peringkat
- Acids and Alkalis NotesDokumen10 halamanAcids and Alkalis NotesNurulAinMatAronBelum ada peringkat
- Workshop Practice Series 08 - Sheet Metal WorkDokumen53 halamanWorkshop Practice Series 08 - Sheet Metal WorkDiego Romero100% (1)
- Experiment Ii Oxidation Number of Nitrogen 1.1 ObjectivesDokumen9 halamanExperiment Ii Oxidation Number of Nitrogen 1.1 ObjectivesAhlish Rahma AlfianaBelum ada peringkat
- Redox DPPDokumen3 halamanRedox DPPAryan PanwarBelum ada peringkat
- Science ReviewerDokumen2 halamanScience ReviewerSamantha CabarlesBelum ada peringkat
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDokumen13 halamanAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidAnindya BhattacharyaBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of SO2 in Ambient AirDokumen20 halamanAnalysis of SO2 in Ambient AirECRDBelum ada peringkat
- Determinacion de Acido LibreDokumen142 halamanDeterminacion de Acido LibrejohncramosBelum ada peringkat
- Non Ferrous Metals FinalDokumen89 halamanNon Ferrous Metals FinalAstilbe AlairBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry 101Dokumen31 halamanChemistry 101slim_101Belum ada peringkat
- What Is 30c8 SteelDokumen3 halamanWhat Is 30c8 SteelSanjay MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- Periodic Table of Elements (Chemistry)Dokumen24 halamanPeriodic Table of Elements (Chemistry)christian jay pilarBelum ada peringkat
- Elements Sheets Elem1-98Dokumen99 halamanElements Sheets Elem1-98hastalosovariosBelum ada peringkat
- Brosur novAA 800 enDokumen18 halamanBrosur novAA 800 enAnsar AbduBelum ada peringkat
- Jai Shree RamDokumen10 halamanJai Shree RamRenu YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Jsa Jis K 0101 1998 PDFDokumen481 halamanJsa Jis K 0101 1998 PDFRiris Trinartika50% (2)
- Billet DefectsDokumen56 halamanBillet Defectsziad90% (10)
- 0620 s11 QP 33Dokumen12 halaman0620 s11 QP 33Kelso ZwariyaBelum ada peringkat
- A Guide To Welding Electrodes On Ships-Part 1Dokumen7 halamanA Guide To Welding Electrodes On Ships-Part 1Salwan ShubhamBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 13 - Testing For Oxidising and Reducing AgentsDokumen3 halamanLab 13 - Testing For Oxidising and Reducing AgentsFina ShoBelum ada peringkat
- Method of Analysis of Hydrochloric Acid Caustic SodaDokumen5 halamanMethod of Analysis of Hydrochloric Acid Caustic SodaSreedhar Patnaik.MBelum ada peringkat
- Gas CalculationsDokumen3 halamanGas CalculationsaizatBelum ada peringkat
- Seminario 1Dokumen5 halamanSeminario 1Javier FrancoBelum ada peringkat