Aluminium Extraction
Diunggah oleh
Miguel ThaxterHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Aluminium Extraction
Diunggah oleh
Miguel ThaxterHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
INDUSTRY AND THE ENVIRONMENT ALUMINIUM 2.
1 DESCRIBE THE PROCESS INVOLVED IN THE PRODUCTION OF ALUMINIUM FROM ITS ORES The process of extraction depends upon the nature of impurities present in the ore. Common steps involved for extraction of metals are as follows: (i) Crushing and grinding (ii) Concentration of ore (iii) Extracting metal from ore (iv) Purification of metal Aluminum is most abundant metal on the earth's Crust. The major ore of aluminum is bauxite (Al2O3.2H2O). It is an oxide of aluminum. Though, aluminum oxide can be reduced by chemical methods, but it is extracted from its ore by electrolysis, because it is highly reactive metal. The extraction of aluminium involves following steps: (i) Purification: Bauxite ore contains lot of impurities which can be removed by treating it chemically. The sequence of its purification is shown in the flow chart given below:
1. Bauxite is mined is mined fom the earth during the excavation process where the ore is scraped up out of the ground. 2. The ore which is aluminium oxide also alumina is then physically broken down by a crusher where it is grind and crushed. 3. The crushed ore is then treated with caustic soda which is concentrated sodium hydroxide(NaOH). It results in the formation of Al(OH)3 , Fe2O3 and some insoluble material. Al2O3 + 6NaOH ----------> 2Al(OH)3 + 3Na2O Na2O + H2O -----------> 2NaOH ( the sodium oxide reacts with moisture in the atmosphere to form sodium hydroxide. 4. Iron oxide does not dissolve in NaOH and thus the products are filtered to get Al(OH)3 . 5. Al(OH)3 is heated and it is decomposed into (aluminum oxide) Al2O3 and H2O which is molten alumina. Al(OH)3 ----------> Al2O3 + H2O (molten alumina) 6. . Hence, pure aluminium oxide Al2O3 is obtained
Electrolysis Method
Commercially, aluminum is prepared by the Hall-Hroult process, which consists essentially of the electrolysis of alumina. The process depends critically on the availability of cheap hydroelectric power. The electrolysis of alumina is carried out in a
steel tank lined inside with graphite. In this tank, cryolite (Na2AlF6) and some fluospar (CaF2) is also added to reduce the
melting point of Al2O3. It also increases the conductivity and helps in breaking Al2O3 to form aluminium ions (Al+3) and oxide ions (O-2). The steel container is coated with carbon (graphite) and this is the negative electrode (cathode). Electrolysis of the alumina/cryolite solution gives aluminium at the cathode and oxygen at the anode.Al+3 ions will move towards cathode and O-2 ions will move towards anode, where they are reduced and oxidised respectively into aluminium (Al) and oxygen (O2).
The reaction taking place at cathode and anode are as follows:Al2O3 -----------> 2Al+3 + 3O-2 On Cathode: On Anode: Al3+ (aq) + 3e- Al (s) 2O2- (aq) 4e- O2 (g) The aluminium ions are discharged at the cathode At the anode oxygen is given off
The overall reaction 4Al3+ (aq) + 12e- 4Al (s) 6O2- (aq) 12e- 3O2 (g) 4Al3+ (aq) + 6O2- (aq) 4Al (s) + 3O2 (g)
The oxygen given off at the anode usually reacts with the carbon electrode and produces carbondioxide.Therefore the anodes have to be replaced regularly carbon + oxygen C(s) + O2(g) carbon dioxide CO2(g).
Aluminium obtained from above process is 99% pure, which is further purified by using electrolytic method.
2.2 EXPLAIN THE USES OF ALUMINIUM IN RELATION TO ITS PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES Physical Properties
Use for making light fittings and rescue blankets because it is a good reflector of visible light as well as heat
Use for making aluminium foil and also for packaging of foods because it is impermeable , odorless and nontoxic Good conduction of heat leads to its use for boilers, cookers and cookware. Easy shaping and corrosion resistance make it a good material for drink cans and roofing materials. Chemical properties Aluminium is used for making fences , roofs because aluminium reacts with oxygen to form aluminium oxide . This forms a protective layer over the metal and which protects the metal beneath and renders it inert to any further reaction.
2.3 ASSESS THE IMPACT OF THE ALUMINIUM INDUSTRY ON THE ENVIRONMENT Economic considerations The high cost of the process because of the huge amounts of electricity it uses. Energy and material costs in constantly replacing the anodes. Energy and material costs in producing the cryolite, some of which gets lost during the electrolysis.
Environmental problems in mining and transporting the bauxite Loss of landscape due to mining, processing and transporting the bauxite. Noise and air pollution (greenhouse effect, acid rain) involved in these operations
Extracting aluminium from the bauxite Loss of landscape due to the size of the chemical plant needed, and in the production and transport of the electricity. Noise pollution Atmospheric pollution from the various stages of extraction. For example: carbon dioxide from the burning of the anodes (greenhouse effect); carbon monoxide (poisonous); fluorine (and fluorine compounds) lost from the cryolite during the electrolysis process (poisonous). Disposal of red mud into unsightly lagoons
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Gaseous Fuel Requirements For GE Aeroderivative Gas TurbinesDokumen15 halamanGaseous Fuel Requirements For GE Aeroderivative Gas TurbinesLibyanManBelum ada peringkat
- Cea - Standard Technical Specification For Main Plant Package (2 500 MW)Dokumen1.011 halamanCea - Standard Technical Specification For Main Plant Package (2 500 MW)vasudevapavanBelum ada peringkat
- ElectrochemistryDokumen38 halamanElectrochemistryShannon SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Material Handling Boq 2Dokumen4 halamanMaterial Handling Boq 2biliiardiansyahBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of Sugar As GlucoseDokumen4 halamanDetermination of Sugar As GlucoseIpsita ChakravartyBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Super Critical CO2Dokumen42 halamanWhat Is Super Critical CO2kesaco100% (2)
- Physical Science Sept2016 KeyDokumen3 halamanPhysical Science Sept2016 Keyjennifer sumbelingBelum ada peringkat
- Section 07 - Fired Heaters PDFDokumen112 halamanSection 07 - Fired Heaters PDFaldoacss_148400122Belum ada peringkat
- CAPE Chemistry Unit 2Dokumen22 halamanCAPE Chemistry Unit 2Audi SweetangelBelum ada peringkat
- Alumina ProcessDokumen16 halamanAlumina Processashwini_kumar1984Belum ada peringkat
- Bhel Block 1 NewDokumen32 halamanBhel Block 1 NewNitin SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Mod1 Nptel Process Exchanger DesignDokumen41 halamanMod1 Nptel Process Exchanger DesignAnirudh KaulBelum ada peringkat
- Cooling Load UERM CANTEENDokumen52 halamanCooling Load UERM CANTEENHenry San PedroBelum ada peringkat
- Shyam Steel Industries LTD EnglishDokumen14 halamanShyam Steel Industries LTD EnglishbalaasenthilBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Iii Fuels and CombustionDokumen30 halamanUnit Iii Fuels and CombustionKKiranKumarBelum ada peringkat
- Hall Heroult Process and Hooper ProcessDokumen9 halamanHall Heroult Process and Hooper ProcesssaadBelum ada peringkat
- Furnaces and Furnace ReactorsDokumen33 halamanFurnaces and Furnace ReactorsSamyak JainBelum ada peringkat
- Yogurt Production PDFDokumen10 halamanYogurt Production PDFMiguel Thaxter100% (2)
- Woodward's RuleDokumen48 halamanWoodward's RuleDeshan Wolfey100% (1)
- Al ExtractionDokumen3 halamanAl ExtractionManoj Khanal100% (1)
- The Bayer ProcessDokumen1 halamanThe Bayer ProcessAqsa BanoBelum ada peringkat
- Bayer Process ChemistryDokumen2 halamanBayer Process Chemistryhi_scribdBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic PumpDokumen3 halamanElectromagnetic PumptowfiqeeeBelum ada peringkat
- LedDokumen20 halamanLedYogesh YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Food Security in IndiaDokumen18 halamanFood Security in IndiaJainee ParekhBelum ada peringkat
- Physics XII Practice PaperDokumen10 halamanPhysics XII Practice PaperAvinashBelum ada peringkat
- Development of Sodium Leak Detectors For PFBRDokumen13 halamanDevelopment of Sodium Leak Detectors For PFBRWilliam MunnyBelum ada peringkat
- EM Five Units Notes PDFDokumen85 halamanEM Five Units Notes PDFRajesh ChidambaramBelum ada peringkat
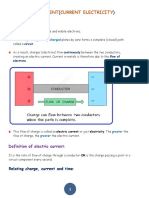
- Electrical Current Notes For IgcseDokumen90 halamanElectrical Current Notes For IgcseAnmol MalgotraBelum ada peringkat
- Extraction of AluminiumDokumen18 halamanExtraction of AluminiumShaquanRobinsonBelum ada peringkat
- 02 Assignment CEDokumen45 halaman02 Assignment CEshafia100% (1)
- Thermoelectric Transducers PDFDokumen19 halamanThermoelectric Transducers PDFAmaravathi PotlaBelum ada peringkat
- A2 Chemistry DefinitionsDokumen3 halamanA2 Chemistry Definitionszurazunaidi75Belum ada peringkat
- Tetragonal Distortion of Octahedral Complexes (Jahn Teller Distortion)Dokumen2 halamanTetragonal Distortion of Octahedral Complexes (Jahn Teller Distortion)Afrah MBelum ada peringkat
- Fitting Shop Operations:: 1. Measuring OperationDokumen7 halamanFitting Shop Operations:: 1. Measuring OperationAliBelum ada peringkat
- Qasam Us Waqt KiDokumen162 halamanQasam Us Waqt KiSamad A NizamaniBelum ada peringkat
- BOOK LIST 2021 - 2022 Grade IX Compulsory SubjectsDokumen2 halamanBOOK LIST 2021 - 2022 Grade IX Compulsory SubjectsaslamBelum ada peringkat
- Ultimate Guide To Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams - Engineer4Free - The #1 Source For Free Engineering Tutorials PDFDokumen4 halamanUltimate Guide To Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams - Engineer4Free - The #1 Source For Free Engineering Tutorials PDFSubhajyoti DasBelum ada peringkat
- Section 3 Handwritten NotesDokumen98 halamanSection 3 Handwritten NotesShelley AllynBelum ada peringkat
- MetalsDokumen7 halamanMetalsritesh kavuruBelum ada peringkat
- MEM201Thermodynamics QB (2018-19) With Syllabus-1 PDFDokumen10 halamanMEM201Thermodynamics QB (2018-19) With Syllabus-1 PDFRohan DubeyBelum ada peringkat
- Class 11 Physics Best Notes For English Medium Session (2023-2024) Chapter-Mechanical Properties of FluidsDokumen73 halamanClass 11 Physics Best Notes For English Medium Session (2023-2024) Chapter-Mechanical Properties of FluidsAyushi ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Report of Jaminy End Quench TestDokumen92 halamanReport of Jaminy End Quench TestBharathi K 2018100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding ICSE Class-10 Concise Chemistry Selina Solutions - ICSEHELP1Dokumen7 halamanChemical Bonding ICSE Class-10 Concise Chemistry Selina Solutions - ICSEHELP1lionelkenethBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple Choice Question Bank (MCQ) Term - I: Class - XDokumen48 halamanMultiple Choice Question Bank (MCQ) Term - I: Class - XAtharva Bhokare100% (1)
- Practical Guide To Energy Conservation & ManagementDokumen8 halamanPractical Guide To Energy Conservation & ManagementniteshBelum ada peringkat
- J. Jarvis Trial Balance As at 31 December 2010Dokumen3 halamanJ. Jarvis Trial Balance As at 31 December 2010Ahmad HaqqyBelum ada peringkat
- Need For Inventions in 18th and 19th Century EnglandDokumen7 halamanNeed For Inventions in 18th and 19th Century Englandaditya jagadeeshwara100% (6)
- O-Level Physics - Current ElectricityDokumen2 halamanO-Level Physics - Current ElectricityGolam HasibBelum ada peringkat
- Ajide Oluwamayowa Oluwatobi 12-30gd017Dokumen103 halamanAjide Oluwamayowa Oluwatobi 12-30gd017Aina Praise OluwashogoBelum ada peringkat
- 12108040-Zinc Extraction in Contrast With ISP Process PDFDokumen20 halaman12108040-Zinc Extraction in Contrast With ISP Process PDFSachin MourBelum ada peringkat
- Vapour Compression RefrigerationDokumen4 halamanVapour Compression RefrigerationAhmadBelum ada peringkat
- 2018 Jan Edexcel A2 PhysicsDokumen28 halaman2018 Jan Edexcel A2 PhysicsAriful IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Shake Table PPT Ist 2K18 (3) - 1Dokumen24 halamanShake Table PPT Ist 2K18 (3) - 1Jayanta Chaudhuri0% (1)
- Accounting PP2 June 2014Dokumen18 halamanAccounting PP2 June 2014Marcelyn MagumiseBelum ada peringkat
- Dev Energy - GASIFIERDokumen33 halamanDev Energy - GASIFIERvinay1999Belum ada peringkat
- Pakistan Aeronautical Complex Kamra Internship ReportDokumen7 halamanPakistan Aeronautical Complex Kamra Internship ReportRai TalalBelum ada peringkat
- 1.list of Monuments of National Importance in HaryanaDokumen41 halaman1.list of Monuments of National Importance in HaryanaSt. PaulsBelum ada peringkat
- Aluminum ExtractionDokumen7 halamanAluminum ExtractionNalini RooplalBelum ada peringkat
- S.6 Chemistry of Aluminium, Group IV Group VIIDokumen78 halamanS.6 Chemistry of Aluminium, Group IV Group VIIABEL JEDIDIAHBelum ada peringkat
- Week 10 ExctMet-AlDokumen37 halamanWeek 10 ExctMet-AlYudha PradhanaBelum ada peringkat
- Luminum: Properties, Uses, Extraction Process, Aluminum AlloysDokumen36 halamanLuminum: Properties, Uses, Extraction Process, Aluminum AlloysismaeelBelum ada peringkat
- SeminarDokumen24 halamanSeminarLalit GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Aluminium MetallurgyDokumen3 halamanAluminium MetallurgyShubham ShuklaBelum ada peringkat
- Metallurgy of AluminiumDokumen9 halamanMetallurgy of Aluminiumhassan materialsBelum ada peringkat
- Metals KS3 4 Iron and Aluminium Extraction Methods Info SheetDokumen5 halamanMetals KS3 4 Iron and Aluminium Extraction Methods Info SheetHappy NthakomwaBelum ada peringkat
- Extraction of MetalsDokumen2 halamanExtraction of Metalsdan964Belum ada peringkat
- Al ExtractionDokumen27 halamanAl Extractionbt19108055 Amarjeet KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Group 13 AluminiumDokumen48 halamanGroup 13 AluminiumLooi Chui Yean100% (1)
- Principle of Atomic Absorption /emission Spectroscopy: Na CL Nacl Na CL Na NaDokumen15 halamanPrinciple of Atomic Absorption /emission Spectroscopy: Na CL Nacl Na CL Na NaMiguel ThaxterBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Science Unit Two Module 1Dokumen4 halamanEnvironmental Science Unit Two Module 1Miguel Thaxter100% (2)
- Chem2601 - Environmental Chemistry: Problem Sheet - SoilsDokumen2 halamanChem2601 - Environmental Chemistry: Problem Sheet - SoilsMiguel ThaxterBelum ada peringkat
- Political Corruption Inhibits Economic Growth in The Caribbean RegionDokumen3 halamanPolitical Corruption Inhibits Economic Growth in The Caribbean RegionMiguel Thaxter100% (1)
- Sociology Internal Assessment (IA)Dokumen27 halamanSociology Internal Assessment (IA)Miguel ThaxterBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Social PsychologyDokumen1 halamanApplied Social PsychologyMiguel ThaxterBelum ada peringkat
- Atlantic Slave Trade LOneDokumen34 halamanAtlantic Slave Trade LOneEduSoft100% (1)
- GutenbergDokumen2 halamanGutenbergMiguel ThaxterBelum ada peringkat
- Zung Self Rated Depression ScaleDokumen2 halamanZung Self Rated Depression ScalehudaBelum ada peringkat
- African Film EssayDokumen3 halamanAfrican Film EssayMiguel ThaxterBelum ada peringkat
- Male Underachieve PDFDokumen22 halamanMale Underachieve PDFMiguel ThaxterBelum ada peringkat
- African Film EssayDokumen3 halamanAfrican Film EssayMiguel ThaxterBelum ada peringkat
- GeneticsDokumen5 halamanGeneticsMiguel ThaxterBelum ada peringkat
- Zung Self Rated Depression ScaleDokumen2 halamanZung Self Rated Depression ScalehudaBelum ada peringkat
- Measurement of Diazepam in TabletsDokumen4 halamanMeasurement of Diazepam in TabletsMiguel ThaxterBelum ada peringkat
- Journal of Advanced Academics-2008-Kidd-164-200 PDFDokumen38 halamanJournal of Advanced Academics-2008-Kidd-164-200 PDFMiguel ThaxterBelum ada peringkat
- 04 05 09Dokumen5 halaman04 05 09mallik789Belum ada peringkat
- HydrogenDokumen18 halamanHydrogenMiguel ThaxterBelum ada peringkat
- 2018 - Hallaaoui - One Dimensional Phosphate Flash Dryer Model For Design ApplicationDokumen11 halaman2018 - Hallaaoui - One Dimensional Phosphate Flash Dryer Model For Design ApplicationGuilherme Venturi RonchiBelum ada peringkat
- Tifr 2011 PhysicsDokumen8 halamanTifr 2011 PhysicsAbhrajit MahapatraBelum ada peringkat
- Yang 2013Dokumen4 halamanYang 2013Dwi suparwatiBelum ada peringkat
- Solution:: 7.2.5 Photoelectric EffectDokumen7 halamanSolution:: 7.2.5 Photoelectric EffectIka Fitria WatiBelum ada peringkat
- Use The Table Below To Answer The Questions That Follow.: A. Multiple-Choice and Bimodal QuestionsDokumen13 halamanUse The Table Below To Answer The Questions That Follow.: A. Multiple-Choice and Bimodal QuestionsHUY NGUYỄN PHƯƠNG PHÚCBelum ada peringkat
- CALORPLAST Immersion Type Polymer Heat ExchangerDokumen4 halamanCALORPLAST Immersion Type Polymer Heat ExchangersukamtoBelum ada peringkat
- Gay LussacDokumen2 halamanGay LussacKelvin BarceLonBelum ada peringkat
- Persian Gum and Xanthan GumDokumen11 halamanPersian Gum and Xanthan GumIoana PeptănaruBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Solutions WS Part I - VocabularyDokumen2 halamanIntroduction To Solutions WS Part I - VocabularyCatherine JeaneBelum ada peringkat
- (1987 England Et Al.) The Movement and Entrapement of Petroleum Fluids in The SubsurfaceDokumen21 halaman(1987 England Et Al.) The Movement and Entrapement of Petroleum Fluids in The SubsurfaceAiwarikiaarBelum ada peringkat
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Set - 1 Code No: Rt32035Dokumen2 halamanWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Set - 1 Code No: Rt32035Asheesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- G10 LAP 4.1 Properties of GasesDokumen5 halamanG10 LAP 4.1 Properties of GasesAzria SolanaBelum ada peringkat
- 2.3 External Mass Transfer EffectsDokumen19 halaman2.3 External Mass Transfer EffectsAstra BeckettBelum ada peringkat
- AGA Stainless Steel MIG MAG Welding Brochure 105x210 UsaDokumen16 halamanAGA Stainless Steel MIG MAG Welding Brochure 105x210 UsaSriram IyerBelum ada peringkat
- ch18 PDFDokumen45 halamanch18 PDFHafidz RafiqiBelum ada peringkat
- Process Design Principles I: BITS PilaniDokumen17 halamanProcess Design Principles I: BITS PilaniAnkit GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Quantum Mechanics de - Broglie Matter WavesDokumen16 halamanQuantum Mechanics de - Broglie Matter Wavesvivek patelBelum ada peringkat
- Comparison of Crystal Structures Among CAAC-InGaZnO, nc-InGaZnO, and Solution-Processed InGaZnODokumen4 halamanComparison of Crystal Structures Among CAAC-InGaZnO, nc-InGaZnO, and Solution-Processed InGaZnORabbi HasnatBelum ada peringkat
- The ALUREC ProcessDokumen7 halamanThe ALUREC ProcesscarlosiqmBelum ada peringkat
- Skew T Adiabatic Diagram: Temperature in Degrees CelsiusDokumen1 halamanSkew T Adiabatic Diagram: Temperature in Degrees CelsiusMihai Mirel RusuBelum ada peringkat
- Msa20111000007 87029177Dokumen5 halamanMsa20111000007 87029177Mario Misael Machado LòpezBelum ada peringkat
- 5070 w19 Ms 21Dokumen10 halaman5070 w19 Ms 21heerBelum ada peringkat