Formulasheetalgebra 2 Trig
Diunggah oleh
api-241258699Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Formulasheetalgebra 2 Trig
Diunggah oleh
api-241258699Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
All Rights Reserved: http://regentsprep.
org
Algebra 2 Things to Remember!
Exponents:
0
1 x =
1
m
m
x
x
m n m n
x x x
+
=
( )
n m n m
x x =
m
m n
n
x
x
x
=
n
n
n
x x
y y
| |
=
|
\ .
( )
n n n
xy x y =
Complex Numbers:
1 i = ; 0 a i a a = >
2
1 i =
14 2
1 i i = = divide exponent
by 4, use remainder, solve.
( ) conjugate ( ) a bi a bi +
2 2
( )( ) a bi a bi a b + = +
2 2
a bi a b + = + absolute value=magnitude
Logarithms
log
y
b
y x x b = =
ln log
e
x x = natural log
e =2.71828
10
log log x x = common log
Change of base formula:
log
log
log
b
a
a
b
=
Factoring:
Look to see if there is a GCF (greatest
common factor) first. ( ) ab ac a b c + = +
2 2
( )( ) x a x a x a = +
2 2 2
( ) 2 x a x ax a + = + +
2 2 2
( ) 2 x a x ax a = +
Factor by Grouping:
Exponentials exp( )
x
e x =
( 0 and 1)
x y
b b x y b b = = > =
If the bases are the same, set the
exponents equal and solve.
Solving exponential equations:
1. Isolate exponential expression.
2. Take log or ln of both sides.
3. Solve for the variable.
ln( ) and
x
x e are inverse functions
ln
x
e x =
lnx
e x =
ln 1 e =
ln4
4 e =
2
2ln3 ln3
9 e e = =
Quadratic Equations:
2
0 ax bx c + + = (Set =0.)
Solve by factoring, completing the square, quadratic formula.
2
4
2
b b ac
x
a
=
2
2
2
4 0 two real unequal roots
4 0 repeated real roots
4 0 two complex roots
b ac
b ac
b ac
>
=
<
2
Square root property: If ,then x m x m = =
Completing the square:
2
2 5 0 x x =
1. If other than one, divide by coefficient of x
2
2. Move constant term to other side
2
2 5 x x =
3. Take half of coefficient of x, square it, add to both sides
2
2 1 5 1 x x + = +
4. Factor perfect square on left side.
2
( 1) 6 x =
5. Use square root property to solve and get two answers. 1 6 x =
Sum of roots:
1 2
b
r r
a
+ = Product of roots:
1 2
c
r r
a
=
Variation: always involves the constant of
proportionality, k. Find k, and then proceed.
Direct variation: y kx =
Inverse variation:
k
y
x
=
Varies jointly: y kxj =
Combo: Sales vary directly
with advertising and inversely
with candy cost.
Absolute Value: 0 a >
; 0
; 0
a a
a
a a
>
=
<
or m b m b m b = = =
m b b m b < < <
or m b m b m b > > <
Inequalities:
2
12 0 x x + s Change to =, factor, locate
critical points on number line, check each section.
(x +4)(x - 3) =0
x =-4; x =3
ANSWER: -4 <x <3 or [-4, 3] (in interval notation)
Properties of Logs:
log 1 log 1 0
log ( ) log log
log log log
log ( ) log
b b
b b b
b b b
r
b b
b
m n m n
m
m n
n
m r m
= =
= +
| |
=
|
\ .
=
Domain: log is 0
b
x x >
ka
y
c
=
All Rights Reserved: http://regentsprep.org
Radicals: Remember to use fractional exponents.
1
a
a
x x =
( )
m
m
n m n
n
x x x = =
n n
a a =
n n n
ab a b =
n
n
n
a a
b b
=
Simplify: look for perfect powers.
12 17 12 16 6 8
x y x y y x y y = =
9 8 3 9 6 2 3 3 2 2
3 3 3
72 89 2 9 x y z x y y z x y z y = =
Use conjugates to rationalize denominators:
5 2 3 10 5 3
10 5 3
2 3 2 3 4 2 3 2 3 9
= =
+ +
Equations: isolate the radical; square both sides
to eliminate radical; combine; solve.
2 2
2
2 5 3 0 (2 3) (5 )
4 12 9 25 : 9; 1/ 4
x x x x
x x x solve x x
= =
+ = = =
CHECK ANSWERS. Answer only x = 9.
Working with Rationals ( Fractions):
Simplify:
remember to look for a factoring of -1:
3 1 1( 3 1
1 3
x x
x
+
=
)
1 3x
1 =
Add: Get the common denominator.
Factor first if possible:
Multiply and Divide: Factor First
Solving Rational Equations:
Get rid of the denominators by mult. all terms by
common denominator.
2
2
22 3 2
2 9 5 2 1 5
2 9 5
22 3( 5) 2(2 1)
22 3 15 4 2
37 3 4 2
35 7
5
x x x x
multiply all by x x and get
x x
x x
x x
x
x
=
+
= +
+ = +
= +
=
=
Great! But the only problem is that
x =5 does not CHECK!!!! There is no solution.
Extraneous root.
Motto: Always CHECK ANSWERS.
Rational Inequalities
2
2 15
0
2
x x
x
>
The critical values
from factoring the numerator are -3, 5.
The denominator is zero at x =2.
Place on number line, and test sections.
Sequences
Arithmetic:
1
( 1)
n
a a n d = +
1
( )
2
n
n
n a a
S
+
=
Geometric:
1
1
n
n
a a r
=
1
(1 )
1
n
n
a r
S
r
Recursive: Example:
1 1
4; 2
n n
a a a
= =
Equations of Circles:
2 2 2
x y r + = center origin
2 2 2
( ) ( ) x h y k r + = center at (h,k)
2 2
0 x y Cx Dy E + + + + = general form
Functions: A function is a set of ordered pairs in which
each x-element has only ONE y-element associated with it.
Vertical Line Test: is this graph a function?
Domain: x-values used; Range: y-values used
Onto: all elements in B used.
1-to-1: no element in B used more than once.
Composition: ( )( ) ( ( )) f g x f g x =
Inverse functions f & g: ( ( )) ( ( )) f g x g f x x = =
Horizontal line test: will inverse be a function?
Transformations:
( ) f x over x-axis; ( ) f x over y-axis
( ) f x a + horizontal shift; ( ) f x a + vertical shift
( ) f ax stretch horizontal; ( ) af x stretch vertical
Complex Fractions:
Remember that the fraction bar means divide:
Method 1: Get common denominator top and bottom
1
2 2
2 2
2 2
2 4 2 4
2 4 4 2 2 4
4 2 4 2
x
x x x
x x x
x
x x
x x x
= = =
2
x
2
x
4 2 x
1 =
Method 2: Mult. all terms by common denominator for
all.
2 2
2 2
2 2
2 2
2 4 2 4
2 4
1
4 2 4 2
4 2
x x
x
x x x x
x
x x
x x x x
= = =
Binomial Theorem:
0
( )
n
n n k k
k
n
a b a b
k
=
| |
+ =
|
\ .
All Rights Reserved: http://regentsprep.org
Trigonometry
Things to Remember!
Radians and Degrees
Change to radians multiply by
180
t
Change to degrees multiply by
180
t
Trig Functions
sin ; cos ; tan
o a o
h h a
u u u = = =
csc ; sec ; cot
h h a
o a o
u u u = = =
Reciprocal Functions
1 1 1
sin ; cos ; tan
csc sec cot
u u u
u u u
= = =
1 1 1
csc ; sec ; cot
sin cos tan
u u u
u u u
= = =
sin
tan
cos
u
u
u
=
cos
cot
sin
u
u
u
=
Arc Length of a Circle = r u (in radians)
Special Right Triangles
Quadrantal angles 0, 90, 180, 270
CoFunctions: examples
sin cos(90 ) u u = ; tan cot(90 ) u u =
Inverse notation:
arcsin(x) =sin
-1
(x)
arccos(x) =cos
-1
(x)
arctan(x) =tan
-1
(x)
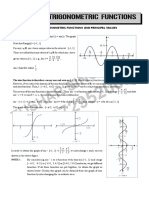
Trig Graphs
sin x cos x
sinusoidal curve =any curve expressed as
y =A sin(B(x C)) +D
amplitude (A) = | max min| (think height)
period =horizontal length of 1 complete cycle
frequency (B) =number of cycles in 2t (period)
horizontal shift (C) movement left/right
vertical shift (D) movement up/down
Law of Sines: uses 2 sides and 2 angles
sin sin sin A B C
a b c
= = Has an ambiguous case.
Law of Cosines: uses 3 sides and 1 angle
2 2 2
2 cos c a b ab C = +
Area of triangle: A = ab sin C
Area of parallelogram: A = ab sin C
Pythagorean Identities:
2 2
sin cos 1 u u + =
2 2
tan 1 sec u u + =
2 2
1 cot csc u u + =
30-60-90 triangle
side opposite 30 =hypotenuse
side opposite 60 =hypotenuse 3
45-45-90 triangle
hypotenuse =leg 2
leg =hypotenuse 2
All Rights Reserved: http://regentsprep.org
Statistics and Probability
Things to Remember!
Normal Distribution and Standard Deviation
Probability
Permutation: without replacement
and order matters
!
( )!
n r
n
P
n r
=
Combination: without replacement
and order does not matter
!
! !( )!
n r
n r
n
P n
C
r r r n r
| |
= = =
|
\ .
Empirical Probability
#of times event occurs
( )
total #of observed occurrences
E
P E =
Theoretical Probability
( ) #of outcomes in
( )
( ) total #of outcomes in
n E E
P E
n S S
= =
P(A and B) = P(A)P(B)
for independent events
P(A and B) = P(A)P(B| A)
for dependent events
P(A ) = 1 P(A)
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) P(A and B)
for not mutually exclusive
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B)
for mutually exclusive
( and )
( | )
( )
P A B
P B A
P A
= (conditional)
Statistics:
1 2
1
... 1
n
n
i
i
x x x
mean x x
n n
=
+ + +
= = =
median =middle number in ordered data
mode =value occurring most often
range =difference between largest and smallest
mean absolute deviation (MAD):
1
1
n
i
i
population MAD x x
n
=
=
variance:
( )
2
2
1
1
variance ( )
n
i
i
population x x x
n
o
=
= =
standard deviation:
( )
2
1
standard deviation =
1
n
i
i
population
x x x
n
o
=
=
Sx =sample standard deviation
x
o =population standard deviation
Binomial Probability
r n r
n r
C p q
exactly r times
or (1 )
r n r
n
p p
r
| |
|
\ .
[TI Calculator: binompdf(n, p, r)]
When computing "at least" and "at most"
probabilities, it is necessary to consider, in
addition to the given probability,
all probabilities larger than the given
probability ("at least")
[TI Calculator: 1 binomcdf(n, p, r-1)]
all probabilities smaller than the given
probability ("at most")
[TI Calculator: binomcdf(n, p, r)]
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ah FormulaeDokumen5 halamanAh FormulaeVijay RajuBelum ada peringkat
- Differential Equations (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDari EverandDifferential Equations (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsDari EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsBelum ada peringkat
- Complex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankDari EverandComplex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankBelum ada peringkat
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDari EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Dari EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Belum ada peringkat
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankDari EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Hyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDari EverandHyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsBelum ada peringkat
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDari EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- A2 Reference Sheet 01Dokumen5 halamanA2 Reference Sheet 01rajbmohanBelum ada peringkat
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankDari EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- Calculus: Introductory Theory and Applications in Physical and Life ScienceDari EverandCalculus: Introductory Theory and Applications in Physical and Life SciencePenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Math 120R WorkbookDokumen163 halamanMath 120R WorkbookDeborah HrrBelum ada peringkat
- Amplify Education (2015)Dokumen16 halamanAmplify Education (2015)Choy CristobalBelum ada peringkat
- Algebra Secret RevealedComplete Guide to Mastering Solutions to Algebraic EquationsDari EverandAlgebra Secret RevealedComplete Guide to Mastering Solutions to Algebraic EquationsBelum ada peringkat
- Trig Formula SheetDokumen3 halamanTrig Formula Sheetpcam11Belum ada peringkat
- Winter HW 2015 Math HL G12Dokumen9 halamanWinter HW 2015 Math HL G12MishaZetov100% (1)
- Definite Integral (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDari EverandDefinite Integral (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- 6.4 Vectors and Dot Products-0Dokumen17 halaman6.4 Vectors and Dot Products-0monicaBelum ada peringkat
- PreCal PreAP Fall Final Exam ReviewDokumen10 halamanPreCal PreAP Fall Final Exam ReviewNikhil SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Geometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankDari EverandGeometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankBelum ada peringkat
- Quadratic Equation: new and easy way to solve equationsDari EverandQuadratic Equation: new and easy way to solve equationsBelum ada peringkat
- Algebra 2 Systems ProjectDokumen2 halamanAlgebra 2 Systems Projectapi-262532023Belum ada peringkat
- Algebra 2 QuestionDokumen9 halamanAlgebra 2 QuestionGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoBelum ada peringkat
- Schaum's Outline of Elementary Algebra, 3edDari EverandSchaum's Outline of Elementary Algebra, 3edPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Algebra: "Algebraist" Redirects Here. For The Novel by Iain M. Banks, See - For Beginner's Introduction To Algebra, SeeDokumen12 halamanAlgebra: "Algebraist" Redirects Here. For The Novel by Iain M. Banks, See - For Beginner's Introduction To Algebra, SeeEduardo DíazBelum ada peringkat
- de Moivres TheoremDokumen18 halamande Moivres TheoremAbdullah SaeedBelum ada peringkat
- CalcI CompleteDokumen506 halamanCalcI CompleteRyde Nixon Dona-al TalataBelum ada peringkat
- NS LCM HCF PDFDokumen9 halamanNS LCM HCF PDFPalak MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- A Collection of Problems in Analytical Geometry: Analytical Geometry in the PlaneDari EverandA Collection of Problems in Analytical Geometry: Analytical Geometry in the PlaneBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Makes Perfect: Algebra II Review and Workbook, Third EditionDari EverandPractice Makes Perfect: Algebra II Review and Workbook, Third EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Math Preparedness WorkbookDokumen26 halamanMath Preparedness WorkbookAnonymous czkmnf100% (1)
- Practice Problems for the SAT ArithmeticDari EverandPractice Problems for the SAT ArithmeticPenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- The Practically Cheating Calculus HandbookDari EverandThe Practically Cheating Calculus HandbookPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (7)
- Sequences and Series - Jim Fowler and Bart SnappDokumen147 halamanSequences and Series - Jim Fowler and Bart SnappFrancisBelum ada peringkat
- Vector Algebra Facts SheetDokumen3 halamanVector Algebra Facts SheetСветлана Дашкевич ЛисовскаяBelum ada peringkat
- Numerical Methods: Design, Analysis, and Computer Implementation of AlgorithmsDari EverandNumerical Methods: Design, Analysis, and Computer Implementation of AlgorithmsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Attacking Problems in Logarithms and Exponential FunctionsDari EverandAttacking Problems in Logarithms and Exponential FunctionsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Schaum's Outline of College Mathematics, Fourth EditionDari EverandSchaum's Outline of College Mathematics, Fourth EditionPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- Business Valuation: Introduction To Financial MethodsDokumen23 halamanBusiness Valuation: Introduction To Financial MethodsfrancescoabcBelum ada peringkat
- Three Basic Candlestick Formations To Improve Your TimingDokumen4 halamanThree Basic Candlestick Formations To Improve Your TimingelisaBelum ada peringkat
- The Incredible Analysis of W D GannDokumen79 halamanThe Incredible Analysis of W D GannJohn Kent97% (31)
- A Complete Guide To Volume Price Analysi - A. CoullingDokumen242 halamanA Complete Guide To Volume Price Analysi - A. CoullingGiundat Giun Dat97% (129)
- Wyckoff - Method of Tape ReadingDokumen405 halamanWyckoff - Method of Tape Readingrcryo90% (10)
- What You Don't Know About Candlesticks: When Candles Work BestDokumen5 halamanWhat You Don't Know About Candlesticks: When Candles Work BestfrancescoabcBelum ada peringkat
- Elliot Wave TheoryDokumen24 halamanElliot Wave TheoryYoderIIIBelum ada peringkat
- Preparing Your DissertationDokumen22 halamanPreparing Your DissertationfrancescoabcBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Elliot WaveDokumen6 halamanBasic Elliot Wavemozack7777Belum ada peringkat
- Shepwavetutorial1 Elliott WaveDokumen4 halamanShepwavetutorial1 Elliott WaveHiren MandaliyaBelum ada peringkat
- Shepwavetutorial1 Elliott WaveDokumen4 halamanShepwavetutorial1 Elliott WaveHiren MandaliyaBelum ada peringkat
- Hilton 2013 ARDokumen118 halamanHilton 2013 ARClaudia MunteanBelum ada peringkat
- EW Swing Sequence SeminarFinalEditedDokumen32 halamanEW Swing Sequence SeminarFinalEditedfrancescoabcBelum ada peringkat
- Global Gaming Outlook 2011 2015 PDFDokumen44 halamanGlobal Gaming Outlook 2011 2015 PDFWilliam AllelaBelum ada peringkat
- ValuationDokumen40 halamanValuationTamjid AhsanBelum ada peringkat
- VBA Book PDFDokumen121 halamanVBA Book PDFAriadiKetutBelum ada peringkat
- M&a FrameworkDokumen12 halamanM&a FrameworkfrancescoabcBelum ada peringkat
- Suburbs & Postcodes: City of MelbourneDokumen1 halamanSuburbs & Postcodes: City of MelbournefrancescoabcBelum ada peringkat
- LBO and MBODokumen81 halamanLBO and MBOfrancescoabcBelum ada peringkat
- Melbourne 3000Dokumen1 halamanMelbourne 3000francescoabcBelum ada peringkat
- Airport Map PDFDokumen1 halamanAirport Map PDFfrancescoabcBelum ada peringkat
- Case Interview HandbookDokumen54 halamanCase Interview HandbookHubert Cierpica100% (1)
- SolChap1 DerivativesMarketsDokumen10 halamanSolChap1 DerivativesMarketsIvan LauBelum ada peringkat
- How To Crack A Case Study InterviewDokumen20 halamanHow To Crack A Case Study InterviewMaia CiobanuBelum ada peringkat
- Guide Case-Interviews PDFDokumen2 halamanGuide Case-Interviews PDFfrancescoabcBelum ada peringkat
- Practice QuestionsDokumen4 halamanPractice QuestionsfrancescoabcBelum ada peringkat
- Derivatives 2Dokumen1 halamanDerivatives 2francescoabcBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Engineering Lesson 2 Asian OptionsDokumen37 halamanFinancial Engineering Lesson 2 Asian OptionsfrancescoabcBelum ada peringkat
- Act2020 Final Exam - 07Dokumen13 halamanAct2020 Final Exam - 07Olivia IuBelum ada peringkat
- Derivatives 1Dokumen1 halamanDerivatives 1francescoabcBelum ada peringkat
- Math Sping Break PacketDokumen10 halamanMath Sping Break PacketKIPPNYCDocsBelum ada peringkat
- DEDokumen26 halamanDERobertBellarmineBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Diwali AssignmentDokumen9 halamanMaths Diwali AssignmentdivyanshuvarmaBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Mathematics Mohamed AltemalyDokumen538 halamanEngineering Mathematics Mohamed AltemalyMahbub Rashid50% (2)
- Properties of Triangle Solved QuestionsDokumen38 halamanProperties of Triangle Solved QuestionsKaran DoshiBelum ada peringkat
- COMPLEX ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS Hand OutDokumen16 halamanCOMPLEX ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS Hand OutZarez Alvarez100% (1)
- Ercole Mirarchi's Conspiracy Theory Lawsuit Over Trump Election ResultsDokumen26 halamanErcole Mirarchi's Conspiracy Theory Lawsuit Over Trump Election ResultsVictor FiorilloBelum ada peringkat
- TRIGONOMETRY Ex 1 To 3 PDFDokumen26 halamanTRIGONOMETRY Ex 1 To 3 PDFGarima PathakBelum ada peringkat
- bkc19 PDFDokumen25 halamanbkc19 PDFrohitrgt4uBelum ada peringkat
- VectorsDokumen9 halamanVectorsdam_allen85Belum ada peringkat
- Vehicle Dynamics NotesDokumen116 halamanVehicle Dynamics NotesJagadesh AbbuBelum ada peringkat
- Sling Load Stress CalculationsDokumen14 halamanSling Load Stress Calculationssethupathy sBelum ada peringkat
- Grobler AJ Chapter4Dokumen14 halamanGrobler AJ Chapter4hieuhuech1Belum ada peringkat
- SAT 2 Past Paper - Mathematics Level 2 Year 2013Dokumen7 halamanSAT 2 Past Paper - Mathematics Level 2 Year 2013Jinhui ZhengBelum ada peringkat
- SUG413 - Advanced Engineering Surveying - Curves CalculationDokumen11 halamanSUG413 - Advanced Engineering Surveying - Curves Calculationmruzainimf100% (2)
- Learning Mathematical SymbolismDokumen7 halamanLearning Mathematical SymbolismEnos Lolang100% (1)
- MA6351Dokumen73 halamanMA6351Prabhakar DasBelum ada peringkat
- 02 - Inverse Trigonometric - PMDDokumen11 halaman02 - Inverse Trigonometric - PMDShweta SaraswatBelum ada peringkat
- 4MA1 1H Que 20190110Dokumen28 halaman4MA1 1H Que 20190110MenaBelum ada peringkat
- Calculus Formula Sheet IIDokumen2 halamanCalculus Formula Sheet IICristan Dave ZablanBelum ada peringkat
- Alternating Current Motors, by Nikola Tesla, 1888Dokumen9 halamanAlternating Current Motors, by Nikola Tesla, 1888dag57Belum ada peringkat
- T4 (8.3-10.5) sp17.tstDokumen3 halamanT4 (8.3-10.5) sp17.tstjuanesz98Belum ada peringkat
- A Distribution Procedure For The Analysis of Slabs Continuous Over Flexible Beams Newmark, N.M.Dokumen126 halamanA Distribution Procedure For The Analysis of Slabs Continuous Over Flexible Beams Newmark, N.M.Marimari MinteaBelum ada peringkat
- Solucionario Parte 4 Matemáticas Avanzadas para Ingeniería - 2da Edición - Glyn JamesDokumen76 halamanSolucionario Parte 4 Matemáticas Avanzadas para Ingeniería - 2da Edición - Glyn JamesKimberly Clark86% (7)
- Signal ProcessingDokumen28 halamanSignal ProcessingNilesh PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Sinyal Dan Sistem Latihan Soal Dan SolusiDokumen12 halamanSinyal Dan Sistem Latihan Soal Dan SolusiMuh Indjra DijeBelum ada peringkat
- Emath and Amath FormulaDokumen21 halamanEmath and Amath FormulaveryveryhappyfeetBelum ada peringkat
- 2021 M11 Wk01 WS Trigonometry 1 (Student) - 1616068594287 - Mpw3oDokumen3 halaman2021 M11 Wk01 WS Trigonometry 1 (Student) - 1616068594287 - Mpw3oRAVI ANANTHAKRISHNANBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4.4 Inverse Circular Functions PDFDokumen5 halamanChapter 4.4 Inverse Circular Functions PDFjiiBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Holiday Homework (Trigonometric Ratios) X-A Roll No 3Dokumen11 halamanMaths Holiday Homework (Trigonometric Ratios) X-A Roll No 3daxe ytBelum ada peringkat