Uterine atony treatment and prevention
Diunggah oleh
YakumaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Uterine atony treatment and prevention
Diunggah oleh
YakumaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
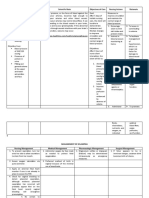
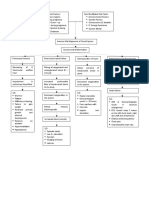
Uterine atony Uterine atony is a loss of tone in the uterine musculature.
Normally, contraction of the uterine muscle compresses the vessels and reduces flow. This increases the likelihood of coagulation and prevents bleeds. Thus, lack of uterine muscle contraction can cause an acute hemorrhage. Clinically, 75 !"# of postpartum hemorrhages are due to uterine atony. Uterine atony$ failure of the myometrium to contract after delivery of the placenta% associated with e&cessive bleeding from the placental implantation site. 'efore (elivery )f you are at risk for uterine atony, your doctor or nurse should make the following preparations in case e&cessive bleeding occurs during or after delivery$ at least one large intravenous line should be established% medication to induce contractions of the uterus o&ytocin *+itocin,, methylergonovine *-ethergine,, and.or prostaglandins should be on hand% and appropriate nursing and anesthesia personnel should be available. )n addition, the blood bank should be notified of the possible need for a blood transfusion for certain high risk patients. /fter (elivery Uterine atony is diagnosed after delivery when there is e&cessive bleeding and a large, rela&ed uterus. The doctor first rules out other potential causes of the bleeding *tears in the vagina or cervi& and fragments of the placenta remaining in the uterus,% these problems should be resolved if they are present. )f the bleeding continues, the uterus may be stimulated to contract with use of massage and intravenous o&ytocin. -any studies show this techni0ue reduces postpartum hemorrhage and the need for blood transfusions. )f heavy bleeding from atony occurs despite the use of o&ytocin after delivery, then two additional medications may be used to help control hemorrhage$ -ethylergonovine, a strong vasoconstrictor derived from ergot, is in1ected into a muscle. )t is not given to patients with preeclampsia or a history of high blood pressure because it can cause high blood pressure. +rostaglandin 2 3 alpha *4emabate, is in1ected under the skin and also directly into the uterus. 2re0uent side effects include diarrhea and vomiting. )t can cause bronchial constriction and is usually avoided in patients with asthma. 5mergency surgery should be performed if atony persists despite these measures to control the bleeding. This may be accomplished by tying off the blood vessels that supply the uterus. )f successful, this procedure should not affect future pregnancies. )n a more involved procedure, the doctor uses & rays to guide a small catheter through blood vessels in the mother6s leg and into the blood vessels supplying the uterus. These blood vessels are then in1ected with gelatin sponge particles or spring coils to obstruct blood flow to the uterus. /lthough successful control of hemorrhage has been reported with this techni0ue, the e0uipment necessary to perform it may not be available in most emergency situations. )f bleeding persists in spite of all conservative measures to control it, a hysterectomy *removal of the uterus, may be necessary. Medical treatment. *a, )ntervenously fluids administered to increase fluid and blood volume. *b, 7&ytocin administration. *c, -ethergine.prostin may be administered to stimulate uterine contractions when o&ytocin is ineffective. *d, 'lood transfusion if the patient6s hematocrit drops too low and.or if she is symptomatic. Nursing interventions. *a, +alpate the fundus fre0uently to determine continued muscle tone. *b, -assage the fundus, if boggy, until firm *do not over massage, this fatigues the muscle,. *c, -onitor patient6s vital signs every 85 minutes until stable. *d, +revent bladder distention. 'ladder distention displaces the uterus and prevents effective uterine contractions. N9: (;$ (eficient fluid volume realted to postpartum hemmorhage /cute pain related to uterine cramping and perineal pain e&perienced <isk for ineffective tissue perfusion related to hemmorhage
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Obstetrics and Gynecology Mock Simulation OutputDokumen4 halamanObstetrics and Gynecology Mock Simulation OutputKathleen Grace ManiagoBelum ada peringkat
- Dysfunctional Labor DystociaDokumen8 halamanDysfunctional Labor Dystociamardsz100% (2)
- Transient Tachypnea of The NewbornDokumen6 halamanTransient Tachypnea of The NewbornTarquin TomadaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study Post Operative - SumbadDokumen3 halamanCase Study Post Operative - SumbadMb SumbadBelum ada peringkat
- EINC ReviewDokumen14 halamanEINC ReviewRifa'atul MahmudahBelum ada peringkat
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism (AFE)Dokumen26 halamanAmniotic Fluid Embolism (AFE)sanjivdas100% (1)
- Uterine AtonyDokumen4 halamanUterine AtonyJohn Cenas100% (1)
- Placenta Abruptio - Topic OverviewDokumen8 halamanPlacenta Abruptio - Topic OverviewLei AbellarBelum ada peringkat
- Abnormal Uterine ActionDokumen27 halamanAbnormal Uterine ActionSameer KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Common Fears Related To Pregnancy, Labor, and Delivery and Coping Mechanisms Among Primigravida MothersDokumen70 halamanCommon Fears Related To Pregnancy, Labor, and Delivery and Coping Mechanisms Among Primigravida MothersSmile Tambanillo0% (1)
- Cord ProlapseDokumen22 halamanCord ProlapseJoyjet Evangelista-murilloBelum ada peringkat
- Uterine AtonyDokumen33 halamanUterine AtonyNonie 'Erni' HastiriniBelum ada peringkat
- Pregnancy Induced HypertentionDokumen2 halamanPregnancy Induced Hypertentionapi-31064465050% (2)
- Abnormal Progress in Labor (Precipitous Labor and Birth & Retraction Rings)Dokumen34 halamanAbnormal Progress in Labor (Precipitous Labor and Birth & Retraction Rings)Ana100% (3)
- Abortion and Ectopic PregnancyDokumen3 halamanAbortion and Ectopic PregnancyJefelson Eu Palaña NahidBelum ada peringkat
- Uterine Atony: Group 3Dokumen23 halamanUterine Atony: Group 3Trisha Mae MarquezBelum ada peringkat
- ProcreationDokumen55 halamanProcreationRoshin TejeroBelum ada peringkat
- OB1 - Problems With The PassengerDokumen9 halamanOB1 - Problems With The PassengerYana100% (1)
- 16 Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDokumen46 halaman16 Amniotic Fluid EmbolismAhmed TarigBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 107 LAB: Catheterization Factors and ProceduresDokumen4 halamanNCM 107 LAB: Catheterization Factors and ProceduresCatherine PradoBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Assessment, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDokumen2 halamanNursing Assessment, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDiana MuañaBelum ada peringkat
- Antepartum Haemorrhage MXDokumen22 halamanAntepartum Haemorrhage MXAmir Hilmi Abd AzizBelum ada peringkat
- Breast FeedingDokumen18 halamanBreast FeedingAnis Rakhmawati100% (1)
- Aklan State University Nursing Readings on Pyloric StenosisDokumen5 halamanAklan State University Nursing Readings on Pyloric Stenosisensoooooooooo100% (1)
- Hemorrhagic ShockDokumen14 halamanHemorrhagic Shockmutiara rizkiBelum ada peringkat
- Premature Rupture of MembranesDokumen38 halamanPremature Rupture of MembranesArwa QishtaBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Assessment ToolDokumen5 halamanPediatric Assessment ToolJude PanlaanBelum ada peringkat
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDokumen3 halamanIneffective Tissue PerfusionJulie Marie PavadoraBelum ada peringkat
- Everything You Need to Know About EpisiotomiesDokumen18 halamanEverything You Need to Know About EpisiotomiesAnnapurna DangetiBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment of A Pregnant FamilyDokumen4 halamanAssessment of A Pregnant FamilyLuna Sang-anBelum ada peringkat
- Incentive SpirometryDokumen3 halamanIncentive SpirometryNursidar Pascual MukattilBelum ada peringkat
- Abruptio Placentae Case StudyDokumen4 halamanAbruptio Placentae Case StudyMonchee YusonBelum ada peringkat
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDokumen1 halamanNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs Affecting Reproductive System: Presented By: BSN 2A Group 1Dokumen34 halamanDrugs Affecting Reproductive System: Presented By: BSN 2A Group 1David BernalBelum ada peringkat
- Issues On Artificial ReproductionDokumen46 halamanIssues On Artificial ReproductionOfficially RandomBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 107 5M Case Analysis PDFDokumen9 halamanNCM 107 5M Case Analysis PDFKisha BethelBelum ada peringkat
- Alterations in Oxygenation 1Dokumen15 halamanAlterations in Oxygenation 1alejandrino_leoaugustoBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care of A Family During Labor and BirthDokumen19 halamanNursing Care of A Family During Labor and BirthPbBelum ada peringkat
- ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyDokumen3 halamanABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyBarda GulanBelum ada peringkat
- Care of Clients With Problem in Oxygenation Quiz 3Dokumen5 halamanCare of Clients With Problem in Oxygenation Quiz 3marsan12Belum ada peringkat
- MMDSTDokumen2 halamanMMDSTJulie Ann Gamboa EwicanBelum ada peringkat
- Nebulization Nursing Procedure at Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityDokumen9 halamanNebulization Nursing Procedure at Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityMitzi BelamideBelum ada peringkat
- Partograph Preparation and UseDokumen48 halamanPartograph Preparation and Useannyeong_123100% (1)
- CP-Rheumatic Heart Disease LandscapeDokumen13 halamanCP-Rheumatic Heart Disease Landscapedecebelle alabaBelum ada peringkat
- Tetralogy of Fallot Pathophysiology & Risk FactorsDokumen1 halamanTetralogy of Fallot Pathophysiology & Risk FactorsEiztirfBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study (CEFUROXIME)Dokumen1 halamanDrug Study (CEFUROXIME)NE TdrBelum ada peringkat
- Meconium-Stained Amniotic Fluid MSAFDokumen54 halamanMeconium-Stained Amniotic Fluid MSAFJhansi PeddiBelum ada peringkat
- Shoulder DystociaDokumen22 halamanShoulder Dystociaamulan_aBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care of The NeonateDokumen12 halamanNursing Care of The NeonateYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Uterine MyomaDokumen45 halamanUterine MyomaAndiniMayudhaBelum ada peringkat
- A Case Analysis OnDokumen27 halamanA Case Analysis Onbunso padillaBelum ada peringkat
- Tetralogy of FallotDokumen33 halamanTetralogy of FallotjeenaejyBelum ada peringkat
- 6 PartographDokumen50 halaman6 PartographEdelyn Arguelles100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDokumen3 halamanDecreased Cardiac OutputCarlojay IniegoBelum ada peringkat
- Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn (TTNDokumen6 halamanTransient Tachypnea of the Newborn (TTNWivan Havilian DjohanBelum ada peringkat
- Managing Labor Pain in PregnancyDokumen2 halamanManaging Labor Pain in PregnancyJACOB AQUINTEYBelum ada peringkat
- Assessing Breasts and AxillaeDokumen32 halamanAssessing Breasts and AxillaeBai-Rhema Marmay100% (1)
- Active Management of Normal LabourDokumen16 halamanActive Management of Normal LabourjincyneeleshBelum ada peringkat
- Uterine AtonyDokumen1 halamanUterine AtonyYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Uterine AtonyDokumen2 halamanUterine AtonyBryan Relado AmbitoBelum ada peringkat
- 3RD BATCH SubmitDokumen51 halaman3RD BATCH SubmitYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- 9 18Dokumen47 halaman9 18YakumaBelum ada peringkat
- TonsilitisDokumen4 halamanTonsilitisYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- OxytocinDokumen3 halamanOxytocinYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Weegy AnswwersDokumen1 halamanWeegy AnswwersYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine Nursing Act of 2002 SummaryDokumen13 halamanPhilippine Nursing Act of 2002 SummaryJenniiLyn Deeo ÜBelum ada peringkat
- Burping A Neonate Health TeachingDokumen1 halamanBurping A Neonate Health TeachingYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Star BurnDokumen1 halamanStar BurnYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Uterine AtonyDokumen1 halamanUterine AtonyYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- AmoebiasisDokumen1 halamanAmoebiasisYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Xylocaine® (Injection) : Essential Prescribing InformationDokumen21 halamanXylocaine® (Injection) : Essential Prescribing InformationYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- PCM + TramadolDokumen2 halamanPCM + TramadolYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- AMOEBIASISDokumen1 halamanAMOEBIASISYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursingbulletin Laws Affecting The Practice of NursingDokumen4 halamanNursingbulletin Laws Affecting The Practice of Nursingseigelystic100% (43)
- Assessing The AbdomenDokumen2 halamanAssessing The AbdomenYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Bill of RightsDokumen2 halamanBill of RightsYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Paracetamol Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanParacetamol Drug StudyYakuma100% (3)
- Diarrhea: Bowel MovementsDokumen1 halamanDiarrhea: Bowel MovementsYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- MetoprololDokumen1 halamanMetoprololYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- The Dangers of Tubal PregnancyDokumen1 halamanThe Dangers of Tubal PregnancyYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- AmoebiasisDokumen1 halamanAmoebiasisYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- TonsilitisDokumen4 halamanTonsilitisYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Paracetamol Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanParacetamol Drug StudyYakuma100% (3)
- Labor MonitoringDokumen3 halamanLabor MonitoringYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Bill of RightsDokumen2 halamanBill of RightsYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- LosartanDokumen1 halamanLosartanYakuma100% (1)
- AMOEBIASISDokumen1 halamanAMOEBIASISYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Amlodipine BesylateDokumen2 halamanAmlodipine BesylateYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Amlodipine BesylateDokumen2 halamanAmlodipine BesylateYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Periodontal LigamentDokumen3 halamanPeriodontal LigamentCzarina DavidBelum ada peringkat
- OBDokumen4 halamanOBCharlie Cotoner FalgueraBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Postpartum Hemorrhage and Third Stage of LaborDokumen7 halamanPathophysiology of Postpartum Hemorrhage and Third Stage of Labornouval_iqbalBelum ada peringkat
- ZCM 822Dokumen59 halamanZCM 822Ema GuillotineBelum ada peringkat
- Balancing The Risk of Your Puppy Contracting Parvovirus Against TheDokumen4 halamanBalancing The Risk of Your Puppy Contracting Parvovirus Against Theapi-255712054Belum ada peringkat
- CH 11Dokumen18 halamanCH 11dazaikun22032003Belum ada peringkat
- Iam MahavetnetDokumen13 halamanIam MahavetnetVet_ashishtklBelum ada peringkat
- Del Suite Report RSCM 7 April 2017 Final Edit Banget Sekali Dengan DataDokumen22 halamanDel Suite Report RSCM 7 April 2017 Final Edit Banget Sekali Dengan DataFedrik Monte Kristo LimbongBelum ada peringkat
- 8.3.2 SPEAKING - Oral Presentation Rubric NAMEDokumen4 halaman8.3.2 SPEAKING - Oral Presentation Rubric NAMEapi-197465646Belum ada peringkat
- Thoracentesis: ProcedureDokumen12 halamanThoracentesis: Procedurealbert manievoBelum ada peringkat
- Human Eye PresentationDokumen15 halamanHuman Eye PresentationDipanshu Nagar93% (14)
- RAISE ORGANIC HOG ReviewerDokumen4 halamanRAISE ORGANIC HOG Reviewermarkdaveasaytuno2Belum ada peringkat
- Upper Midline CorrectionDokumen5 halamanUpper Midline CorrectionmutansBelum ada peringkat
- LAMPIRAN RET PELAYANAN KESEHATAN (Rev)Dokumen167 halamanLAMPIRAN RET PELAYANAN KESEHATAN (Rev)RafliBelum ada peringkat
- GCE Biology-Human Biology-Teachers' Guide Revised 18-02-14Dokumen93 halamanGCE Biology-Human Biology-Teachers' Guide Revised 18-02-14mariumrana40Belum ada peringkat
- Gas Gangrene.Dokumen24 halamanGas Gangrene.Jared GreenBelum ada peringkat
- ToxocaraDokumen313 halamanToxocaradiana2_0_0_2Belum ada peringkat
- Erythropoiesis: Presented by DR Etu-Efeotor T. PDokumen88 halamanErythropoiesis: Presented by DR Etu-Efeotor T. PPrincewill SeiyefaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Thyroid and Parathyroid GlandsDokumen14 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of The Thyroid and Parathyroid GlandsSidiq AboobakerBelum ada peringkat
- Early Human DietsDokumen3 halamanEarly Human DietsDouglas CamposBelum ada peringkat
- Factors That Damage the Stomach LiningDokumen8 halamanFactors That Damage the Stomach LiningTania Louise Pioquinto AbuanBelum ada peringkat
- Care Sheet - Axolotl (Ambystoma Mexicanum)Dokumen3 halamanCare Sheet - Axolotl (Ambystoma Mexicanum)John GamesbyBelum ada peringkat
- February 17, 2017 Strathmore TimesDokumen24 halamanFebruary 17, 2017 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesBelum ada peringkat
- Anaesthesia For Paediatric Dentistry: Lola Adewale MBCHB DCH FrcaDokumen8 halamanAnaesthesia For Paediatric Dentistry: Lola Adewale MBCHB DCH FrcaJavier Farias VeraBelum ada peringkat
- Grabovoi NumbersDokumen29 halamanGrabovoi Numberssillyminds100% (3)
- 2009 Nec Hiv Dec Aidsreg2009Dokumen3 halaman2009 Nec Hiv Dec Aidsreg2009Jing CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Female and Male GenitaliaDokumen5 halamanFemale and Male GenitaliaMary Mae BuellaBelum ada peringkat
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies OverviewDokumen35 halamanAssisted Reproductive Technologies OverviewPraluki HerliawanBelum ada peringkat
- Conduct of Normal Labor and DeliveryDokumen29 halamanConduct of Normal Labor and DeliveryEzekiel ArtetaBelum ada peringkat
- Sharks of The World Volume 4 Part 2Dokumen414 halamanSharks of The World Volume 4 Part 2cavrisBelum ada peringkat