Mathematics Formula
Diunggah oleh
deenawantsHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Mathematics Formula
Diunggah oleh
deenawantsHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
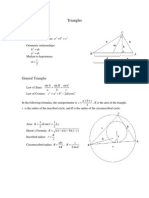
Mathematics Formula (E-Maths)
Symbols used: - pi r - radius l - slanted height h - height
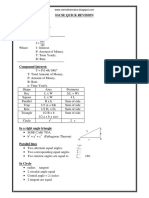
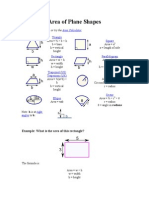
Area and Perimeter
Area of a square - Length Area of a triangle !
Length
Length Height
Area of a rectangle - Length "readth Area of a parallelogram - Length Height Area of a rhombus - Length Length Area of a trapezium !
(Sum o# $arallel lines) Height
Area of a circle - r% Circumference of a circle - r Curved surface area of a cylinder - rh Surface area of a cylinder - r% & rh Curved surface area of a cone - rl Surface area of a sphere - 'r%
(olume
Volume of a cube - Length Length Length Volume of a cuboid - Length "readth Height Volume of a cylinder - r%h Volume of a pyramid Volume of a cone ! Area o# "ase Height ) ! r 2 l )
Volume of a prism - Sur#ace area o# the base
' 3 Volume of a sphere - r )
Height
Algebra
( a + b ) = a + ab + b ( a + b ) = a ab+ b ( a + b )( a b ) = a b ( a + b )( c + d ) = ac + ad + bc + bd
*uadratic E+uations Formula
ax% & bx + c , -:
b b ' ac a
Pythagoras .heorem
This formula only applies to right-angled triangle.
a% + b% = c% here c is the hypotenuse.
/ndices
a m a n = a m +n am = a m n # "here a !. an
m n
(a )
= a mn
m m
.ero indices - a 0 = ! , "here a !. ! -egative indices - a - n = n # "here a !. a ,ractional indices# "here a > - and n is a positive integer :
! m
a m b m = ( a b )
an =n a
an =
( a)
n
am a = # "here b !. bm b
0oordinate 1eometry
$radient of a line y y! x x !
%ength of a line - ( x x! ) + ( y y! ) &quation of a line - y = mx + c
Standard 2e3iation
'ngrouped data:
s= )x x2 n
(
$rouped data# frequency distribution:
s= ) fx ( x2 f
Polygon
Sum of all the angles in a n-sided polygon - !4- (n 5 ) !4- ( n ) &ach angles of a n-sided regular polygon n
S$eed
Speed = *istance Time
2ensity
*ensity = +ass Volume
.rigonometry
Sine /ule
a b c sin A sin B sinC = = = = or sin A sinB sinC a b c ! ! !
Area of triangle formula:
= = = ab sinC bc sin A ac sinB
Cosine /ule
a = b + c bc cos A b = a + c ac cos B c = a + b ab cosC
0ongruency and Similarity
0f the t"o triangles belo" are similar# 0f the t"o solids belo" are similar#
Area of 423/ 23 = Area of 4A1C A1
Volume of A h6 = Volume of 1 h(
Arc6 Sector and Segment
! r r sin Area of segment r Arc length in *egree )7 )7- r Area of sector in *egree )7-
Converting degree to radian
Converting radian to degree
- +ultiply the angle in degree by Arc length in /adian - r Area of sector in /adian ! r
. !4-
- +ultiply the angle in radian by
!4- .
Matrices
The matrices belo" must be in the same order.
a b $ + a + $ b + + c d + = r s c +r d +s a b $ + a $ b + c d = r s c r d s
Scalar Multi$lication
a 8 d b e c 8a = # 8d 8b 8e 8c 8#
Multi$lication The number of columns in the first matri7 must be equal to the ro"s of the second matri7.
a c b $ d r + a$ + br = s c$ + dr a+ + bs c+ + ds
(ectors in .9o 2imensions
Addition of Vector 0f u# v and w are vectors# then Addition 6. u + v = v + u# 8commutative la"9 (. 8u + v9 : w = u + 8v + w9. 8associative la"9 Subtraction u v = u + 8-v9 a : 8-a9 ; ! for any vector a. Scalar +ultiplication 0f u and v are vectors# and m and n are real numbers# then 6. m8nu9 ; n8mu9 ; 8mn9u< (. 8m + n9u ; mu + nu< 5. m8u + v9 ; mu + mv. 2osition Vectors
Vectors on Coordinate 2lates
x The magnitude of a column vector y =
x +y .
x6 x ( x6 + x( y + = 6 y ( y6 + y ( x6 x( x6 x ( y = 6 y( y6 y(
x kx k y = # "here k is a scalar. ky
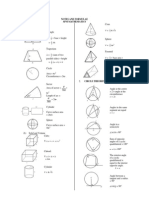
1eometrical Pro$erties o# 0ircles
A+ ; 1+ &qual chords# A1 and => A1 ; =># ?+ ; ?-
Tangent is perpendicular T"o tangents. :PA = :P" # A:P = ":P . to the centre.
The angle at the centre of a circle O is t"ice the angle at the circumference:
Angle in a semicircle. A21 =@!
Angles in the same Angles in opposite segments are segments. supplementary. A1C + A*C =6A! A21 = A/1
1A* + 1C* =6A!
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- MA8351-Discrete Mathematics PDFDokumen14 halamanMA8351-Discrete Mathematics PDFAnand RajBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Solving Strategy Building A ModelDokumen19 halamanProblem Solving Strategy Building A Modelkellyting90Belum ada peringkat
- 7.2 Washer Method and Disk Continued PDFDokumen12 halaman7.2 Washer Method and Disk Continued PDFHector Pacheco PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Trigonometric Functions - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen18 halamanTrigonometric Functions - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadaniyalhassan2789Belum ada peringkat
- Drones in EducationDokumen2 halamanDrones in EducationNico TicacBelum ada peringkat
- Formula Sheet For MathsDokumen5 halamanFormula Sheet For Mathsbobd123Belum ada peringkat
- Prep 3 TestDokumen5 halamanPrep 3 TestlovelBelum ada peringkat
- Vector SpacesDokumen6 halamanVector Spacesas_5kBelum ada peringkat
- Symmetric GroupDokumen13 halamanSymmetric GroupPriyanka PatelBelum ada peringkat
- MAT220-Algebra NotesDokumen56 halamanMAT220-Algebra NotesSofia Tirabassi100% (1)
- Exploring Engineering: Newton's Laws of Motion and KinematicsDokumen22 halamanExploring Engineering: Newton's Laws of Motion and KinematicsrenniALWAYSBelum ada peringkat
- Mat 213 Groups, Rings and FieldsDokumen69 halamanMat 213 Groups, Rings and FieldsEnenamahBelum ada peringkat
- PREP 4 Mathematics Updated 080620Dokumen5 halamanPREP 4 Mathematics Updated 080620lovelBelum ada peringkat
- Volume NesDokumen42 halamanVolume NesMauricio PenagosBelum ada peringkat
- Emath and Amath FormulaDokumen21 halamanEmath and Amath FormulaveryveryhappyfeetBelum ada peringkat
- Additional Mathematics Formulae List Form 5Dokumen28 halamanAdditional Mathematics Formulae List Form 5Sayantani GhoshBelum ada peringkat
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDokumen38 halamanTrigonometric Identitiesetamil87Belum ada peringkat
- Faiz Ul HassanDokumen5 halamanFaiz Ul HassanFaiz Ul HassanBelum ada peringkat
- CMATDokumen20 halamanCMATsrk2success100% (1)
- Nota 2010Dokumen78 halamanNota 2010Muhammad NuruddinBelum ada peringkat
- Polar Coordinate GraphsDokumen19 halamanPolar Coordinate GraphseclairezBelum ada peringkat
- GRE Quant Formulas PDFDokumen5 halamanGRE Quant Formulas PDFPrerna TripathiBelum ada peringkat
- Jackson 5 3 Homework SolutionDokumen4 halamanJackson 5 3 Homework SolutionJefferson FerreiraBelum ada peringkat
- Kaplan Math Foundation Review Trigonometry and Geometry HighlightsDokumen24 halamanKaplan Math Foundation Review Trigonometry and Geometry HighlightstwsttwstBelum ada peringkat
- Exam Yr 11 YearlyDokumen7 halamanExam Yr 11 Yearlyhr_kapaniBelum ada peringkat
- Ecuaciones Parametricas 13 14Dokumen19 halamanEcuaciones Parametricas 13 14feuchisBelum ada peringkat
- Notes MathDokumen4 halamanNotes MathNaveed Atta UllahBelum ada peringkat
- 5 C O N I C S: ParabolaDokumen6 halaman5 C O N I C S: ParabolaDattatray NerkarBelum ada peringkat
- CXC MATHS Formula SheetDokumen7 halamanCXC MATHS Formula SheetEric D Medeci100% (1)
- Algebraic FormulaDokumen73 halamanAlgebraic Formulagspkishore7953Belum ada peringkat
- 15 SAT Practice QuestionsDokumen30 halaman15 SAT Practice QuestionsknownstillhaveBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Trigonometry ConceptsDokumen23 halamanEssential Trigonometry ConceptsTitis PohanBelum ada peringkat
- Handy_Quantitative_Aptitude_FormulaeDokumen8 halamanHandy_Quantitative_Aptitude_FormulaeParitosh GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Double Angle Identities Worksheet With Graphysc CalculatorDokumen4 halamanDouble Angle Identities Worksheet With Graphysc CalculatorErin PhillipsBelum ada peringkat
- Physics P3 SPM 2014 A Modul Melaka GemilangDokumen10 halamanPhysics P3 SPM 2014 A Modul Melaka GemilangCikgu FaizalBelum ada peringkat
- Quant 50 Important Formulae: 1. AveragesDokumen26 halamanQuant 50 Important Formulae: 1. AveragesVishal GovilBelum ada peringkat
- K. F. Riley M. P. Hobson Student Solution Manual For Mathematical Methods For Physics and Engineering Third Edition 2006 Cambridge University PressDokumen15 halamanK. F. Riley M. P. Hobson Student Solution Manual For Mathematical Methods For Physics and Engineering Third Edition 2006 Cambridge University PresskfiriewBelum ada peringkat
- - DC.docx Ii7 y n.3 i Ju吗 你 那 有 44。很 他。。 。 。 1st k8bDokumen10 halaman- DC.docx Ii7 y n.3 i Ju吗 你 那 有 44。很 他。。 。 。 1st k8bumaima khanBelum ada peringkat
- TRIGONOMETRYDokumen8 halamanTRIGONOMETRYurfriend_jjn05100% (1)
- Topic 20 Further TrigonometryDokumen22 halamanTopic 20 Further TrigonometryAntwayne Youcantstopmaprogress HardieBelum ada peringkat
- Indices Arc of A Circle: M N M+N 3 2 3+2 5Dokumen4 halamanIndices Arc of A Circle: M N M+N 3 2 3+2 5Sarbu GeorgeBelum ada peringkat
- ARML TheoremsDokumen27 halamanARML Theoremsfreefall014Belum ada peringkat
- GRE (Graduate Record Examination) Quant Formulas 1. SquareDokumen8 halamanGRE (Graduate Record Examination) Quant Formulas 1. SquareJeevitha BandiBelum ada peringkat
- Maths School WorkDokumen65 halamanMaths School WorkPrincess SuncityBelum ada peringkat
- KMA002 - L05a - GeometryDokumen35 halamanKMA002 - L05a - GeometrymikeyBelum ada peringkat
- Algebra Basic Rules in Algebra: M N M+N M N M-N M N MN M M M M M M M/N - M M oDokumen61 halamanAlgebra Basic Rules in Algebra: M N M+N M N M-N M N MN M M M M M M M/N - M M oChristian ArloBelum ada peringkat
- Maths IGCSE Quick RevisionDokumen6 halamanMaths IGCSE Quick Revisionfarsxdchg100% (1)
- M Ath P Ractice Section 2: M Edium D IfficultDokumen15 halamanM Ath P Ractice Section 2: M Edium D IfficultsdBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Formulas For Class 10 PDFDokumen6 halamanMaths Formulas For Class 10 PDFSUBHADEEP GHOSH100% (2)
- Maths Formulas For Class 10 PDFDokumen6 halamanMaths Formulas For Class 10 PDFAparna ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Area of Plane ShapesDokumen6 halamanArea of Plane ShapesDon King EvangelistaBelum ada peringkat
- SPM MATHS FORMULA GUIDEDokumen9 halamanSPM MATHS FORMULA GUIDENurAinKhalidBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Formulas For Class 10 PDFDokumen18 halamanMaths Formulas For Class 10 PDFJivendra Kumar100% (1)
- 1 Geometry Theorems BookletDokumen28 halaman1 Geometry Theorems BookletMin Chong100% (1)
- Formula Sheet - MathDokumen3 halamanFormula Sheet - MathDevansh SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- 10th STD - Mathematical Formulae - 2Dokumen4 halaman10th STD - Mathematical Formulae - 2ambresh.09Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4 (Compatibility Mode)Dokumen26 halamanLecture 4 (Compatibility Mode)Anonymous dGnj3bZBelum ada peringkat
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDari EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (8)
- Employee Grievances Discipline and CounselingDokumen24 halamanEmployee Grievances Discipline and Counselingpallavi07_bhu8196Belum ada peringkat
- Key Performance Indicators To Benchmark Hospital Information Systems - A Delphi StudyDokumen11 halamanKey Performance Indicators To Benchmark Hospital Information Systems - A Delphi StudydeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- Oracle Exam SyllabusDokumen3 halamanOracle Exam SyllabusdeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- Trigonometric Formulas - Handy Summary Sheet: 1 0 0 0 Cos SinDokumen2 halamanTrigonometric Formulas - Handy Summary Sheet: 1 0 0 0 Cos SindeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- Ugc - Iqac TemplateDokumen23 halamanUgc - Iqac TemplatedeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- 1z0 548 Exam Study Guide 311792Dokumen5 halaman1z0 548 Exam Study Guide 311792Sriram KalidossBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen5 halamanAn Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologydeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Science: Tables & Formulas: SI Base UnitsDokumen11 halamanPhysical Science: Tables & Formulas: SI Base Unitsdeenawants100% (1)
- Statistics FormulaDokumen5 halamanStatistics FormuladeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacy Service Evaluation QuestionnaireDokumen2 halamanPharmacy Service Evaluation QuestionnairedeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- Inventory InternalDokumen2 halamanInventory InternaldeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- How To Calculate A Chi Square Using ExcelDokumen4 halamanHow To Calculate A Chi Square Using ExceldeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- Educational Performance EvaluationDokumen2 halamanEducational Performance EvaluationdeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- Educational Performance EvaluationDokumen2 halamanEducational Performance EvaluationdeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- New FormatDokumen1 halamanNew FormatdeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen4 halamanUntitleddeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- Educational Performance EvaluationDokumen2 halamanEducational Performance EvaluationdeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- Patient SafetyDokumen7 halamanPatient SafetydeenawantsBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson - Exemplar - GRADE 5Dokumen9 halamanLesson - Exemplar - GRADE 5Luisa GarcillanBelum ada peringkat
- Reverse, or Ogee, CurveDokumen1 halamanReverse, or Ogee, Curveapi-3762222Belum ada peringkat
- CH 13 CongruenceDokumen29 halamanCH 13 CongruenceAditya SalianBelum ada peringkat
- Characterizations of The Symmedian LineDokumen4 halamanCharacterizations of The Symmedian LinevnmanhvnlcBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematical Analysis of Spherical Triangle (Application of HCR's Theory & Inverse Cosine Formula)Dokumen10 halamanMathematical Analysis of Spherical Triangle (Application of HCR's Theory & Inverse Cosine Formula)Asad Abozed100% (1)
- @cetexamgroup: A Complete Guide On Quantitative Aptitude For Banking & Insurance ExaminationsDokumen33 halaman@cetexamgroup: A Complete Guide On Quantitative Aptitude For Banking & Insurance ExaminationsDivyaBelum ada peringkat
- CENG 7503 - Shell StructuresDokumen10 halamanCENG 7503 - Shell StructuresabadittadesseBelum ada peringkat
- Appendix (Clil Lesson - The Geometric Shapes)Dokumen18 halamanAppendix (Clil Lesson - The Geometric Shapes)Jason McdanielBelum ada peringkat
- MA1200 Hand-In Assignment #1 Due Week 3Dokumen2 halamanMA1200 Hand-In Assignment #1 Due Week 3na2 squareBelum ada peringkat
- G3 MMC Reviewer - Perimeter and Area - Part 1Dokumen2 halamanG3 MMC Reviewer - Perimeter and Area - Part 1Harry Magbanua PradoBelum ada peringkat
- Elementry Shapes-1Dokumen3 halamanElementry Shapes-1SHEIKH SHABIRBelum ada peringkat
- The Nine-Point Circle: William M. Faucette May 2007Dokumen11 halamanThe Nine-Point Circle: William M. Faucette May 2007VamsiMadupuBelum ada peringkat
- DEVELOPMENT OF SURFACES AND SOLIDS WITH CUTOUTSDokumen7 halamanDEVELOPMENT OF SURFACES AND SOLIDS WITH CUTOUTSNagaraj MuniyandiBelum ada peringkat
- Week 1. Regular ShapesDokumen29 halamanWeek 1. Regular ShapesLinh TranBelum ada peringkat
- Xercise: Advanced Subjective QuestionsDokumen4 halamanXercise: Advanced Subjective QuestionsAnant DwivediBelum ada peringkat
- 14 Parabola Formula Sheets QuizrrDokumen9 halaman14 Parabola Formula Sheets QuizrrChandanBelum ada peringkat
- Volume of A Circular Truncated Cone Calculator - High Accuracy CalculationDokumen2 halamanVolume of A Circular Truncated Cone Calculator - High Accuracy CalculationAVINASHRAJBelum ada peringkat
- Hyperbola - 03 - ExerciseDokumen16 halamanHyperbola - 03 - ExerciseRaju SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Circle Theorem 1Dokumen3 halamanCircle Theorem 1yaw197Belum ada peringkat
- How To Draw Manga Sketching Manga Style Vol 5 Sketching Props PDFDokumen200 halamanHow To Draw Manga Sketching Manga Style Vol 5 Sketching Props PDFJoel Ortiz100% (1)
- 1.6.1 Parts of The CircleDokumen2 halaman1.6.1 Parts of The CircleHeyKyYoureSoFine0% (1)
- MathHL IA (SolidsOfRevolution) PDFDokumen13 halamanMathHL IA (SolidsOfRevolution) PDFlaiba bilal67% (3)
- Engineering Drawing Class 9Dokumen7 halamanEngineering Drawing Class 9GopiKrishnaValireddyBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 9 Surface Area and Volume: Answer The QuestionsDokumen10 halamanGrade 9 Surface Area and Volume: Answer The QuestionsClever RatBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Revision Test Paper 06 For Board Exam 2021. (Chapter 01 To 13)Dokumen6 halamanMaths Revision Test Paper 06 For Board Exam 2021. (Chapter 01 To 13)dinesh lalwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Aops Community 2018 Iranian Geometry Olympiad: 5Th IgoDokumen4 halamanAops Community 2018 Iranian Geometry Olympiad: 5Th IgoNguyễn Hữu ĐứcBelum ada peringkat
- Duality of polyhedra explored using 3D graphicsDokumen27 halamanDuality of polyhedra explored using 3D graphicsMario DalcínBelum ada peringkat
- Geometry VocabularyDokumen50 halamanGeometry Vocabularynew vivyBelum ada peringkat
- GradeDokumen11 halamanGradejadipa123Belum ada peringkat
- Geometry: in This Chapter You Will AnswerDokumen19 halamanGeometry: in This Chapter You Will Answerstq100% (1)