ME3112-PART 2 Tutorial 2 & 3: Shahrokh
Diunggah oleh
Yin HauJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ME3112-PART 2 Tutorial 2 & 3: Shahrokh
Diunggah oleh
Yin HauHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ME3112-PART 2
TUTORIAL 2 & 3
Shahrokh
Review (tutorial 2)
Natural Vibration
Finding natural frequency and mode shapes
Equation of motion
Newtons second law
Energy conservation equation
Other methods
Forced Vibration
Force frequency
Natural frequency
No damping
Damped vibration
Under damped
Critical damping
Over damped
Review (tutorial 2)
X
m
=
P
m
k
1
n
2
2
+
2
n
2
1 2
X
m
=
P
m
k
1
n
2
Tutorial 2-Q1
Assumptions:
Uniform mass distribution
Natural vibration
Given:
AB = AC = 0.5 and BC = 0.6
Required:
Natural frequency ???
n
=
mgy
Cu
I
A
CG
G
1
G
3
G
2
y
x
Tutorial 2-Q1
h
1
=h
3
=0.2
From the geometry, AC = AB = 0.5 m, BC = 0.6 m,
therefore AG
2
= 0.4 m
Total length of wireframe : 0.5 + 0.5 + 0.6= 1.6 m
Mass per unit length : m/L=1.6/1.6 = 1 kg/m
Mass of AB = 0.5 kg
Mass of AC = 0.5 kg
Mass of BC = 0.6 kg
Center of Mass: dCG
Let d be the distance from CG (the center of mass from A),
m
tot
y
Cu
= m
y
: m
tot
J = m
AB
1
+ m
AC
3
+ m
BC
(A0
2
)
1.6 (d) = 0.5 (0.2) + 0.5 (0.2) + 0.6 (0.4)
d = 0.44/1.6 = 0.275 m
d
Tutorial 2-Q1
CG
G
1
G
3
d
h
1
=h
3
=0.2
G
2
Natural Frequency:
n
n
=
K
cq
m
tot
=
mgJ
I
A
Moment of Inertia: I
A
I
A
= I
AB
+ I
AC
+ I
BC
I
A
=(1/3)(0.5)(0.5)
2
+ (1/3)(0.5)(0.5)
2
+
(1/12)(0.6) (0.6)
2
+ 0.6 (0.4)
2
= 0.1973 kg m2
Tutorial 2-Q2
At max potential energy T
1
= 0
V
1
= (1/2) ((k
B
/4) + k
C
)L
2
q
m
2
At max kinetic energy, V
2
= 0
T
2
= (1/2) (1/3)mL
2
(
n
q
m
)
2
T1 + V1 = T2 + V2
n
2
= (3/m) ((k
B
/4) + k
C
)
n
=
K
cq
m
K
cq
= 3
k
B
4
+ k
C
T
1
= 0
V
1
0
V
2
= 0
T
2
0
n
= 31.72 roJ/s
Tutorial 2-Q3
X
m
=
P
m
k
1
n
2
2
+
2
n
2
1 2
X
m
=
P
m
k
1
n
2
P
m
= mr
2
P = P
m
sin t
n
=
k
cq
m
= 1800
Cr
min
= 1800
2n
60
roJ
s
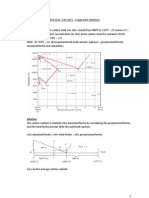
A 25 kg motor is supported by four springs,
each having a constant of 200 kN/m. The
unbalance of the rotor is equivalent to a
mass of 30g located 125 mm from the axis
of rotation. Knowing that the motor is
constrained to move vertically, determine
the amplitude of the steady state vibration of
the motor at a speed of 1800 rpm, assuming
that (a) no damping is present. (b) the
damping factor is 0.125.
Answers: (a) 1.509 mm (b) 0.583 mm.
Tutorial 2-Q4
X
m
=
P
m
k
1
n
2
2
+
2
n
2
1 2
n
=
k
cq
m
c
c
= 2m
n
=
c
c
c
A machine element having a mass of 500
kg is supported by two springs, each
having a constant of 48 kN/m. A periodic
force of maximum magnitude equal to 150
N is applied to the element with a
frequency of 2.4 Hz. Knowing that the
coefficient of damping is 1600 Ns/m,
determine the amplitude of the steady state
vibration of the element. Answer: 5.02 mm.
= 2n
Review (tutorial 3)
Degrees of freedom of a Mechanism
The 4-bar mechanism analysis
2-point formula (or I.C.R.)
Starting with the link with known angular velocity
DOF=3(n-1) -2L -h
Where
DOF = total degrees of freedom in the mechanism
n = number of links(including the frame)
L = number of lower pairs(one degree of freedom)
h = number of higher pairs(two degrees of freedom)
Tutorial 3-Q1
n= 4
L =4
h=0
DOF = 1
DOF =3(n-1) -2L -h
n= 4
L =4
h=0
DOF = 1
n= 4
L =4
h=0
DOF = 1
n= 9
L =11
h=0
DOF = 2
Tutorial 3 - Q2 and Q3
:
B
=
AB
AB
_
:
= :
B
+
B
B
:
=
L
E
o
B
=
AB
AB
AB + o
AB
AB
_
o
= o
B
+
B
B
B + o
B
B
o
=
L
L
E + o
L
E
B
= 4
roJ
s
C. w.
L
= 6.67
roJ
s
C. C. w.
Summary:
Final answers:
o
L
= 28.9
rad
s
2
C. W.
o
L
= 124
rad
s
2
C. C. W.
B
= 29.33
roJ
s
C. w.
L
= 11.29
roJ
s
C. C. w. o
L
= 860.08
rad
s
2
C. C. W.
o
L
= 356.15
rad
s
2
C. W.
Q2 Q3
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Harmonically Excited VibrationDokumen61 halamanHarmonically Excited VibrationSiddharth MohanBelum ada peringkat
- DynpacDokumen51 halamanDynpacRossBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration EngineeringDokumen37 halamanVibration EngineeringAlen Benguit II0% (1)
- Design, Analysis and Manufacturing of Four Degree of Freedom Wireless (Wi-Fi) Controlled Robotic ARMDokumen12 halamanDesign, Analysis and Manufacturing of Four Degree of Freedom Wireless (Wi-Fi) Controlled Robotic ARMMasood Akhtar VaheedBelum ada peringkat
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsDari EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsBelum ada peringkat
- Response Spectrum Analysis PDFDokumen30 halamanResponse Spectrum Analysis PDFSujay SantraBelum ada peringkat
- Given A Potential Energy Graph, Oscillations Will Occur Between Turning Points Determined byDokumen9 halamanGiven A Potential Energy Graph, Oscillations Will Occur Between Turning Points Determined byjdlawlisBelum ada peringkat
- EC1301 Mid-Term Exam Questions (09102009 - Make-Up Exam)Dokumen11 halamanEC1301 Mid-Term Exam Questions (09102009 - Make-Up Exam)Yin Hau100% (1)
- STPM Physic FormulaDokumen4 halamanSTPM Physic FormulaWee Soon ChaiBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration in Two Lectures: Free, Forced, Damped and Undamped SystemsDokumen12 halamanVibration in Two Lectures: Free, Forced, Damped and Undamped SystemsUjjawal GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresDari EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Assignment 1Dokumen11 halamanAssignment 1राधे कृष्णा वर्ल्डBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration Analysis FundamentalsDokumen20 halamanVibration Analysis FundamentalsVivek PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- ME2142E Feedback Control Systems-CheatsheetDokumen2 halamanME2142E Feedback Control Systems-CheatsheetPhyo Wai Aung67% (9)
- Mechanical Intro 17.0 M06 Connections and Remote Boundary ConditionsDokumen67 halamanMechanical Intro 17.0 M06 Connections and Remote Boundary ConditionsSamedŠkuljBelum ada peringkat
- MNO1001X Cheat SheetDokumen8 halamanMNO1001X Cheat SheetYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Formula Sheet - Applied Mechanics & DesignDokumen11 halamanFormula Sheet - Applied Mechanics & DesignAnkur Jay38% (8)
- Vibration SolutionsDokumen8 halamanVibration Solutionschintha007Belum ada peringkat
- ME3112 Mechanics of Machines Solution To Problem Set 5Dokumen4 halamanME3112 Mechanics of Machines Solution To Problem Set 5webvenkyBelum ada peringkat
- Test Date: 15/04/2018 Test Time: 9:30 AM - 12:30 PM Subject: JEE Main 2018 CBT EHDokumen29 halamanTest Date: 15/04/2018 Test Time: 9:30 AM - 12:30 PM Subject: JEE Main 2018 CBT EHChirag YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Damped Linear Systems ResponseDokumen6 halamanDamped Linear Systems ResponseUSERABelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3: Dynamic Analysis: Part 1: General Part 2: Earthquake/1D Part 3: Earthquake/nDDokumen30 halamanChapter 3: Dynamic Analysis: Part 1: General Part 2: Earthquake/1D Part 3: Earthquake/nDYasser AlghrafyBelum ada peringkat
- MM FormulaeDokumen2 halamanMM FormulaeReddyvari VenugopalBelum ada peringkat
- Review of Dynamics and Mechanisms of Machinery: MECH 103Dokumen92 halamanReview of Dynamics and Mechanisms of Machinery: MECH 103Sunilkumar ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- KEAM 2014 Physics Solutions For All Codes A1, A2, A3 & A4Dokumen16 halamanKEAM 2014 Physics Solutions For All Codes A1, A2, A3 & A4Lokesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- AIPMT 2009 Solved PaperDokumen27 halamanAIPMT 2009 Solved PaperFirdosh Khan100% (3)
- Natural Frequency Analysis of Multi-Degree SystemsDokumen87 halamanNatural Frequency Analysis of Multi-Degree SystemswanpudinBelum ada peringkat
- Chapt 3 FrenchDokumen61 halamanChapt 3 FrenchSaurabh BorseBelum ada peringkat
- Examples On SDOF - NewDokumen15 halamanExamples On SDOF - NewTsiNat NathaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment CoverpageDokumen12 halamanAssignment Coverpageajay shresthaBelum ada peringkat
- Torsional Vibration of Long Uniform ShaftDokumen3 halamanTorsional Vibration of Long Uniform Shaftdaongocha108Belum ada peringkat
- Aieee Solution 2011Dokumen15 halamanAieee Solution 2011Arun Prasath RamamoorthyBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Free Vibration: Any System Possessing Mass and Elasticity Is Capable of VibrationDokumen11 halaman2 Free Vibration: Any System Possessing Mass and Elasticity Is Capable of VibrationNumkang KangBelum ada peringkat
- A2 41c Shm&OscillationsDokumen47 halamanA2 41c Shm&OscillationsHany ElGezawyBelum ada peringkat
- Test 3 HoffmanDokumen9 halamanTest 3 HoffmanTravisBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1Dokumen27 halamanModule 1Sunny SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- II IIT IRP Physics Worksheet - 14 Q + Soln - SHMDokumen17 halamanII IIT IRP Physics Worksheet - 14 Q + Soln - SHMAshwin KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamics and VibrationsDokumen19 halamanDynamics and Vibrationsadhi2796Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 13Dokumen14 halamanChapter 13Adrian PredaBelum ada peringkat
- Exam III PHY 2049 Summer C July 16, 2008Dokumen7 halamanExam III PHY 2049 Summer C July 16, 2008Ytzel NëssieBelum ada peringkat
- Answers of Problems: Biochemical Engineering: A Textbook For Engineers, Chemists and BiologistsDokumen32 halamanAnswers of Problems: Biochemical Engineering: A Textbook For Engineers, Chemists and BiologistsMcLovin .MOHBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Formulas and ConceptsDokumen8 halamanPhysics Formulas and ConceptsJijolalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen2 halamanChapter 5Ananthan RameshBelum ada peringkat
- AIPMT 2016 Physics Paper With Ans & Solution by Allen KotaDokumen10 halamanAIPMT 2016 Physics Paper With Ans & Solution by Allen KotaMohitBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration Lectures Part 1Dokumen71 halamanVibration Lectures Part 1AshokBelum ada peringkat
- Spring Mass Couple PDFDokumen52 halamanSpring Mass Couple PDFatiqah umairahBelum ada peringkat
- Homework frequency and stiffness changesDokumen8 halamanHomework frequency and stiffness changesJayvee NeridaBelum ada peringkat
- Eamcet-Pb-Physics-Sr Inter Physics-02 01wave Motion 1-26Dokumen13 halamanEamcet-Pb-Physics-Sr Inter Physics-02 01wave Motion 1-26Rachel TaylorBelum ada peringkat
- M 470 FL 04 Ex 1 SolDokumen9 halamanM 470 FL 04 Ex 1 SolEng Hussein ObeidatBelum ada peringkat
- Section2 5Dokumen6 halamanSection2 5sonti11Belum ada peringkat
- ENERGY STORAGE DEVICES QuestionsDokumen10 halamanENERGY STORAGE DEVICES QuestionskanishkaBelum ada peringkat
- Dyn AssignmentDokumen8 halamanDyn AssignmentTekle AschuBelum ada peringkat
- Elementary Tutorial: Fundamentals of Linear VibrationsDokumen51 halamanElementary Tutorial: Fundamentals of Linear VibrationsfujinyuanBelum ada peringkat
- Files-3-Handouts Solved Problems Chapter 3 Mechanical Systems PDFDokumen7 halamanFiles-3-Handouts Solved Problems Chapter 3 Mechanical Systems PDFHemanta DikshitBelum ada peringkat
- M 470 HWDokumen11 halamanM 470 HWMohsen0% (1)
- 2 4 PDFDokumen8 halaman2 4 PDFshian ervin lopezBelum ada peringkat
- 2 - 4 Spring MassDokumen8 halaman2 - 4 Spring Masshemal4379Belum ada peringkat
- Exam 2Dokumen3 halamanExam 2Mark Cliffton BadlonBelum ada peringkat
- Analyze Vibrations of Two Degree SystemsDokumen17 halamanAnalyze Vibrations of Two Degree SystemsMohammad Al BastakiBelum ada peringkat
- Gek 1540 Tut 2 QBDokumen2 halamanGek 1540 Tut 2 QBYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Entropy 15 01221Dokumen11 halamanEntropy 15 01221Yin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Laplace Transform TableDokumen3 halamanLaplace Transform TableYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Gek1540 Chapter 6Dokumen4 halamanGek1540 Chapter 6Yin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics and Its Application in RefrigerationDokumen8 halamanThermodynamics and Its Application in RefrigerationYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Engineers & EnvironmentDokumen8 halamanEngineers & EnvironmentYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- CA Lab Manual ScopeDokumen10 halamanCA Lab Manual Scopea2367916100% (1)
- ME3162 Questions PDFDokumen2 halamanME3162 Questions PDFYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 7 Suggested AnswersDokumen4 halamanTutorial 7 Suggested AnswersYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Properties and Testing of Materials Chapter 2Dokumen7 halamanMechanical Properties and Testing of Materials Chapter 2Yin HauBelum ada peringkat
- TimetableDokumen2 halamanTimetableYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- LSM1301Dokumen7 halamanLSM1301Yin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer Radiation Problem SetDokumen1 halamanHeat Transfer Radiation Problem SetLakshmi BalasubramaniamBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 7 Suggested AnswersDokumen4 halamanTutorial 7 Suggested AnswersYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- MLE1101 Tutorial 4 - Suggested Solutions AnalysisDokumen7 halamanMLE1101 Tutorial 4 - Suggested Solutions AnalysisYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer Radiation Problem SetDokumen1 halamanHeat Transfer Radiation Problem SetLakshmi BalasubramaniamBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 15Dokumen2 halamanChapter 15Yin HauBelum ada peringkat
- 12 TransientDokumen39 halaman12 TransientYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- MLE1101 - Tutorial 6 - Suggested SolutionsDokumen5 halamanMLE1101 - Tutorial 6 - Suggested SolutionsYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- MLE1101 - Tutorial 1 - Suggested SolutionsDokumen5 halamanMLE1101 - Tutorial 1 - Suggested SolutionsYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- MLE1101 - Tutorial 5 - Suggested SolutionsDokumen5 halamanMLE1101 - Tutorial 5 - Suggested SolutionsYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- MLE1101 - Tutorial 3 - Suggested SolutionsDokumen4 halamanMLE1101 - Tutorial 3 - Suggested SolutionsYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- MLE1101 Tutorial 2 - Suggested Solutions for BCC Crystal Structure, Lattice Constant and Element IdentificationDokumen8 halamanMLE1101 Tutorial 2 - Suggested Solutions for BCC Crystal Structure, Lattice Constant and Element IdentificationYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- LSM1301Dokumen7 halamanLSM1301Yin HauBelum ada peringkat
- EC1301 - Tutorial 4 (14-18 September 2009) - AnswersDokumen9 halamanEC1301 - Tutorial 4 (14-18 September 2009) - AnswersYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- L2 - LeadershipDokumen2 halamanL2 - LeadershipYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration of Elastic Systems FundamentalsDokumen45 halamanVibration of Elastic Systems FundamentalsMD SHAHRIARMAHMUDBelum ada peringkat
- Manuscript AOne DOFCompliantGripperMechanismDokumen28 halamanManuscript AOne DOFCompliantGripperMechanismHo Nhat LinhBelum ada peringkat
- Software Verification: EXAMPLE 6-004Dokumen7 halamanSoftware Verification: EXAMPLE 6-004Sushil DhunganaBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery Solutions ManualDokumen2 halamanKinematics and Dynamics of Machinery Solutions ManualGustavo CopplaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Classification of Indeterminate Structures: StructureDokumen21 halamanUnit Classification of Indeterminate Structures: StructureAyana AlemuBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Android Controlled Pick and Place Robotic ARM Using Bluetooth TechnologyDokumen9 halamanAdvanced Android Controlled Pick and Place Robotic ARM Using Bluetooth Technologypramo_dassBelum ada peringkat
- Very Basic GSADokumen46 halamanVery Basic GSATim ChongBelum ada peringkat
- ME8492 Kinematics of Machinery 03 - by LearnEngineering - inDokumen76 halamanME8492 Kinematics of Machinery 03 - by LearnEngineering - inPrasanna SekarBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics of Machines Fundamental ConceptsDokumen64 halamanMechanics of Machines Fundamental ConceptsRavi TarunBelum ada peringkat
- Optimal Design of a Robotic Positioning Stand for Laparoscopic SurgeryDokumen8 halamanOptimal Design of a Robotic Positioning Stand for Laparoscopic SurgeryEyad Al-MohatwaryBelum ada peringkat
- Robotics Assignment GTU Sem 8 BE Instrumentation and Control EngineeringDokumen2 halamanRobotics Assignment GTU Sem 8 BE Instrumentation and Control Engineeringnandkishor joshiBelum ada peringkat
- Dynpac (EDI SACS Guide)Dokumen78 halamanDynpac (EDI SACS Guide)kleidi85Belum ada peringkat
- Exercise 8 - Femap Example 11 - Analyzing A Beam ModelDokumen24 halamanExercise 8 - Femap Example 11 - Analyzing A Beam ModelDak KaizBelum ada peringkat
- Stiffness by Definition and Direct Stiffness MethodsDokumen56 halamanStiffness by Definition and Direct Stiffness MethodsSmartEngineerBelum ada peringkat
- Machine Elements 1: Engr. Maricel M. MatutoDokumen31 halamanMachine Elements 1: Engr. Maricel M. MatutoCllyan ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Robot ManipulatorDokumen33 halamanIntroduction To Robot Manipulatorchibssa alemayehuBelum ada peringkat
- Solidworks MotionDokumen13 halamanSolidworks MotionJulio Cesar Montoya DelgadoBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematic Motion Analysis of The Human Arm During A Manipulation TaskDokumen7 halamanKinematic Motion Analysis of The Human Arm During A Manipulation TaskPedro RoyuelaNavarroBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematics of Machinery NotesDokumen25 halamanKinematics of Machinery Notesnishanth87Belum ada peringkat
- 2 DOF and 3 DOF Helicopter System Specifications v1.1Dokumen4 halaman2 DOF and 3 DOF Helicopter System Specifications v1.1Laura PrietoBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Robots Part ADokumen12 halamanFundamentals of Robots Part ACody LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank 1st UnitDokumen2 halamanQuestion Bank 1st UnitAlapati RajasekharBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Description: Material PropertiesDokumen9 halamanProblem Description: Material PropertiesAbhishekBelum ada peringkat
- SprutCAM 11 User GuideDokumen1 halamanSprutCAM 11 User GuideRourkela Fabrications Pvt. Ltd.Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 02-Theory of MachinesDokumen6 halamanChapter 02-Theory of Machinesthiva30Belum ada peringkat
- Kinematics of MachineDokumen314 halamanKinematics of MachineMd Ibrahim KhanBelum ada peringkat
- JCG221S11 JCSS Guide To Uncertainty Estimate (Standard Solution) 1/11Dokumen11 halamanJCG221S11 JCSS Guide To Uncertainty Estimate (Standard Solution) 1/11Imad AghilaBelum ada peringkat