Crown Block
Diunggah oleh
Nigin ParambathDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Crown Block
Diunggah oleh
Nigin ParambathHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
11/25/13
CROWN BLOCK
07. CROWN BLOCK 7.1 FUNCTION
- Crown block definition The Crown Block is a fixed set of pulleys(called sheaves) located at the top of thederrick or mast, over which the drilling line isthreaded.The companion blocks to these pulleys arethe travelling blocks. By using two sets ofblocks in this fashion, great mechanicaladvantage is gained, enabling the use ofrelatively small drilling line to hoist loadsmany times heavier than the cable couldsupport as a single strand. - Sheave characteristics The number of sheaves on the two Blocks(Crown and Travelling ) can range from 5 to8 and is a function of the Hoisting systemcapability.The rating of the Crown Block must behigher than the Travelling Blocks.The diameter and the groove of sheavesdepends on the diameter of drilling line inuse. This values are established by thebuilder based the recommendations of APIRP 9B.The ratio of sheaves diameter to drilling linediameter should be between 30-40. Crown Block - API specifications The Crown Block, Travelling Block and the Hook are built in accordance with API specifications8A or 8C. 7.2 TYPES AND CHARACTERISTICS - Groove size The groove on the sheaves must be samesize as the diameter of drilling line used toprovide the right support. (Fig.
apirigroup.com/crown_block.html 1/6
11/25/13
CROWN BLOCK
77) A groove to wide will flatten the drillingline, while a groove to narrow will causehigh friction and excessive wear on thedrilling line. Groove (Fig. 77)
- Typical Derrick Crown Block
7.3 INSPECTIONS
apirigroup.com/crown_block.html 2/6
11/25/13
CROWN BLOCK
- Periodic inspections The Crown Block, as with all Hoisting equipment, must have periodic inspections according to thebuilder's recommendations and API RP 8B.ENI procedures stipulate that the Crown Block be certified every 5 years, in addition to themandatory periodic inspections. - Frequency of Periodic Inspections The frequency of periodic inspections is: - Daily - Monthly - Semi -annual - Annual - Five-year - Table: Periodic Inspection and Maintenance Categories and Frequencies - API Recommended Practice 8B CAT E G OR IE S Category I Observation of equipment during operation for indications of inadequate performance. Category II Category I inspection, plus further inspection for corrosion; deformation; loose or missingcomponents; deterioration; proper lubrication; visible external cracks; and adjustment.
apirigroup.com/crown_block.html 3/6
11/25/13
CROWN BLOCK
Category III Category II inspection, plus further inspection which should include NDE of exposed criticalareas and may involve some disassembly to access specific components and identify wearthat exceeds the manufacturer's allowable tolerances. Category IV Category III inspection, plus further inspection where the equipment is disassembled to theextent necessary to conduct NDE of all primary load carrying components as defined bythe manufacturer. FR E QUE NCY The owner or user of the equipment should develop his own schedule of inspections basedon experience, manufacturer's recommendations, and consideration of one or more of thefollowing factors: - environment; - load cycles; - regulatory requirements; - operating time; - testing; - repairs; - remanufacture As an alternative the owner or user may use Table 1.
- Example of DimensionalInspection a. scheme b. Measures and Methods The Drilling Contractors must havea sheave gauge to carry out thechecks and measurements toevaluate wears.
apirigroup.com/crown_block.html
4/6
11/25/13
CROWN BLOCK
- Example of NDT Inspection
apirigroup.com/crown_block.html
5/6
11/25/13
CROWN BLOCK
apirigroup.com/crown_block.html
6/6
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- API RP 8B Hoisting EquipmentDokumen8 halamanAPI RP 8B Hoisting EquipmentTony NietoBelum ada peringkat
- API Inspection GuideDokumen14 halamanAPI Inspection Guidesouilah100% (1)
- API 4G Inspections PDFDokumen20 halamanAPI 4G Inspections PDFrabeemhBelum ada peringkat
- API RP 8B - Procedures For Inspections, Maintenance, Repair, and Remanufacture of Hoisting EquipmentDokumen8 halamanAPI RP 8B - Procedures For Inspections, Maintenance, Repair, and Remanufacture of Hoisting EquipmentRashid Ghani80% (5)
- API Inspection Categories Drilling RIG Equipment HoistingDokumen5 halamanAPI Inspection Categories Drilling RIG Equipment Hoistingmalikpdj100% (6)
- MAST & SUBSTRUCTURE INSPECTION GUIDEDokumen10 halamanMAST & SUBSTRUCTURE INSPECTION GUIDEAhmed Imtiaz Rao0% (1)
- API RP 4G InspectionDokumen7 halamanAPI RP 4G InspectionChandrasekhar Sonar100% (2)
- Derrick-Mast Inspection ProcedureDokumen3 halamanDerrick-Mast Inspection ProcedureChandrasekhar Sonar100% (3)
- Api RP 8BDokumen6 halamanApi RP 8BAntonio França0% (1)
- NOV Elevator Link CompatibilityDokumen2 halamanNOV Elevator Link CompatibilityisamelgqBelum ada peringkat
- Rig Equipment Audit ChecklistDokumen3 halamanRig Equipment Audit ChecklistKBBelum ada peringkat
- Api 4G PDFDokumen12 halamanApi 4G PDFAluosh AluoshBelum ada peringkat
- +2.5% Metric Stainless Steel Sheave Gauges - API RP-9BDokumen1 halaman+2.5% Metric Stainless Steel Sheave Gauges - API RP-9BDhanraj PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Cat III Inspection Mud 2021Dokumen56 halamanCat III Inspection Mud 2021Fāōū ZīBelum ada peringkat
- HH-Travling BlockDokumen3 halamanHH-Travling Blockabdi rachman100% (2)
- Derrick, Crown & Accessories, National 516 HojasDokumen516 halamanDerrick, Crown & Accessories, National 516 HojasMartin Guerrero100% (7)
- BVM Catelogue New-2016 PDFDokumen116 halamanBVM Catelogue New-2016 PDFOperation100% (1)
- Operation and Maintenance Manual: Samsung Mosvold Main FRH-200-8C Rotary Slip Deadline AnchorDokumen28 halamanOperation and Maintenance Manual: Samsung Mosvold Main FRH-200-8C Rotary Slip Deadline AnchorLukaszBelum ada peringkat
- CP-MP-001 Mud PumpsDokumen6 halamanCP-MP-001 Mud PumpsEd CalheBelum ada peringkat
- Bop Chain Hoists: Subsea Handling EquipmentDokumen2 halamanBop Chain Hoists: Subsea Handling EquipmentLeonardoViannaBelum ada peringkat
- M5329-R0 Dead Line AnchorDokumen26 halamanM5329-R0 Dead Line Anchorandrei20041100% (2)
- YC450-2 Traveling Block Parts ListDokumen1 halamanYC450-2 Traveling Block Parts ListMohamed Medany100% (1)
- RP 10.0 Drawworks Brake Load Path Components VFinal (March 2016)Dokumen15 halamanRP 10.0 Drawworks Brake Load Path Components VFinal (March 2016)NataliyaLukovskaBelum ada peringkat
- QC 006 Rig Inspection WorkshopDokumen132 halamanQC 006 Rig Inspection WorkshopJahel Looti100% (3)
- Api RP 4g OperacionDokumen1 halamanApi RP 4g OperacionÁngel BermúdezBelum ada peringkat
- Stabilizer TypeDokumen14 halamanStabilizer TypeAdin PraviMoški PartAdisBelum ada peringkat
- API 4G InspectionsDokumen20 halamanAPI 4G InspectionsRandy Arnold100% (3)
- Preventive Maintenance Program For Spherical Blowout PreventerDokumen19 halamanPreventive Maintenance Program For Spherical Blowout Preventernjava1978100% (1)
- Intermediate Inspection Criteria, Well Control Equipment: Equipment Group: Shooting NippleDokumen2 halamanIntermediate Inspection Criteria, Well Control Equipment: Equipment Group: Shooting NippleKaleem UllahBelum ada peringkat
- Rig Inspection OutlineDokumen4 halamanRig Inspection OutlineAdolfo Angulo100% (1)
- API RP 7C-11F EnginesDokumen3 halamanAPI RP 7C-11F Enginesmoonstar_dme100% (1)
- Top Drive Inspection PDFDokumen20 halamanTop Drive Inspection PDFAhmed Imtiaz Rao100% (6)
- B+V Manual - Elevator Links PDFDokumen10 halamanB+V Manual - Elevator Links PDFYina UsecheBelum ada peringkat
- Rutong DH 吊环使用说明书(ZY)2013 links - 1Dokumen3 halamanRutong DH 吊环使用说明书(ZY)2013 links - 1QAMAR ALI KHANBelum ada peringkat
- API 16C Choke and KillDokumen26 halamanAPI 16C Choke and Killrps197750% (2)
- API5b Changes in 16th EditionDokumen4 halamanAPI5b Changes in 16th EditionMostafa FikryBelum ada peringkat
- Rig InspectionDokumen7 halamanRig InspectionHuy Ip100% (2)
- Blowout Preventers: Invention Unique Design & Extraordinary CraftsmanshipDokumen40 halamanBlowout Preventers: Invention Unique Design & Extraordinary CraftsmanshipRoxxana Roxxana1990Belum ada peringkat
- Deadline Anchors BrochureDokumen3 halamanDeadline Anchors Brochurejlmunozv100% (2)
- Advance Energy API 4G Inspection ReportDokumen90 halamanAdvance Energy API 4G Inspection ReportMohamed Ismail100% (1)
- Manual Tong WTMDokumen45 halamanManual Tong WTMYuliana Andrea Zapata Rubio100% (1)
- Slips Maintenance, Inspection, & Wear Data PDFDokumen3 halamanSlips Maintenance, Inspection, & Wear Data PDFcorsini999100% (1)
- API Spec 4E App B PDFDokumen3 halamanAPI Spec 4E App B PDFeochiufpic100% (1)
- Hoist Equipment Inspection ProcedureDokumen5 halamanHoist Equipment Inspection ProcedureAhmed Imtiaz Rao100% (1)
- Heavy Lift 25 Ton Rod Elevator Operators Manual: ContentDokumen6 halamanHeavy Lift 25 Ton Rod Elevator Operators Manual: ContentAngel BermudezBelum ada peringkat
- Manual: CDQ (S) Sucker Rod ElevatorsDokumen5 halamanManual: CDQ (S) Sucker Rod ElevatorsDarshan MakwanaBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Operated ElevatorsDokumen124 halamanManual Operated ElevatorsChandrasekhar Sonar100% (3)
- API Standards and Well ControlDokumen9 halamanAPI Standards and Well ControlRobertok1234Belum ada peringkat
- Manual MPC Manual MPCH Master BushingH Master BushingDokumen28 halamanManual MPC Manual MPCH Master BushingH Master BushingMEREUEULEUBelum ada peringkat
- 100027D-CRTi Running Procedure PDFDokumen9 halaman100027D-CRTi Running Procedure PDFAhmed Eid FarhBelum ada peringkat
- API Inspection RP 7G Intervals Drilling RIG & Hoisting Equipment DS1Dokumen2 halamanAPI Inspection RP 7G Intervals Drilling RIG & Hoisting Equipment DS1agusnurcahyo100% (2)
- API Commonly Used Spec's & RP notes: Relevant API Spec'sDokumen11 halamanAPI Commonly Used Spec's & RP notes: Relevant API Spec'sTateoka Manabu100% (1)
- Maintenance Manual Varco ST 80 Roughneck 2 PDFDokumen42 halamanMaintenance Manual Varco ST 80 Roughneck 2 PDFNAMRAJ SHARMABelum ada peringkat
- Bridge Crane Installation ProcedureDokumen7 halamanBridge Crane Installation Procedurenike_y2kBelum ada peringkat
- Enbridge Pipeline Repair Workplan WeldingDokumen23 halamanEnbridge Pipeline Repair Workplan WeldingJesus MaestreBelum ada peringkat
- Module 7 (Maintenance Practices) Sub Module 7.13 (Control Cables) PDFDokumen10 halamanModule 7 (Maintenance Practices) Sub Module 7.13 (Control Cables) PDFshareyhouBelum ada peringkat
- Enbridge Pipeline Repair Workplan Welding PDFDokumen23 halamanEnbridge Pipeline Repair Workplan Welding PDFquiron2014Belum ada peringkat
- QC Fit Sheaves Final ReportDokumen23 halamanQC Fit Sheaves Final ReportJuan Manuel Ortiz RoseroBelum ada peringkat
- IndexDokumen12 halamanIndexdaburto2Belum ada peringkat
- API Rig InspectionDokumen12 halamanAPI Rig Inspectionsmithyry201493% (14)
- Ram PreventerDokumen19 halamanRam PreventerNigin Parambath100% (1)
- Mud PumpsDokumen16 halamanMud PumpsNigin Parambath100% (1)
- Drill PipeDokumen14 halamanDrill PipeNigin Parambath100% (2)
- B5Dokumen1 halamanB5Nigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- Stainless Steel Pressure RatingsDokumen7 halamanStainless Steel Pressure RatingsNauman KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Inside BopDokumen5 halamanInside BopNigin Parambath100% (1)
- DiverterDokumen9 halamanDiverterNigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- Heavy Wall DP & Drill CollarsDokumen13 halamanHeavy Wall DP & Drill CollarsNigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- DerrickDokumen17 halamanDerrickNigin Parambath100% (4)
- HookDokumen11 halamanHookNigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- Nuflo Orifice Plate PDFDokumen8 halamanNuflo Orifice Plate PDFNigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- Jis Gate ValveDokumen1 halamanJis Gate ValveNigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- Boneless Chilly CHICKENDokumen5 halamanBoneless Chilly CHICKENNigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- Ori Flo PDFDokumen14 halamanOri Flo PDFNigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- ASME B16.5 Ring Joint Facings Table DimensionsDokumen1 halamanASME B16.5 Ring Joint Facings Table DimensionsNigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- Know Your Gym: Exercise SafetyDokumen2 halamanKnow Your Gym: Exercise SafetyNigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- Pfi-Es-44 (1999)Dokumen13 halamanPfi-Es-44 (1999)elangopi89100% (1)
- Of-Pla NF00074 1001D PDFDokumen8 halamanOf-Pla NF00074 1001D PDFNigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- KTR Kat99pp01Dokumen0 halamanKTR Kat99pp01Nigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- Chicken GingerDokumen1 halamanChicken GingerNigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- FL4013Dokumen4 halamanFL4013elenic777Belum ada peringkat
- Chicken RoastDokumen5 halamanChicken RoastNigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter5 - Drive CouplingsDokumen90 halamanChapter5 - Drive Couplingsvijay219100% (1)
- Coupling 2Dokumen19 halamanCoupling 2tushar9810080Belum ada peringkat
- KTR Pump-Couplings PDFDokumen44 halamanKTR Pump-Couplings PDFGeorge_Wabag_2014Belum ada peringkat
- InspireFitness M2 WallChartDokumen1 halamanInspireFitness M2 WallChartNigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- Grundfos White PaperDokumen8 halamanGrundfos White PapermishraenggBelum ada peringkat
- Bend Tooling's Tube Bending Tools Set-Up GuideDokumen3 halamanBend Tooling's Tube Bending Tools Set-Up GuideNigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
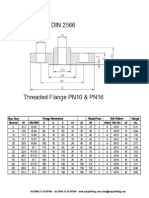
- DIN 2566 Threaded Flange PN10 and PN16Dokumen1 halamanDIN 2566 Threaded Flange PN10 and PN16Nigin ParambathBelum ada peringkat
- Cummins KTA19-G4 Genset Spec SheetDokumen6 halamanCummins KTA19-G4 Genset Spec SheetRonald BoocBelum ada peringkat
- Swimming at Key Stages 1 and 2 Schemes of Work and Session Plans For Advanced SwimmersDokumen20 halamanSwimming at Key Stages 1 and 2 Schemes of Work and Session Plans For Advanced SwimmersShadrack MutisoBelum ada peringkat
- Sine and Cosine Functions WorksheetDokumen6 halamanSine and Cosine Functions WorksheetManya MBelum ada peringkat
- Band III VHF Antennas 174 240 MHZDokumen14 halamanBand III VHF Antennas 174 240 MHZragiBelum ada peringkat
- Aimcat 2201Dokumen29 halamanAimcat 2201Anshul YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Export PDF Tabledit HowDokumen2 halamanExport PDF Tabledit HowWalterBelum ada peringkat
- CV - Nguyen Trung KienDokumen1 halamanCV - Nguyen Trung KienNguyễn Trung KiênBelum ada peringkat
- NetflixDokumen10 halamanNetflixJosue Yael De Los Santos DelgadoBelum ada peringkat
- Subscriber Loop Design LectureDokumen36 halamanSubscriber Loop Design LectureAlas Mallari DonatoBelum ada peringkat
- Barangay Clearance2014Dokumen68 halamanBarangay Clearance2014Barangay PangilBelum ada peringkat
- 9 Little Translation Mistakes With Big ConsequencesDokumen2 halaman9 Little Translation Mistakes With Big ConsequencesJuliany Chaves AlvearBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines For The Operation of Digital FM Radio BroadcastDokumen3 halamanGuidelines For The Operation of Digital FM Radio BroadcastmiyumiBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Hydroelectric Power PlantsDokumen6 halamanDesign of Hydroelectric Power PlantsPDN PRGBelum ada peringkat
- Computers & Industrial Engineering: Guohui Zhang, Xinyu Shao, Peigen Li, Liang GaoDokumen10 halamanComputers & Industrial Engineering: Guohui Zhang, Xinyu Shao, Peigen Li, Liang Gaocloud69windBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S1366554522001557 MainDokumen23 halaman1 s2.0 S1366554522001557 MainMahin1977Belum ada peringkat
- Rutherford Gate Condominiums BLDG C Feature SheetDokumen2 halamanRutherford Gate Condominiums BLDG C Feature SheetCarringtonBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Rooms for Every HomeDokumen4 halamanEssential Rooms for Every HomePamela Joy SangalBelum ada peringkat
- Iso Tc6 ĿDokumen12 halamanIso Tc6 Ŀzrilek1Belum ada peringkat
- Manual Controlador C90Dokumen442 halamanManual Controlador C90Fabián MejíaBelum ada peringkat
- MSCP HND Computing Lo1Dokumen29 halamanMSCP HND Computing Lo1yuulooBelum ada peringkat
- Operation: ManualDokumen43 halamanOperation: Manualsolmolina20100% (1)
- C5-2015-03-24T22 29 11Dokumen2 halamanC5-2015-03-24T22 29 11BekBelum ada peringkat
- Altair's Student Guides - CAE and Design Optimization - AdvancedDokumen70 halamanAltair's Student Guides - CAE and Design Optimization - AdvancedKFourMetrics100% (11)
- Mari Andrew: Am I There Yet?: The Loop-De-Loop, Zigzagging Journey To AdulthoodDokumen4 halamanMari Andrew: Am I There Yet?: The Loop-De-Loop, Zigzagging Journey To Adulthoodjamie carpioBelum ada peringkat
- Factors Affecting Reading at Elsie Lund SchoolDokumen3 halamanFactors Affecting Reading at Elsie Lund SchoolLouise Mikylla LimBelum ada peringkat
- Muhammad Usama: Internship at Ibrahim Fibres Limited, Polyester PlantDokumen20 halamanMuhammad Usama: Internship at Ibrahim Fibres Limited, Polyester PlantUsamaBelum ada peringkat
- 2 X 660MWNCC POWER PROJECT UPS SIZING CALCULATIONDokumen5 halaman2 X 660MWNCC POWER PROJECT UPS SIZING CALCULATIONkkumar_717405Belum ada peringkat
- Methodologies For Sign Language Recognition A SurveyDokumen4 halamanMethodologies For Sign Language Recognition A SurveyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Landscapes: Applications To Clusters, Biomolecules and Glasses (Cambridge Molecular Science)Dokumen6 halamanEnergy Landscapes: Applications To Clusters, Biomolecules and Glasses (Cambridge Molecular Science)darlyBelum ada peringkat
- 5S PDFDokumen41 halaman5S PDFpranayrulzBelum ada peringkat