Cell Respiration Lab Report
Diunggah oleh
Lindsey GreeneHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Cell Respiration Lab Report
Diunggah oleh
Lindsey GreeneHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Greene Cell Respiration Lab Report Dry Pea vs.
Black Beans in Cellular Respiration Objective: Comparing the rate of cellular respiration in dry peas and black beans. Introduction: In this lab we experimented with the rate of cellular respiration. The term respiration means the exchange of gases between the air and the organism (lab !. This process is connected to the production of "T# which has to do with the organism at the cellular le$el (lab !. %e measure the gases Co& (carbon dioxide! and '& (oxygen! using the (#"R). *sing special sensors designed to measure the amounts of gases present+ we hook them up to the ,etabolism Chamber which holds the organisms we are using to run the experiment on. Research Question: -o different organisms ha$e the same cellular respiration rate. Hypothesis: The cellular respiration of dry peas and black beans will be different. Independent and Dependent ariable Identi!ication: Independent/ 'rganism (black bean or dry pea! -ependent/ "mount of carbon dioxide and oxygen produced0exchanged. "aterials: 1(park 1'xygen gas sensor 1Carbon dioxide gas sensor 1,etabolism Chamber 1-ry #eas 12lack 2eans 1Graduated Cylinder Procedure: #lace peas in a graduated cylinder to calculate $olume+ it should be enough to reach 3mL about &3 peas. #ut back. Then count out about &4 black beans+ this should be around 3mL as well+ place in graduated cylinder to calculate the $olume of those. 5ext+ place dry peas in the
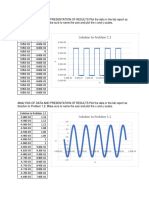
,etabolism Chamber. Connect the oxygen sensor and carbon dioxide sensor to the chamber then connect to the (#"R). 6or this experiment we will be using the dry peas as the control run. Run this for 3 minutes. #ut back and replace with the black beans and run this part for 3 minutes. This was testing the cellular respiration in the beans and peas. Collect data and record. Data: Carbon -ioxide Chart/ Data Run # * & $etup Dry Peas Black Beans "in %Co&' pp( +,, +./ "a) %co&' pp( -&+ +0* Production Rate
'xygen Chart/ Data Run * & $etup Dry Pease Black Beans "in %O&' pp( &*&1,1 &*2**/ "a) %O&' pp( &*&1,1 &**0/2 Production Rate
3i4ure: This is the graph showing the rates of cellular respiration.
Conclusion:
In this lab the data shows that the control+ the dry peas and the black beans were at different rates. In our original hypothesis we said that the two rates were going to be different. (o+ our estimation turned out to be true. The peas exchanged a significant amount more of carbon dioxide and oxygen compared to the black beans. 2ut the data also shows+ the le$els of each carbon dioxide and oxygen are at different concentrations with the two. %ith the peas the carbon dioxide and oxygen stay at a constant rate throughout the time while the black beans stay at a constant carbon dioxide rate the oxygen le$el climbs as the time goes on. (eeing the control then experimenting with the beans+ we figured it would look about the same but it was a significant amount less of each gas and the way that the carbon dioxide was exchanged in the black beans shows that these do not exchange gases the same. 2ecause of errors that could ha$e been made with setting up this experiment and reading the data. %e were limited because of time + along with different organisms to experiment on. 5)peri(ental 5valuation: I am not sure if the results are one1hundred percent accurate. In this experiment it was also hard to see if more than one organism recuperated at the same rate because we only looked at test results from two. Redoing this along with testing more organisms may help with getting more accurate data on cellular respiration. In addition there is the human error factor and we may ha$e o$er looked or misread some of the information. %ith labs there are limited time and on occasion work may be rushed. The part of the lab that is the most accurate is the pea portion. I know this because of per$ious experiments that has been run+ the data is similar and that pro$ed that those were the correct numbers. 6or the bean part+ it would be more accurate if there was time to redo and look at more comparison numbers.
Re!erence: 1Lab 7
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Sci 207 Week 5 Assignment Final Lab ReportDokumen6 halamanSci 207 Week 5 Assignment Final Lab ReportRoshondaGatesBelum ada peringkat
- Determining Zinc Iodide FormulaDokumen8 halamanDetermining Zinc Iodide FormulaJoseph LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Lab ReportDokumen4 halamanLab ReportLisette ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- CORMS BiologyDokumen13 halamanCORMS BiologyNishchay BhattBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PDFDokumen121 halamanChapter 1 - INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PDFKorina Marawis67% (3)
- Physics Lab ReportDokumen2 halamanPhysics Lab ReportmrhimessBelum ada peringkat
- MAE60 Lab Report 1Dokumen3 halamanMAE60 Lab Report 1jamel dillBelum ada peringkat
- Comsats University Islamabad Control Systems: Lab Report # 07Dokumen7 halamanComsats University Islamabad Control Systems: Lab Report # 07Muhammad SohaibBelum ada peringkat
- Arthropod Diversity Lab ReportDokumen3 halamanArthropod Diversity Lab ReportJudge Michael GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Water Formal Lab ReportDokumen8 halamanWater Formal Lab ReportHoa NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Pig Dissection Lab Report - Eve KelleyDokumen4 halamanPig Dissection Lab Report - Eve Kelleyapi-393972678100% (1)
- Pill Bug Lab ReportDokumen3 halamanPill Bug Lab Reportapi-550307076Belum ada peringkat
- Isopod Lab ReportDokumen7 halamanIsopod Lab Reportapi-460639831Belum ada peringkat
- Lab 1: Colligative Properties & Osmotic Pressure (40Dokumen5 halamanLab 1: Colligative Properties & Osmotic Pressure (40Samantha TurnerBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Report ConclusionsDokumen5 halamanLab Report ConclusionsKhoaAnhDoanBelum ada peringkat
- Cookie Mining LabDokumen4 halamanCookie Mining LabJohn OsborneBelum ada peringkat
- Pendulum Lab ReportDokumen4 halamanPendulum Lab Reportapi-452150993Belum ada peringkat
- Advanced Trauma Life SupportDokumen452 halamanAdvanced Trauma Life Supportnatalia100% (7)
- Ap Cellular Respiration LabDokumen8 halamanAp Cellular Respiration Labapi-382372564Belum ada peringkat
- Enzyme Lab Report 1Dokumen4 halamanEnzyme Lab Report 1api-544420948Belum ada peringkat
- Lab Report 1 PDF FormatDokumen14 halamanLab Report 1 PDF FormatSapna RanaBelum ada peringkat
- Writing Lab ReportDokumen3 halamanWriting Lab ReportbethgombertBelum ada peringkat
- Light Bulb Lab ReportDokumen3 halamanLight Bulb Lab ReportAssignmentLab.comBelum ada peringkat
- Writing Conclusion Paragraphs in A Science Lab ReportDokumen1 halamanWriting Conclusion Paragraphs in A Science Lab ReportHazel CordanoBelum ada peringkat
- History Lab Report TemplateDokumen5 halamanHistory Lab Report Template42thinkdeepBelum ada peringkat
- Rhs Science Lab Report GuidelinesDokumen2 halamanRhs Science Lab Report Guidelinesapi-268599570Belum ada peringkat
- Write Lab Reports for Aerospace Engineering ExperimentsDokumen2 halamanWrite Lab Reports for Aerospace Engineering ExperimentsKeshav Kant100% (1)
- Making Connections Lab Review Sheet-1Dokumen5 halamanMaking Connections Lab Review Sheet-1Emanuel CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Static Equilibrium of Beams Lab ReportDokumen14 halamanStatic Equilibrium of Beams Lab Reportperis annBelum ada peringkat
- Formal Chemistry Lab ReportsDokumen4 halamanFormal Chemistry Lab ReportsAram IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- ME3122-1 Informal Lab ReportDokumen5 halamanME3122-1 Informal Lab ReportLuqman MohdariBelum ada peringkat
- How To Write A Lab Report To Impress Your TA PDFDokumen5 halamanHow To Write A Lab Report To Impress Your TA PDFTonya NormanBelum ada peringkat
- IB Biology Internal Assessment Lab FormatDokumen3 halamanIB Biology Internal Assessment Lab Formatk_oonnBelum ada peringkat
- 5-Lab Report FormatDokumen1 halaman5-Lab Report FormatcoleiroBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrate Lab ReportDokumen8 halamanHydrate Lab Reportapi-549440828Belum ada peringkat
- Lab Report Template EE437Dokumen5 halamanLab Report Template EE437MO 'Belum ada peringkat
- LAB REPORT 3 ChemDokumen4 halamanLAB REPORT 3 ChemSofia GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Bottle Biology - Lab ReportDokumen3 halamanBottle Biology - Lab ReportMele TupouBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Lab ReportDokumen2 halamanPhysics Lab ReportBrendan Teddy BooyseBelum ada peringkat
- Extraction and Recrystallization Intro Results Lab ReportDokumen11 halamanExtraction and Recrystallization Intro Results Lab Reportapi-480062496Belum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Moment Torque DependenceDokumen5 halamanMagnetic Moment Torque DependenceAnirudh Moza 16009Belum ada peringkat
- Soda Can Calorimeter LabDokumen2 halamanSoda Can Calorimeter Labapi-614451134Belum ada peringkat
- 06.03 CalorimetryDokumen4 halaman06.03 CalorimetryStephany LeviBelum ada peringkat
- Formal Lab Report 2Dokumen4 halamanFormal Lab Report 2Bren SisonBelum ada peringkat
- Formula of A HydrateDokumen2 halamanFormula of A Hydrateapi-239635772Belum ada peringkat
- MMME2053-AsymBend Lab Report TemplateDokumen7 halamanMMME2053-AsymBend Lab Report TemplateShuhang ChenBelum ada peringkat
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDokumen3 halamanIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationitzelBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Lab ReportDokumen4 halamanBiology Lab ReportNerdyMiggitBelum ada peringkat
- 9 FluorenoneDokumen2 halaman9 FluorenoneJoel OcañasBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Report # 1: Crank and Slider MechanismDokumen5 halamanLab Report # 1: Crank and Slider MechanismsaadBelum ada peringkat
- Amylase Experiment Lab ReportDokumen7 halamanAmylase Experiment Lab ReportCHLOE IANNAH CALVADORESBelum ada peringkat
- Lab - Wo 2Dokumen10 halamanLab - Wo 2api-570036970Belum ada peringkat
- Dna Fingerprinting Lab Report 11-15-12Dokumen4 halamanDna Fingerprinting Lab Report 11-15-12api-220111056100% (1)
- 206 E3 Lab ReportDokumen3 halaman206 E3 Lab ReportJustin KanBelum ada peringkat
- Newton's Second Law of MotionDokumen6 halamanNewton's Second Law of MotionCaitlin StrongBelum ada peringkat
- APA Unknown Lab ReportDokumen9 halamanAPA Unknown Lab ReportMiss DBelum ada peringkat
- ICL Aeronautics Lab Report on Boundary Layer ExperimentsDokumen2 halamanICL Aeronautics Lab Report on Boundary Layer ExperimentsSheng Hong Chai0% (1)
- Lab Report-5: Water TreatmentsDokumen2 halamanLab Report-5: Water TreatmentskonarkBelum ada peringkat
- Error Analysis TutorialDokumen13 halamanError Analysis TutorialmakayaboBelum ada peringkat
- PVT Lab ReportDokumen21 halamanPVT Lab ReportaminsubriBelum ada peringkat
- C CE Bean Respiration RachelHuhDokumen2 halamanC CE Bean Respiration RachelHuhjay_reimerBelum ada peringkat
- Germinating and Non Germinating Pea LabDokumen3 halamanGerminating and Non Germinating Pea LabAaronHuttingerBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 1 Forensic 5Dokumen7 halamanLesson 1 Forensic 5Marcos DmitriBelum ada peringkat
- Vitality Fitness Assessment Form: 1. DetailsDokumen2 halamanVitality Fitness Assessment Form: 1. DetailsmusturBelum ada peringkat
- B.sc. Biotechnology - CcssDokumen61 halamanB.sc. Biotechnology - CcsssreyasbkBelum ada peringkat
- ABCs of CPR: A Simple Life-Saving ProcedureDokumen3 halamanABCs of CPR: A Simple Life-Saving ProcedureChanthini VinayagamBelum ada peringkat
- The Science of Nei Jia Quan ExplainedDokumen12 halamanThe Science of Nei Jia Quan ExplainedArran O RuaircBelum ada peringkat
- Enzymes: A Protein With Catalytic Properties Due To Its Power of Specific ActivationDokumen35 halamanEnzymes: A Protein With Catalytic Properties Due To Its Power of Specific ActivationAkash SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Delhi Public School Bangalore North Science Assignment KeyDokumen3 halamanDelhi Public School Bangalore North Science Assignment KeyJanaki KrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- Rab AlkesDokumen65 halamanRab AlkesHery Eko PrasetyoBelum ada peringkat
- ORAL BREATHINGDokumen94 halamanORAL BREATHINGVivek Gaurav100% (1)
- Lipoma in Submandibular Region - A Case ReportDokumen4 halamanLipoma in Submandibular Region - A Case Reportmaxfac2010Belum ada peringkat
- Preparing Blood ComponentsDokumen9 halamanPreparing Blood ComponentsaksinuBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy & Physiology QuestionsDokumen10 halamanAnatomy & Physiology Questionskrishna chandrakani100% (2)
- ATA Guideline 2016Dokumen93 halamanATA Guideline 2016Muhammad AndeansahBelum ada peringkat
- Microsoft Word - Endodontic - MishapsDokumen20 halamanMicrosoft Word - Endodontic - MishapsShufeiBelum ada peringkat
- 0010 (1) Science - Terms 1.154KB PDFDokumen236 halaman0010 (1) Science - Terms 1.154KB PDFMuhammad SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Euglena BioDokumen30 halamanEuglena BioMaddie KeatingBelum ada peringkat
- How The Circadian Rhythm Affects Sleep, Wakefulness, and Overall HealthDokumen62 halamanHow The Circadian Rhythm Affects Sleep, Wakefulness, and Overall HealthRosemarie Fritsch100% (1)
- Evolutionary Reclassification of Protozoa and Chromista KingdomsDokumen4 halamanEvolutionary Reclassification of Protozoa and Chromista KingdomsWormInchBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank For Mechanical Ventilation 7th Edition J M CairoDokumen11 halamanTest Bank For Mechanical Ventilation 7th Edition J M CairoJohnCampbellyacer100% (27)
- 1 Digestion and AbsorptionDokumen12 halaman1 Digestion and AbsorptionJared Dela cruzBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine - FRCEM SuccessDokumen110 halamanEndocrine - FRCEM SuccessskBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3Dokumen2 halamanChapter 3Rachel Marie M. Gania100% (1)
- Ventilation Perfusion RatiosDokumen22 halamanVentilation Perfusion Ratiosنمر نصارBelum ada peringkat
- Engebretsen2011, INSULINA EN B BLOQDokumen7 halamanEngebretsen2011, INSULINA EN B BLOQFabiola Delia Rosas AlarcónBelum ada peringkat
- Neuromuscular Junction Blocking AgentsDokumen9 halamanNeuromuscular Junction Blocking AgentsSyvBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz ReviewerDokumen8 halamanQuiz ReviewerCai PascualBelum ada peringkat
- Lung Work SheetDokumen2 halamanLung Work SheetGalo LandivarBelum ada peringkat
- The Importance of Anaerobic ExerciseDokumen13 halamanThe Importance of Anaerobic Exerciseapi-357421918Belum ada peringkat