Lecture Notes 6
Diunggah oleh
Peter Jean-jacquesHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Lecture Notes 6
Diunggah oleh
Peter Jean-jacquesHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
'ecture (
GE)$ECH*+C,' +*PU$ F)R $HE DE"+G* )F RE$E*$+)* "$RUC$URE"
J. David Rogers, Ph.D., P.E., P.G.
Karl F. Hasselmann Chair in Geological Engineering Missouri Universit o! "cience # $echnolog !or the course
GE %%& Geotechnical Construction Practice
"tac-ed c clo.ean masonr /alls have .rovided e0cellent service !or man centuries $his is a c clo.ean /all using native roc- and cement mortar, on $ioga Pass high/a , 1ust outside 2osemite *ational Par-, /hich /as com.leted in &3(%
Masonr
/alls can 4e ver resilient
Masonr gravit retaining /all s stems have 4een constructed since ((55 6C in Jericho. 7e can learn much !rom o4serving /hat has survived and /hat has not. $he 4asic o41ective o! earl /alls /as to .rovide militar 4astions and .rotection !rom attac-. Most o! these structures /ere 4uilt using roc- !acing /ith random !ill, as s-etched a4ove.
"tac-ed masonr /all at Macchu Pichu, the lost +nca cit sitting at an altitude o! 8%55 !eet in the Peruvian ,ndes 7ithout mortar or rein!orcement, these /alls have /ithstood centuries o! earth9ua-es, .reci.itation and neglect
,4ove le!t: "tac-ed c clo.ean masonr /all in Guatemala ,4ove right: Undulating masonr roc- retaining /all a4out &55 ears old in Glen/ood ".rings, C). Gravit /alls can /ithstand minor !oundation movements and di!!erential settlement
Masonr retaining /all in Cincinnati accommodates the grade 4 em.lo ing vertical o!!sets, or ;ste.s.< "te.s are usuall em.lo ed 4ecause there is some sacri!ice in load ca.acit i! the /all is 4uilt on=grade. $he di!!erence in cost can 4e su4stantial, /hile the increased active .ressure is usuall 4et/een & and && >, !or ?> to ?5> grades.
Part &
GR,@+$2 7,''"
Gravit 7alls: )ldest and Most
Common 7all " stem
Gravit /alls are designed to use
their e!!ective /eight to resist the lateral .ressures engendered 4 soil 4ac-!ill, considering see.age, surcharge, and earth9ua-e loads
Common !orms o! gravit retaining /all s stems in the modern era
Conventional gravit /alls li-e those sho/n at le!t are graduall 4eing re.laced 4 com4ination s stems, such as the Mechanicall "ta4iliAed Em4an-ment structure, sho/n at right
Four 4asic !ailure modes are considered in the design o! gravit retaining s stems: 4asal slidingB overturning, tiltingC4earing !ailure and glo4al slo.e sta4ilit . 2ouDd 4e sur.rised ho/ o!ten E% is !orgotten or ignored
$he Resultant $hrust, R, must !all /ithin middle third o! the 4ase
F active load against /all 7 F dead /eight o! the /all R F resultant vector thrust
,
$he most 4asic re9uirement o! a gravit /all is that the resultant thrust, R, must .ro1ect /ithin the middle third o! the !ooting
6attered Masonr 7alls
,4ove le!t # right: ,ncient masonr /alls /ere usuall constructed /ith a health 4atter, and drained through natural ga.s. 'o/er le!t: modern e9uivalents are em.lo /ee.holes andCor geomem4rane drains
Roosevelt Dam on the "alt River in ,riAona /as constructed as a c clo.ean masonr gravit dam 4 the U" Reclamation "ervice in &35G=&&
$a.ered or !lared toe
,ncient !orti!ications, li-e Heme1i Castle in Ja.an, /hich dates to &G%(, em.lo ed !lared /alls designed to s.read load over a 4road area, /hile discouraging ascent o! the increasingl stee. !ace
Gravit Retaining 7all "ta4ilit Criteria H Continued
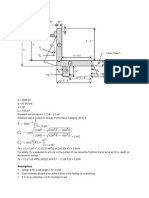
?. Resistance to "liding
= effective thrust of wall, after subtracting the pore pressure
$he 6a less Dam near ,ustin, Penns lvania !ailed 4 4asal sliding along a shale !oundation in &3&&, des.ite the reservoir 4eing lo/ered 4 notching the dam Ile!tJ.
Methods commonl em.lo ed to increase 4ase !riction
$hough not common, 4asal sli. can also occur i! the !ooting em4edment is com.romised and the 4ase o! the !ooting is l ing /ithin saturated ground
, more com.licated chec- is that against 4earing ca.acit and di!!erential settlement, /hich can result 4ecause o! eccentric !orces and inade9uate !ooting design
Passive reaction /edges !orm under di!!ering conditions o! soil !riction. *ote that high !riction soils in!luence a much greater area than lo/er !riction soils
Chart sho/ing decrease in design 4earing ca.acit versus slo.e set4ac- versus .hi angle o! !oundation materials
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Soil PenetrometerDokumen4 halamanSoil PenetrometerPeter Jean-jacquesBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Custom ElementsDokumen5 halamanDesign of Custom ElementsPeter Jean-jacquesBelum ada peringkat
- Sports Field DrainageDokumen3 halamanSports Field DrainagePeter Jean-jacquesBelum ada peringkat
- Keyboard ShortcutsDokumen2 halamanKeyboard ShortcutsUmt KcBelum ada peringkat
- Equipment: Method of Assessment:: Block Extraction and ExaminationDokumen2 halamanEquipment: Method of Assessment:: Block Extraction and ExaminationPeter Jean-jacquesBelum ada peringkat
- Argos Usa - Cements For MasonryDokumen39 halamanArgos Usa - Cements For MasonryPeter Jean-jacques0% (1)
- Cathedral Roof Truss StructureDokumen1 halamanCathedral Roof Truss StructurePeter Jean-jacquesBelum ada peringkat
- RICS Standard Form For Consultants AppointmentDokumen39 halamanRICS Standard Form For Consultants AppointmentPeter Jean-jacquesBelum ada peringkat
- Steel Sheet Piling SpecificationDokumen5 halamanSteel Sheet Piling SpecificationPeter Jean-jacquesBelum ada peringkat
- Approach Slab DetailsDokumen2 halamanApproach Slab DetailsPeter Jean-jacquesBelum ada peringkat
- Metal Spiral Stairs Install ManualDokumen36 halamanMetal Spiral Stairs Install ManualPeter Jean-jacquesBelum ada peringkat
- f' f φ = 29° γ = 120 pcf: AssumptionsDokumen3 halamanf' f φ = 29° γ = 120 pcf: AssumptionsPeter Jean-jacquesBelum ada peringkat
- Weep Hole Part Elevation Section: Drawn: Checked: Approved: Date: CAW 5/9/2011Dokumen1 halamanWeep Hole Part Elevation Section: Drawn: Checked: Approved: Date: CAW 5/9/2011Peter Jean-jacquesBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- A Feasibility/Project Study OnDokumen14 halamanA Feasibility/Project Study OnWilson Domingo LazarteBelum ada peringkat
- Clause: Extra Element + Independent Clause Dependent ClauseDokumen1 halamanClause: Extra Element + Independent Clause Dependent ClauseTieng HuangBelum ada peringkat
- Infinity Tower, Dubai, UAEDokumen10 halamanInfinity Tower, Dubai, UAEryan rakhmat setiadiBelum ada peringkat
- Openstack Deployment Ops Guide PDFDokumen197 halamanOpenstack Deployment Ops Guide PDFBinank PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Project Proposal Environmental Protection Program-DeNRDokumen57 halamanProject Proposal Environmental Protection Program-DeNRLGU PadadaBelum ada peringkat
- (EN) Google Developer Policy - September 1, 2021Dokumen56 halaman(EN) Google Developer Policy - September 1, 2021JimmyBelum ada peringkat
- Kindergarten ArchitectureDokumen65 halamanKindergarten ArchitectureAnushka Khatri83% (6)
- Glide Reflection Folding InstructionsDokumen1 halamanGlide Reflection Folding Instructionsapi-355107616Belum ada peringkat
- Internship Proposal FormDokumen3 halamanInternship Proposal FormMuhammad FidaBelum ada peringkat
- South WestDokumen1 halamanSouth WestDarren RadonsBelum ada peringkat
- 1.4 Creating Graphic OrganizerDokumen1 halaman1.4 Creating Graphic OrganizerTrixie Roselle Y. MesiasBelum ada peringkat
- Demand, Elasticity of Demand and Demand ForecastingDokumen16 halamanDemand, Elasticity of Demand and Demand Forecastingankit thapliyal100% (1)
- West Bengal State University Department of EnglishDokumen33 halamanWest Bengal State University Department of Englishnandan yadavBelum ada peringkat
- Bcos 186Dokumen3 halamanBcos 186Shiv KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Business Advantage Pers Study Book Intermediate PDFDokumen98 halamanBusiness Advantage Pers Study Book Intermediate PDFCool Nigga100% (1)
- Title: Speech of Corazon C. Aquino Before The US Congress: 3 Hours)Dokumen3 halamanTitle: Speech of Corazon C. Aquino Before The US Congress: 3 Hours)Verna TrillanaBelum ada peringkat
- Uplifting Hauora Maori RealDokumen32 halamanUplifting Hauora Maori RealFano AsiataBelum ada peringkat
- Wipro Home Office RangeDokumen8 halamanWipro Home Office RangePrashant RawatBelum ada peringkat
- (Bible in History - La Bible Dans L'histoire 8) John T. Willis - Yahweh and Moses in Conflict - The Role of Exodus 4-24-26 in The Book of Exodus-Peter Lang International Academic Publishers (2010)Dokumen244 halaman(Bible in History - La Bible Dans L'histoire 8) John T. Willis - Yahweh and Moses in Conflict - The Role of Exodus 4-24-26 in The Book of Exodus-Peter Lang International Academic Publishers (2010)Anonymous s3LTiHpc8100% (2)
- PEOPLE v. ROBERTO QUIACHON Y BAYONADokumen11 halamanPEOPLE v. ROBERTO QUIACHON Y BAYONAMarkBelum ada peringkat
- SSP 861603 - EN - Tire Pressure Monitoring SystemsDokumen42 halamanSSP 861603 - EN - Tire Pressure Monitoring Systemsa.diedrichsBelum ada peringkat
- Region XiDokumen2 halamanRegion XiGarcia, Rafael Rico O.Belum ada peringkat
- Neighbor'S Plot - : Sheet No Rev No R0Dokumen1 halamanNeighbor'S Plot - : Sheet No Rev No R0jibeesh cmBelum ada peringkat
- Resume For Singapore Spass Civil EngineerDokumen8 halamanResume For Singapore Spass Civil EngineerArul SD100% (1)
- Small Incision Cataract SurgeryDokumen249 halamanSmall Incision Cataract SurgeryAillen YovitaBelum ada peringkat
- Why Do Climates Change ?: Climate Changes Over The Last MillenniumDokumen44 halamanWhy Do Climates Change ?: Climate Changes Over The Last Millenniumshaira alliah de castroBelum ada peringkat
- AutoPIPE Tutorial PDFDokumen156 halamanAutoPIPE Tutorial PDFdhaktodesatyajitBelum ada peringkat
- Theological Differences Between Christianity and IslamDokumen18 halamanTheological Differences Between Christianity and IslamMencari KhadijahBelum ada peringkat
- Cooper - Formal Review of Karla Noles RaDokumen6 halamanCooper - Formal Review of Karla Noles RaMark CooperBelum ada peringkat
- Motivation MBADokumen31 halamanMotivation MBAAkshitaBelum ada peringkat