Sample 1st Midterm 2
Diunggah oleh
Dr. Madhukar VableHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Sample 1st Midterm 2
Diunggah oleh
Dr. Madhukar VableHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EXAM 1
MEEM 4150
Oct. 7th, 2003
y
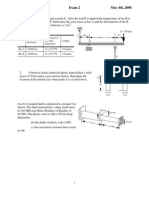
Answers are at of this exam. 1. (a) Show the non-zero stress components on the A,B, and C faces of the cube. Use the coordinate system that is given only.
xx = 80MPa ( T ) yx = 30 MPa zx = 0 xy = 30 MPa yy = 0 zy = 70MPa xz = 0 yz = 70MPa zz = 40MPa ( C )
z
. .
x
(b) Draw the shear stress due to torsion on the stress cubes at points A and B. Is the shear stress positive or negative? Circle the appropriate answers
x
A
y x
A B
(xy)A = positive / negative
x
(xy)B = positive / negative
(c) Assuming a positive shear force Vy in bending (a) sketch the direction of the shear ow along the center-line on the thin cross-sections shown. (b) At points A, B, C, and D, determine if the stress component is xy or xz and if it is positive, negative, or zero. Circle the appropriate answers
y B
(xy)A or (xz)A positive / negative / zero
D
(xy)B or (xz)B positive / negative/ zero (xy)C or (xz)C positive / negative/ zero
C A
(xy)D or (xz)D positive / negative/ zero
0.2 ( 40 x )
(d) The axial strain in a 20 in. long rod is given by xx = --------------------- . Determine the elongation of the rod. 2 (e) The displacements u and v in the x and y directions respectively were measured by Moire' interferometry. Displacements of 9 points on the body and are as given below.Using central difference, determine the shear strain xy at point 5.
Point 1 2 3 4 5 u (mm) 0.000 -0.112 -0.128 0.112 -0.032 v (mm) 0.000 0.144 0.256 0.176 0.224 Point 6 7 8 9 u (mm) -0.080 0.128 -0.048 0.128 v (mm) 0.240 0.384 0.336 0.384
y 7 h 4 h 1
h = 0.0005 mm
8 5 2 h h 9 6 3 x
2.
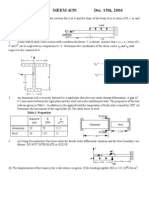
The stress at a point is given by the stress matrix:
40 20 10 20 30 0 ksi 10 0 zz
The three principal stresses of the matrix are: 1 = 56.21 ksi ( T ) 2 = 14.95 ksi ( T ) 3 = 51.16 ksi ( C ) (a) Determine the three stress invariants. (b) Determine the stress zz. (c) Determine the orientation of principal direction associated with principal stress 14.95 ksi (T). (d) The material yield stress is 120 ksi in tension. Determine the factor of safety at the point using octahedral shear stress theory (e) A crack was discovered on a plane that has an outward normal at angles of 36.87o, 60.0o, and 70.63o with the x, y and z axis respectively. The critical stress intensity factor for the material is 22 ksi in , what would be the critical crack length on that plane. 3. A beam is loaded and supported as shown. Determine the slope and the reaction force at point B in terms of w, L, E, and I. Use the coordinate system shown.( BE METHODICAL)
y w kN./m
3 2 -- wL kN-m 2
wL kN.
Lm
Lm
Answers
1b (xy)A = negative (xy)B = positive 1c (xz)A negative (xz)B positive 1d. Elongation = 0.005 in 2a. I1= 20 ksi I2= - 2800 ksi2 (xy)C positive 1e. xy = 128 rads I3= - 42991.8 ksi3. y =37.29o or 142.7o z =-84.8o or 95.2o (xz)D negative
2b zz = 50 ksi (C) 2c. x = 53.2o or 126.8o 2d. K=1.27 2e. 2acrit = 0.4305 in
5wL ------------- rads 3. slope= 48EI
3
- kN force= -------
wL 8
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Statics ReviewDokumen0 halamanStatics ReviewDr. Madhukar VableBelum ada peringkat
- Numerical Methods ReviewDokumen0 halamanNumerical Methods ReviewDr. Madhukar VableBelum ada peringkat
- Matrix Algebra ReviewDokumen0 halamanMatrix Algebra ReviewDr. Madhukar VableBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Final Exam 1Dokumen1 halamanSample Final Exam 1Dr. Madhukar VableBelum ada peringkat
- Sample SyllabusDokumen1 halamanSample SyllabusDr. Madhukar VableBelum ada peringkat
- Introductory Mechanics of Materials ReviewDokumen0 halamanIntroductory Mechanics of Materials ReviewDr. Madhukar Vable100% (1)
- Sample Final Exam 2Dokumen2 halamanSample Final Exam 2Dr. Madhukar VableBelum ada peringkat
- Final MEEM 4150 Dec. 16th, 2003: Fig. 1 Fig. 2Dokumen1 halamanFinal MEEM 4150 Dec. 16th, 2003: Fig. 1 Fig. 2Rayleight SilversBelum ada peringkat
- EM 440 Exam 2 May 4th, 2000: P 20 KipsDokumen2 halamanEM 440 Exam 2 May 4th, 2000: P 20 KipsRayleight SilversBelum ada peringkat
- Exam 2 MEEM 4150 Nov. 19th, 2003: I 0.463 10 MM I 1.013 10 MMDokumen2 halamanExam 2 MEEM 4150 Nov. 19th, 2003: I 0.463 10 MM I 1.013 10 MMRayleight SilversBelum ada peringkat
- Using energy methods to find reaction force and slope of a beamDokumen2 halamanUsing energy methods to find reaction force and slope of a beamRayleight SilversBelum ada peringkat
- Sample 1st Midterm 3Dokumen2 halamanSample 1st Midterm 3Dr. Madhukar VableBelum ada peringkat
- Sample 2nd Midterm 2Dokumen2 halamanSample 2nd Midterm 2Dr. Madhukar VableBelum ada peringkat
- Sample 1st Midterm 1Dokumen2 halamanSample 1st Midterm 1Dr. Madhukar VableBelum ada peringkat
- Sample 1st Midterm 4Dokumen2 halamanSample 1st Midterm 4Dr. Madhukar VableBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics of Materials GlossaryDokumen0 halamanMechanics of Materials GlossaryDr. Madhukar Vable100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- 1.experiment On Single Rotor SystemDokumen8 halaman1.experiment On Single Rotor SystemRahul Kumar DwivediBelum ada peringkat
- SX001a en EU Example Simply Supported Laterally UnrestrainedDokumen9 halamanSX001a en EU Example Simply Supported Laterally UnrestrainedJamesBelum ada peringkat
- Turbomacchine PDFDokumen2 halamanTurbomacchine PDFCarlos RodriguesBelum ada peringkat
- EmtlDokumen62 halamanEmtlsiri.pogulaBelum ada peringkat
- Rajasthan Public Service Commission - 2016: Paper: VPITI-CivilDokumen24 halamanRajasthan Public Service Commission - 2016: Paper: VPITI-CivilCgpscAspirantBelum ada peringkat
- 8403 - PDF - CH07 - Cópia PDFDokumen28 halaman8403 - PDF - CH07 - Cópia PDFRichard De Medeiros CastroBelum ada peringkat
- CE-515: Design of Steel StructuresDokumen15 halamanCE-515: Design of Steel StructuresZiaullahBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis Main GuruDokumen44 halamanThesis Main GuruGuruprasad KadamBelum ada peringkat
- Group Theory ReportDokumen12 halamanGroup Theory ReportlunarcausticacBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 3 Equilibrium: Engineering MechanicsDokumen6 halamanChapter - 3 Equilibrium: Engineering MechanicsSagheer AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- MATH 181-Oblique Triangles and Vectors (11) Term 0306Dokumen16 halamanMATH 181-Oblique Triangles and Vectors (11) Term 0306SharmaineTaguitagOmliBelum ada peringkat
- Molecular spectroscopy energy levelsDokumen5 halamanMolecular spectroscopy energy levelsAHANA MAITYBelum ada peringkat
- Formation Damage MechanismSkinDokumen101 halamanFormation Damage MechanismSkinBolsec14100% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics Unit 5Dokumen68 halamanEngineering Mechanics Unit 5SundraBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Semiconductor DevicesDokumen658 halamanPrinciples of Semiconductor Deviceskrechba92% (13)
- Forces in Equilibrium on Inclined PlanesDokumen16 halamanForces in Equilibrium on Inclined PlanesPauling ChiaBelum ada peringkat
- Turbidity Currents and Hydraulic JumpsDokumen37 halamanTurbidity Currents and Hydraulic JumpsVenkataraju BadanapuriBelum ada peringkat
- Jan 2017Dokumen7 halamanJan 2017kirthikaBelum ada peringkat
- Atomic Physics and Nuclear PhysicsDokumen8 halamanAtomic Physics and Nuclear Physicskaranubhab3Belum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic Forces in COMSOLDokumen10 halamanElectromagnetic Forces in COMSOLAlkalin100% (1)
- Types of Radio Waves and ApplicationsDokumen11 halamanTypes of Radio Waves and Applicationsultra dubsBelum ada peringkat
- Encyclopedia of Mathematical Physics Vol.5 S-Y Ed. Fran Oise Et AlDokumen471 halamanEncyclopedia of Mathematical Physics Vol.5 S-Y Ed. Fran Oise Et AlDavid Iveković100% (9)
- Chapter 01 IntroductionDokumen21 halamanChapter 01 Introductionprraaddeej chatelBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Chemistry ModelsDokumen19 halamanNuclear Chemistry ModelsAbdul Jabbar Abdul JabbarBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes On X RayDokumen6 halamanLecture Notes On X RayHyacinthe KOSSIBelum ada peringkat
- Exp-2 Compression TestDokumen10 halamanExp-2 Compression TestHanamant HunashikattiBelum ada peringkat
- Grains Structure of IngotsDokumen6 halamanGrains Structure of Ingotshayder1920Belum ada peringkat
- Transmission Lines and Wave GuidesDokumen2 halamanTransmission Lines and Wave Guidesमेनसन लाखेमरूBelum ada peringkat
- The SIESTA Method For Ab Initio Order-N Materials SimulationDokumen36 halamanThe SIESTA Method For Ab Initio Order-N Materials SimulationsolisiusBelum ada peringkat
- A Worm GearDokumen19 halamanA Worm GearPetrus Malailak0% (1)