ICE Plant
Diunggah oleh
01parthHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ICE Plant
Diunggah oleh
01parthHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
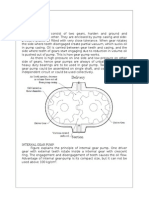
ICE PLANT: Figure shows the layout of an ICE plant.
The ice used for commercial purposes is produced by freezing potable water in standard cans placed in rectangular tanks which are filed with chilled brine. In order to enhance the heat transfer from the water, agitators are employed to keep brine solution in constant motion. The brine temperature is maintained at - 10 0C to - 12 0C by the refrigeration plant. The refrigerant used is generally ammonia as it has excellent thermal properties like high refrigerating effect per kg of refrigerant and low specific volume. Working: The high temperature, high pressure refrigerant vapours leaving the compressor are condensed in the condenser (shell and tube type or evaporative type). The condensed liquid refrigerant is collected in the receiver and then expanded through the expansion valve. Due to expansion, the pressure of the liquid refrigerant is considerably reduced. The liquid refrigerant then passes through the evaporator coils surrounding the brine tank in which brine is filled. The low pressure liquid refrigerant absorbs the heat from the brine solution (equivalent to latent heat of vaporization), get converted to vapour state and once again fed to the compressor to complete the cycle. Generally NaCl (sodium chloride) or CaCl (calcium chloride) is used as brine. NaCl is preferably used because of its low cost and as it is less injurious.The ice cans are fabricated from the galvanized steel sheets and are given chromium plating to prevent corrosion due to chemical reactions.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
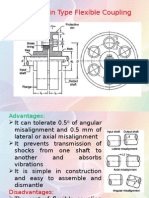
- Levers:: Pivoted About The FulcrumDokumen14 halamanLevers:: Pivoted About The Fulcrum01parthBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulic FluidsDokumen5 halamanHydraulic Fluids01parthBelum ada peringkat
- Hermetically Sealed CompressorDokumen1 halamanHermetically Sealed Compressor01parthBelum ada peringkat
- Venturi MeterDokumen4 halamanVenturi Meter01parthBelum ada peringkat
- Bushed Pin CouplingDokumen12 halamanBushed Pin Coupling01parthBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Water CoolersDokumen4 halamanStudy of Water Coolers01parth0% (1)
- Study of Power Transmission DevicesDokumen11 halamanStudy of Power Transmission Devices01parthBelum ada peringkat
- Isometric Drawing Exercises 3Dokumen2 halamanIsometric Drawing Exercises 301parth0% (1)
- Hydraulic Pumps - Gear PumpsDokumen2 halamanHydraulic Pumps - Gear Pumps01parthBelum ada peringkat
- Actuation of Double Acting Cylinder:: Hydraulic CircuitsDokumen2 halamanActuation of Double Acting Cylinder:: Hydraulic Circuits01parthBelum ada peringkat
- PLCDokumen31 halamanPLC01parthBelum ada peringkat
- How Two Stroke Engine WorksDokumen7 halamanHow Two Stroke Engine Works01parthBelum ada peringkat
- Steam Jet Refrigeration System and ICe RefrigerationDokumen9 halamanSteam Jet Refrigeration System and ICe Refrigeration01parthBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Exhaust Gas AnalyserDokumen7 halamanStudy of Exhaust Gas Analyser01parth100% (1)
- Gear PumpDokumen2 halamanGear Pump01parth100% (1)
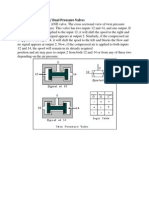
- Twin Pressure ValveDokumen1 halamanTwin Pressure Valve01parth50% (2)
- Shuttle Valve:: ApplicationsDokumen1 halamanShuttle Valve:: Applications01parthBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Reciprocating Air CompressorDokumen4 halamanStudy of Reciprocating Air Compressor01parth100% (5)
- Refrigeration ApplicationsDokumen3 halamanRefrigeration Applications01parth100% (2)
- Windows Air ConditionerDokumen6 halamanWindows Air Conditioner01parthBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)