Human Digestive System
Diunggah oleh
fatimah17Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Human Digestive System
Diunggah oleh
fatimah17Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Human Digestive System
Digestive System Label Me! Printout (Simple version) Digestive System Label Me! Printout
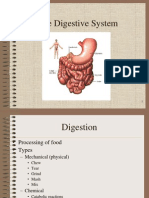
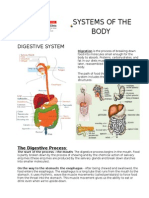
The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that processes food. In order to use the food we eat, our body has to break the food down into smaller molecules that it can process; it also has to excrete waste. Most of the digestive organs (like the stomach and intestines) are tube-like and contain the food as it makes its way through the body. The digestive system is essentially a long, twisting tube that runs from the mouth to the anus, plus a few other organs (like the liver and pancreas) that produce or store digestive chemicals.
The Digestive Process:
The start of the process - the mouth: The digestive process begins in the mouth. Food is partly broken down by the process of chewing and by the chemical action of salivary enzymes (these enzymes are produced by the salivary glands and break down starches into smaller molecules). On the way to the stomach: the esophagus - After being chewed and swallowed, the food enters the esophagus. The esophagus is a long tube that runs from the mouth to the stomach. It uses rhythmic, wave-like muscle movements (called peristalsis) to force food from the throat into the stomach. This muscle movement gives us the ability to eat or drink even when we're upside-down. In the stomach - The stomach is a large, sack-like organ that churns the food and bathes it in a very strong acid (gastric acid). Food in the stomach that is partly digested and mixed with stomach acids is called chyme.
In the small intestine - After being in the stomach, food enters the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine. It then enters the jejunum and then the ileum (the final part of the small intestine). In the small intestine, bile (produced in the liver and stored in the gall bladder), pancreatic enzymes, and other digestive enzymes produced by the inner wall of the small intestine help in the breakdown of food. In the large intestine - After passing through the small intestine, food passes into the large intestine. In the large intestine, some of the water and electrolytes (chemicals like sodium) are removed from the food. Many microbes (bacteria like Bacteroides, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella) in the large intestine help in the digestion process. The first part of the large intestine is called the cecum (the appendix is connected to the cecum). Food then travels upward in the ascending colon. The food travels across the abdomen in the transverse colon, goes back down the other side of the body in the descending colon, and then through the sigmoid colon. The end of the process - Solid waste is then stored in the rectum until it is excreted via the anus.
Digestive System Glossary:
abdomen - the part of the body that contains the digestive organs. In human beings, this is between the diaphragm and the pelvis alimentary canal - the passage through which food passes, including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, and anus. anus - the opening at the end of the digestive system from which feces (waste) exits the body. appendix - a small sac located on the cecum. ascending colon - the part of the large intestine that run upwards; it is located after the cecum. bile - a digestive chemical that is produced in the liver, stored in the gall bladder, and secreted into the small intestine. cecum - the first part of the large intestine; the appendix is connected to the cecum. chyme - food in the stomach that is partly digested and mixed with stomach acids. Chyme goes on to the small intestine for further digestion. descending colon - the part of the large intestine that run downwards after the transverse colon and before the sigmoid colon. digestive system - (also called the gastrointestinal tract or GI tract) the system of the body that processes food and gets rid of waste. duodenum - the first part of the small intestine; it is C-shaped and runs from the stomach to the jejunum. epiglottis - the flap at the back of the tongue that keeps chewed food from going
down the windpipe to the lungs. When you swallow, the epiglottis automatically closes. When you breathe, the epiglottis opens so that air can go in and out of the windpipe. esophagus - the long tube between the mouth and the stomach. It uses rhythmic muscle movements (called peristalsis) to force food from the throat into the stomach. gall bladder - a small, sac-like organ located by the duodenum. It stores and releases bile (a digestive chemical which is produced in the liver) into the small intestine. gastrointestinal tract - (also called the GI tract or digestive system) the system of the body that processes food and gets rid of waste. ileum - the last part of the small intestine before the large intestine begins. intestines - the part of the alimentary canal located between the stomach and the anus. jejunum - the long, coiled mid-section of the small intestine; it is between the duodenum and the ileum. liver - a large organ located above and in front of the stomach. It filters toxins from the blood, and makes bile (which breaks down fats) and some blood proteins. mouth - the first part of the digestive system, where food enters the body. Chewing and salivary enzymes in the mouth are the beginning of the digestive process (breaking down the food). pancreas - an enzyme-producing gland located below the stomach and above the intestines. Enzymes from the pancreas help in the digestion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the small intestine. peristalsis - rhythmic muscle movements that force food in the esophagus from the throat into the stomach. Peristalsis is involuntary - you cannot control it. It is also what allows you to eat and drink while upside-down. rectum - the lower part of the large intestine, where feces are stored before they are excreted. salivary glands - glands located in the mouth that produce saliva. Saliva contains enzymes that break down carbohydrates (starch) into smaller molecules. sigmoid colon - the part of the large intestine between the descending colon and the rectum. stomach - a sack-like, muscular organ that is attached to the esophagus. Both chemical and mechanical digestion takes place in the stomach. When food enters the stomach, it is churned in a bath of acids and enzymes. transverse colon - the part of the large intestine that runs horizontally across the abdomen.
Eye Anatomy
Our eyes are organs that let us see. Eyes detect both brightness and color. Having two eyes separated on our face enables us to have depth perception (the ability to see the world in three dimensions - 3D).
How we see: A whole series of events happens in order for us to see something. First, light must reflect off an object. The light travels through the clear cornea of the eye, and then the lens, which focuses the light onto the retina (the sensory tissue lining the back of the eye). In the retina, cells called rods detect light (they are photoreceptors) and cones detect colors. The rods and cones convert light rays into electrical impulses that are relayed to the brain along the optic nerve. The brain interprets the signals from the eyes and we then "see" what we are looking at.
Definitions:
Aqueous humor - the clear, watery fluid inside the eye. It provides nutrients to the eye. Astigmatism - a condition in which the lens is warped, causing images not to focus properly on the retina. Binocular vision - the coordinated use of two eyes which gives the ability to see the world in three dimensions - 3D. Cones - cells the in the retina that sense color. People have three types of cones, L cones that sense long wavelengths (reds, yellows), M cones that sense medium wavelengths (greens), and S cones that sense medium wavelengths (violets, blues). Cornea - the clear, dome-shaped tissue covering the front of the eye. Eyebrow - a patch of dense hair located above the eye. Eyelash - one of the many hairs on the edge of the eyelids. Eyelid - the flap of skin that can cover and protect the eye. Farsighted - (also called hyperopia) a condition in which distant objects are seen more clearly than nearby objects because light is focused behind the retina, not on it. Iris - the colored part of the eye - it controls the amount of light that enters the eye by changing the size of the pupil. Lens - a crystalline structure located just behind the iris - it focuses light onto the retina. Nearsighted - (also called myopia) a condition in which nearby objects are seen more clearly than distant objects because light is focused in front of the the retina, not on it.
Optic nerve - (also called cranial nerve II) the nerve that transmits electrical impulses from the retina to the brain. Pupil - the opening in the center of the iris- it changes size as the amount of light changes (the more light, the smaller the hole). Retina - light-sensitive tissue that lines the back of the eye. It contains millions of photoreceptors (rods and cones) that convert light rays into electrical impulses that are relayed to the brain via the optic nerve. Rods - cells the in the retina that sense brightness (they are photoreceptors). Night vision involves mostly rods (not cones). There are many more rods than cones. Tear - clear, salty liquid that is produced by glands in the eyes. Vitreous - a thick, transparent liquid that fills the center of the eye - it is mostly water and gives the eye its form and shape (also called the vitreous humor). 20/20 Vision - normal human vision, a condition in which a person can see a letter of a specific size from a distance of 20 feet.
Label the Eye Diagram #2
Human Anatomy
Read the definitions, then label the eye anatomy diagram below.
Cornea - the clear, dome-shaped tissue covering the front of the eye. Eyebrow - a patch of dense hair located above the eye. Eyelash - one of the many hairs on the edge of the eyelids. Eyelid - the flap of skin that can cover and protect the eye. Iris - the colored part of the eye - it controls the amount of light that enters the eye by changing the size of the pupil. Lens - a crystalline structure located just behind the iris - it focuses light onto the retina. Optic nerve - the nerve that transmits electrical impulses from the retina to the brain. Pupil - the opening in the center of the iris- it changes size as the amount of light changes (the more light, the smaller the hole). Retina - sensory tissue that lines the back of the eye. It contains millions of photoreceptors (rods and cones) that convert light rays into electrical impulses that are relayed to the brain via the optic nerve. Tear - clear, salty liquid that is produced by glands in the eyes. Vitreous - a thick, transparent liquid that fills the center of the eye - it is mostly water and gives the eye its form and shape (also called the vitreous humor).
Questions regarding the Digestive System
1. Which of the following is not part of the accessory organs in the digestive system? a) b) c) d) liver pancreas large intestines sublingual salivary gland
2. The structure of the alimentary canal wall has 4 layers, from deep to superficial, they are a) b) c) d) mucosa, submucosa, serosa, muscularis layer mucosa, submucosa, muscularis layer, serosa mucosa, muscularis layer, submucosa, serosa mucosa, serosa, muscularis layer, submucosa
3. The mouth is adapted to take in food from the external environment and to begin preparing it for a) b) c) absorption secretion reabsorption
d)
digestion
4. What is the function of the soft palate? a) b) c) d) to keep opening to nasal cavity open at all times to keep opening to nasal cavity open during swallowing to keep opening to nasal cavity closed during swallowing to keep opening nasal cavity closed at all times
5. There are _______ deciduous teeth and _________ permanent teeth. a) b) c) d) 20, 30 20, 32 18, 30 18, 32
6. Which of the following is not a function of salivary glands? a) b) c) d) start digestion of proteins helps bind food particles secrete saliva makes taste possible
7. What are the names of the 3 salivary glands? a) b) c) d) parotid glands, submandibular glands, submaxillary glands parotid glands, submandibular glands, sublaryngeal glands parotid glands, submandibular glands, sublingual glands parotid glands, submandibular glands, subpharygneal glands
8. Which of the following is not a function of the stomach? a) receives food
b) c) d)
mixes food with gastric juice carries out limited amount of absorption moves food into the large intestine
9. The sphincter that serves as a valve between the stomach and small intestine is a) b) c) d) cardiac sphincter pyloric sphincter glossopharygeal sphincter intestinal sphincter
10. The regulation of gastric secretion is enhanced by a) b) c) d) stimulation of parasympathetic nervous system and the hormone gastrin stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system and the hormone gastrin inhibition of the parasympathetic nervous system and the hormone gastrin inhibition of the sympathetic nervous system and the hormone secretin
11. The presence of food in the small intestine a) b) c) increase gastric secretion inhibit gastric secretion has no effect on gastric secretion
12. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes that can split a) b) c) d) carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals carbohydrates, proteins, fats, nucleic acids proteins, fats, nucleic acid, water proteins, fats, nucleic acid, vitamins
13. The names of the 2 hormones that influence pancreatic secretion are
a) b) c) d)
secretin, cholecystokinin secretin, renin aldosterone, cholecystokinin vasopressin, cholecystokinin
14. The function of the liver is to a) b) c) d) metabolize carbohydrates, lipids and proteins filtration of blood detoxification of chemicals all of the above
15. Bile is just one of the livers many secretions that directly influence digestion. a) b) this statement is true this statement is false
16. The components of bile include: bile salts, bile pigments, cholesterol and various electrolytes. Which of the components in bile have digestive functions? a) b) c) d) bile salts bile pigments cholesterol all of the above
17. Which of the following is not a function of the small intestines? a) b) c) d) receives secretions from the pancreas and liver completes digestion of nutrients absorbs products of digestion transports the residue to the anal canal
18. The parts of the small intestine (start with the part closest to the stomach) are a) b) c) d) duodenum, jejunum, ileum duodenum, ileum, jejunum ileum, jejunum, duodenum ileum, duodenum, jejunum
19. Which of the following statement is false regarding absorption in the small intestines? a) b) c) d) villi increase the surface area of the intestinal wall to increase absorption monosaccharides, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol can be absorbed by the villi fat molecules enter from the lacteals of the villi all of the above is true
20. Which of the following statement is false regarding the function of the large intestines? a) b) c) d) the only important secretion is mucous feces are formed and stored here main absorption is water and electrolytes digestive activity remain high in the large intestines
21. Which of the following is not a source of carbohydrates? a) b) c) d) starch amino acids glycogen disaccharides
22. Which of the following concerning lipids is false? a) b) lipids are organic compounds that supply energy lipids are used to build cell structures
c) d)
all lipids contain fat-soluble vitamins metabolism of triglycerides is controlled predominately by liver and adipose tissues
23. Some of the functions of proteins include a) b) c) d) serves as structural material and act as enzymes provide energy a and b none of the above
24. The digestive enzyme pepsin secreted by gastric glands begins the digestion of a) b) c) carbohydrates protein fat
25. Which of the following enzymes is present in secretions of the mouth, stomach, and pancreas? a) b) c) d) amylase trypsin lipase lactase
26. Carbohydrates are ingested in such foods as a) b) c) meat and seafoods bread and pasta butter and margarine
27. Glucose can be stored as glycogen in the a) blood plasma
b) c)
connective tissue liver
28. Carbohydrates are acted on by a) b) c) d) peptidases, trypsin and chymotrypsin amylase, maltase and sucrase lipases peptidases, lipases and galactase
29. The parasympathetic nervous system influences digestion by a) b) c) d) relaxing smooth muscles stimulating peristalsis and secretatory activity constricting sphincters none of these
30. The digestive juice product containing enzymes capable of digesting all 4 major foodstuff categories is a) b) c) d) pancreatic gastric salivary biliary
31. The site of production of cholecystokinin is a) b) c) d) the stomach the small intestine the pancreas the large intestine
32. Which of the following is not a characteristic of the large intestine?
a) b) c) d)
it is divided into ascending, transverse, and descending portions it contains abundant bacteria, some of which synthesize certain vitamins is the main absorptive site it absorbs much of the water and salts remaining in the wastes
33. The gallbladder a) b) c) d) produces bile is attached to the pancreas stores and concentrates bile produces secretin
Digestive System Quiz
The first section of the quiz is True or False statements. Read the statements carefully and then click on the word TRUE or FALSE that comes after each statement.
1. The job of the digestive system is to break food down so that our bodies 2. 3. 4.
5. 6.
can use it as fuel or energy. TRUE or FALSE Your stomach is located right behind your belly button. TRUE or FALSE Your small intestine is approximately 20 - 25 inches long. TRUE or FALSE The Large Intestine is responsible for removing water from the undigested food, turning it from a liquid paste into solid waste. TRUE or FALSE The esophagus is a muscular tube that carries food from our mouth to our stomach. TRUE or FALSE Everything we eat is completely digested and used by our bodies. TRUE or FALSE
This section is multiple choice. Read the question then click on the answer you think is correct.
1. What is inside your stomach that helps break food down into a thick
liquid paste? a) water b) acids and enzymes c) villi 2. What are the tiny finger-like projections called that are inside the small intestine? These tiny finger-like projections absorb the nutrients form the food and send the vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates and fats into our bloodstream. a) esophagus b) arteries c) villi 3. After the food leaves our stomach it heads into which part of the digestive system? a) esophagus b) pancreas c) small intestine d) large intestine 4. What is removed from the undigested food when it is in the Large Intestine? a) water b) nutrients c) energy d) sugar
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Circulatory SystemDokumen10 halamanCirculatory SystemKent Clark VillaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Note Human Anatomy and Fisiologi (Skeletal System)Dokumen13 halamanLecture Note Human Anatomy and Fisiologi (Skeletal System)Muhammad FaizBelum ada peringkat
- Muscle SystemDokumen7 halamanMuscle System910907Belum ada peringkat
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDokumen4 halamanRespiratory and Circulatory SystemsRommel BauzaBelum ada peringkat
- Reproductive SystemDokumen6 halamanReproductive SystemDara BMBelum ada peringkat
- BiologyDokumen30 halamanBiologyChristel Ramos100% (1)
- Human Digestive SystemDokumen39 halamanHuman Digestive SystemSha KhinaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology: The CellDokumen8 halamanAnatomy and Physiology: The Celllourd nabBelum ada peringkat
- Homeostasis and Physiological Processes - ScholisticoDokumen23 halamanHomeostasis and Physiological Processes - ScholisticojoffuhBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Activity No. 9: The Frog Respiratory SystemDokumen4 halamanLaboratory Activity No. 9: The Frog Respiratory SystemMaricris GuillermoBelum ada peringkat
- Foundations of Pharmacology NotesDokumen5 halamanFoundations of Pharmacology NotesSheril MarekBelum ada peringkat
- Chloroplast Photosynthesis-FileDokumen17 halamanChloroplast Photosynthesis-Filesiguro hwahahahBelum ada peringkat
- Homeostasis Grade XDokumen32 halamanHomeostasis Grade XFebrian Andrei100% (1)
- Digestive System in HumanDokumen20 halamanDigestive System in Humanapi-400692183Belum ada peringkat
- Inorganic Compounds and SolutionsDokumen22 halamanInorganic Compounds and SolutionsSophia RoseBelum ada peringkat
- Ection I. The Female Reproductive System 1-1. GENERALDokumen9 halamanEction I. The Female Reproductive System 1-1. GENERALNheil_Christop_4211Belum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology by DoctorDokumen3 halamanPharmacology by DoctorLae DujonBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology of ThyroidDokumen9 halamanPhysiology of ThyroidAbby EvangelistaBelum ada peringkat
- Digestive SystemDokumen36 halamanDigestive Systembjbitscs21Belum ada peringkat
- Female Reproductive SystemDokumen7 halamanFemale Reproductive SystemyannieBelum ada peringkat
- HomeostasisDokumen16 halamanHomeostasisDr M K GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Types of MusclesDokumen1 halamanTypes of Musclesapi-323141584Belum ada peringkat
- Anatomy: Blood Is A Specialized Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances SuchDokumen5 halamanAnatomy: Blood Is A Specialized Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Suchjeoffrey_castroBelum ada peringkat
- Human Respiration HandoutDokumen4 halamanHuman Respiration HandoutJulius GutierrezBelum ada peringkat
- Biodiversity and Conservation A Level NotesDokumen8 halamanBiodiversity and Conservation A Level NotesNaseer SiddiquiBelum ada peringkat
- PharmaDokumen12 halamanPharmaPamela Reinn SulpaBelum ada peringkat
- Chap OutlineDokumen8 halamanChap OutlinedurrieBelum ada peringkat
- Circulatory System SummaryDokumen3 halamanCirculatory System SummaryNiel S. DefensorBelum ada peringkat
- The Human Nervous Syste1Dokumen10 halamanThe Human Nervous Syste1taytay321Belum ada peringkat
- Integumentary System OutlineDokumen7 halamanIntegumentary System OutlineRogie P. BacosaBelum ada peringkat
- Handouts in Skeletal SystemDokumen6 halamanHandouts in Skeletal SystemShiela Mae EslumBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 AnaPhy Notes - ReviewerDokumen6 halamanChapter 1 AnaPhy Notes - ReviewerDanielle LeighBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory System: Nose and NostrilsDokumen8 halamanRespiratory System: Nose and NostrilsKabang MoaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure and Functions PPT 5Dokumen24 halamanCell Structure and Functions PPT 5rajesh dua100% (1)
- Nervous System: Plant Responses To Environmental Changes Are Coordinated by Hormones. Hormones, Also Referred ToDokumen6 halamanNervous System: Plant Responses To Environmental Changes Are Coordinated by Hormones. Hormones, Also Referred ToJan Alixia BasilioBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction of AnatomyDokumen18 halamanIntroduction of Anatomyjames nginyangiBelum ada peringkat
- Homeostasis LessonDokumen34 halamanHomeostasis LessonPrab NathanBelum ada peringkat
- Skeletal Muscle Lab ReportDokumen3 halamanSkeletal Muscle Lab Reportapi-296589762Belum ada peringkat
- Female Reproduction Female Reproductive Parts and Functions II. Oogenesis and OvulationDokumen4 halamanFemale Reproduction Female Reproductive Parts and Functions II. Oogenesis and OvulationLana GalloBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem Pencernaan (Digestion System)Dokumen28 halamanSistem Pencernaan (Digestion System)PaRaDoX eLaKSaMaNaBelum ada peringkat
- Excretory System FinalDokumen15 halamanExcretory System FinalJames AysonBelum ada peringkat
- The CerebrumDokumen27 halamanThe Cerebrumapi-19916399Belum ada peringkat
- Body TissuesDokumen29 halamanBody TissuesRod100% (1)
- Control and Coordination NotesDokumen5 halamanControl and Coordination NotesNyra HillsBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology NotesDokumen4 halamanPhysiology NotesGizem OsmanogluBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of Digestive SystemDokumen34 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of Digestive SystemIan IsidroBelum ada peringkat
- HomeostasisDokumen12 halamanHomeostasisTimothy StanleyBelum ada peringkat
- Hapter: Cell As A Unit of LifeDokumen29 halamanHapter: Cell As A Unit of LifeShu85Belum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of Urinary SystemDokumen43 halamanAnatomy of Urinary SystemIrfan Ali JunejoBelum ada peringkat
- Short Note Biology Form 5-Chapter 3 Coordination and ResponseDokumen6 halamanShort Note Biology Form 5-Chapter 3 Coordination and Responsesalamah_sabri75% (4)
- Anatomy & Physiology: What Is Anatomy? Maintaining LifeDokumen10 halamanAnatomy & Physiology: What Is Anatomy? Maintaining LifeRachel MarquezBelum ada peringkat
- Study Guide 24 - Urinary SystemDokumen19 halamanStudy Guide 24 - Urinary SystemcharlesBelum ada peringkat
- The Nervous SystemDokumen8 halamanThe Nervous SystemananthBelum ada peringkat
- Sheep Heart Dissection LabDokumen6 halamanSheep Heart Dissection Labchocoangel21Belum ada peringkat
- The Integumentary SystemDokumen16 halamanThe Integumentary SystemRix Casas AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- Human Digestive SystemDokumen3 halamanHuman Digestive SystemFazil AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- The Digestive System - Docx - WengDokumen6 halamanThe Digestive System - Docx - WengRowena Panga CalibaraBelum ada peringkat
- Digestive SystemDokumen4 halamanDigestive SystemVictoria VictoriaBelum ada peringkat
- Systems of The Body (Digestive)Dokumen3 halamanSystems of The Body (Digestive)KryztalGhail LlanoraBelum ada peringkat
- The Mouth Starts Everything MovingDokumen10 halamanThe Mouth Starts Everything MovingGedette L. de TazaBelum ada peringkat
- Optimal Nutrition For ExerciseDokumen19 halamanOptimal Nutrition For ExerciseEashwar Prasad Meenakshi100% (2)
- First Periodical Test Science & Health IvDokumen4 halamanFirst Periodical Test Science & Health Ivcrisanto_oroceoBelum ada peringkat
- CHBH13 - Laboratory Manual 4Dokumen8 halamanCHBH13 - Laboratory Manual 4Ysa DienteBelum ada peringkat
- BIO103 Course Syllabus - IQACDokumen14 halamanBIO103 Course Syllabus - IQACBarnardoBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of Biomedical Treatments For Autism: by James B. Adams, PH.DDokumen28 halamanSummary of Biomedical Treatments For Autism: by James B. Adams, PH.DOtto F OttOBelum ada peringkat
- GRDDS 2021Dokumen94 halamanGRDDS 2021Shubh AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Isabela State University City of Ilagan CampusDokumen27 halamanIsabela State University City of Ilagan CampusCharlz ZipaganBelum ada peringkat
- Agriculture Paper 2Dokumen16 halamanAgriculture Paper 2tuhvohhBelum ada peringkat
- TissueSalts PDFDokumen2 halamanTissueSalts PDFkanpsn100% (10)
- To Study The Digestion of Starch by SaliDokumen13 halamanTo Study The Digestion of Starch by Salibalbir rajBelum ada peringkat
- Sodium Carbonate, Milk and Indicator LipaseDokumen14 halamanSodium Carbonate, Milk and Indicator LipaseStephen AreriBelum ada peringkat
- Schuessler Tissue Salts HandbookDokumen52 halamanSchuessler Tissue Salts HandbookBashir Ahmed100% (2)
- Digestive TractDokumen5 halamanDigestive TractSharon GabrielBelum ada peringkat
- Project On FlourDokumen31 halamanProject On FlourRanjeet Rajput100% (5)
- Year 4 Reading Your Digestive SystemDokumen11 halamanYear 4 Reading Your Digestive SystemMa Donabel LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Monogastric Digestive SystemDokumen25 halamanMonogastric Digestive SystemMae Sntg OraBelum ada peringkat
- محاضرات الكيمياء كاملة PDFDokumen124 halamanمحاضرات الكيمياء كاملة PDFفراس الموسويBelum ada peringkat
- Anemia Nursing Care PlanDokumen3 halamanAnemia Nursing Care PlanRosita HutamiBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Ayurveda For Yoga Practitioners - Part III - Agni and AmaDokumen3 halamanEssential Ayurveda For Yoga Practitioners - Part III - Agni and AmaArvind PavariyaBelum ada peringkat
- Wax and EstersDokumen7 halamanWax and EstersPamela Mae UcabBelum ada peringkat
- Trắc Nghiệm AVCN Dược 1Dokumen12 halamanTrắc Nghiệm AVCN Dược 119150004Belum ada peringkat
- Inglés II - TP 1 ResueltoDokumen15 halamanInglés II - TP 1 ResueltoDani100% (1)
- Fit For Life - Food CombiningDokumen6 halamanFit For Life - Food CombininghistorymakeoverBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 ProteinDokumen11 halamanChapter 4 ProteinAmbreen GhafoorBelum ada peringkat
- Parasitic Adaptation PDFDokumen6 halamanParasitic Adaptation PDFmubarik Hayat50% (2)
- Food PyramidDokumen12 halamanFood PyramidAgnes Enya LorraineBelum ada peringkat
- Feed Product ListDokumen2 halamanFeed Product ListBrian BobbyBelum ada peringkat
- 10X SARQ - F - Life ProcessesDokumen2 halaman10X SARQ - F - Life Processesdevsindhuofficial1379Belum ada peringkat
- Science SeminarDokumen9 halamanScience SeminarLeo PrabhuBelum ada peringkat
- Soalan Science PMR Kertas 1 2006Dokumen21 halamanSoalan Science PMR Kertas 1 2006Azim SufieBelum ada peringkat
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Dari EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Penilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDari EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (404)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDari EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsBelum ada peringkat
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDari EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (31)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (42)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDari EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDari EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BePenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDari EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (82)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryDari EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (46)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDari EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDari EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (4)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDari EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesDari EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (1412)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDari EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearDari EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (23)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Dari EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (110)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDari EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDari EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (170)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDari EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (8)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDari EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (328)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassDari EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (27)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingDari EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1138)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeDari EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (253)