(C) (F) Metals and Metal Alloys Plain Carbon and Low Alloy Steels
Diunggah oleh
Reza KurniawanJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
(C) (F) Metals and Metal Alloys Plain Carbon and Low Alloy Steels
Diunggah oleh
Reza KurniawanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
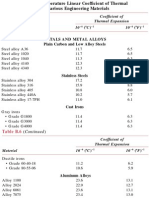
Table B.
6 Room-Temperature Linear Coefficient of Thermal
Expansion Values for Various Engineering Materials
Coefficient of
Thermal Expansion
Material
Steel
Steel
Steel
Steel
Steel
10
alloy
alloy
alloy
alloy
alloy
Stainless
Stainless
Stainless
Stainless
Stainless
A36
1020
1040
4140
4340
alloy
alloy
alloy
alloy
alloy
304
316
405
440A
17-7PH
( C)
10
METALS AND METAL ALLOYS
Plain Carbon and Low Alloy Steels
11.7
11.7
11.3
12.3
12.3
6.5
6.5
6.3
6.8
6.8
Stainless Steels
17.2
15.9
10.8
10.2
11.0
9.6
8.8
6.0
5.7
6.1
Cast Irons
Gray irons
Grade G1800
Grade G3000
Grade G4000
11.4
11.4
11.4
6.3
6.3
6.3
(F)
Table B.6 (Continued)
Coefficient of
Thermal Expansion
Material
10
Ductile irons
Grade 60-40-18
Grade 80-55-06
11.2
10.6
Alloy
Alloy
Alloy
Alloy
Alloy
1100
2024
6061
7075
356.0
C11000
C17200
C26000
C36000
C71500
C93200
(electrolytic tough pitch)
(berylliumcopper)
(cartridge brass)
(free-cutting brass)
(coppernickel, 30%)
(bearing bronze)
Alloy AZ31B
Alloy AZ91D
(C)
10
6.2
5.9
Aluminum Alloys
23.6
22.9
23.6
23.4
21.5
13.1
12.7
13.1
13.0
11.9
Cop
p er Alloys
17.0
16.7
19.9
20.5
16.2
18.0
9.4
9.3
11.1
11.4
9.0
10.0
Magnesium Alloys
26.0
26.0
14.4
14.4
Titanium Alloys
Commercially pure (ASTM grade 1)
8.6
Alloy Ti-5Al-2.5Sn
9.4
Alloy Ti-6Al-4V
8.6
4.8
5.2
4.8
Precious Metals
14.2
9.1
19.7
7.9
5.1
10.9
Gold (commerically pure)
Platinum (commercially pure)
Silver (commercially pure)
Refractory Metals
Molybdenum (commercially pure)
4.9
Tantalum (commercially pure)
6.5
Tungsten (commercially pure)
4.5
Miscellaneous Nonferrous Alloys
Nickel 200
13.3
Inconel 625
12.8
Monel 400
13.9
Haynes alloy 25
12.3
Invar
1.6
Super invar
0.72
Kovar
5.1
Chemical lead
29.3
Antimonial lead (6%)
27.2
Tin (commercially pure)
23.8
LeadTin solder (60Sn-40Pb)
24.0
Zinc (commercially pure)
23.032.5
Zirconium, reactor grade 702
5.9
( F)
2.7
3.6
2.5
7.4
7.1
7.7
6.8
0.9
0.40
2.8
16.3
15.1
13.2
13.3
12.718.1
3.3
Table B.6 (Continued)
Coefficient of
Thermal Expansion
Material
10
(C)
10
( F)
GRAPHITE, CERAMICS, AND SEMICONDUCTING MATERIALS
Aluminum oxide
99.9% pure
7.4
4.1
96%
7.4
4.1
90%
7.0
3.9
Concrete
10.013.6
5.67.6
Diamond (natural)
0.111.23
0.060.68
Gallium arsenide
5.9
3.3
Glass, borosilicate (Pyrex)
3.3
1.8
Glass, sodalime
9.0
5.0
Glass ceramic (Pyroceram)
6.5
3.6
Graphite
Extruded
2.02.7
1.11.5
Isostatically molded
2.26.0
1.23.3
Silica, fused
0.4
0.22
Silicon
2.5
1.4
Silicon carbide
Hot pressed
4.6
2.6
Sintered
4.1
2.3
Silicon nitride
Hot pressed
2.7
1.5
Reaction bonded
3.1
1.7
Sintered
3.1
1.7
9.6
5.3
Zirconia, 3 mol% Y2O3
POLYMERS
Elastomers
Butadiene-acrylonitrile (nitrile)
Styrene-butadiene (SBR)
Silicone
Epoxy
Nylon 6,6
Phenolic
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT)
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polyester (thermoset)
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
Polyethylene
Low density (LDPE)
High density (HDPE)
Ultrahigh molecular weight
(UHMWPE)
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)
Polypropylene (PP)
Polystyrene (PS)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
235
220
270
81117
144
122
108171
122
100180
7285
130
125
150
4565
80
68
6095
68
55100
4047
180400
106198
234360
100220
59110
130200
117
90162
146180
90150
126216
90180
65
5090
81100
5083
70120
50100
Table B.6 (Continued)
Coefficient of
Thermal Expansion
Material
10
(C)
10
( F)
FIBER MATERIALS
Aramid (Kevlar 49)
Longitudinal direction
Transverse direction
Carbon (PAN precursor)
Standard modulus
Longitudinal direction
Transverse direction
Intermediate modulus
Longitudinal direction
High modulus
Longitudinal direction
Transverse direction
E Glass
COMPOSITE
Aramid fibers-epoxy matrix (Vf 0.6)
Longitudinal direction
Transverse direction
High modulus carbon fibers-epoxy
matrix (Vf
0.6)
Longitudinal direction
Transverse direction
0.6)
E glass fibers-epoxy matrix (Vf
Longitudinal direction
Transverse direction
Wood
Douglas fir (12% moisture)
Parallel to grain
Perpendicular to grain
Red oak (12% moisture)
Parallel to grain
Perpendicular to grain
2.0
60
1.1
33
0.6
10.0
0.3
5.6
0.6
0.3
0.5
7.0
5.0
0.28
3.9
2.8
MATERIALS
4.0
70
2.2
40
0.5
32
0.3
18
6.6
30
3.7
16.7
3.85.1
25.433.8
2.22.8
14.118.8
4.65.9
30.639.1
2.63.3
17.021.7
Sources: ASM Handbooks, Volumes 1 and 2, Engineered Materials Handbooks, Volumes 1 and 4, Metals Handbook: Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and
Pure Metals, Vol. 2, 9th edition, and Advanced Materials & Processes, Vol. 146, No.
4, ASM International, Materials Park, OH; Modern Plastics Encyclopedia 96, The
McGraw-Hill Companies, New York, NY; R. F. Floral and S. T. Peters, Composite Structures and Technologies, tutorial notes, 1989; and manufacturers technical
data sheets.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Thermal Expansion Data Table Tb06Dokumen4 halamanThermal Expansion Data Table Tb06Brandon HillBelum ada peringkat
- DeZURIK KCG Knife Gate ValvesDokumen12 halamanDeZURIK KCG Knife Gate ValvesKithkarnonBelum ada peringkat
- A Guide To Nickel AlloysDokumen2 halamanA Guide To Nickel Alloysaliali2662Belum ada peringkat
- A07-297 OD Expanded Small PartsDokumen12 halamanA07-297 OD Expanded Small PartsKyle DriscollBelum ada peringkat
- TUBACEX Power Generation 10Dokumen12 halamanTUBACEX Power Generation 10walitedisonBelum ada peringkat
- A 106 GR BDokumen3 halamanA 106 GR BEzequiel CeccarelliBelum ada peringkat
- 2016-2017 Shurjoint General CatalogDokumen217 halaman2016-2017 Shurjoint General CatalogsafirioBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Index For ManufacturingDokumen6 halamanCost Index For ManufacturingSari OctavianiBelum ada peringkat
- E ValuesDokumen3 halamanE ValuesthirumalaichettiarBelum ada peringkat
- Linear Coefficients of ExpansionDokumen12 halamanLinear Coefficients of ExpansionVBT1Belum ada peringkat
- MaterialData - 14076 HDS H13Dokumen2 halamanMaterialData - 14076 HDS H13Amol KulkarniBelum ada peringkat
- ECOLINE GL - 7247.11-10 - Type Series BookletDokumen8 halamanECOLINE GL - 7247.11-10 - Type Series BookletpauloBelum ada peringkat
- Pipes and Tubes - Temperature ExpansionDokumen3 halamanPipes and Tubes - Temperature ExpansionkaderovichBelum ada peringkat
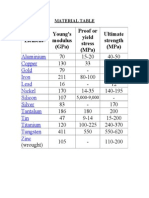
- Element Young'S Modulus (Gpa) Proof or Yield Stress (Mpa) Ultimate Strength (Mpa)Dokumen3 halamanElement Young'S Modulus (Gpa) Proof or Yield Stress (Mpa) Ultimate Strength (Mpa)Rudrendu ShekharBelum ada peringkat
- Line Pipe StandardsDokumen70 halamanLine Pipe StandardsggrapsasBelum ada peringkat
- Selection of Engg Materials of Equipment and Piping SystemDokumen17 halamanSelection of Engg Materials of Equipment and Piping SystemNiraj PandyaBelum ada peringkat
- Bronze Ball Valves: 600 PSI/41.4 Bar Non-Shock Cold Working Pressure 150 PSI/10.3 Bar Saturated SteamuDokumen1 halamanBronze Ball Valves: 600 PSI/41.4 Bar Non-Shock Cold Working Pressure 150 PSI/10.3 Bar Saturated SteamuRuben AranaBelum ada peringkat
- Alloy Guide 2011Dokumen12 halamanAlloy Guide 2011bbmoksh100% (1)
- 15-7 Mo Data BulletinDokumen16 halaman15-7 Mo Data BulletinmsdoharBelum ada peringkat
- Production Technology Ch05Dokumen11 halamanProduction Technology Ch05Nimmagadda BharathBelum ada peringkat
- Data Sheet: C-Mag Hs 7Dokumen2 halamanData Sheet: C-Mag Hs 7SarahBlueGazitanBelum ada peringkat
- Cyclohexane Production Unit: Presented by Brian CliftonDokumen28 halamanCyclohexane Production Unit: Presented by Brian Cliftonalpha2013Belum ada peringkat
- Downhole Tubing/casingDokumen6 halamanDownhole Tubing/casingDwiki RamadhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Ball Valve Full Bore - Butt Weld End: 1 No MaterialDokumen1 halamanBall Valve Full Bore - Butt Weld End: 1 No Materialshashikanth79Belum ada peringkat
- PTE LTD: Dimensional Specification (Inch) For Stud Bolts As Per Asme B18.2.1Dokumen4 halamanPTE LTD: Dimensional Specification (Inch) For Stud Bolts As Per Asme B18.2.1Balderas Rosas WilibaldoBelum ada peringkat
- Shurjoint Geral 2015 English v3 ImpDokumen218 halamanShurjoint Geral 2015 English v3 ImpBárbara VoltarelliBelum ada peringkat
- ASTM A426 Centrifugally Cast Ferritic Alloy Steel Pipe For High - Temperature ServiceDokumen4 halamanASTM A426 Centrifugally Cast Ferritic Alloy Steel Pipe For High - Temperature ServiceSumedh ParadkarBelum ada peringkat
- TEP0011Dokumen2 halamanTEP0011slygerBelum ada peringkat
- 42crmo4 - HardnessDokumen8 halaman42crmo4 - HardnessavijayakumarsamyBelum ada peringkat
- Astm A 576Dokumen5 halamanAstm A 576Chistian AcostaBelum ada peringkat
- BETE TF MetricDokumen2 halamanBETE TF Metricajo2402Belum ada peringkat
- Datasheet DMV 347 HFGDokumen4 halamanDatasheet DMV 347 HFGClaudia MmsBelum ada peringkat
- The Theory and Practice of Steam Reforming: By: Gerard B. Hawkins Managing Director, CEODokumen0 halamanThe Theory and Practice of Steam Reforming: By: Gerard B. Hawkins Managing Director, CEOBalaji RamanBelum ada peringkat
- UBAN Catalogue EDokumen12 halamanUBAN Catalogue EErcan YilmazBelum ada peringkat
- AppDokumen55 halamanAppJediKnight012Belum ada peringkat
- Engineering and Technical Data: High-Pressure Hose PumpsDokumen2 halamanEngineering and Technical Data: High-Pressure Hose PumpsterrorfordBelum ada peringkat
- Plastic Material SelectionDokumen62 halamanPlastic Material SelectiondarshanmrBelum ada peringkat
- CDA110 Specifaction SheetDokumen5 halamanCDA110 Specifaction SheetGendakensBelum ada peringkat
- Stainless AISI 3XXDokumen3 halamanStainless AISI 3XXThitaphol HuyananBelum ada peringkat
- Boiler and AuxiliariesDokumen29 halamanBoiler and Auxiliariesnsarav100% (1)
- Datasheet DMV 304 HCu 20081118Dokumen4 halamanDatasheet DMV 304 HCu 20081118Anuj ShahiBelum ada peringkat
- Temperature Expansion Coefficients For Some Common Piping MaterialsDokumen4 halamanTemperature Expansion Coefficients For Some Common Piping MaterialsJesseBautistaBelum ada peringkat
- Student Name ID: Aysha Housani 200503484 Maha Al Shehhi 200509462 Hessa Al Shehhi 200509582 Mona Thabet 200521150Dokumen78 halamanStudent Name ID: Aysha Housani 200503484 Maha Al Shehhi 200509462 Hessa Al Shehhi 200509582 Mona Thabet 200521150minumcincauBelum ada peringkat
- Typ 08417 1 enDokumen1 halamanTyp 08417 1 enSanthoesh srinivasanBelum ada peringkat
- Cross Reference of The Engg MaterialDokumen18 halamanCross Reference of The Engg Materialrksahay100% (1)
- Spring Materials (Round Wire)Dokumen6 halamanSpring Materials (Round Wire)Kishore BhatBelum ada peringkat
- No10 Machine Ability RatingsDokumen6 halamanNo10 Machine Ability RatingsochoadavidBelum ada peringkat
- SteelDokumen38 halamanSteelArdeela IlezBelum ada peringkat
- PeDokumen55 halamanPeمنير أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- Advances in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells XDari EverandAdvances in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells XMihails KusnezoffBelum ada peringkat
- Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsDari EverandPipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (10)
- Fundamentals of Industrial Heat Exchangers: Selection, Design, Construction, and OperationDari EverandFundamentals of Industrial Heat Exchangers: Selection, Design, Construction, and OperationBelum ada peringkat
- Recent Advances in the Science and Technology of Zeolites and Related Materials: Proceedings of the 14th International Zeolite Conference, Cape Town, South Africa, 25-30th April 2004Dari EverandRecent Advances in the Science and Technology of Zeolites and Related Materials: Proceedings of the 14th International Zeolite Conference, Cape Town, South Africa, 25-30th April 2004Belum ada peringkat
- Heating Systems Troubleshooting & Repair: Maintenance Tips and Forensic ObservationsDari EverandHeating Systems Troubleshooting & Repair: Maintenance Tips and Forensic ObservationsBelum ada peringkat
- Materials Data for Cyclic Loading: Low-Alloy SteelsDari EverandMaterials Data for Cyclic Loading: Low-Alloy SteelsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Oil and Gas Pipelines and Piping Systems: Design, Construction, Management, and InspectionDari EverandOil and Gas Pipelines and Piping Systems: Design, Construction, Management, and InspectionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (16)
- Ceramics for Environmental SystemsDari EverandCeramics for Environmental SystemsLianzhou WangBelum ada peringkat
- (C) (F) Metals and Metal Alloys Plain Carbon and Low Alloy SteelsDokumen4 halaman(C) (F) Metals and Metal Alloys Plain Carbon and Low Alloy SteelsReza KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- Achieving Technical Milestones: Continuity and Change During 175 Years of SulzerDokumen3 halamanAchieving Technical Milestones: Continuity and Change During 175 Years of SulzerReza KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- SS304 304L Data SheetDokumen2 halamanSS304 304L Data SheetPrakash KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Chloe Grace MoretzDokumen1 halamanChloe Grace MoretzReza Kurniawan0% (1)
- 34 Jigs and Fixtures For Machine ShopDokumen12 halaman34 Jigs and Fixtures For Machine ShopPRASAD326100% (8)
- Powder Metallurgy Powders & Equipment ManufacturersDokumen2 halamanPowder Metallurgy Powders & Equipment ManufacturersReza KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Cad/Cam Using MastercamDokumen29 halamanIntroduction To Cad/Cam Using MastercammangulupradhanBelum ada peringkat
- Working Plan: NO Urutan Kerja Alat Potong VC N A FZ F VFDokumen1 halamanWorking Plan: NO Urutan Kerja Alat Potong VC N A FZ F VFReza KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- Chloe Grace MoretzDokumen1 halamanChloe Grace MoretzReza KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- Bottle Caps: 1. Process of ManufacturingDokumen5 halamanBottle Caps: 1. Process of ManufacturingReza KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- Program Setup SheetDokumen5 halamanProgram Setup SheetReza KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- Bottle Caps: 1. Process of ManufacturingDokumen5 halamanBottle Caps: 1. Process of ManufacturingReza KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- ResaDokumen4 halamanResaReza KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- ResaDokumen4 halamanResaReza KurniawanBelum ada peringkat