Physics SPM
Diunggah oleh
Iman0%(1)0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
6K tayangan2 halamanImportant notes and law for SPM physics.
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniImportant notes and law for SPM physics.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0%(1)0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
6K tayangan2 halamanPhysics SPM
Diunggah oleh
ImanImportant notes and law for SPM physics.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
SPM Physics 2009.
Speed Distance / Time taken
Velocity Displacement / Time taken
Newton’s First Law of Object will remain moving / rest unless acted by
Motion (Inertia) unbalance fore
Momentum Product of mass and velocity. mv
Conservation of If there’s a collision, initial momentum = final
momentum momentum
Balanced force Do not affect an object’s motion. Eg, Engine speed up
the car, air resistance slow down the car. But the force
is balance. Therefore, car move in constant speed &
direction.
Unbalanced force Affect an object’s motion.
Newton’s Second Law Acceleration directly proportional to net force but
of Motion inversely proportional to mass. F=ma
Impulsive force Rate of change of momentum
Impulse Change in momentum
Equilibrium force Zero net force
Work Product of applied force and displacement. W=Fs
Conservation of energy Energy can transform from one kind to another
Hooke’s Law Force applied to a spring is directly proportional to
spring extension
Pressure Force / Area
Pascal’s Principle Force applied = force produced . FA=FA
Archimedes Principle Buoyant force = Fluid displaced by object
Bernoulli’s Principle When speed increase, pressure decrease
Thermal equilibrium No net heat flow
Specific heat capacity Amount of heat needed to change temperature of 1 kg
by 1 K
Boyle’s Law Pressure increase, volume decrease (inversely
proportional) PV
Charles’ Law Volume increase, temperature increase (directly
proportional) V/T
Pressure Law Pressure increase, temperature increase (directly
proportional) P/T
Damping Oscillating system that loses energy to the surrounding
Reflection of wave Constant frequency, wavelength, speed
Refraction of wave Constant frequency.
Change wavelength and speed.
*in deep area, longer wavelength and less speed
Diffraction of wave Constant frequency, wavelength, speed. Only direction
of propagation changed.
Coherent wave Same wavelength, frequency
Interference Two wave meets
Sound wave AmpLitude – Louder
Frequency – Pitch
Electromagnetic Range of low frequency to high frequency
spectrum
Ohm’s Law Current is directly proportional to potential difference
Circuits Series Circuit Parallel Circuit
Iman’s Property 2009
I=I=I I=I+I
V=V+V V=V=V
R=R+R 1/R=1/R+1/R
Electromotive force (V) Work done by cell
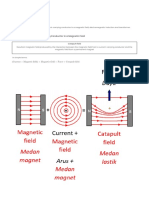
Electromagnet Magnet made by winding a coil round a soft iron core.
Magnetic force is produced when current passed thru
the coil.
Induced current When a wire cuts magnetic flux
Lenz’s Law Direction of induced current will opposed
Faraday’s Law Magnitude of induced current is directly proportional to
the rate of cutting the magnetic flux
Direct current Current which flow in one direction
Alternating current Current that flows to and fro in two opposite direction
Thermionic emission Emission of electron when a metal surface is heated
Doping Adding impurities to semiconductor to increase their
conductivity
Rectification Using diode to convert alternating current into direct
current
Capacitor To maintain a steady output voltage. (smoothing the
capacitor)
Transistor Amplify small current
Logic gate Digital circuit that design to make decision
Nucleon number Total proton & neutrons. Known as mass number.
Isotopes Same proton, different nucleon
Radioactivity Natural disintegration of unstable nucleus
Radioisotopes Unstable isotopes that give out radioactivity emissions
Nuclear fission Splitting a heavy nucleus into two lighter nuclei
Nuclear fusion Combining of two lighter nuclei to form heavier nucleus
Iman’s Property 2009
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Physics Notes SPM at JMCODokumen31 halamanPhysics Notes SPM at JMCOJac Chin96% (23)
- E Essay Physics - SPMDokumen42 halamanE Essay Physics - SPMKwongKH50% (4)
- SPM Physics Terms and DefinitionDokumen12 halamanSPM Physics Terms and Definitionnursuhailah100% (3)
- Physics SPM Paper 1, 2 and 3 Tips - 153 DEFINITION and AnswerDokumen6 halamanPhysics SPM Paper 1, 2 and 3 Tips - 153 DEFINITION and AnswerCikgu Faizal75% (4)
- Chapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideDokumen39 halamanChapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideMuhd Rifaie RodzilBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 6Dokumen9 halamanChemistry Form 4 Chapter 6Steven Wong50% (2)
- Physics Form 4Dokumen10 halamanPhysics Form 4Woody CysBelum ada peringkat
- F5 ExperimentsDokumen27 halamanF5 ExperimentsNarend Gunner80% (5)
- Physics Chapter 4 Form 4 DEFINITIONDokumen3 halamanPhysics Chapter 4 Form 4 DEFINITIONAnnie HonBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 1 Physics Form4 SBP 2007 Mid YearDokumen19 halamanPaper 1 Physics Form4 SBP 2007 Mid Yearruslawati100% (3)
- Chapter 10 Radioactivity Teacher Guide1Dokumen29 halamanChapter 10 Radioactivity Teacher Guide1SuadrifRunDamahumBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Dokumen37 halamanChapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (6)
- Analysis Past Year Chemistry SPM Question (2003-2017)Dokumen7 halamanAnalysis Past Year Chemistry SPM Question (2003-2017)Ting TCBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Checklist For ChemistryDokumen23 halamanSPM Checklist For Chemistryadella75100% (3)
- SPM Chemistry Trial 2015-2017 ModuleDokumen119 halamanSPM Chemistry Trial 2015-2017 Modulekhangsiean8950% (2)
- Physics p3 ExperimentDokumen18 halamanPhysics p3 ExperimentJosh, LRT88% (17)
- P 2Dokumen7 halamanP 2qq235100% (3)
- Physics Form 5 Chapter 5Dokumen22 halamanPhysics Form 5 Chapter 5Charlene87% (15)
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 4Dokumen33 halamanPhysics Form 4 Chapter 4Eric LengBelum ada peringkat
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 6 Coordinate GeometryDokumen14 halamanForm 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 6 Coordinate GeometryManisha Sekaran Muniandy0% (1)
- SPM Tips PhysicDokumen2 halamanSPM Tips PhysicIzzuddin AzizanBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding States of Matter and Chemical BondingDokumen46 halamanUnderstanding States of Matter and Chemical Bondingsaz14Belum ada peringkat
- Exercise Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Dokumen7 halamanExercise Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Wa Wa Jackson WongBelum ada peringkat
- Design Experiment SPM BiologyDokumen32 halamanDesign Experiment SPM BiologyEma94% (36)
- Nota Ringkas FizikDokumen2 halamanNota Ringkas FizikcikgusyaBelum ada peringkat
- General Notes and Definitions For InstanDokumen12 halamanGeneral Notes and Definitions For Instandazai osamuBelum ada peringkat
- Waves and Oscillations: Properties and ApplicationsDokumen6 halamanWaves and Oscillations: Properties and ApplicationsYinxin OngBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - WAVESDokumen6 halamanChapter 1 - WAVESSiraf IldaBelum ada peringkat
- 100 Physics One Liner For WBCS 2020Dokumen2 halaman100 Physics One Liner For WBCS 2020Saurav BandyopadhyayBelum ada peringkat
- All 9702 DefinitionsDokumen4 halamanAll 9702 DefinitionsGame ZoneBelum ada peringkat
- Laws/Definition: 1. Introduction To PhysicsDokumen2 halamanLaws/Definition: 1. Introduction To PhysicsSiti Salmah ErangBelum ada peringkat
- Exam QuestionsDokumen10 halamanExam QuestionsJohnBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation - Basic Aircraft Familiarization Course - AvionicsDokumen39 halamanPresentation - Basic Aircraft Familiarization Course - AvionicsFlorencioPautangBelum ada peringkat
- Waves Atom OpticsDokumen25 halamanWaves Atom OpticsAdal GanisBelum ada peringkat
- Definitions & LawsDokumen4 halamanDefinitions & LawsNabyh AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Science DefinitionsDokumen8 halamanPhysical Science DefinitionsJason KampsBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetism: 4.1 Force On A Current-Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic FieldDokumen7 halamanElectromagnetism: 4.1 Force On A Current-Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic FieldEv LamBelum ada peringkat
- GCSC Physics GlossaryDokumen8 halamanGCSC Physics GlossarysmeenaBelum ada peringkat
- Waves and Electricity Chapter SummaryDokumen8 halamanWaves and Electricity Chapter SummaryQiun LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Class X PhysicsDokumen13 halamanClass X Physicsapi-492628083Belum ada peringkat
- Fundamental of PhysicsDokumen38 halamanFundamental of PhysicsRICHA DHARANIBelum ada peringkat
- WsedrftgyhujDokumen3 halamanWsedrftgyhujGadiell Zeynn Carag PaclibarBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4 - BUILDING UTILITIES - Electrical SystemDokumen116 halamanLecture 4 - BUILDING UTILITIES - Electrical Systemjona serranoBelum ada peringkat
- The WTF A Level Package Physics Cheat SheetDokumen7 halamanThe WTF A Level Package Physics Cheat Sheet7063673nasBelum ada peringkat
- IB HL Physics DefinitionsDokumen7 halamanIB HL Physics DefinitionsshinyrayquazaBelum ada peringkat
- Current Electricity: Sura PublicationsDokumen21 halamanCurrent Electricity: Sura PublicationsVignesh N100% (1)
- All Definitions For Physics 0625 &0972Dokumen8 halamanAll Definitions For Physics 0625 &0972Ahmed SherifBelum ada peringkat
- 物理定义Dokumen4 halaman物理定义Ming ZengBelum ada peringkat
- 7d. Electromagnetic InductionDokumen9 halaman7d. Electromagnetic InductionLitiaMikoBelum ada peringkat
- IAL Physics DefinitionsDokumen5 halamanIAL Physics DefinitionsNayan KeraiBelum ada peringkat
- Physics GlossaryDokumen21 halamanPhysics GlossaryKing VaibhavBelum ada peringkat
- Phy Form 5 DefDokumen4 halamanPhy Form 5 DefvitthiyamuruBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic InductionDokumen12 halamanElectromagnetic InductionPrasad MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- Circuit 1 PDFDokumen14 halamanCircuit 1 PDFLeedo OneusBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 2Dokumen187 halamanPhysics 2Bilal Hussain ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Formula and Glossary GuideDokumen213 halamanPhysics Formula and Glossary GuideBilal Hussain Shah100% (1)
- Mechanics & Materials Definitions for LearningDokumen10 halamanMechanics & Materials Definitions for LearningRERORI GAMINGBelum ada peringkat
- Bus BarDokumen11 halamanBus BarDawit Adane KebedeBelum ada peringkat
- Electrostatics - Stationary ChargesDokumen39 halamanElectrostatics - Stationary ChargesmkanwarsBelum ada peringkat
- A GENERAL PHYSICS I 12 Q2M2 Teacher PDFDokumen17 halamanA GENERAL PHYSICS I 12 Q2M2 Teacher PDFRETCHIE JOY PISANABelum ada peringkat
- Metodo de FuerzaDokumen37 halamanMetodo de FuerzaJheysson Raphael Lopez guevaraBelum ada peringkat
- The Mechanics of TractorDokumen166 halamanThe Mechanics of TractorAbhijeet joseph50% (2)
- MAN L28/32H: Imo Tier Ii Project GuideDokumen449 halamanMAN L28/32H: Imo Tier Ii Project GuideNazikBelum ada peringkat
- PIPE FLANGE DIMENSIONSDokumen5 halamanPIPE FLANGE DIMENSIONSViral ParmarBelum ada peringkat
- CE441 - Lec05 - Settlement of Shallow FoundationDokumen68 halamanCE441 - Lec05 - Settlement of Shallow FoundationMd. Nahin Al ZakiBelum ada peringkat
- Lab ManualDokumen12 halamanLab ManualTheApplepie3456Belum ada peringkat
- Design For Torsion (Beams BS 8110)Dokumen3 halamanDesign For Torsion (Beams BS 8110)dhanya1995100% (1)
- Site Response Analysis: Understanding How Soil Properties Affect Ground MotionsDokumen90 halamanSite Response Analysis: Understanding How Soil Properties Affect Ground MotionsM YusupBelum ada peringkat
- Repair Instructions - Off Vehicle: A/Trans Case AssemblyDokumen94 halamanRepair Instructions - Off Vehicle: A/Trans Case AssemblyHidromaticos RBelum ada peringkat
- Pressure Vessel RT TestDokumen3 halamanPressure Vessel RT TestAriq FauzanBelum ada peringkat
- Diesel Powered Generating Sets: Our Energy Working For YouDokumen2 halamanDiesel Powered Generating Sets: Our Energy Working For YouAndres Felipe Torres PradaBelum ada peringkat
- Guentner W Shape Units Info enDokumen4 halamanGuentner W Shape Units Info enAnonymous 5moojwBelum ada peringkat
- Keep 316Dokumen68 halamanKeep 316AdityaBelum ada peringkat
- Design Guide For Structural Hollow Section ConnectionsDokumen213 halamanDesign Guide For Structural Hollow Section ConnectionsAnonymous 8f2veZf83% (6)
- Year 11 Physics Dynamics Notes Part 1 1 PDFDokumen5 halamanYear 11 Physics Dynamics Notes Part 1 1 PDFMark Quach100% (2)
- Town and Contry 4.0 2008Dokumen4 halamanTown and Contry 4.0 2008Jessica BustillosBelum ada peringkat
- Geng 2017Dokumen6 halamanGeng 2017robinwilson888Belum ada peringkat
- Guideline For Examining Failed Parts (1000, 7000) : Applied Failure AnalysisDokumen70 halamanGuideline For Examining Failed Parts (1000, 7000) : Applied Failure AnalysisKusuma Jaya100% (1)
- Condaria - Catalog - MARITIMUS - WZ c1Dokumen35 halamanCondaria - Catalog - MARITIMUS - WZ c1Beltazor HellboyBelum ada peringkat
- Extrusion of Thermoplastics EXTRUSION Plays A Prominent Part On The Plastics Industry. Extrusion, UnlikeDokumen21 halamanExtrusion of Thermoplastics EXTRUSION Plays A Prominent Part On The Plastics Industry. Extrusion, UnlikeParag NambiarBelum ada peringkat
- K45 Series DP, 45 PA : Full Fillet, Involute Spline ContinuedDokumen2 halamanK45 Series DP, 45 PA : Full Fillet, Involute Spline ContinuedCAT MINING SHOVELBelum ada peringkat
- Design of SpindleDokumen36 halamanDesign of SpindleAMIT SOLANKI0% (1)
- Winmena - TRRDokumen6 halamanWinmena - TRRFAIYAZ AHMEDBelum ada peringkat
- Triplex Pump Part 1Dokumen30 halamanTriplex Pump Part 1Rodolfo Castro86% (7)
- UDOT Seismic Design Manual SectionDokumen82 halamanUDOT Seismic Design Manual Sectionyoungc71Belum ada peringkat
- GSE EnVision ProcessFund Sim IDokumen2 halamanGSE EnVision ProcessFund Sim IFungky KingBelum ada peringkat
- Design of basement retaining wall shutteringDokumen4 halamanDesign of basement retaining wall shutteringSenthilkumar KBelum ada peringkat
- EngMech - Lecture 1.1Dokumen18 halamanEngMech - Lecture 1.1omay12Belum ada peringkat
- Jgeen 22 00051Dokumen35 halamanJgeen 22 00051d_diasol38Belum ada peringkat