Nursing Care Plan
Diunggah oleh
Cristina L. JaysonDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nursing Care Plan
Diunggah oleh
Cristina L. JaysonHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
NURSING CARE PLAN Nursing Diagnosis: Excess fluid volume r/t decrease cardiac output Cause Analysis: As cardiac
output falls, compensatory mechanisms cause salt and water retention increasing blood volume. This increased fluid volume places additional stressed on an already failing ventricles, making them harder to move the fluid load. References: Medical Surgical Nursing by: Lemone and Burke vol.1 p.883 Cues Objectives Nursing interventions Rationale Outcomes Subjective findings: Short Term Objectives: -Assess respiratory status - decliningrespiratory status Client may verbalize -after 6 hours of nursing and auscultate lung sounds indicates worsening left complaints of abdominal interventions, the client will be at least every 4hours. ventricle. discomfort. able to: Demonstrate weight loss -monitor intake and output. - Careful monitoring of fluid Decreases edema, jugular Notify the physician if urine volume is important during is less than 30 ml/hr. treatment of Hf. A fall in UO vein distension and may indicate reduced CO and abdominal distension renal ischemia. Objectives findings: -weigh daily. - Weight is an objective Presence of edema measure of fluid status. noted in the lower Long Term Objectives: extremities -after 2 days of nursing -record abdominal girth -venous congestion can lead to Weight gain interventions, the client will be every shift. Note any ascites and may affect able to: Nausea abdominal discomfort or gastrointestinal function and Achieve his/her normal weight. Jugular vein distension nausea. nutritional status. Abdominal distension -restrict fluids as ordered. Allow choices of fluid type and timing of intake and scheduling most of fluid intake during morning and afternoon - Offer ice chips and frequent mouth care -providing choices to the client allow clients sense of control.
-Ice chips an hard candies and mouth care relieves mouth dry thirst and promote comfort.
NURSING CARE PLAN Nursing Diagnosis: Activity intolerance r/t imbalance between O2 demand and supply Cause Analysis: Clients w/ heart failure have little or no cardiac reserve to meet increased O2 demand. As the disease progresses and cardiac function is further compromised, activity intolerance increases. Reference: Medical Surgical Nursing by: Lemone and Burke Vol.2 P.883 Cues Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Outcomes STO: 1. Organize nursing care to -grouping activities together After 8 hours of nursing allow rest periods. allow adequate time to interventions patient will be recharge able to participate in desired 2. Assist w/ ADL as needed. activities related to self-care Encourage - assisting with ADLs helps within her capacity independence within ensure that care needs are prescribe limit. met while reducing workload. OBJECTIVE: Involving the client promote LTO: a sense of control and After 2 days of duty, patient reduces helplessness. Decreased performance will achieve measurable 3. Plan and implements on ADLs increase in activity tolerance progressive activities. Inability to maintain as evidenced by reduced Use passive ROM -progressive activity slowly usual routine weakness and fatigue exercises as appropriate. increase capacity by Patient prefers lying on Consult physical strengthening and improving bed and sitting. therapist on activity Cardiac function without Patient appears drowsy plan. strain. Activity also helps and exhausted prevent complication. 4. Provide written and verbal information -written information provides about the activity after a reference of important discharge. information. Verbal information allows clarification and validation of material.
NURSING CARE PLAN Nursing Diagnosis: Imbalance Nutrition related to Anorexia and nausea secondary to right sided heart failure Cause Analysis: The loss of appetite contributes to improper / inadequate intake of food thus resulting to imbalance nutrition Reference: Medical Surgical Nursing by: Lemone and Burke Vol.2 Cues Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale STO: 1. Encourage rest period of - Helps reduce fatigue during After 4 hours of implementing one hour before and after mealtime, and provide nursing interventions, patient meals. Provide frequent opportunity to increase total will be able to improve his small feedings. caloric intake. appetite. 2. Make selective menu available, and allow patient to control choices as much as possible. - Patient who gains confidence in self and feels in control of environment is more likely to eat preferred foods.
Outcomes
OBJECTIVES: * Weakness * Pallor * Minimal amount of food consumed per meal
LTO:
After 2 days of implementing nursing interventions, patient will be able to note increase in weight after improved appetite and will maintain optimal nutritional status.
3. Take into consideration patients lifestyle, cultural -helps the patient to increase background, activity level, food intake and food preferences. 4. Elicit patients explanation of why he is unable to eat more.
- His explanation may present easily corrected practices
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsDokumen2 halamanImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsSundaraBharathiBelum ada peringkat
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDokumen3 halamanImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliBelum ada peringkat
- Cu 4Dokumen3 halamanCu 4Paul SahagunBelum ada peringkat
- NCP PainDokumen4 halamanNCP PainMark Allison BuenaventuraBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedDokumen5 halamanAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing DiagnosisDokumen3 halamanNursing DiagnosislesternBelum ada peringkat
- Cord ProlapseDokumen2 halamanCord ProlapseUsman Ali AkbarBelum ada peringkat
- Imbalnce Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsDokumen3 halamanImbalnce Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementselheezaBelum ada peringkat
- Health Assessment FHP - Nutrition and MetabolismDokumen25 halamanHealth Assessment FHP - Nutrition and MetabolismKim DajaoBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Risk For ConstipationDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Risk For Constipationkenneth_bambaBelum ada peringkat
- LESSON PLAN in Herbal MakingDokumen5 halamanLESSON PLAN in Herbal MakingCheenee Serenuela-Monto100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDokumen2 halamanNURSING CARE PLAN - Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDaniel Andre S. SomorayBelum ada peringkat
- Imbalanced NutritionDokumen3 halamanImbalanced NutritionIlisa ParilBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Problem Explanation Goal Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDokumen1 halamanNursing Problem Explanation Goal Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveZed P. EstalillaBelum ada peringkat
- APOLONIO, JC - Natural Theory - Thomas AquinasDokumen3 halamanAPOLONIO, JC - Natural Theory - Thomas AquinasJustin ApolonioBelum ada peringkat
- NCP PainDokumen2 halamanNCP PainApril_Ivy_Raga_3835Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan For Special ChildrenDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan For Special Childrenharas_dcsaisBelum ada peringkat
- Lapkas HegDokumen1 halamanLapkas HegkurniaBelum ada peringkat
- Activity IntoleranceDokumen4 halamanActivity IntoleranceShermane Criszen F. SallanBelum ada peringkat
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDokumen2 halamanAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plans For Activity IntoleranceDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plans For Activity IntolerancethebigtwirpBelum ada peringkat
- III. Nursing Care Plan Nursing Priority No. 1: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Accumulation of Secretions Secondary To PneumoniaDokumen6 halamanIII. Nursing Care Plan Nursing Priority No. 1: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Accumulation of Secretions Secondary To PneumoniaRae Marie Aquino100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDokumen1 halamanActivity IntoleranceAndrea Francesca SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Student Nurses' Community Nursing Care PlanDokumen3 halamanStudent Nurses' Community Nursing Care PlanMussaib MushtaqBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen2 halamanNCPJamaica SaranquinBelum ada peringkat
- HTP of AsthmaDokumen1 halamanHTP of AsthmaMarland Faith Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For StokeDokumen5 halamanNCP For StokeMemedBelum ada peringkat
- Simple NCPDokumen3 halamanSimple NCPLeny GallardoBelum ada peringkat
- Post Stroke PamphletDokumen2 halamanPost Stroke PamphletRgn McklBelum ada peringkat
- Cues/Data Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Objectives/Plan Nursing Intervention Nursing EvaluationDokumen1 halamanCues/Data Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Objectives/Plan Nursing Intervention Nursing EvaluationChloe Morningstar100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermDokumen4 halamanAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermGensen Cu RoxasBelum ada peringkat
- Tonsilitis & Allergic Rhinitis NCPDokumen11 halamanTonsilitis & Allergic Rhinitis NCPJorgia SalardaBelum ada peringkat
- Intussusception: PathophysiologyDokumen8 halamanIntussusception: PathophysiologyNaufal AndaluBelum ada peringkat
- Cap MRDokumen3 halamanCap MRRhio Grulla RamboyongBelum ada peringkat
- F Discharge Plan 2019Dokumen1 halamanF Discharge Plan 2019Besael BaccolBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching PlanDokumen3 halamanTeaching PlanGeralyn KaeBelum ada peringkat
- St. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingDokumen5 halamanSt. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingChristian UmosoBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen15 halamanNCPCamille PinedaBelum ada peringkat
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDokumen2 halamanScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study NCPDokumen4 halamanCase Study NCPKelly OstolBelum ada peringkat
- Community Health Profile Worksheet (Worksheet C)Dokumen10 halamanCommunity Health Profile Worksheet (Worksheet C)Jahay NielBelum ada peringkat
- Leukemias: Care SettingDokumen11 halamanLeukemias: Care SettingTinBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveFreisanChenMandumotanBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokumen8 halaman1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceEsel Mae DinamlingBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen2 halamanAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Diagnosis Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen11 halamanAssessment Diagnosis Intervention Rationale EvaluationBenjie DimayacyacBelum ada peringkat
- Cues Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen2 halamanCues Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationhaniehaehaeBelum ada peringkat
- Annex A Exercise PrescriptionDokumen3 halamanAnnex A Exercise Prescriptionalyanna alanoBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For COPDDokumen3 halamanNCP For COPDcy belBelum ada peringkat
- Think Critically and AnswerDokumen3 halamanThink Critically and AnswerSareno PJhēaBelum ada peringkat
- RSDokumen12 halamanRSKamalchandra NaikBelum ada peringkat
- Health Teaching Plan AMLDokumen2 halamanHealth Teaching Plan AMLInah Floresta BesasBelum ada peringkat
- HTP Ineffective BreathingDokumen3 halamanHTP Ineffective BreathingShyrra Edades PinderBelum ada peringkat
- FyhffDokumen44 halamanFyhffRico Torregosa Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- Ecologic Model NRMFDokumen4 halamanEcologic Model NRMFgreyzelBelum ada peringkat
- NCP FinalDokumen18 halamanNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlansDokumen6 halamanNursing Care PlansTwobee Kriz LeghidBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlansDokumen10 halamanNursing Care PlansClaire Alcantara50% (2)
- NCPDokumen7 halamanNCPBeverLyBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlansDokumen6 halamanNursing Care PlansDJ Marie VelosoBelum ada peringkat
- OooDokumen1 halamanOooCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- Individual Therapy Key PointsDokumen9 halamanIndividual Therapy Key PointsCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- Mindanao Sanitarium & Hospital College: D.R. Form Actual Delivery FormDokumen1 halamanMindanao Sanitarium & Hospital College: D.R. Form Actual Delivery FormCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- 3 RDDokumen1 halaman3 RDCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- 1 STPRCDokumen1 halaman1 STPRCCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- HelloDokumen1 halamanHelloCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- PRC TinaDokumen4 halamanPRC TinaCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- BibliographyDokumen1 halamanBibliographyCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- New Bon-NleDokumen3 halamanNew Bon-NleCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- May 2014 NLE Rooms CDODokumen71 halamanMay 2014 NLE Rooms CDOCoolbuster.NetBelum ada peringkat
- HAAD ReviewerDokumen35 halamanHAAD ReviewerSydRey92% (24)
- Grand Case Presentation InformationDokumen7 halamanGrand Case Presentation InformationCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- FBDokumen1 halamanFBCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- CorrectionsDokumen4 halamanCorrectionsCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- 634379489751247500Dokumen32 halaman634379489751247500Cristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing HistoryDokumen1 halamanNursing HistoryCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
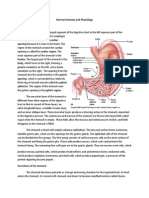
- Normal Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen8 halamanNormal Anatomy and PhysiologyCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen10 halamanNCPCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic TestsDokumen11 halamanDiagnostic TestsCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic TestsDokumen11 halamanDiagnostic TestsCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- GordonsDokumen3 halamanGordonsCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- IrisDokumen4 halamanIrisYazmin Vasquez BarreraBelum ada peringkat
- PerosDokumen5 halamanPerosCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- References For Drug Study and Diagnostic TestsDokumen2 halamanReferences For Drug Study and Diagnostic TestsCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- 1st Phase ReportDokumen42 halaman1st Phase ReportCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- Phytoplankton Data DipsinDokumen125 halamanPhytoplankton Data DipsinCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- Final DefenseDokumen16 halamanFinal DefenseCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- Project Contract For Phyto Ra-2Dokumen1 halamanProject Contract For Phyto Ra-2Cristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- Project Contract For Phyto Ra-2Dokumen1 halamanProject Contract For Phyto Ra-2Cristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- 3vital Information: Year) - BSED BioDokumen3 halaman3vital Information: Year) - BSED BioCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- Peo 20051026 IssueDokumen92 halamanPeo 20051026 IssueAlan EscobedoBelum ada peringkat
- 001 F LTV 1200 and 1150 Ops Manual PDFDokumen301 halaman001 F LTV 1200 and 1150 Ops Manual PDFJoão Francisco MontanhaniBelum ada peringkat
- MOVIMIENTO Gray Cook Assessing Movement Part One TranscriptDokumen22 halamanMOVIMIENTO Gray Cook Assessing Movement Part One TranscriptFranco Suazo MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- BronchiectasisDokumen71 halamanBronchiectasisvijay1234568883Belum ada peringkat
- OET Candidate Fact SheetDokumen3 halamanOET Candidate Fact SheetDr.Anurag FursuleBelum ada peringkat
- Theraputic Alliance EssayDokumen15 halamanTheraputic Alliance Essaymiimii33100% (1)
- Practice Bulletin: Medical Management of Ectopic PregnancyDokumen7 halamanPractice Bulletin: Medical Management of Ectopic PregnancyChangBelum ada peringkat
- Guidance Office Referral FormDokumen2 halamanGuidance Office Referral FormHainee Caoile-MinasBelum ada peringkat
- Trends in Anaesthesia and Critical Care: Brendan A. Mcgrath, Daniel HaleyDokumen3 halamanTrends in Anaesthesia and Critical Care: Brendan A. Mcgrath, Daniel HaleyRima RaisyiahBelum ada peringkat
- The Soul SanctuaryDokumen17 halamanThe Soul SanctuaryRohan SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- A Guide To Rational Living in An Irrational World - (Original) Albert Ellis & Robert A. HarperDokumen194 halamanA Guide To Rational Living in An Irrational World - (Original) Albert Ellis & Robert A. Harperinnersensation100% (2)
- Benign Breast Diseases29.7Dokumen65 halamanBenign Breast Diseases29.7api-3701915Belum ada peringkat
- Psychology VocabDokumen11 halamanPsychology VocabAlgeo OlmillaBelum ada peringkat
- Ben Sebastian - COSI COSI - Louise Nowra: ThemesDokumen9 halamanBen Sebastian - COSI COSI - Louise Nowra: ThemesAliMichaels2Belum ada peringkat
- Theory Class 9Dokumen21 halamanTheory Class 9Lavanya KalapalaBelum ada peringkat
- Care of The Ventilated ChildDokumen5 halamanCare of The Ventilated ChildBrahadheeswaran KannanBelum ada peringkat
- Nintendo's Wii Game Used in Stroke RehabDokumen1 halamanNintendo's Wii Game Used in Stroke RehabEva BannisterBelum ada peringkat
- Acupuncture Review and Analysis of Reports On Controlled Clinical Trials PDFDokumen96 halamanAcupuncture Review and Analysis of Reports On Controlled Clinical Trials PDFPongsathat TreewisootBelum ada peringkat
- Learn Massage (Pindot Sarap) in Ten (10) Easy StepsDokumen2 halamanLearn Massage (Pindot Sarap) in Ten (10) Easy StepsBenjie EugenioBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical GuidelinesDokumen34 halamanClinical GuidelinesAlberto PachecoBelum ada peringkat
- Biomechanics Poture AnalysisDokumen84 halamanBiomechanics Poture AnalysisMuqeet76Belum ada peringkat
- Defense Mechanisms: Organized By: Anna FreudDokumen35 halamanDefense Mechanisms: Organized By: Anna Freudjohn john33% (3)
- Nle Tips MS PDFDokumen11 halamanNle Tips MS PDFjthsBelum ada peringkat
- Mental Health and Well BeingDokumen33 halamanMental Health and Well BeingJoelleMaineBergonio100% (1)
- P CPLDokumen10 halamanP CPLJean FlorencondiaBelum ada peringkat
- Profitable Herb Growing and Collecting (1916)Dokumen204 halamanProfitable Herb Growing and Collecting (1916)6755kdp100% (3)
- Vibrational Nos Ws NotesDokumen2 halamanVibrational Nos Ws NotesAmi Patel Mehta100% (1)
- Prescription Analysis-Group ReportDokumen18 halamanPrescription Analysis-Group Report17_narsKBelum ada peringkat
- Shouldice Hospital CaseDokumen4 halamanShouldice Hospital CaseRikiAchinta100% (1)
- AnisocoriaDokumen11 halamanAnisocoriaChaturangaNSenerathBelum ada peringkat
- The Bodies of Others: The New Authoritarians, COVID-19 and The War Against the HumanDari EverandThe Bodies of Others: The New Authoritarians, COVID-19 and The War Against the HumanPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (12)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (9)
- Do You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineDari EverandDo You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineBelum ada peringkat
- Deaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismDari EverandDeaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (30)
- Uncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicDari EverandUncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicBelum ada peringkat
- Mama Might Be Better Off Dead: The Failure of Health Care in Urban AmericaDari EverandMama Might Be Better Off Dead: The Failure of Health Care in Urban AmericaBelum ada peringkat
- Epic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.Dari EverandEpic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (13)
- There Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceDari EverandThere Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PricePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (11)
- The Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsDari EverandThe Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (6)
- The Varicose Veins Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint for Complete Varicose Veins ManagementDari EverandThe Varicose Veins Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint for Complete Varicose Veins ManagementBelum ada peringkat
- The Nocebo Effect: When Words Make You SickDari EverandThe Nocebo Effect: When Words Make You SickBelum ada peringkat
- Clean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyDari EverandClean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (18)
- There Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceDari EverandThere Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PricePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (15)
- The Price of Health: The Modern Pharmaceutical Industry and the Betrayal of a History of CareDari EverandThe Price of Health: The Modern Pharmaceutical Industry and the Betrayal of a History of CarePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeDari EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (21)
- Heat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoDari EverandHeat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (40)
- The Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusDari EverandThe Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (10)
- The Hair Color Mix Book: More Than 150 Recipes for Salon-Perfect Color at HomeDari EverandThe Hair Color Mix Book: More Than 150 Recipes for Salon-Perfect Color at HomePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (7)
- Vax-Unvax: Let the Science SpeakDari EverandVax-Unvax: Let the Science SpeakPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- The Wuhan Cover-Up: And the Terrifying Bioweapons Arms RaceDari EverandThe Wuhan Cover-Up: And the Terrifying Bioweapons Arms RaceBelum ada peringkat
- Coronary: A True Story of Medicine Gone AwryDari EverandCoronary: A True Story of Medicine Gone AwryPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- Fatal Conveniences: The Toxic Products and Harmful Habits That Are Making You Sick—and the Simple Changes That Will Save Your HealthDari EverandFatal Conveniences: The Toxic Products and Harmful Habits That Are Making You Sick—and the Simple Changes That Will Save Your HealthPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (7)
- Inflamed: Deep Medicine and the Anatomy of InjusticeDari EverandInflamed: Deep Medicine and the Anatomy of InjusticePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (12)
- Beyond the Next Village: A Year of Magic and Medicine in NepalDari EverandBeyond the Next Village: A Year of Magic and Medicine in NepalBelum ada peringkat
- COVID-19: The Victims, The Heroes, The Comlicit, and Our New NormalDari EverandCOVID-19: The Victims, The Heroes, The Comlicit, and Our New NormalBelum ada peringkat
- Mercury, Mining, and Empire: The Human and Ecological Cost of Colonial Silver Mining in the AndesDari EverandMercury, Mining, and Empire: The Human and Ecological Cost of Colonial Silver Mining in the AndesBelum ada peringkat
- Healthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityDari EverandHealthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)