Foreign Body Aspirations
Diunggah oleh
Ezzati AizaDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Foreign Body Aspirations
Diunggah oleh
Ezzati AizaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Foreign Body Aspirations
Introduction
Foreign body aspiration may be fatal or went symptomless depending on the type of foreign bodies. Solid or semi solid object may dislodged in respiratory airway and lead to asphyxia or dyspnea varies according to exact site they are dislodged. As children grow and explore the new world, they tend to put small objects they found into their mouth and swallow it. They complained of some signs and symptoms or perhaps detected by their parents.
Site of foreign body aspirations
The foreign body is either obstructing the respiratory airway or the gastrointestinal tract. But most commonly is the respiratory airway. Depending on size of the foreign body, it may be obstructing the laryngeal inlet or beyond the trachea. Small objects blocking the laryngeal inlet may be dangerous as it completely obstruct the airway while obstruction beyond level of trachea or in the bronchus has better prognosis. But this may subjected to type of foreign body trapped and distance of it from the main bronchi. The right bronchus is commonly affected as it is more into line with the trachea and more widely than left bronchus (Figure 1).
Figure 1 show the percentage of foreign body location affecting the airway.
Foreign bodies
Foreign bodies that get swallowed or inhaled are usually radiopaque objects which are visible in X ray examination such as buttons, pins, screw, button batteries and toy parts (Figure 3). Foods
can also be trapped such as peanuts, beans, seed and others. These objects may irritate the lining mucosa of the trachea and bronchus as these food objects can initiate an inflammatory action which may lead to congestion and edema. The edematous swelling can cause airway obstruction either complete or partial and suppuration in lungs. Percentage of foreign body types
Figure 2 show percentage of foreign body types commonly affect children.
Figure 3 above show some foreign bodies retrieved by endoscopy
Person at high risk of foreign body aspirations
Children aged 1-3 years are at risk of foreign body aspiration as they tend to put objects into their mouth and the way they chew the food. At this age, the molar tooth is not developed yet. So they usually chew with incisor teeth and the chewing may not become complete. Adults are also suspected at risk of foreign body aspiration if they had undergone oropharyngeal procedures,
intoxicated, have several oral appliances, receive sedatives, or having neurologic or pscyhologic disorder which increased probability of foreign body ingestion.
Sign and symptoms
Signs and symptoms present might be early and chronic. Some of the early signs and symptoms are choking, coughing, fever, dyspnea, haemoptysis and chest pain. Foreign body such as inorganic material and inert bone may go symptomless or has delayed diagnosis which takes few months and years. Choking may not go frequently or being misdiagnosed. In some chronic symptoms, patient may misdiagnosed as having asthma attack or chronic bronchitis. In patients suspected with foreign body aspirations, signs shown maybe cough, wheezing, stridor and reduced breath sounds. Cyanosis happens if the obstruction is severe (Figure 4).
Figure 4 show infant cyanosis that could be happen if obstruction is severe.
Complications
Complications resulting from foreign body aspirations are atelectasis which is due to prolonged airway obstruction. The complete obstruction of airway cause the alveoli of lung to collapse. The other complications are bronchiectasis. Pathogenesis of this disease is due to destruction of muscle and elastic tissue of respiratory muscle. This is caused by chronic infections which can be initiated by foreign body obstruction. Complication risk is increased if the extraction of foreign body is delayed.
Diagnosis
There are few tests can be take to identify these foreign body as well as diagnosing foreign body aspirations. Firstly, the chest radiograph which can show the exact locations of the foreign body in respiratory airway (Figure 5). If the obstruction is complete, no residual air present as it was
absorbed and no air entry. This condition leads to opacification of distal lung which can be seen in chest radiograph (Figure 6). However, in partial obstruction, an area of overinflation will be seen in the lung distal to the affected bronchi (Figure 6).
Figure 5 show chest radiograph that reveal foreign body objects dislodged in trachea of patient.
Figure 6 show chest radiograph reveals hyperinflation of right lung and opacity of lower lobe left lung Second test that can diagnose foreign body aspirations is CT scanning (Figure 7). It can reveal the material and site of object dislodged. Moreover, it can also detect the focal airway edema.
Figure 7 show suspected foreign body in CT scan (arrow). Then, other test that can be undergone is fluoroscopy test. It will scan the chest and reveal diaphragmatic and mediastinal shifting or the location of air trapping. Bronchoscopy procedures may also undergo which will be explained later. However beside these scientific test, action showed by patients may indicate that they are having foreign body aspirations. If the patients are holding their neck, coughing and could not talk, they maybe suspected of it. In case of children, they may admitted by themselves to the parents or they witness by themselves the children swallowed the foreign body.
Treatment and management
Procedures that can be performed is bronchoscopy test. Bronchoscophy is a test used to view the airway, diagnose lung disease and for treatment purpose. It has a light and small camera which allows the doctor to view the airway. There are three types of bronchoscopes that are rigid, flexible and CT (computed tomography) virtual. Rigid bronchoscope advantages are it has a wider diameter tube which can facilitate passage of grasping device which functions to grasp the foreign body and lead it out (Figure 8). Also, the air ventilation of the patient can be maintained throughout the procedures. Rigid bronchoscope is a treatment of choice in most patients as it is easy and does not have many complications.
Figure 8 show rigid bronchoscope being inserted into patient.
But in patients with maxillofacial or cervical trauma, flexible bronchoscope is highly recommended to avoid any serious injury (Figure 9). It also has more advantage as it can pass as far to the subsegmental bronchi due to its smaller diameter. CT virtual bronchoscopy is newly developed technique (Figure 10). It is a non invasive technique. Bronchoscopy test will be accompanied with anesthesia either local or general.
Figure 9 show close up of flexible bronchoscope
Figure 10 show CT virtual bronchoscopy that reveal foreign body.
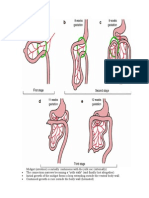
Hiemlich maneuver or abdominal thrust is performed if the children cannot speak or cry or having respiratory distress (Figure 11). These conditions may refer to complete obstruction of airway. However, Hiemlich maneuver is contraindicated if the patients are able to speak. The object may shift its position to where it can cause complete obstruction. Back blows can also be performed to force foreign body out.
Figure 11 show how to do Hiemlich maneuver and back blows in kids and baby.
References
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003857.htm http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/298940-overview http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/bron/ http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1001253-workup#showall http://earnosethroatclinic.blogspot.com/2010/12/management-of-foreign-body-in.html http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM194611142352002 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1406903/?page=13
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Wilderfeast Quickstart 1.0Dokumen85 halamanWilderfeast Quickstart 1.0Chris Hughes100% (3)
- CBLM Tle Afa LG GR 9 Animal Pro PDFDokumen210 halamanCBLM Tle Afa LG GR 9 Animal Pro PDFJexter E. Jacome100% (8)
- Non Hodgkin Lymphoma in ChildrenDokumen4 halamanNon Hodgkin Lymphoma in ChildrenMilzan MurtadhaBelum ada peringkat
- Phimosis in ChildrenDokumen7 halamanPhimosis in ChildrenfeonajaparBelum ada peringkat
- The European Trauma Course Manual: Edition 4.0Dokumen10 halamanThe European Trauma Course Manual: Edition 4.0Ghenea Catalin-StefanBelum ada peringkat
- Hematologic Disorders and PregnancyDokumen12 halamanHematologic Disorders and PregnancyAngelie RojasBelum ada peringkat
- Herpes Antidote UnlockedDokumen125 halamanHerpes Antidote Unlockedfcuevaspr180% (5)
- Foreign Bodies of The AirwayDokumen6 halamanForeign Bodies of The AirwayCharmila Sari100% (1)
- Obstetrical Hemorrhage: Reynold John D. ValenciaDokumen82 halamanObstetrical Hemorrhage: Reynold John D. ValenciaReynold John ValenciaBelum ada peringkat
- Disorders During PregnancyDokumen12 halamanDisorders During PregnancyazlanBelum ada peringkat
- Benson Relaxation Technique in Reducing Pain Intensity in Women After Cesarean SectionDokumen5 halamanBenson Relaxation Technique in Reducing Pain Intensity in Women After Cesarean SectionMarinaBelum ada peringkat
- SepsisDokumen14 halamanSepsisyreshgemBelum ada peringkat
- Intestinal AtresiaDokumen16 halamanIntestinal AtresiaMalueth AnguiBelum ada peringkat
- Mal RotationDokumen13 halamanMal RotationkavyarkrnagarBelum ada peringkat
- Peptic Ulcer Disease - EMEDICINE.2020Dokumen47 halamanPeptic Ulcer Disease - EMEDICINE.2020qayyum consultantfpsc100% (1)
- Intestinal Stomas PDFDokumen10 halamanIntestinal Stomas PDFAmyandBelum ada peringkat
- PhimosisDokumen6 halamanPhimosisfarissauBelum ada peringkat
- Ovarian Cysts Overview: Menstrual Cycle Pregnancy UltrasoundDokumen13 halamanOvarian Cysts Overview: Menstrual Cycle Pregnancy Ultrasoundzerocoolz123Belum ada peringkat
- Testicular TorsionDokumen20 halamanTesticular TorsionDarshan SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Abdominal Trauma: Dr. Sri Indah Aruminingsih, SP - RadDokumen135 halamanAbdominal Trauma: Dr. Sri Indah Aruminingsih, SP - RadwidyastutiBelum ada peringkat
- DHARSHINI (PPH)Dokumen5 halamanDHARSHINI (PPH)Rashvinder Kaur PurbaBelum ada peringkat
- Brief History of The DiseaseDokumen17 halamanBrief History of The DiseaseJon Corpuz AggasidBelum ada peringkat
- Phimosis 5 PDFDokumen4 halamanPhimosis 5 PDFNurul YaqinBelum ada peringkat
- Congenital Malformations of The New BornDokumen14 halamanCongenital Malformations of The New BornMartha LubasiBelum ada peringkat
- Genital FistulaeDokumen15 halamanGenital Fistulaesangeetha francisBelum ada peringkat
- Pyloric StenosisDokumen2 halamanPyloric Stenosisgeorgeloto12Belum ada peringkat
- Colonic Irrigation - Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMCDokumen3 halamanColonic Irrigation - Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMCWaNda GrBelum ada peringkat
- HerniasDokumen30 halamanHerniasWinnie PillyBelum ada peringkat
- Obstetric EmergenciesDokumen11 halamanObstetric EmergenciesAaronMaroonFiveBelum ada peringkat
- Bleeding During PregnancyDokumen8 halamanBleeding During Pregnancyfernandezrachelle44Belum ada peringkat
- Sepsis 1Dokumen6 halamanSepsis 1icu demangBelum ada peringkat
- PhimosisDokumen4 halamanPhimosisHelvia Septarini TanjungBelum ada peringkat
- Vaginal HysterectomyDokumen7 halamanVaginal HysterectomySleepy Winter0% (1)
- Urinary Diversion Is Any One of SeveralDokumen4 halamanUrinary Diversion Is Any One of SeveralKirstele Nicole QuijanoBelum ada peringkat
- Vasa PraeviaDokumen14 halamanVasa Praeviakhadzx100% (2)
- (New) Early Pregnancy Complications RDokumen51 halaman(New) Early Pregnancy Complications RMesk Banat100% (2)
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB)Dokumen45 halamanAbnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB)asdf0% (1)
- Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDokumen18 halamanAmniotic Fluid EmbolismmanjuBelum ada peringkat
- Endometrial PolypsDokumen14 halamanEndometrial PolypsMusaBelum ada peringkat
- Miscarriage Early Pregnancy LossDokumen10 halamanMiscarriage Early Pregnancy LossiwennieBelum ada peringkat
- Post Partum ComplicationDokumen29 halamanPost Partum ComplicationPutri Rizky AmaliaBelum ada peringkat
- Newborn AdaptationDokumen13 halamanNewborn Adaptationrevathidadam55555Belum ada peringkat
- Bartholin's Cyst/AbscessDokumen6 halamanBartholin's Cyst/AbscessJane NathaniaBelum ada peringkat
- Cervical CancerDokumen5 halamanCervical Cancerjinoop100% (1)
- Vacuum DeliveryDokumen3 halamanVacuum DeliveryKinjal Mistri100% (2)
- Submitted By: Diana M. Resultay A301/Group-3B Submitted To: Ms. ReyesDokumen9 halamanSubmitted By: Diana M. Resultay A301/Group-3B Submitted To: Ms. ReyesDiannetotz MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 1Dokumen36 halamanPresentation 1madhurima kunduBelum ada peringkat
- Ectopic Pregnancy: by Amielia Mazwa Rafidah Obstetric and Gynecology DepartmentDokumen43 halamanEctopic Pregnancy: by Amielia Mazwa Rafidah Obstetric and Gynecology DepartmentAlrick AsentistaBelum ada peringkat
- Intestinal Stomas - AKTDokumen49 halamanIntestinal Stomas - AKTTammie YoungBelum ada peringkat
- Prolonged LabourDokumen3 halamanProlonged Labourgeorgeloto12Belum ada peringkat
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDokumen53 halamanBleeding in Early PregnancyTemahlungwaneBelum ada peringkat
- MANUAL OF PLACENTAL PATHOLOGY FinaleDokumen24 halamanMANUAL OF PLACENTAL PATHOLOGY FinaleAnonymous wE02eRBelum ada peringkat
- Premature LaborDokumen59 halamanPremature LaborAmiel Francisco ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal FistulaDokumen28 halamanEsophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal FistulaarifBelum ada peringkat
- Uterine TumorsDokumen11 halamanUterine TumorsMuhammad Bilal DosaniBelum ada peringkat
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: - Rou'a Eyad - Rahaf EyadDokumen35 halamanAbnormal Uterine Bleeding: - Rou'a Eyad - Rahaf EyadYazeed Asrawi0% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy (Autosaved)Dokumen56 halamanEctopic Pregnancy (Autosaved)susmita shresthaBelum ada peringkat
- Female Genital TuberculosisDokumen6 halamanFemale Genital TuberculosisallauddinbarackzaiBelum ada peringkat
- Threatened AbortionDokumen9 halamanThreatened AbortionYien-yin MuachBelum ada peringkat
- EndometriosisDokumen10 halamanEndometriosisSivaram Shanmugha VilasBelum ada peringkat
- Obstructed Labor & Prolonged LaburDokumen22 halamanObstructed Labor & Prolonged LaburOmari Kabelwa100% (1)
- Antepartum HaemorrhageDokumen45 halamanAntepartum HaemorrhageGeorge C. KasondaBelum ada peringkat
- The Ideal Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Super Diet Guide To Replenish Overall Health For A Vibrant Lifestyle With Nourishing RecipesDari EverandThe Ideal Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Super Diet Guide To Replenish Overall Health For A Vibrant Lifestyle With Nourishing RecipesBelum ada peringkat
- 356 India Fact Sheets PDFDokumen2 halaman356 India Fact Sheets PDFgomathi ShankarBelum ada peringkat
- SOALBIGXIDokumen127 halamanSOALBIGXIAris WinarnoBelum ada peringkat
- Mr. Ashish YadavDokumen1 halamanMr. Ashish YadavSameer JogasBelum ada peringkat
- Rat DissectionDokumen5 halamanRat DissectionAcidri AbdulkarimBelum ada peringkat
- John W. Campbell - Who Goes There-Rosettabooks (2001)Dokumen56 halamanJohn W. Campbell - Who Goes There-Rosettabooks (2001)Manuel KlosterBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Dairy RanchingDokumen3 halamanWhat Is Dairy RanchingBright SamuelBelum ada peringkat
- About HyenaDokumen24 halamanAbout HyenaRiswan Hanafyah Harahap0% (1)
- The Death of The Moth - Annie DillardDokumen3 halamanThe Death of The Moth - Annie DillardjcfxBelum ada peringkat
- Power Taiji Vol 1Dokumen99 halamanPower Taiji Vol 1English Teaching100% (3)
- Methemoglobin Reductase PathwayDokumen2 halamanMethemoglobin Reductase PathwayinshBelum ada peringkat
- ClearStart Quick Start InstructionsDokumen3 halamanClearStart Quick Start InstructionsHisWellness100% (1)
- Karakteristik Ibu Hamil Dengan Ketuban Pecah Dini Di Rsu Assalam, Gemolong, SragenDokumen7 halamanKarakteristik Ibu Hamil Dengan Ketuban Pecah Dini Di Rsu Assalam, Gemolong, SragenaniBelum ada peringkat
- Reproductive Nursing SystemDokumen17 halamanReproductive Nursing SystemBobby Dwi PutraBelum ada peringkat
- Mother's Class BFDokumen55 halamanMother's Class BFriz04_fortitudessa5178Belum ada peringkat
- Prostho#8Dokumen9 halamanProstho#8api-19840404Belum ada peringkat
- 20 Yoga Poses For Losing Weight Fast - 990Dokumen22 halaman20 Yoga Poses For Losing Weight Fast - 990Ku Esyra Hani Ku IshakBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment of The Ears Rev 4-2013Dokumen8 halamanAssessment of The Ears Rev 4-2013alphabennydelta4468Belum ada peringkat
- Milia AriaDokumen8 halamanMilia AriaAtsabitFarisBelum ada peringkat
- Legal Med. Report-QueenDokumen61 halamanLegal Med. Report-QueenQuinnee VallejosBelum ada peringkat
- Worm Infestation and HomoeopathyDokumen15 halamanWorm Infestation and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (2)
- Pharmacology and Its Brief HistoryDokumen4 halamanPharmacology and Its Brief HistoryNiala AlmarioBelum ada peringkat
- Physical DiagnosisDokumen97 halamanPhysical Diagnosisaxmedfare138Belum ada peringkat
- 3478-Article Text-13352-1-10-20220210Dokumen12 halaman3478-Article Text-13352-1-10-20220210Danu MuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- Omega 3 and 6 in Fats Oils Nuts Seeds Meat and Seafood 2Dokumen3 halamanOmega 3 and 6 in Fats Oils Nuts Seeds Meat and Seafood 2Arhip CojocBelum ada peringkat
- Practical PhysiologyDokumen436 halamanPractical Physiologyaastha212002100% (1)
- LT-23 SPL (G-1) Morphology of Animals - 04-09-21Dokumen6 halamanLT-23 SPL (G-1) Morphology of Animals - 04-09-21orisBelum ada peringkat
- Referat HemothoraksDokumen28 halamanReferat HemothoraksitsmediBelum ada peringkat