NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS
Diunggah oleh
Uday Prakash SahuJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS
Diunggah oleh
Uday Prakash SahuHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
1 Multiple-Choice and Bimodal Questions 1) What percentage of electricity generated in the U.S. is from commercial nuclear plants? A) 1% B) 10% C) 20% D) 50% E) 90% 2) By what process does thorium-230 decay to radium-226? A) gamma emission B) alpha emission C) beta emission
D) electron capture
E) positron emission
3) The alpha decay of what isotope of what element produces lead-206? A) polonium-210 4) In balancing the nuclear reaction 238 U 234 E 4 He , the identity of element E is __________. 92 90 2 A) Pu B) Np C) U D) Pa E) Th 210 206 Po Pb _____ 5) This reaction is an example of __________. 84 82 A) alpha decay B) beta emission C) gamma emission D) positron emission E) electron capture 6) The missing product from this reaction is __________. 121I 121Te _____ 53 52 1 0 4 A) He B) e C) n D) 0 e E) 0 0 0 1 2 1 7) This reaction is an example of __________. 41Ca 41K _____ 20 19 A) alpha decay B) beta decay C) positron decay D) electron capture E) gamma emission 8) The missing product in this reaction would be found in which group of the periodic table? 24 Na 0 e _____ 11 1 A) 1A B) 2A C) 3A D) 8A E) 7A 9) The missing product in this reaction combines with oxygen to form a compound with the formula __________. 42 K 0 e _____ 19 1 A) M 2O B) MO C) MO2 D) M 2O E) M3O 10) Radium undergoes alpha decay. The product of this reaction also undergoes alpha decay. What is the product of this second decay reaction? A) Po B) Rn C) U D) Th E) Hg
Ambedkar Nagar
11) 41Ca decays by electron capture. The product of this reaction undergoes alpha decay. What is the product of this second decay reaction? A) Ti B) Ca C) Ar D) Cl E) Sc 12) What is the mass number of a neutron? A) 2 B) 1 C) 3
D) 4
E) 0
13) Nuclei above the belt of stability can lower their neutron-to-proton ratio by __________. A) beta emission B) gamma emission C) positron emission D) electron capture E) Any of the above processes will lower the neutron-to-proton ratio.
Prime Classes for IIT JEE/PMT, Ambedkar Nagar UPS 1
14) What is the largest number of protons that can exist in a nucleus and still be stable? A) 206 B) 50 C) 92 D) 83 15) The three radioactive series that occur in nature end with what element? A) Bi B) U C) Po D) Pb
E) 84
E) Hg
16) The largest number of stable nuclei have an __________ number of protons and an __________ number of neutrons. A) even, even B) odd, odd C) even, odd D) odd, even E) even, equal 17) In the nuclear transmutation represented by 16 O(p, ) 13 N , the emitted particle is __________. 8 7 A) a beta particle. B) an alpha particle. C) a proton. D) a positron. E) a neutron. 18) Bombardment of uranium-235 with a neutron generates tellurium-135, 3 neutrons, and __________. A) zirconium-98. B) krypton-101. C) krypton-103. D) strontium-99. E) zirconium-99. 19) The reaction shown below is responsible for creating 14C in the atmosphere. What is the bombarding 14 N _____ 14 C 1H particle? 7 6 1 A) alpha particle B) electron C) neutron D) positron E) proton 20) How many neutrons are emitted when a californium-249 nucleus (Z=98) is bombarded with a carbon-12 nucleus to produce a 257 Rf nucleus ? 104 A) one B) three C) two D) four E) zero 21) How many neutrons are emitted when a californium-249 nucleus (Z=98) is bombarded with a nitrogen-15 nucleus to produce a 260 Db nucleus? 105 A) two B) three C) four D) one E) zero 22) What order process is radioactive decay? A) zeroth B) first C) second D) third E) fourth 23) 131I has a half-life of 8.04 days. Assuming you start with a 1.53 mg sample of 131I, how many mg will remain after 13.0 days? A) 0.835 B) 0.268 C) 0.422 D) 0.440 E) 0.499 24) The decay of a radionuclide with a half-life of 4.3 105 years has a rate constant (in yr 1 ) equal to ________. A) 6.2 105 B) 1.6 106 C) 2.3 106 D) 2.8 103 E) 5.9 108 25) Due to the nature of the positron, __________ is actually detected in positron emission tomography. A) alpha radiation B) beta radiation C) gamma radiation D) x-ray emission E) neutron emission 26) The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867 amu. What is the mass defect (in amu) of a 60 Co nucleus? (The mass of a cobalt-60 nucleus is 59.9338 amu.) 27 A) 27.7830 B) 0.5489 C) 0.5405 D) 0.0662 E) 0.4827 27) What is the typical percent of uranium-235 in the enriched UO2 pellets used in nuclear reactors? A) 0.7 B) 1 C) 3 D) 5 E) 14
Prime Classes for IIT JEE/PMT, Ambedkar Nagar UPS 2
Ambedkar Nagar
28) On average, __________ neutrons are produced by every fission of a uranium-235 nucleus. A) 4 B) 3.5 C) 1 D) 2.4 E) 2 29) What drives the turbine in a nuclear power plant? A) the moderator B) steam C) the control rods 30) Who is credited with first achieving fission of uranium-235? A) Fermi B) Rutherford C) Curie
D) the primary coolant
E) UF6 gas
D) Dalton
E) Faraday
31) When ionizing radiation enters the body, what is the predominant free radical produced? A) H B) H3O C) protein D) OH 32) The nuclear disintegration series of __________ is the source of radon-222 in soil. A) 235U B) 238U C) 236Pb D) 235Th 2 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) All atoms of a given element have the same A) mass number. B) number of nucleons. E) atomic number. 2) Atoms containing radioactive nuclei are called A) radionuclides. B) radioisotopes.
E) H 2O
E) 14C
C) atomic mass.
D) number of neutrons.
C) nucleons.
D) nuclides.
E) radioisophores.
3) What happens to the mass number and the atomic number of an element when it undergoes beta decay? A) Neither the mass number nor the atomic number change. B) The mass number decreases by 4 and the atomic number decreases by 2. C) The mass number does not change and the atomic number increases by 1. D) The mass number does not change and the atomic number decreases by 2. E) The mass number increases by 2 and the atomic number increases by 1. 4) Which one of the following is a correct representation of a beta particle? B) 1 C) 0 e D) 0 e A) 4 e 0 1 2 1 5) Which one of the following processes results in an increase in the atomic number? A) gamma emission B) positron emission C) beta emission D) alpha emission
E) 2 4 E) corrosion
Ambedkar Nagar
6) Of the following processes, which one changes the atomic number? A) alpha emission B) beta emission C) electron capture E) All of these processes change the atomic numbers.
D) positron emission
7) What radioactive element is used to diagnose medical conditions of the heart and arteries? A) cobalt-60 B) thallium-201 C) radium-226 D) radon-222
E) Th-234
8) In what type of radioactive decay does the atomic number of the product increase by one? A) alpha B) beta C) gamma D) positron emission E) electron capture 9) Which type of radioactive decay results in no change in mass number and atomic number for the starting nucleus? A) alpha B) beta C) positron emission D) electron capture E) gamma
Prime Classes for IIT JEE/PMT, Ambedkar Nagar UPS 3
10) Alpha decay produces a new nucleus whose __________ than those respectively of the original nucleus. A) atomic number is 2 less & mass number is 2 less B) atomic number is 1 less & mass number is 2 less C) atomic number is 2 less & mass number is 4 less D) atomic number is 2 more & mass number is 4 more E) atomic number is 2 more & mass number is 2 less 11) What is the missing product from this reaction? 32 P 32 S _____ 15 16 A) 4 He B) 0 e C) 0 D) 0 e E) 0 p 0 1 2 1 1 12) What is the atomic number of a neutron? A) 3 B) 1 C) 2 D) 0 E) 4 13) What happens to the mass number and the atomic number of an element when it emits gamma radiation? A) The mass number remains unchanged while the atomic number decreases by one. B) The mass number decreases by four and the atomic number decreases by two. C) The mass number increases by four and the atomic number increases by two. D) The mass number remains unchanged while the atomic number increases by one. E) The mass number and atomic numbers remain unchanged. 14) Atoms with the same atomic number and different mass numbers A) do not exist. B) isomers. C) are isotopes. D) are allotropes 15) How many radioactive decay series exist in nature? A) 0 B) 1 C) 2
E) are resonance structures.
D) 3
E) 10
16) At approximately what number of protons, or neutrons, does the 1:1 ratio of protons to neutrons start to produce unstable nuclei? A) 10 B) 20 C) 30 D) 50 E) 80 17) Carbon-11 decays by __________. A) alpha emission B) beta emission
C) positron emission D) electron capture
E) neutron capture
18) The formation of krypton from rubidium decay is a result of __________. A) alpha emission B) beta emission C) positron emission D) electron capture 19) The mode of decay of 32P is __________. A) alpha emission B) beta emission C) positron emission D) electron capture 20) The belt of nuclear stability ends with the element __________. A) lead B) polonium C) radon D) astatine 21) Which of these nuclides is most likely to be radioactive? A) 39 K B) 27 Al C) 127 I 19 13 53
E) neutron capture
E) neutron capture
Ambedkar Nagar
E) bismuth
D) 243 Am 95
E) 209 Bi 83
22) What is required for a nuclear transmutation to occur? A) very high temperature B) a corrosive environment C) a particle to collide with a nucleus D) spontaneous nuclear decay E) gamma emission 23) In the nuclear transmutation, 16 O(p, ) 13 N , what is the bombarding particle? 8 7 A) an alpha particle B) a beta particle C) a gamma photon D) a proton E) a phosphorus nucleus
Prime Classes for IIT JEE/PMT, Ambedkar Nagar
UPS
24) Cobalt-60 is produced by a three reaction process involving neutron capture, beta-emission, and neutron capture. The initial reactant in the production of cobalt-60 is __________. A) 59Co B) 56Fe C) 58Fe D) 61Co E) 60Fe 25) The product of the nuclear reaction in which 28Si is subjected to neutron capture followed by alpha emission is _________. A) 31S B) 33S C) 23Mg D) 25Mg E) 25Al 26) Transuranium elements have atomic numbers greater than __________. A) 90 B) 91 C) 92 D) 93 E) 94 27 24 27) What is emitted in the nuclear transmutation, Al(n, ?) Na ? 13 11 A) an alpha particle B) a beta particle C) a neutron D) a proton E) a gamma photon 28) In the nuclear transmutation represented by 239 Pu( 4 He, 1n)? , what is the product? 94 2 0 A) uranium-242 B) curium-245 C) curium-242 D) uranium-245 E) uranium-243 29) In the nuclear transmutation represented by 14 N( 1n, 1p)? , what is the emitted particle? 7 0 1 A) neutron B) proton C) positron D) alpha particle E) electron 30) In the nuclear transmutation represented by 14 N( 1n, 1p)? , what is the product? 7 0 1 A) carbon-12 B) carbon-16 C) carbon-14 D) nitrogen-16 E) nitrogen-15 31) Which one of the following requires a particle accelerator to occur? A) 59 Fe 59 Co 0 e B) 59 Co 1n 60 Co C) 238 U 1n 239 Np 0 e 26 27 1 27 0 27 92 0 93 1 D) 239 Pu 4 He 242 Cm 1n E) none of the above 94 2 96 0 32) What are the "dees" on a particle accelerator? A) vibration places B) transmutated bees C) electrodes D) magnets E) targets 33) Bombardment of uranium-238 with a deuteron (hydrogen-2) generates neptunium-237 and _____ neutrons. A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 34) Which of the following correctly represents the transmutation in which neptunium-239 is produced via bombardment of uranium-238 with a neutron? A) 238 U( 1n, 0 e) 239 Np B) 238 U( 1n, 1p) 239 Np C) 238 U(1n, ) 239 Np 92 0 1 93 92 0 1 93 92 1 93 D) 238 U( 1n, 4 ) 239 Np E) 238 U( 1n, 1n) 239 Np 92 0 2 93 92 0 0 92 35) Which of the following correctly represents the transmutation in which a curium-242 nucleus is bombarded with an alpha particle to produce a californium-245 nucleus? A) 242 Cm( 4 He, 1n) 245 Cf B) 242 Cm( 4 He, 1p) 245 Cf C) 242 Cm( 4 He, 1e) 245 Cf 96 2 0 98 96 2 1 98 96 2 1 98 D) 242 Cm( 1n, 4 He) 245 Cf E) 242 Cm( 4 He, 21p) 245 Cf 96 0 2 98 96 2 1 98 36) Which one of the following can be done to shorten the half-life of the radioactive decay of uranium-238? A) freeze it B) heat it C) convert it to UF6 D) oxidize it to the +2 oxidation state E) none of the above 37) The beta decay of cesium-137 has a half-life of 30.0 years. How many years must pass to reduce a 25 mg sample of cesium 137 to 8.7 mg? A) 46 B) 32 C) 3.2 D) 50 E) 52
Ambedkar Nagar
Prime Classes for IIT JEE/PMT, Ambedkar Nagar
UPS
38) The half-life for beta decay of strontium-90 is 28.8 years. A milk sample is found to contain 10.3 ppm strontium-90. How many years would pass before the strontium-90 concentration would drop to 1.0 ppm? A) 92.3 B) 0.112 C) 186 D) 96.9 E) 131 39) The half-life of 131I is 0.50 years. How much of a 500.0 mg sample remains after 4 years? A) 375 mg B) 560 mg C) 250 mg D) 125 mg E) 450 mg 40) The carbon-14 dating method can be used to determine the age of a A) flint arrowhead. B) papyrus scroll. C) stone axe head. D) clay pot. 41) The basis for the carbon-14 dating method is that A) the amount of carbon-14 in all objects is the same. B) carbon-14 is very unstable and is readily lost from the atmosphere. C) the ratio of carbon-14 to carbon-12 in the atmosphere is a constant. D) living tissue will not absorb carbon-14 but will absorb carbon-12. E) All of the above are correct. 42) 210Pb has a half-life of 22.3 years and decays to produce206Hg. If you start with 7.50 g of 210Pb, how many grams of 206Hg will you have after 17.5 years? A) 4.35 B) 3.15 C) 3.09 D) 0.0600 E) 1.71 43) The half-life of a radionuclide A) is constant. B) gets shorter with passing time. C) gets longer with passing time. D) gets shorter with increased temperature. E) gets longer with increased temperature. 44) The curie is a measure of the A) number of disintegrations per second of a radioactive substance. B) total energy absorbed by an object exposed to a radioactive source. C) lethal threshold for radiation exposure. D) number of alpha particles emitted by exactly one gram of a radioactive substance. E) None of the above is correct. Consider the following data for a particular radionuclide:
E) rock.
Ambedkar Nagar
45) What is the rate constant (in min 1 ) for the decay of this radionuclide? A) 45 B) 31 C) 0.024 D) 0.032 46) What is the half-life (in min) of this radionuclide? A) 0.024 B) 0.022 C) 31
E) 0.022
D) 0.032
E) 45
47) Cesium-137 undergoes beta decay and has a half-life of 30.0 years. How many beta particles are emitted by a 14.0-g sample of cesium-137 in three minutes? A) 6.11013 B) 6.2 1022 C) 8.4 1015 D) 1.3 108 E) 8.11015
Prime Classes for IIT JEE/PMT, Ambedkar Nagar UPS 6
48) What is a phosphor? A) an oxide of phosphorus C) a bioluminescent substance E) an alkali metal phosphide
B) a substance that thermally reduces to phosphorus D) a substance that emits light when excited by radiation
49) Which one of the following devices converts radioactive emissions to light for detection? A) Geiger counter B) photographic film C) scintillation counter D) none of the above E) radiotracer 50) Which one of the following is used as a radiotracer to study blood? A) iron-59 B) technetium-99 C) sodium-23 D) iodine-131 51) Which one of the following is true? A) Some spontaneous nuclear reactions are exothermic. B) Some spontaneous nuclear reactions are endothermic. C) All spontaneous nuclear reactions are exothermic. D) There is no relationship between exothermicity and spontaneity in nuclear reactions. E) All spontaneous nuclear reactions are endothermic. 52) The mass of a proton is 1.673 1024 g . The mass of a neutron is 1.675 1024 g . mass of the nucleus of an 56Fe atom is 9.289 1023 g . What is the nuclear binding energy (in J) for a 56Fe nucleus? (C 3.00 108 m s) A) 2.57 1016 B) 7.72 108 C) 8.36 109 D) 7.72 1011 E) 6.07 106
E) phosphorus-32
53) When two atoms of 2H are fused to form one atom of 4He, the total energy evolved is 3.83 1012 J What is the total change in mass (in kg) for this reaction? (C 3.00 108 m s) A) 1.28 1017 B) 4.26 1026 C) 3.45 108 D) 1.15 E) 4.26 1029
54) The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867 amu. What is the binding energy (in J) of a 60 Co nucleus? (The mass of a cobalt-60 nucleus is 59.9338 amu.) 27 B) 9.12 1028 C) 4.94 1013 D) 8.20 1011 E) 2.74 1016 A) 2.74 1019 55) The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867 amu. What is the binding energy per nucleon (in J) of a 60 Co nucleus? (The mass of a cobalt-60 nucleus is 59.9338 amu.) 27 12 A) 1.37 10 B) 3.04 1012 C) 2.49 1012 D) 9.43 1013 E) 7.011014
Ambedkar Nagar
56) The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867 amu. What is the mass defect (in amu) of a 60 Ni nucleus? (The mass of a nickel-60 nucleus is 59.9308 amu.) 29 A) 0.5449 B) 1.2374 C) 0.5491 D) 28.7930 E) 1.3066 57) In terms of binding energy per nucleon, what element divides fission and fusion processes? A) H B) He C) C D) Fe E) U 58) What type of reaction is known as a thermonuclear reaction? A) fission B) fusion C) transmutation
D) beta emission
E) neutron emission
Prime Classes for IIT JEE/PMT, Ambedkar Nagar
UPS
59) The main scientific difficulty in achieving a controlled fusion process is the A) enormous repulsion between the electrons of atoms being fused. B) enormous repulsion between nuclei being fused. C) very large number of positrons emitted. D) very large number of x-rays emitted. E) very large number of gamma rays emitted. 60) What exposure level to radiation is fatal to most humans? A) 100 rem B) 200 rem C) 600 rem
D) 300 rem
E) 1000 rem
61) Which one of the following is not true concerning radon? A) It decays by alpha emission. B) It decays to polonium-218, an alpha emitter. C) It is chemically active in human lungs. D) It has been implicated in lung cancer. E) It is generated as uranium decays. 62) Which one of the following forms of radiation can penetrate the deepest into body tissue? A) alpha B) beta C) gamma D) positron E) proton 3 Short Answer Questions 1) What happens in the nucleus of an atom that undergoes positron emission? 2) What is the predominant isotope of uranium? 3) What happens to the atomic mass number and the atomic number of a radioisotope when it undergoes alpha emission? 4) High speed electrons emitted by an unstable nucleus are called __________. 5) 0 e represents __________. 1 6) What isotope of what element is produced if krypton-81 undergoes beta decay? 7) Stable nuclei with low atomic numbers, up to 20, have a neutron to proton ratio of approximately ______. 8) The first nuclear transmutation resulted in the conversion of nitrogen-14 to __________. 9) Conversion of one nucleus into another was first demonstrated in 1919 by __________. 10) The half-life for the beta decay of potassium-40 is 1.3 109 years . What is the rate constant for this decay?
t1 2 0.693/ k 1.3 109 years 0.693/ k k 5.3 10 10 year 1 11) __________ discovered radioactivity. Becquerel 12) Carbon-11, fluorine-18, oxygen-15 and nitrogen-13 are all used in the clinical diagnostic technique known as __________. positron emission tomography; PET 13) What is the source of the tremendous energies produced by nuclear reactions? 14) Control rods in a nuclear reactor are composed of boron and __________. cadmiun 15) The amount of fissionable material necessary to maintain a chain reactions is called the ___. critical mass 16) When living tissue is irradiated most of the energy is absorbed by __________. water 19) The relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values of beta rays, gamma rays, and alpha rays are, respectively . 1, 1, 10 20) The major type of cancer caused by radiation is __________. leukemia 21) Radioactive seeds that are implanted into a tumor are coated with __________ to stop alpha and beta ray penetration. platinum
Ambedkar Nagar
4 True/False Questions 1) Gamma radiation only changes the atomic number but not the mass number of a nucleus. False 2) Positron emission causes a decrease of one in the atomic number. True 3) The neutron/proton ratio of stable nuclei increases with increasing atomic number. True 4) Charged particles are accelerated because the faster they move there is a greater chance of producing a nuclear reaction. True 5) Radioactive decay is a first order kinetic process. True 6) In radioactive dating the ratio of carbon-12 to carbon-14 is related to the time of death of the animal or plant
Prime Classes for IIT JEE/PMT, Ambedkar Nagar UPS 8
under investigation. False 7) In the formula k 0.693/ t1 2 , k is the decay constant. True 8) The energy produced by the sun is the result of nuclear fusion. True 9) The SI unit of an absorbed dose of radiation is the gray. True 10) The relative biological effectiveness (RBE) is 10 fold greater for gamma radiation than for alpha radiation. False 5 Essay Questions 1) Electrons do not exist in the nucleus, yet beta emission is ejection of electrons from the nucleus. How does this happen? 2) List the common particles and their symbols used in descriptions of radioactive decay and nuclear transformations.
3) When an isotope undergoes electron capture, what happens to the captured electron? 6 Algorithmic Questions 1) The half-life of cobalt-60 is 5.20 yr. How many milligrams of a 2.000-mg sample remains after 6.55 years? A) 0.837 B) 3.23 1015 C) 4.779 D) 1.588 E) 1.163 2) Strontium-90 is a byproduct in nuclear reactors fueled by the radioisotope uranium-235. The half-life of Strontium-90 is 28.8 yr. What percentage of a strontium-90 sample remains after 75.0 yr? A) 68.1 B) 16.5 C) 7.40 D) 38.4 E) 2.60 3) Carbon-11 is used in medical imaging. The half-life of this radioisotope is 20.4 min. What percentage of a sample remains after 60.0 min? A) 71.2 B) 5.28 C) 13.0 D) 34.0 E) 2.94
Ambedkar Nagar
4) A rock contains 0.313 mg of lead-206 for each milligram of uranium-238. The half-life for the decay of uranium-238 to lead-206 is 4.5 109 yr . The rock was formed __________ yr ago. A) 1.41109 B) 1.08 109 C) 1.39 109 D) 2.00 109 E) 1.56 109 5) Potassium-40 decays to argon-40 with a half-life of 1.27 109 yr. The age of a mineral sample that has a mass ratio of 40Ar to 40K of 0.812 is __________ yr. A) 1.56 109 B) 1.02 109 C) 1.47 109 D) 7.55 108 E) 1.09 109 6) If we start with 1.000 g of strontium-90, 0.908 g will remain after 4.00 yr. This means that the half-life of strontium-90 is __________ yr. A) 3.05 B) 4.40 C) 28.8 D) 3.63 E) 41.6
Prime Classes for IIT JEE/PMT, Ambedkar Nagar
UPS
7) If we start with 1.000 g of cobalt-60, 0.675 g will remain after 3.00 yr. This means that the half-life of cobalt60 is __________ yr. A) 3.08 B) 4.44 C) 2.03 D) 5.30 E) 7.65 8) A freshly prepared sample of curium-243 undergoes 3312 disintegrations per second. After 6.00 yr, the activity of the sample declines to 2755 disintegrations per second. The half-life of curium-243 is __________ yr . A) 4.99 B) 32.6 C) 7.21 D) 0.765 E) 22.6 11 11 0 9) Carbon-11 decays by positron emission: C B e 6 5 1 11 The decay occurs with a release of 2.87 10 J per mole of carbon-11. When 4.00 g of carbon-11 undergoes this radioactive decay, __________ g of mass is converted to energy. A) 1.16 103 B) 3.48 105 C) 1.16 106 D) 8.62 102 E) 1.28 102 10) How much energy (in J) is produced when 0.082 g of matter is converted to energy? A) 7.4 1018 B) 7.4 1012 C) 2.5 104 D) 7.4 1015 E) 2.5 107
Ambedkar Nagar
Prime Classes for IIT JEE/PMT, Ambedkar Nagar
UPS
10
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- SCH 102: Organic Chemistry IDokumen152 halamanSCH 102: Organic Chemistry IH to O ChemistryBelum ada peringkat
- Balancing Equations PDFDokumen6 halamanBalancing Equations PDFFeli CiaBelum ada peringkat
- Radioisotopes SeminarDokumen23 halamanRadioisotopes SeminarDrVikasBelum ada peringkat
- Study Guide Nuclear ChemistryDokumen4 halamanStudy Guide Nuclear ChemistryAdam100% (1)
- Electron ArrangementDokumen39 halamanElectron ArrangementSakib AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Electrochemistry 494 PDFDokumen55 halamanElectrochemistry 494 PDFHarsh SaxenaBelum ada peringkat
- Cellular Respiration PathwaysDokumen5 halamanCellular Respiration PathwaysStealthstr1keBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry - Practice - Final - ExamDokumen7 halamanGeneral Chemistry - Practice - Final - ExamReyes Ilagan MyrnaBelum ada peringkat
- SBI4U0 Exam Review GuideDokumen6 halamanSBI4U0 Exam Review GuideSukhvir AujlaBelum ada peringkat
- Empirical and Molecular Formulae WorksheetDokumen3 halamanEmpirical and Molecular Formulae WorksheetJohnclyde Ferry100% (1)
- Electron Arrangement in An AtomDokumen47 halamanElectron Arrangement in An AtomRomalyn GalinganBelum ada peringkat
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Homework - Bruno BiologyDokumen2 halamanPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Homework - Bruno Biologyapi-2769442650% (1)
- 07 Test BankDokumen46 halaman07 Test Banke1153353Belum ada peringkat
- Formulae, equations and calculationsDokumen39 halamanFormulae, equations and calculationsNandi100% (1)
- Limiting Reagents and Percentage Yield WorksheetDokumen1 halamanLimiting Reagents and Percentage Yield WorksheetFandy ArdyBelum ada peringkat
- ChemistryDokumen27 halamanChemistryFatmawati MnBelum ada peringkat
- Acid Base Reactions WorksheetDokumen5 halamanAcid Base Reactions WorksheetOmar IjazBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry ReviewerDokumen4 halamanChemistry ReviewerCyreel ManaloBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To Organic Chemistry:: The Saturated HydrocarbonsDokumen73 halamanAn Introduction To Organic Chemistry:: The Saturated HydrocarbonsGabz Gabby0% (1)
- Environmental Chemistry PDFDokumen3 halamanEnvironmental Chemistry PDFAnnesa MukherjeeBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of Atom PDFDokumen25 halamanStructure of Atom PDFNitika GrewalBelum ada peringkat
- Molecularity of Molecules in ChemistryDokumen13 halamanMolecularity of Molecules in ChemistryAhmed HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 9. Chemical BondingDokumen55 halamanLecture 9. Chemical BondingDione Gale NavalBelum ada peringkat
- 1020-Lewis and Shapes PDFDokumen4 halaman1020-Lewis and Shapes PDFJaya Chitra Degala RamaluBelum ada peringkat
- Atoms and The Periodic TableDokumen16 halamanAtoms and The Periodic TableRainBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet-Nernst Equation PDFDokumen4 halamanWorksheet-Nernst Equation PDFLedd SleddBelum ada peringkat
- Photosynthesis Light Reaction ATP Formation Electron Transport Cytochromes ChloroplastsDokumen4 halamanPhotosynthesis Light Reaction ATP Formation Electron Transport Cytochromes ChloroplastsFarooq AliBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Test ADokumen7 halamanChapter 1 The Science of Biology Test ATUTORKIMBelum ada peringkat
- First Grading G8 Summative 3 and 4Dokumen3 halamanFirst Grading G8 Summative 3 and 4Ederzon IlustricimoBelum ada peringkat
- D and f Block Elements PropertiesDokumen8 halamanD and f Block Elements Propertiessrivathson7Belum ada peringkat
- Organic ChemistryDokumen60 halamanOrganic ChemistryddddddffdfdfBelum ada peringkat
- Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen24 halamanExam Multiple Choice QuestionsJoýce SilveiraBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry 445 Lecture 18 MO Theory and D-D SpectraDokumen22 halamanChemistry 445 Lecture 18 MO Theory and D-D SpectraAbhinav JainBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Chemistry GC Women University, Sialkot: Name: Roll No.Dokumen2 halamanDepartment of Chemistry GC Women University, Sialkot: Name: Roll No.Esha Rani Waheed100% (1)
- The Development of The Periodic TableDokumen95 halamanThe Development of The Periodic TableSherren NalaBelum ada peringkat
- 1.2 Mole ConceptDokumen66 halaman1.2 Mole Conceptnurain syuhadaBelum ada peringkat
- The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules: BiologyDokumen32 halamanThe Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules: BiologyUyyykllBelum ada peringkat
- Organic Chemistry ACS Sample QuestionsDokumen20 halamanOrganic Chemistry ACS Sample QuestionsNajmusawwa Aulia RahmahBelum ada peringkat
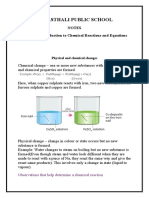
- Chemical Reactions and Equations Notes from Vanasthali Public SchoolDokumen8 halamanChemical Reactions and Equations Notes from Vanasthali Public SchoolPlatinum Gaming Warrior100% (1)
- Quantum Physics Introduction Exploring Frontiers ResearchDokumen3 halamanQuantum Physics Introduction Exploring Frontiers ResearchAboSulieman100% (1)
- 15.2 Born-Haber Cycle: 15.2.2 Explain How The Relative Sizes and The Charges of IonsDokumen16 halaman15.2 Born-Haber Cycle: 15.2.2 Explain How The Relative Sizes and The Charges of IonsGiselle PeachBelum ada peringkat
- 2.1 Molecules To Metabolism WorksheetDokumen3 halaman2.1 Molecules To Metabolism WorksheetSayedMuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- How thermochemistry explains daily life reactionsDokumen13 halamanHow thermochemistry explains daily life reactionsNicholas LeongBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Module 3Dokumen14 halamanChemistry Module 3MASHBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionDokumen63 halamanChemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionSiti Nursyafiqah100% (7)
- Photosynthesis Converts Light Energy to Chemical EnergyDokumen13 halamanPhotosynthesis Converts Light Energy to Chemical EnergyMina IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Average Atomic Mass Practice ProblemsDokumen1 halamanAverage Atomic Mass Practice ProblemsApril Joy BallenerBelum ada peringkat
- 5 - Electromagnetic Waves PDFDokumen8 halaman5 - Electromagnetic Waves PDFthinkiit100% (1)
- Chemistry Final Study Guide Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen22 halamanChemistry Final Study Guide Multiple Choice Questionssrahimi@verizon.netBelum ada peringkat
- L2 Che101Dokumen16 halamanL2 Che101Musa Ahammed MahinBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bond QuizDokumen5 halamanChemical Bond QuizBrielle Kyle O. SERRANO0% (1)
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes 2017pptxDokumen96 halamanAlkanes and Cycloalkanes 2017pptxEgbebessemenow oben ashuBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of AtomDokumen5 halamanStructure of AtomSaurabh DhyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of Atom Chem 9thDokumen6 halamanStructure of Atom Chem 9thPrashant ZadeBelum ada peringkat
- 2-Revision Atomic Structure & Periodic TableDokumen14 halaman2-Revision Atomic Structure & Periodic TableMohamudBelum ada peringkat
- Akash Neet Question Bank PDFDokumen440 halamanAkash Neet Question Bank PDFUday Prakash Sahu75% (4)
- Coordinate Geometry Booster For IIT JEE Main and Advanced PDFDokumen383 halamanCoordinate Geometry Booster For IIT JEE Main and Advanced PDFUday Prakash Sahu100% (5)
- Drum Press, Temp CalDokumen22 halamanDrum Press, Temp CalUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Reactions of Aldehydes and KetonesDokumen1 halamanReactions of Aldehydes and KetonesUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- ToDokumen2 halamanToUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
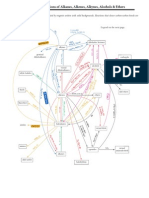
- Roadmap For Reactions of Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes, Alcohols & EthersDokumen5 halamanRoadmap For Reactions of Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes, Alcohols & EthersUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Revised Internal Campus Bus ScheduleDokumen2 halamanRevised Internal Campus Bus ScheduleUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- 9th Maths Ch-03 Coordinate Geometry FinalDokumen20 halaman9th Maths Ch-03 Coordinate Geometry FinalUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Chapter 2 Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen74 halamanChemistry Chapter 2 Multiple Choice QuestionsUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Rotary ActuatorDokumen20 halamanRotary ActuatorUday Prakash Sahu100% (1)
- Acid Base RXNDokumen7 halamanAcid Base RXNUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Collision and Mean Free Path 40 CDokumen2 halamanCollision and Mean Free Path 40 CUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Proforma For OBC NC CertificateDokumen1 halamanProforma For OBC NC CertificateUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- E2 EliminationDokumen2 halamanE2 EliminationUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Test Paper TwelfthDokumen1 halamanTest Paper TwelfthUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Optics 10Dokumen24 halamanOptics 10Uday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid MechanicsDokumen3 halamanFluid MechanicsUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Circular Motion Practice QuestionsDokumen28 halamanCircular Motion Practice QuestionsUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Science Class-10 Sample PaperDokumen8 halamanScience Class-10 Sample PaperUday Prakash Sahu100% (1)
- 01 Lecture KMDokumen44 halaman01 Lecture KMUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Ambedkar Nagar: Prime Classes For IIT-JEE/PMT, Ambedkar NagarDokumen2 halamanAmbedkar Nagar: Prime Classes For IIT-JEE/PMT, Ambedkar NagarUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- PaperDokumen3 halamanPaperUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Bohr's Model QuestionsDokumen2 halamanBohr's Model QuestionsUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- CHEM Study Guide on Atomic StructureDokumen4 halamanCHEM Study Guide on Atomic StructureUday Prakash Sahu0% (1)
- Class 9 Oct 09Dokumen3 halamanClass 9 Oct 09Uday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Samudra ManthanDokumen4 halamanSamudra ManthanUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Pages From 10 Ct-22Dokumen1 halamanPages From 10 Ct-22Uday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Ambedkar Nagar: Prime Classes For IIT-JEE/PMT, Ambedkar NagarDokumen2 halamanAmbedkar Nagar: Prime Classes For IIT-JEE/PMT, Ambedkar NagarUday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz - Compressors and Compressed Air SystemsDokumen3 halamanQuiz - Compressors and Compressed Air SystemsUday Prakash Sahu100% (1)
- Compressed Air System Design ManualDokumen26 halamanCompressed Air System Design ManualBadrul HishamBelum ada peringkat
- Atomic & Nuclear BatteryDokumen6 halamanAtomic & Nuclear BatteryIJAMTESBelum ada peringkat
- PHY 142 (FAVOUR) QuestionsDokumen60 halamanPHY 142 (FAVOUR) QuestionsAbdulganeey Horlarmilekan Muheez100% (1)
- Test Bank For Chemistry in Context Applying Chemistry To Society 7th Edition Acs Full DownloadDokumen29 halamanTest Bank For Chemistry in Context Applying Chemistry To Society 7th Edition Acs Full Downloadsaraboydtfwqybmone100% (36)
- Scientific Methods in ArchaeologyDokumen3 halamanScientific Methods in ArchaeologyHassan Sulaiman MusaBelum ada peringkat
- RADIATION Fact or FictionDokumen2 halamanRADIATION Fact or FictionAljann Rhyz GemillanBelum ada peringkat
- Using Phet Simulahons For Chemistry Inquiry: Free Research - Based Resources On The WebDokumen4 halamanUsing Phet Simulahons For Chemistry Inquiry: Free Research - Based Resources On The WebLiliana GarcíaBelum ada peringkat
- 11 PDF Fslce Physics QPDokumen28 halaman11 PDF Fslce Physics QPAT SinaBelum ada peringkat
- FDR Gamma Ray SourceDokumen1 halamanFDR Gamma Ray Sourceu2006262918Belum ada peringkat
- Radiation Physics and Dosimetry: Fundamentals of Ionizing Radiation and Its MeasurementDokumen51 halamanRadiation Physics and Dosimetry: Fundamentals of Ionizing Radiation and Its MeasurementOmar A. MohammadBelum ada peringkat
- Theory - Physics - XII - Ambernath - 27-11-2019 Pjha (Correction) PDFDokumen9 halamanTheory - Physics - XII - Ambernath - 27-11-2019 Pjha (Correction) PDFSayyed AliabbasBelum ada peringkat
- Use of Hydrogen Isotopes in Ground-Water StudiesDokumen29 halamanUse of Hydrogen Isotopes in Ground-Water StudiesDevendra SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- FT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Radioactivity)Dokumen17 halamanFT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Radioactivity)lelon81Belum ada peringkat
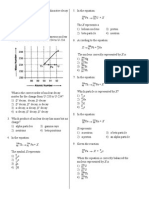
- Represent Real-Life Situations Using Exponential FunctionsDokumen34 halamanRepresent Real-Life Situations Using Exponential FunctionsFretchie Anne C. LauroBelum ada peringkat
- CO2-Sessionwise Problems-2022Dokumen5 halamanCO2-Sessionwise Problems-2022Black PantherBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Physics MT2007Dokumen5 halamanNuclear Physics MT2007manni_tx4414Belum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Manual For Introductory Geology PDFDokumen361 halamanLaboratory Manual For Introductory Geology PDFJhinsher TagleBelum ada peringkat
- Radioactive Decay Equations & Half-Life CalculationsDokumen14 halamanRadioactive Decay Equations & Half-Life Calculationsshabbir626Belum ada peringkat
- Alchemy - The Secret of Immortality Finally Revealed PDFDokumen73 halamanAlchemy - The Secret of Immortality Finally Revealed PDFjoe333100% (2)
- (183 Marks) : (1 Mark)Dokumen33 halaman(183 Marks) : (1 Mark)Yu SunBelum ada peringkat
- JC2 Physics H2 2018 RafflesDokumen88 halamanJC2 Physics H2 2018 RafflesVarshLokBelum ada peringkat
- 1 RT Tos 2021 Radiation Physics Equipment Biology ProtectionDokumen7 halaman1 RT Tos 2021 Radiation Physics Equipment Biology ProtectionChona CastorBelum ada peringkat
- Letters to the Editor reports on parity violation in beta decayDokumen3 halamanLetters to the Editor reports on parity violation in beta decayMendoza JohnyBelum ada peringkat
- Measurement of Body Composition in Children - UpToDateDokumen27 halamanMeasurement of Body Composition in Children - UpToDatemarina alvesBelum ada peringkat
- Stanford Neurodiagnostics Policies Manual 2010Dokumen241 halamanStanford Neurodiagnostics Policies Manual 2010Felipe Kanda50% (2)
- Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceDokumen43 halamanChemistry: The Molecular ScienceMikaila Denise LoanzonBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Stage 3 Exam 2015Dokumen40 halamanPhysics Stage 3 Exam 2015ACrazyNakedManBelum ada peringkat
- Etextbook 978 0131495081 Physics For Scientists Engineers With Modern Physics 4th EditionDokumen61 halamanEtextbook 978 0131495081 Physics For Scientists Engineers With Modern Physics 4th Editionbeatrice.bump837100% (42)
- Past Papers IGCSE 2023 21Dokumen8 halamanPast Papers IGCSE 2023 21David ThydetBelum ada peringkat
- General Biology 2: 2 Semester - Module 4Dokumen20 halamanGeneral Biology 2: 2 Semester - Module 4Almira IbbaBelum ada peringkat
- Earths Internal HeatDokumen26 halamanEarths Internal HeatmikhaelaBelum ada peringkat