Broadcast Control Channel
Diunggah oleh
telecomstuffs7931Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Broadcast Control Channel
Diunggah oleh
telecomstuffs7931Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Broadcast Control Channel
The Broadcast Control Channel is transmitted by the BTS at all times. The RF carrier used to transmit the BCCH is referred to as the BCCH carrier. The MS monitors the information carried on the BCCH periodically (at least every 3 secs!" #hen it is s#itched on and not in a call. The BCCH Consists of$ a. Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH!$ Carries the follo#in% information$
&ocation 'rea (dentity (&'(!. &ist of nei%hborin% cells that should be monitored by the MS. &ist of fre)uencies used in the cell. Cell identity. *o#er control indicator. +T, permitted. 'ccess control (i.e." emer%ency calls" call barrin% ... etc.!. CBCH description.
The BCCH is transmitted at constant po#er at all times" and all MS that may see- to use it to measure its si%nal stren%th. .+ummy/ bursts are transmitted to ensure continuity #hen there is no BCCH carrier traffic. b. Fre)uency Correction Channel (FCCH!$ This is transmitted fre)uently on the BCCH timeslot and allo#s the mobile to synchroni0e its o#n fre)uency to that of the transmittin% base site. The FCCH may only be sent durin% timeslot on the BCCH carrier fre)uency and therefore it acts as a fla% to the mobile to identify Timeslot . c. Synchroni0ation Channel (SCH! The SCH carries the information to enable the MS to synchroni0e to the T+M' frame structure and -no# the timin% of the individual timeslots. The follo#in% parameters are sent$
Frame number. Base Site (dentity Code (BS(C!.
The MS #ill monitor BCCH information from surroundin% cells and store the information from the best si1 cells. The SCH information on these cells is also stored so that the MS may )uic-ly resynchroni0e #hen it enters a ne# cell.
Common Control Channels
The Common Control Channel (CCCH! is responsible for transferrin% control information bet#een all mobiles and the BTS. This is necessary for the implementation of .call ori%ination/ and .call pa%in%/ functions. (t consists of the follo#in%$ a. Random 'ccess Channel (R'CH! 2sed by the mobile #hen it re)uires %ainin% access to the system. This occurs #hen the mobile initiates a call or responds to a pa%e. b. *a%in% Channel (*CH! 2sed by the BTS to pa%e MS" (pa%in% can be performed by an (MS(" TMS( or (M3(!. c. 'ccess 4rant Control Channel ('4CH! 2sed by the BTS to assi%n a dedicated control channel to a MS in response to an access messa%e received on the Random 'ccess Channel. The MS #ill move to the dedicated channel in order to proceed #ith either a call setup" response to a pa%in% messa%e" &ocation 'rea 2pdate or Short Messa%e Service. d. Cell Broadcast Channel (CBCH! This channel is used to transmit messa%es to be broadcast to all MS5s #ithin a cell. The CBCH uses a dedicated control channel to send its messa%es" ho#ever it is considered a common channel because all mobiles in the cell can receive the messa%es. 'ctive MS5s must fre)uently monitor both BCCH and CCCH. The CCCH #ill be transmitted on the RF carrier #ith the BCCH.
Dedicated Control Channels
The +CCH is a sin%le timeslot on an RF carrier that is used to convey ei%ht Stand6alone +edicated Control Channels (S+CCH!. ' sin%le MS for call setup" authentication" location updatin% and SMS point to point use a S+CCH. 's #e #ill see later" S+CCH can also be found on a BCCH7CCCH timeslot" this confi%uration only allo#s four S+CCHs. b. Slo# 'ssociated Control Channel (S'CCH! Conveys po#er control and timin% information in the do#nlin- direction (to#ards the MS! and Receive Si%nal Stren%th (ndicator (RSS(!" and lin)uality reports in the uplin- direction. c. Fast 'ssociated Control Channel (F'CCH! The F'CCH is transmitted instead of a TCH. The F'CCH 88steals/ the TCH burst and inserts its o#n information. The F'CCH is used to carry out user authentication" handovers and immediate assi%nment.
'll of the control channels are re)uired for system operation" ho#ever" in the same #ay that #e allo# different users to share the radio channel by usin% different timeslots to carry the conversation data" the control channels share timeslots on the radio channel at different times. This allo#s efficient passin% of control information #ithout #astin% capacity that could be used for call traffic. To do this #e must or%ani0e the timeslots bet#een those" #hich #ill be used for traffic" and those" #hich #ill carry control si%nalin%.
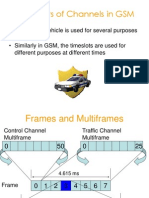
Channel Combination
The different lo%ical channel types mentioned are %rouped into #hat are called channel combination. The four most common channel combination are listed belo#$ 9. Full Rate Traffic Channel Combination : TCH;7F'CCH < S'CCH =. Broadcast Channel Combination : BCCH < CCCH 3. +edicated Channel Combination : S+CCH; < S'CCH; >. Combined Channel Combination : BCCH<CCCH<S+CCH><S'CCH> ?. Half Rate Traffic Channel Combination : TCH9@7F'CCH < S'CCH The Half Rate Channel Combination (#hen introduced! #ill be very similar to the Full Rate Traffic Combination.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 1 Broadcast Control ChannelDokumen3 halaman1 Broadcast Control ChannelRaafat YounisBelum ada peringkat
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedDari EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedBelum ada peringkat
- 7.GSM ChannelsDokumen24 halaman7.GSM Channelsmanthasaikarthik100% (1)
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesDari EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- 7GSM ChannelsDokumen24 halaman7GSM ChannelsNishant Amit MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksDari EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Channels1 PDFDokumen46 halamanGSM Channels1 PDFNutan Prakash SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- The Internet of Things: Key Applications and ProtocolsDari EverandThe Internet of Things: Key Applications and ProtocolsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Lec1 (Channels)Dokumen29 halamanLec1 (Channels)Nazir AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Channels & Air InterfaceDokumen31 halamanGSM Channels & Air InterfaceCabdallaBelum ada peringkat
- The International Telecommunications Regime: Domestic Preferences And Regime ChangeDari EverandThe International Telecommunications Regime: Domestic Preferences And Regime ChangeBelum ada peringkat
- GSM ChannelsDokumen20 halamanGSM Channelsshashikala kotiBelum ada peringkat
- Radio Access Networks for UMTS: Principles and PracticeDari EverandRadio Access Networks for UMTS: Principles and PracticePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- GSM Physical and Logical ChannelsDokumen20 halamanGSM Physical and Logical ChannelsJamshid IbragimovBelum ada peringkat
- Radio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftDari EverandRadio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- GSM Channels: Prepared By:-Mohd Nazir ShakeelDokumen20 halamanGSM Channels: Prepared By:-Mohd Nazir ShakeelNguyễn HùngBelum ada peringkat
- GSM ChannelsDokumen46 halamanGSM ChannelsAshish KushwahBelum ada peringkat
- Ziaullah 075 A2Dokumen4 halamanZiaullah 075 A2Umar FarooqBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Channel TypesDokumen3 halamanGSM Channel Typessanu81Belum ada peringkat
- 2G Channels and 3GDokumen5 halaman2G Channels and 3Gkn09Belum ada peringkat
- Global System For MobileDokumen26 halamanGlobal System For MobileAditi AnandBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Radio ConceptsDokumen3 halamanGSM Radio ConceptsMD SahidBelum ada peringkat
- BTS Make-Nokia, Ericsson, ZTE, Alcatel Etc. 2206,2964 MCC, IMSI (International Subscriber Identity Moduel) SIM (Subscriber Identity Module)Dokumen4 halamanBTS Make-Nokia, Ericsson, ZTE, Alcatel Etc. 2206,2964 MCC, IMSI (International Subscriber Identity Moduel) SIM (Subscriber Identity Module)AnujBelum ada peringkat
- GSM ChannelsDokumen3 halamanGSM ChannelsImran AslamBelum ada peringkat
- Logical Channels & Multi-Frame StructuresDokumen20 halamanLogical Channels & Multi-Frame Structuresfahadmalik89Belum ada peringkat
- GSM Frame StructureDokumen25 halamanGSM Frame StructureVarun SoodBelum ada peringkat
- Logical Channels of GSMDokumen7 halamanLogical Channels of GSMAhmad HusaeriBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Channels - MyDokumen11 halamanGSM Channels - MyDeepan BhattacharyyaBelum ada peringkat
- Logical Channels in GSM: DownlinkDokumen3 halamanLogical Channels in GSM: DownlinkchillcasterBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Logical ChannelsDokumen5 halamanGSM Logical ChannelsRahul SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Concepts of Channels in GSMDokumen13 halamanConcepts of Channels in GSMSana DanyalBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Channels: Prepared By:-Mohd Nazir ShakeelDokumen20 halamanGSM Channels: Prepared By:-Mohd Nazir Shakeelhi2nazirBelum ada peringkat
- Logical Channels in GSMDokumen10 halamanLogical Channels in GSMshridon123Belum ada peringkat
- Various Interfaces and Their Mapping: Skgochhayat RTTC, BhubaneswarDokumen43 halamanVarious Interfaces and Their Mapping: Skgochhayat RTTC, BhubaneswarKuldeep BishtBelum ada peringkat
- Vikas GSM NotesDokumen27 halamanVikas GSM NotesVicky SehrawatBelum ada peringkat
- Downlink Both Ways: Signaling Dedicated To A UserDokumen6 halamanDownlink Both Ways: Signaling Dedicated To A Userverma_ravinderBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3: GSM Call and GSM Frame Structure S. B. Bhosle Government Polytechnic, YavatmalDokumen12 halamanLecture 3: GSM Call and GSM Frame Structure S. B. Bhosle Government Polytechnic, YavatmalSarojkumar BhosleBelum ada peringkat
- Figure 1. General Architecture of A GSM NetworkDokumen15 halamanFigure 1. General Architecture of A GSM NetworkPiyush MalviyaBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Network ArchitectureDokumen8 halamanGSM Network ArchitectureAvanish SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- ChannelsDokumen51 halamanChannelsHammad AnsariBelum ada peringkat
- 2G Logical ChannelsDokumen14 halaman2G Logical ChannelsAkhtar Khan100% (1)
- GSM Channel ConceptDokumen35 halamanGSM Channel ConceptShachi P GowdaBelum ada peringkat
- Channels and Identiies in GSMDokumen5 halamanChannels and Identiies in GSMshashikala kotiBelum ada peringkat
- 1.5 Radio Interface 1.5.1 General CharacteristicsDokumen20 halaman1.5 Radio Interface 1.5.1 General CharacteristicsThomas Daniel HaYfordBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Logical ChannelsDokumen8 halamanGSM Logical ChannelsfarhadfzmBelum ada peringkat
- Rationale Behind Use of Channels: Channel. Physical Channel Is Specified by Specific Time Slot/carrier FrequencyDokumen9 halamanRationale Behind Use of Channels: Channel. Physical Channel Is Specified by Specific Time Slot/carrier FrequencyEC20B1007 Dheeban Kumar GBelum ada peringkat
- Frequency Channels in GSMDokumen34 halamanFrequency Channels in GSMFarzeen FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Training DocumentDokumen1.087 halamanGSM Training Documentrezameza100% (1)
- Some Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1Dokumen23 halamanSome Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1nileshBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Pocket GuideDokumen11 halamanGSM Pocket GuidehanitkBelum ada peringkat
- ProjectDokumen37 halamanProjectSurina KondillyaBelum ada peringkat
- ChannelsDokumen27 halamanChannelsRaju KumarBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Logical ChannelsDokumen25 halamanGSM Logical ChannelsSachin K GowdaBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Originating Call FlowDokumen1 halamanGSM Originating Call FlowMohd SajidBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Radio Parameter Setting and Adjustment: GSM P&O DepartmentDokumen60 halamanGSM Radio Parameter Setting and Adjustment: GSM P&O DepartmentAhmed Hamed BadrBelum ada peringkat
- MC NotesDokumen109 halamanMC Notesprithwirajsrimani2Belum ada peringkat
- 02 ChannelsDokumen27 halaman02 ChannelsRathnaKumarBelum ada peringkat
- 02 Channels - PpsDokumen27 halaman02 Channels - PpsAbdul HameedBelum ada peringkat
- You Can't Joke About That: Why Everything Is Funny, Nothing Is Sacred, and We're All in This TogetherDari EverandYou Can't Joke About That: Why Everything Is Funny, Nothing Is Sacred, and We're All in This TogetherBelum ada peringkat
- The Importance of Being Earnest: Classic Tales EditionDari EverandThe Importance of Being Earnest: Classic Tales EditionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (44)
- The House at Pooh Corner - Winnie-the-Pooh Book #4 - UnabridgedDari EverandThe House at Pooh Corner - Winnie-the-Pooh Book #4 - UnabridgedPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (5)
- The Inimitable Jeeves [Classic Tales Edition]Dari EverandThe Inimitable Jeeves [Classic Tales Edition]Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Take My Advice: Letters to the Next Generation from People Who Know a Thing or TwoDari EverandTake My Advice: Letters to the Next Generation from People Who Know a Thing or TwoJames L. HarmonPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5)
- Welcome to the United States of Anxiety: Observations from a Reforming NeuroticDari EverandWelcome to the United States of Anxiety: Observations from a Reforming NeuroticPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (10)
- The Narrow Road to the Interior and HojokiDari EverandThe Narrow Road to the Interior and HojokiPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (61)





































































![The Inimitable Jeeves [Classic Tales Edition]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/711420909/198x198/ba98be6b93/1712018618?v=1)








