Cases Compensation Management
Diunggah oleh
Mitika MahajanHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Cases Compensation Management
Diunggah oleh
Mitika MahajanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Salary inequities at Acme Manufacturing
Joe Black was trying to figure out what to do about a problem salary situation he had in his plant. Black recently took over as president of Acme Manufacturing. The founder and former president, Bill George, had been president for 35 years. The company was family owned and located in a small eastern Arkansas town. It had approximately 250 employees and was the largest employer in the community. Black was the member of the family that owned Acme, but he had never worked for the company prior to becoming the president. He had an MBA and a law degree, plus five years of management experience with a large manufacturing organization, where he was senior vice president for human resources before making his move to Acme. A short time after joining Acme, Black started to notice that there was considerable inequity in the pay structure for salaried employees. A discussion with the human resources director led him to believe that salaried employees pay was very much a matter of individual bargaining with the past president. Hourly paid factory employees were not part of this problem because they were unionized and their wages were set by collective bargaining. An examination of the salaried payroll showed that there were 25 employees, ranging in pay from that of the president to that of the receptionist. A closer examination showed that 14 of the salaried employees were female. Three of these were front-line factory supervisors and one was the human resources director. The other 10 were non management. This examination also showed that the human resources director appeared to be underpaid, and that the three female supervisors were paid somewhat less than any of the male supervisors. However, there were no similar supervisory jobs in which there were both male and female job incumbents. When asked, the Hr director said she thought the female supervisors may have been paid at a lower rate mainly because they were women, and perhaps George, the former president, did not think that women needed as much money because they had working husbands. However, she added she personally thought that they were paid less because they supervised less-skilled employees than did the male supervisors. Black was not sure that this was true. The company from which Black had moved had a good job evaluation system. Although he was thoroughly familiar with and capable in this compensation tool, Black did not have time to make a job evaluation study at Acme. Therefore, he decided to hire a compensation consultant from a nearby university to help him. Together, they decided that all 25 salaried jobs should be in the same job evaluation cluster, that a modified ranking method of job evaluation should be used, and that the job descriptions recently completed by the HR director were current, accurate, and usable in the study. The job evaluation showed that the HR director and the three female supervisors were being underpaid relative to comparable male salaried employees.
Black was not sure what to do. He knew that if the underpaid female supervisors took the case to the local EEOC office, the company could be found guilty of sex discrimination and then have to pay considerable back wages. He was afraid that if he gave these women an immediate salary increase large enough to bring them up to where they should be, the male supervisors would be upset and the female supervisors might comprehend the total situation and want back pay. The HR director told Black that the female supervisors had never complained about pay differences. The HR director agreed to take a sizable salary increase with no back pay, so this part of the problem was solved. Black believed he had for choices relative to the female supervisors: 1. To do nothing. 2. To gradually increase the female supervisors salaries. 3. To increase their salaries immediately. 4. To call the three supervisors into his office, discuss the situation with them, and jointly decide what to do. Questions:
1. What would you do if you were Black? 2. How do you think the company got into a situation like this in the first place? 3. Why would you suggest Black pursue the alternative you suggested?
Variable Pay Nitin Arora was wrapping up for the day, when his phone rang. "Hi, Nitin, Anil here. Can I pop in for a few minutes?" "Yes, if you can be here in two minutes flat" Arora said. "You got it," the other man said and hung up. Anil Mathur was a Brand Manager at Care Soft, a large fast-moving consumer products company. In fact, it was Arora who had, as the Chief of hr at Care Soft, recruited Mathur from a medium-sized company in Mumbai. Over the years, they had built up a good rapport. In any case, Arora was known to be one of the more friendly top executives in the company. He had to be; he was after all the hr guy. Arora had a vague idea of what Mathur might want to discuss, but he decided to frame his replies as he went along. As promised, the 36-year-old brand manager was in Arora's room in less than two minutes. "When was the last time we had a semi-formal meeting like this one?" Arora asked his guest. "I don't remember, may be six months ago," Mathur replied. "8:30 on a Friday evening, you've made me stay back. So this had better be important," Arora pretended to threaten his colleague. "You are darn right, this is important," said Mathur. "I am unhappy with my pay hike for last fiscal." "But you got your letter a month ago, why are you bringing it up only now?" Arora asked. "I have been thinking about it, and trying to find out if I am the only one feeling let down by the new variable pay scheme," said Mathur. A little over a year ago, Care Soft had decided to replace its fixed compensation system with variable pay. In fact, the whole exercise was done in three months flat, and implemented with little advance notice to the employees, who were not altogether surprised since the word had gotten around as soon as the hr consultancy was hired to draw up the new compensation structure. An article in the in-house magazine and an e-mail from the CEO announced the scheme. The company, which had a turnover of Rs 1,200 crore the previous fiscal, hadn't yet moved to stock options, but it had introduced a profit-sharing plan. The variable component, usually paid out annually, was linked to the performance of both the individual and his team. Understandably,
individual performance had a higher weightage than team performance. That apart, there were peer incentives for team and individual performances. These rewarded performance in kind-a paid holiday, gift vouchers, or gifts. Since the concept of variable pay was new to Care Soft, it had decided to implement it at only the senior and middle management levels, apart from shopfloor workers-leaving out the junior management. The senior management-starting from a general manager to the CEO-had a variable component ranging from 15-40 per cent. Those below had just 5-15 per cent in variable pay. Mathur, as a brand manager, came in at the general manager level. And last year had been particularly bad for the toothbrush division he headed. Volume sales had dropped by 5 per cent, and rupee sales by 15 per cent because of price cuts, promotions, and discounts. Besides, a new toothbrush that had been slated for launch in the second half of last year hadn't been launched. This was a low-end brush that was expected to rake in Rs 1 crore in sales. Fiscal 2001-02 was the first full year of variable pay, and Arora could tell that the executives weren't happy with it. Already, a VP and another general manager had made their displeasure known to Arora. Mathur leaving would not only encourage the other two to follow suit, but also impact the new pay plan. "My performance targets were unreal," continued Mathur. ''Show me one company that has increased its toothbrush sales and I'll walk out of this room and never complain." "True," said Arora. "But look at it from the organisation's point of view. There are other units that have taken a hit, with the result that our sales for last year were down. We've tried to do the best under the circumstances." "Probably, but why penalise me for somebody else's fault," Mathur complained. "I don't understand." "I am referring to the new toothbrush that my team was supposed to launch in the second half of last year," Mathur explained. "We couldn't introduce it because the design team sat on it for a long time, and then the engineering team took its own sweet time bringing it into production. By the time we were ready to go, we realised that the launch expense wouldn't be worth it. The variable component in my compensation is 20 per cent and it's been a double-whammy for me. The fact that we didn't meet our targets ensured zero-increase in my incentives, and the increase in base pay doesn't even beat the rate of inflation." "Anil, don't forget that most of us in Care Soft are in the same boat. That said, I do think we have an issue here. Here's what I can promise: I'll put forth these issues to the compensation committee. I cannot promise anything else." Both men looked at the clock on Arora's table. It was well past 10.
"I have to pick up medicines for my son," said Arora. "If I don't find a chemist open now, I'll be signing my divorce papers tomorrow." Both men laughed and parted. On Monday, the first thing Arora did was to call his CEO, Rishab Patel, and advise him to convene a compensation committee meeting. "This week I have a diary so full that a knife wouldn't go through it," the CEO told Arora. "Do me a favour, Nitin. I'll send out the meeting request, but could you handle it?" "But how can we decide on anything without you being there?" Arora asked. "Don't. Flesh out the issues and keep them ready for me. Let me finish with our foreign partners' visit this week." "Should we have the meeting next week in that case?" "No, go ahead. We can have a second meet next week." One thing that had irked Arora all along was the fact that Patel seemed inadequately concerned with hr problems. He was more concerned about what he called "strategic issues". By afternoon, Arora had got a confirmation to the meeting request sent out by Patel. The committee would meet on Wednesday pre-lunch. (''Can't tackle hr post lunch,'' somebody had wise-cracked in acknowledgement.) Care Soft's compensation committee comprised, apart from Patel and Arora, the CFO Narayan Shastri, coo Niranjan Roy, Director (Marketing) Utpal Sinha, a principal from the consulting company that had drawn up the new compensation structure Anurag Kesaria, and an independent director, who was a chartered accountant by profession, and widely regarded for his management wisdom Raman Behl. The agenda for the meeting had already been circulated the previous day. Therefore, all the men were aware of the issues at hand. "How widespread is the discontent, Nitin?" coo Roy set the ball rolling. "I have reason to believe that it is quite widespread," said Arora, "although only a handful of people have taken it up with me so far." "In that case, may be we are over-reacting," said Shastri. "We need to give the new system more time. After all, it's just a year old." "I don't think one can possibly over-react to such an issue," noted Behl. "The worst thing that we can do now is to let the morale take a hit." "I agree," said Arora.
"I couldn't agree more," added Sinha, Director of marketing. "I just can't afford to lose any of my men. And certainly not good men like Anil Mathur. I don't care if we have to pay him more." "That's not a good idea," pointed out Arora. "We cannot be seen as being selective in our rewards. The whole idea behind variable pay was to motivate people across the board with the promise of greater rewards for better performance. We cannot make changes arbitrarily." "Then, may be we didn't implement the new structure properly," bristled Sinha. "Or may be we should simply revert to the old fixed system, which according to me worked just fine." "You are right about poor implementation," consultant Kesaria said. "But it would be a strategic mistake to bring back the old system. After all, the reasons why we introduced variable pay still hold. The business environment is changing, and we cannot afford to reward people based on the quaint notion of entitlement. Executives have to justify what they earn." "Besides," the Chief Financial Officer, Shastri, intervened, "variable pay is a great way to control costs and improve productivity. Not to mention that such a system automatically attracts highcalibre people." "Yes, when the going is good in the market, there is no problem with variable pay," noted Sinha. "But when the markets crash, like they have now, your profits shrink. Do you then ask people to forget all the hard work they've done, and say 'sorry, can't give you any increments because we've had a bad year'. Believe me, it will take less than six months to clean out talent from this company. Don't forget that the next year is going to be equally bad for FMCG companies." "The IT industry is not only benching people, but asking them to take pay cuts," pointed out Shastri. "May be," retorted Sinha. "But how many code-jocks can join insurance, banking, pharma, or any other industry as marketing heads or even CEOs? And asking people to deliver 15 per cent growth in a market that is shrinking is the surest way of losing them." ''Actually it is worth looking at what is going wrong with the system," said Behl. "As I understand it, even shop-floor workers-whose variable pay is linked to productivity-are affected since the company has cut back on production to liquidate dealer inventory.'' "As far as I can see," said Kesaria, "it seems to be a problem of implementation. May be we didn't communicate adequately, perhaps we need to tweak our measurement systems, review them more frequently and reward people closer to the date of their achievements." "That is a good idea," said Behl. "Money may not be the only reason why people work, but it is one of the biggest reasons. Besides, a change like this needs significant lead time. It's a cultural change and people must be prepared for it." "I would have loved to do this over a period of one year," defended Arora. "But I was asked to
implement it within three months of the board deciding on it. Besides, where is the top management commitment to this initiative? Who is the champion of this variable pay? I could be, but it will have more credibility if the CEO also showed that he was committed to it." "Meanwhile," Behl refocused the discussion, "we need to figure out a few things. One, how to convince people like Mathur that variable pay will actually help them in the long run. Two, how to achieve a buy-in across the organisation. And three, how to rectify some of the errors we may have made in its implementation. Finally, here's the worst-case option, whether we really want to scrap variable pay and return to the fixed system." What should Care Soft do?
Performance Linked Variable Bonus We are a medium sized Engineering/ Manufacturing co. Last year we had introduced the system of Performance Linked Variable Bonus for our officers in Engineering segment of business. We have given increments in two components: Fixed increase on existing CTC. Annual Performance Linked bonus (Calculated as certain %age of avg. in a grade). The ratio of two components (Fixed : Variable :: 60 %:40%) The resultant Compensation structure is now guaranteed pay to Variable: 95%: 5%. This year we want to make it 92 %: 8% But we are facing certain issues in the second year, which are outlined below and we want to clarify as to what are industry practices (in your company pl.) Whether the Variable Performance Bonus (Linked to performance) given in a particular year is included in CTC for the purpose of: Deciding salary of new recruit within the range of the company levels in a particular grade. If it is included then whether variable bonus forms part of comp. Package of new recruit. If yes how it is given and how much.(Corresponding to what performance Level.) Giving increments next year? e.g. if the ratio of guaranteed pay to variable pay is 95 : 5 % . Then the increments next year would mean: Performance Linked increase (covers incidence of inflation also) on existing CTC : i.e. increase on 95 % or 100%.(Pl. clarify) Calculation of performance linked Variable Bonus levels (Last year we calculated it as % age of averages in a grade). Now would it mean calculating bonus amounts (as %age of avg.) at different performance Levels on 95% or 100%(i.e. including last years bonus amount as well). 3. Current Ratio of two increment components. Because of first time introduction in our case it was high: 60 % : 40 %.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 9 To 5 Props PresetsDokumen4 halaman9 To 5 Props Presetsapi-300450266100% (1)
- Case Study Job EvaluationDokumen2 halamanCase Study Job Evaluationkushagrakul86% (7)
- Case Studies Case HRMDokumen2 halamanCase Studies Case HRMSuman Poudel67% (18)
- Salary Inequities at Acme ManufacturingDokumen3 halamanSalary Inequities at Acme Manufacturingsantosh80% (5)
- Compensation ManagementDokumen24 halamanCompensation ManagementAmit Sharma100% (1)
- Performance Management Link With HRM FunctionsDokumen7 halamanPerformance Management Link With HRM FunctionsWinifrida50% (2)
- STRATEGIC COMPENSATION MANAGEMENTDokumen22 halamanSTRATEGIC COMPENSATION MANAGEMENTbijuanitha50% (2)
- Three Actors of IRDokumen7 halamanThree Actors of IRbuvan100% (2)
- Human Resource Management Case StudyDokumen2 halamanHuman Resource Management Case StudyAnooja SajeevBelum ada peringkat
- Differences Between Traditional Pay Systems and Incentive Pay SystemsDokumen2 halamanDifferences Between Traditional Pay Systems and Incentive Pay Systemshammad memon100% (1)
- Case SummaryDokumen7 halamanCase SummaryManjurul Haque100% (1)
- Case Study On Job AnalysisDokumen15 halamanCase Study On Job Analysisbokamanush0% (1)
- Research Proposal Organizational ManagementDokumen6 halamanResearch Proposal Organizational ManagementMitika Mahajan100% (2)
- Critically Evaluate The Application of Leadership Theories To A Leader in An Organisational ContextDokumen8 halamanCritically Evaluate The Application of Leadership Theories To A Leader in An Organisational ContextMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Employee Onboarding ToolkitDokumen60 halamanEmployee Onboarding ToolkitMitika Mahajan100% (2)
- UMR Introduction 2023Dokumen110 halamanUMR Introduction 2023tu reves mon filsBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study: Salary Inequities at Acme Manufacturing: So... TheDokumen2 halamanCase Study: Salary Inequities at Acme Manufacturing: So... TheMehwish Rasheed50% (2)
- Performance Management AssignmentDokumen8 halamanPerformance Management AssignmentZoya KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Job Evaluation: Analyzing and Rating Jobs to Determine Relative WorthDokumen22 halamanJob Evaluation: Analyzing and Rating Jobs to Determine Relative WorthPragya SachdevaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study On HRMDokumen15 halamanCase Study On HRMAmarBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Compensation ManagementDokumen14 halamanPrinciples of Compensation ManagementBrijesh KanwarBelum ada peringkat
- Wage DifferentialDokumen89 halamanWage Differentialankit13mba132100% (1)
- HRM NotesDokumen37 halamanHRM NotesMohima ChakravortyBelum ada peringkat
- Compensation Management ProjectDokumen40 halamanCompensation Management Projecthaseeb_tankiwala100% (6)
- Compensation Pay Structure in IndiaDokumen6 halamanCompensation Pay Structure in IndiaShruti VadherBelum ada peringkat
- Incentives & Fringe BenefitsDokumen8 halamanIncentives & Fringe Benefitsmail_pooja850% (2)
- Human Resource Development: Topic: HRD For WorkersDokumen20 halamanHuman Resource Development: Topic: HRD For WorkersDealer XyzBelum ada peringkat
- Study Notes On Job EvaluationDokumen8 halamanStudy Notes On Job EvaluationkomalBelum ada peringkat
- Inter-Intra Industry Wage DiffrentialsDokumen6 halamanInter-Intra Industry Wage DiffrentialsArdhendu Srivastava50% (2)
- Hrd-Recent Trends and ChallengesDokumen55 halamanHrd-Recent Trends and ChallengesS- Ajmeri100% (1)
- Philosophy and Introduction To Industrial RelationsDokumen12 halamanPhilosophy and Introduction To Industrial RelationsAshish Das100% (1)
- HRM Notes Case StudyDokumen18 halamanHRM Notes Case StudyAanika AeryBelum ada peringkat
- Comp &ben (Question Bank)Dokumen13 halamanComp &ben (Question Bank)Saumyadeep Dutta100% (1)
- Facilities Planning & Training AidsDokumen9 halamanFacilities Planning & Training AidsFibin Haneefa100% (1)
- Rating Less AppraisalsDokumen14 halamanRating Less Appraisalshrhrh0% (2)
- Human Resource Management EthicsDokumen48 halamanHuman Resource Management Ethicsswapnil_b100% (3)
- MBA Notes - Strategic HRM First ChapterDokumen9 halamanMBA Notes - Strategic HRM First ChapterSubhash RedekarBelum ada peringkat
- Reward System Process IssuesDokumen16 halamanReward System Process IssuesKalpesh Solanki100% (1)
- Risky Hire Case StudyDokumen3 halamanRisky Hire Case Studyvoleti990% (1)
- Factor Evaluation SystemDokumen4 halamanFactor Evaluation Systemk.srikanth ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- How To Improve Industrial Relations in An OrganizationDokumen3 halamanHow To Improve Industrial Relations in An Organizationaravindan260Belum ada peringkat
- Salary MatrixDokumen15 halamanSalary MatrixSuparna Dv0% (1)
- Workforce Utilisation and Employment PracticesDokumen12 halamanWorkforce Utilisation and Employment PracticesHOD Commerce100% (1)
- Human Resource Management: by Prof. JayalakshmiDokumen19 halamanHuman Resource Management: by Prof. JayalakshmiDiyana100% (1)
- Changing Role of HRDDokumen10 halamanChanging Role of HRDRenjul Paravur100% (1)
- Evolution of HR in India from Ancient TimesDokumen15 halamanEvolution of HR in India from Ancient TimesParas AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Tamil Nadu Catering Establishment Act 1958Dokumen4 halamanTamil Nadu Catering Establishment Act 1958send2hemant83% (6)
- Questionnaire For Employee Reward and RecognitionDokumen6 halamanQuestionnaire For Employee Reward and RecognitionAnonymous d2ZSDEBelum ada peringkat
- Workers Participation Case IDokumen3 halamanWorkers Participation Case IAlka Jain100% (1)
- Reward System in IndiaDokumen2 halamanReward System in Indiaramraj02Belum ada peringkat
- Irll NotesDokumen26 halamanIrll NotesKopuri Mastan ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Compensation ManagementDokumen60 halamanCompensation Managementaakine0% (1)
- Employee Overload Case StudyDokumen5 halamanEmployee Overload Case StudyAlviyaBelum ada peringkat
- Nature and Scope of OBDokumen4 halamanNature and Scope of OBMbaStudent56Belum ada peringkat
- Compensation TheoriesDokumen34 halamanCompensation TheoriesdollyguptaBelum ada peringkat
- Standing Orders and Grievance ResolutionDokumen29 halamanStanding Orders and Grievance Resolutionthulasie_600628881100% (1)
- CBHRM-Competency Mapping MCQsDokumen11 halamanCBHRM-Competency Mapping MCQsNimmy MathewBelum ada peringkat
- Using Talent Management To Drive A Culture of ExcellenceDokumen2 halamanUsing Talent Management To Drive A Culture of ExcellenceHARSHIT KUMARBelum ada peringkat
- Workers Participation in Management Benefits and FormsDokumen44 halamanWorkers Participation in Management Benefits and FormsSamBelum ada peringkat
- Promotion Transfer and SeparationDokumen17 halamanPromotion Transfer and SeparationUpasana Kanchan67% (3)
- HRM CompensationDokumen46 halamanHRM CompensationShassotto Chatterjee100% (2)
- The Case of Variable PayDokumen5 halamanThe Case of Variable PayragsthevikingBelum ada peringkat
- Resolve Salary Inequities at Acme ManufacturingDokumen2 halamanResolve Salary Inequities at Acme ManufacturingKhushbu BavishiBelum ada peringkat
- Salary Inequities at Acme ManufacturingDokumen3 halamanSalary Inequities at Acme ManufacturingPUJA PODDARBelum ada peringkat
- Docit - Tips HRM Case Study 2 Human Resource Management EmploymentDokumen6 halamanDocit - Tips HRM Case Study 2 Human Resource Management EmploymentjyothibsBelum ada peringkat
- Ethical Leadership and Sustainable EnterpriseDokumen7 halamanEthical Leadership and Sustainable EnterpriseMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Operation Management: Unit-1 (BBA Sem V)Dokumen30 halamanOperation Management: Unit-1 (BBA Sem V)Mitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Q-1 Multiple Choice Questions: (1 Mark Each)Dokumen3 halamanQ-1 Multiple Choice Questions: (1 Mark Each)Mitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Critically Evaluate The Application of Leadership Theories To A Leader in An Organisational ContextDokumen8 halamanCritically Evaluate The Application of Leadership Theories To A Leader in An Organisational ContextMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment-1 Industrial Relations and Labour Legislations 24 August 2013Dokumen1 halamanAssignment-1 Industrial Relations and Labour Legislations 24 August 2013Mitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE 1 - 1 Problem Solving PDFDokumen17 halamanMODULE 1 - 1 Problem Solving PDFMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Leadership StylesDokumen28 halamanLeadership StylesMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Q-1 Multiple Choice Questions: (1 Mark Each)Dokumen4 halamanQ-1 Multiple Choice Questions: (1 Mark Each)Mitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1Dokumen5 halamanUnit 1Mitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2Dokumen37 halamanUnit 2Mitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Union Structure and Trade Union Movement: Prepared By: Prof. Mitika MahajanDokumen18 halamanUnion Structure and Trade Union Movement: Prepared By: Prof. Mitika MahajanMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- IBE Unit 5Dokumen39 halamanIBE Unit 5Mitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- ME Unit 3 Managerial EconomicsDokumen30 halamanME Unit 3 Managerial EconomicsMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5 Business EconomicsDokumen20 halamanUnit 5 Business EconomicsMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Irll 1Dokumen26 halamanIrll 1Mitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- ME Unit-2Dokumen67 halamanME Unit-2Mitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- ME Unit-5Dokumen20 halamanME Unit-5Mitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- PersonalityDokumen25 halamanPersonalityMitika Mahajan100% (2)
- Economic DevelopmentDokumen24 halamanEconomic DevelopmentMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Nature of Business Environment ExplainedDokumen26 halamanNature of Business Environment ExplainedMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Economic DevelopmentDokumen24 halamanEconomic DevelopmentMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Environment and Economic Development: Prepared By: Prof. Mitika MahajanDokumen18 halamanEnvironment and Economic Development: Prepared By: Prof. Mitika MahajanMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- CaseDokumen7 halamanCaseMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- IBE UNit-4Dokumen10 halamanIBE UNit-4Mitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Nature of Business Environment ExplainedDokumen26 halamanNature of Business Environment ExplainedMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 MIR LLDokumen1 halamanAssignment 1 MIR LLMitika MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- 07 Chapter2Dokumen16 halaman07 Chapter2Jigar JaniBelum ada peringkat
- NCMA 217 - Newborn Assessment Ma'am JhalDokumen5 halamanNCMA 217 - Newborn Assessment Ma'am JhalMariah Blez BognotBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Resources in PakistanDokumen5 halamanNatural Resources in PakistanSohaib EBelum ada peringkat
- Reach Out and Read Georgia Selected For AJC Peachtree Road Race Charity Partner ProgramDokumen2 halamanReach Out and Read Georgia Selected For AJC Peachtree Road Race Charity Partner ProgramPR.comBelum ada peringkat
- Proper restraint techniques for dogs and catsDokumen153 halamanProper restraint techniques for dogs and catsjademattican75% (4)
- Nitric OxideDokumen20 halamanNitric OxideGanesh V GaonkarBelum ada peringkat
- Reading and Listening 2Dokumen4 halamanReading and Listening 2Hải Anh TạBelum ada peringkat
- 2 English Course BDokumen8 halaman2 English Course BAnjana27Belum ada peringkat
- Tugas B InggrisDokumen9 halamanTugas B InggrisDellyna AlmaBelum ada peringkat
- wch13 01 Rms 20230817Dokumen24 halamanwch13 01 Rms 20230817halcieeschBelum ada peringkat
- Micdak BackgroundDokumen3 halamanMicdak Backgroundappiah ernestBelum ada peringkat
- Schneider Electric PowerPact H-, J-, and L-Frame Circuit Breakers PDFDokumen3 halamanSchneider Electric PowerPact H-, J-, and L-Frame Circuit Breakers PDFAnonymous dH3DIEtzBelum ada peringkat
- Jounce Therapeutics Company Events and Start DatesDokumen48 halamanJounce Therapeutics Company Events and Start DatesEquity NestBelum ada peringkat
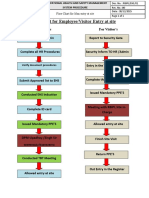
- fLOW CHART FOR WORKER'S ENTRYDokumen2 halamanfLOW CHART FOR WORKER'S ENTRYshamshad ahamedBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 7 Tabata TrainingDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan 7 Tabata Trainingapi-392909015100% (1)
- Chapter 5Dokumen16 halamanChapter 5Ankit GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Wastewater Treatment Plant Design PDFDokumen68 halamanWastewater Treatment Plant Design PDFmostafa1alaahobaBelum ada peringkat
- Study On Marketing Strategies of Fast Food Joints in IndiaDokumen35 halamanStudy On Marketing Strategies of Fast Food Joints in IndiaNiveditaParaashar100% (1)
- Impact of Covid-19 On Audit Quality: Presented byDokumen13 halamanImpact of Covid-19 On Audit Quality: Presented byMST. SADIYA SULTANABelum ada peringkat
- Slaked Lime MSDS Safety SummaryDokumen7 halamanSlaked Lime MSDS Safety SummaryFurqan SiddiquiBelum ada peringkat
- GSIS vs. de LeonDokumen9 halamanGSIS vs. de Leonalwayskeepthefaith8Belum ada peringkat
- Cap 716 PDFDokumen150 halamanCap 716 PDFjanhaviBelum ada peringkat
- Workplace Hazard Analysis ProcedureDokumen12 halamanWorkplace Hazard Analysis ProcedureKent Nabz60% (5)
- Lesson 1 CA 3Dokumen13 halamanLesson 1 CA 3myndleBelum ada peringkat
- Strauss Dental Catalog 2013Dokumen74 halamanStrauss Dental Catalog 2013d3xt3rokBelum ada peringkat
- Notice: Use of Segways® and Similar Devices by Individuals With A Mobility Impairment in GSA-Controlled Federal FacilitiesDokumen2 halamanNotice: Use of Segways® and Similar Devices by Individuals With A Mobility Impairment in GSA-Controlled Federal FacilitiesJustia.comBelum ada peringkat
- Hotel Housekeeping EQUIPMENTDokumen3 halamanHotel Housekeeping EQUIPMENTsamahjaafBelum ada peringkat