Analog and Digital Modulation Techniques
Diunggah oleh
Amit JhaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Analog and Digital Modulation Techniques
Diunggah oleh
Amit JhaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Analog and Digital Modulation Techniques
Computer Networks Assignment 1 Amit Kumar Jha 201201087 Introduction
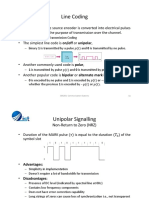
Modulation is the process of varying some parameter of a periodic waveform in order to use that signal to convey a message.It is used mostly in the transmission of data from one point to another. Although there are many types of modulation, there are two basic types; analog modulation and digital modulation. The main difference between analog modulation and digital modulation is in the manner that they transmit data. With analog modulation, the input needs to be in the analog format, while digital modulation needs the data in a digital format. Because of the differences in the input signal, the output signal is also quite different. In analog modulation, any value between the maximum and minimum is considered to be valid. It is not so with digital modulation as only two values are considered valid; one value to represent 1 and another to represent 0. All other values are considered noise and are rejected. Because most signals that we transmit are analog in nature, like ones voice, it is far simpler to do analog modulation than digital. If you want to transmit a voice using digital modulation, youd need to pass it through an analog-to-digital converter before transmission and a digital-toanalog converter at the receiver to recover the original signal. The additional stages needed for transmitting digital modulation increases both the cost and complexity of the transmitter and receiver. The major advantage that digital modulation has over analog transmission is how it achieves greater fidelity. With analog modulation, any noise or interference that falls in the given frequency bandwidth gets mixed with the actual signal. Although there are a number of ways to mitigate noise, it will still cause some amount of degradation. Because digital modulation only recognizes 0s and 1s, any noise is virtually eliminated once the receiver discerns whether a 0 or a 1 was transmitted. Unless the signal is very badly distorted, the output signal will be literally identical to what was transmitted. Under both analog modulation and digital modulation, there are a number of other modulation techniques each with its own strengths and weaknesses. But each technique has its basic commonalities of transmitting either a digital or analog signal.
Type of Modulation Techniques
Sr. No 01 Modulation Techniques Analog Modulation Techniques. Type (i) Amplitude Modulation (ii) Frequency Modulation (iii) Phase Modulation 02 Digital Modulation Techniques (i) Amplitude Shift Keying (ii) Frequency Shift Keying (iii)Phase Shift Keying Notation A.M. F.M. P.M. A.S.K. F.S.K. P.S.K.
Analog Modulation Techniques
Amplitude Modulation Amplitude Modulation modifies the amplitude of the carrier to represent 1s or 0s.In the above example, a 1 is represented by the presence of the carrier for a predefined period of 3 cycles of carrier. Absence--or no carrier--indicates a 0.
Advantages:
Simple to design.
Disadvantages:
Noise spikes on transmission medium interfere with the carrier signal. Loss of connection is read as 0s.
Frequency Modulation Frequency Modulation modifies the frequency of the carrier to represent the 1s or 0s. In the above example, a 0 is represented by the original carrier frequency, and a 1 by a much higher frequency (the cycles are spaced closer together).
Advantages:
Immunity to noise on transmission medium. Always a signal present. Loss of signal easily detected
Disadvantages:
Requires 2 frequencies Detection circuit needs to recognize both frequencies when signal is lost.
Phase Modulation
Phase Modulation modifies the phase of the carrier to represent a 1 or 0.
The carrier phase is switched at every occurrence of a 1 bit, but remains unaffected for a 0 bit. The phase of the signal is measured relative to the phase of the preceding bit. The bits are timed to coincide with a specific number of carrier cycles (3 in this example = 1 bit).
Advantage:
Only 1 frequency used Easy to detect loss of carrier
Disadvantages:
Complex circuitry that is required to generate and detect phase changes.
Digital Modulation Techniques
Amplitude Shift Keying(ASK) This is a form of amplitude modulation that represents digital data as variations in the amplitude of a carrier wave. In an ASK system, binary symbol 1 is represented by transmitting carrier wave of fixed amplitude and fixed frequency for the bit duration T seconds. ASK assigns a unique patter of binary digits to a finite number of amplitudes. Each pattern of the bits form a symbol which is represented by a particular amplitude. The equation of the wave generated by the ASK is given by: S (t) = m (t). Ac cos (2fct).
Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) In this scheme digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier wave. In binary FSK, the simplest FSK scheme a pair of discrete frequencies are used to transmit binary information. In this scheme 1 is called the mark frequency and 0 is called space frequency.
Phase-shift keying (PSK) It is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by changing, or modulating, the phase of a reference signal (the carrier wave). PSK assigns a unique pattern of binary digits to a finite number of phases. Each pattern of bits forms the symbol that is represented by the particular phase.
Comparison of Various Techniques
With respect to Analog Techniques it has been found that frequency modulation is much better than amplitude modulation. The main factor for that is that the amplitude modulation has much more chances of being disrupted by noise which effects
Amplitude causing it to change the signal present in the amplitude modulated wave. But AM can travel larger distances then FM due to the fact that FM waves have a tendency to interfere with physical objects due to their lower wavelengths. If we consider Digital Techniques we find that FSK is better than ASK because it is not disrupted easily by interference and is easily generated with modern electronic equipment. But it is not right to define which technique is better just because of the fact that each of the techniques have use cases where other techniques are not ideal to be used. In general digital techniques are valid only when digital information has to be sent and analog techniques are valid when the signal is analog.
References http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Modulation http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Communication_Systems/What_is_Modulation%3F NCERT 12th Class Textbook
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- RF Analog Impairments Modeling for Communication Systems Simulation: Application to OFDM-based TransceiversDari EverandRF Analog Impairments Modeling for Communication Systems Simulation: Application to OFDM-based TransceiversBelum ada peringkat
- 00 - Mobile Communication (404189) - Syllabus - OKDokumen32 halaman00 - Mobile Communication (404189) - Syllabus - OKvydeoBelum ada peringkat
- Partial-Update Adaptive Signal Processing: Design Analysis and ImplementationDari EverandPartial-Update Adaptive Signal Processing: Design Analysis and ImplementationBelum ada peringkat
- Advantages of Coaxial CableDokumen24 halamanAdvantages of Coaxial CableBurhanudheen KodiyathoorBelum ada peringkat
- Cellular ConceptDokumen50 halamanCellular Conceptyanuar1976100% (1)
- Understanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeDari EverandUnderstanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeMaciej NawrockiBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1wireless Communication NotesDokumen99 halamanUnit 1wireless Communication NotesMahesh AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Pulse Code ModulationDokumen11 halamanPulse Code ModulationMaryam ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Cellular Mobile CommunicationsDokumen93 halamanCellular Mobile CommunicationsPrabhakara RaoBelum ada peringkat
- Ec7101-Telecommunication Switching Circuits & NetworksDokumen8 halamanEc7101-Telecommunication Switching Circuits & NetworksAbhijeet BishtBelum ada peringkat
- 2 PSTN PDFDokumen38 halaman2 PSTN PDFRamyAyashBelum ada peringkat
- Millimicrosecond Pulse Techniques: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationDari EverandMillimicrosecond Pulse Techniques: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationBelum ada peringkat
- Analog and Digital Communications TechniquesDokumen3 halamanAnalog and Digital Communications TechniquesSrinivas SamalBelum ada peringkat
- Mobile Communication by ANBARASANDokumen29 halamanMobile Communication by ANBARASANAnbarasan RamamoorthyBelum ada peringkat
- Emerging Technologies in Information and Communications TechnologyDari EverandEmerging Technologies in Information and Communications TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- Wireless Communication 2 MarksDokumen14 halamanWireless Communication 2 MarksBala Subramani100% (2)
- Interview QuestionsDokumen4 halamanInterview QuestionsAlbert YehBelum ada peringkat
- Amplitude Modulation of PSK Project ReportDokumen6 halamanAmplitude Modulation of PSK Project ReportEngr Muhammad Imran100% (2)
- The Fundamentals of Signal Transmission: Optical Fibre, Waveguides and Free SpaceDari EverandThe Fundamentals of Signal Transmission: Optical Fibre, Waveguides and Free SpaceBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4 Satellite AccessDokumen23 halamanUnit 4 Satellite AccessSoundararajan RajagopalanBelum ada peringkat
- Optimizing and Testing WLANs: Proven Techniques for Maximum PerformanceDari EverandOptimizing and Testing WLANs: Proven Techniques for Maximum PerformanceBelum ada peringkat
- Telecommunications Engineering II by Jorma KekalainenDokumen608 halamanTelecommunications Engineering II by Jorma KekalainenJorma KekalainenBelum ada peringkat
- CAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkDari EverandCAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkPenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (1)
- Cellular Communication (Jaga (Edited) )Dokumen25 halamanCellular Communication (Jaga (Edited) )RajKiran100% (1)
- Electronic Engineering Applications of Two–Port Networks: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionDari EverandElectronic Engineering Applications of Two–Port Networks: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionBelum ada peringkat
- Telecom Networks Lecture1Dokumen31 halamanTelecom Networks Lecture1Basir Usman100% (2)
- LTE OFDMA SimulationDokumen9 halamanLTE OFDMA Simulationrajendra4343Belum ada peringkat
- Ch-1-2 Introduction To Cellular Mobile CommunicationsDokumen63 halamanCh-1-2 Introduction To Cellular Mobile Communicationsapi-3717973100% (5)
- Dipole Simulation Using ANSYS EDTDokumen37 halamanDipole Simulation Using ANSYS EDTNix FaineBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank Module 1: An Overview of JavaDokumen4 halamanQuestion Bank Module 1: An Overview of JavaVaishnavi SrinathBelum ada peringkat
- An Overview of The GSM SystemDokumen32 halamanAn Overview of The GSM System0796105632Belum ada peringkat
- SECTION 4 - RF System DesignDokumen44 halamanSECTION 4 - RF System DesignBelachew AndualemBelum ada peringkat
- No 4 ESS Toll Switch ArchitectureDokumen18 halamanNo 4 ESS Toll Switch ArchitectureManjushree KumaravelBelum ada peringkat
- Teletraffic Engineering and Network PlanningDokumen14 halamanTeletraffic Engineering and Network PlanningMuhammad RidlonBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT-one-IT2402-MOBILE COMMUNICATION Unit 1 2 MarksDokumen6 halamanUNIT-one-IT2402-MOBILE COMMUNICATION Unit 1 2 Marksdatatycoon100% (1)
- Mobile Communication ComputingDokumen11 halamanMobile Communication ComputingvenkateshmukharjiBelum ada peringkat
- 1V. Satellite Access - 2Dokumen49 halaman1V. Satellite Access - 2Sai TejaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture No 41Dokumen7 halamanLecture No 41Afzal100% (1)
- Wireless Sensor Network Architecture and ProtocolsDokumen42 halamanWireless Sensor Network Architecture and ProtocolsMounisha g bBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes on Mobile Communication SystemsDokumen181 halamanLecture Notes on Mobile Communication SystemsUsama LatifBelum ada peringkat
- Solution Manual of Mobile Communication and NetworksDokumen5 halamanSolution Manual of Mobile Communication and NetworksZarnigar AltafBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 PDFDokumen43 halamanLecture 1 PDF1saifulBelum ada peringkat
- Echo Cancellation Project ProposalDokumen2 halamanEcho Cancellation Project ProposalmidhunBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 22 Transport LayerDokumen25 halamanChapter 22 Transport LayerAbhay DharamshiBelum ada peringkat
- Wireless T NG H PDokumen24 halamanWireless T NG H PPhương Linh TrầnBelum ada peringkat
- The Network Layer: Andrew S. Tanenbaum Computer Networks Fourth Edition PP. 343-396Dokumen82 halamanThe Network Layer: Andrew S. Tanenbaum Computer Networks Fourth Edition PP. 343-396Ss ShetBelum ada peringkat
- ECE Interview Questions With AnswersDokumen7 halamanECE Interview Questions With AnswersRohit Xavier100% (1)
- 50 Top Electronics System Design Lab Viva Questions and Answers Electronics System Design Lab Viva QuestionDokumen9 halaman50 Top Electronics System Design Lab Viva Questions and Answers Electronics System Design Lab Viva QuestionDINESHBelum ada peringkat
- Wireless and Mobile Network ArchitectureDokumen45 halamanWireless and Mobile Network Architecturepruthvi mpatilBelum ada peringkat
- CDMA PresentationDokumen14 halamanCDMA Presentationapi-376836388% (8)
- Spread Spectrum Multiple AccessDokumen6 halamanSpread Spectrum Multiple AccessgauravsanadhyaBelum ada peringkat
- WSN Introduction: Wireless Sensor Network Design Challenges and ProtocolsDokumen48 halamanWSN Introduction: Wireless Sensor Network Design Challenges and ProtocolsVaishnavi BalasubramanianBelum ada peringkat
- DebugDokumen10 halamanDebugAmit JhaBelum ada peringkat
- Global DependenceDokumen2 halamanGlobal DependenceAmit JhaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1: Arachnophobia: 1 GoalDokumen3 halamanAssignment 1: Arachnophobia: 1 GoalAmit JhaBelum ada peringkat
- Newtonian GodDokumen1 halamanNewtonian GodAmit JhaBelum ada peringkat
- GATE Previous Year Solved Papers ECE PDFDokumen276 halamanGATE Previous Year Solved Papers ECE PDFsathisBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Modulation TechniquesDokumen60 halamanDigital Modulation TechniquesĐặng Hoài TiếnBelum ada peringkat
- Bit Rate - WikipediaDokumen11 halamanBit Rate - Wikipediarommel baldagoBelum ada peringkat
- Digital TV Ring & Recipes Part 2 DVB-CDokumen27 halamanDigital TV Ring & Recipes Part 2 DVB-CΔημητρα ΣωτηρακηBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Viasat MEOLink Modem O3b UserManualDokumen70 halamanManual Viasat MEOLink Modem O3b UserManualfaisalzaheer0% (1)
- Steer RF Chapter1Dokumen86 halamanSteer RF Chapter1قرين لطفيBelum ada peringkat
- Multi Carrier ModulationDokumen22 halamanMulti Carrier ModulationmuseBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Signal Processing (DSP)Dokumen5 halamanDigital Signal Processing (DSP)abdullahBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Digital Communications and Data TransmissionDokumen114 halamanFundamentals of Digital Communications and Data TransmissionRitu JangraBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Communication MCQDokumen1 halamanDigital Communication MCQAmol Ghodake50% (2)
- 63180en 01Dokumen157 halaman63180en 01Samuel MarquezBelum ada peringkat
- Study of LoraDokumen6 halamanStudy of LoraAnimeshBelum ada peringkat
- Week 6Dokumen39 halamanWeek 6shahzadjaffar100% (1)
- Digital CommunicationDokumen148 halamanDigital CommunicationValBelum ada peringkat
- Mobile ComputingDokumen7 halamanMobile ComputingDivya NadarBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Communication UNIT 3Dokumen5 halamanDigital Communication UNIT 3Nihal GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Bit RateDokumen8 halamanBit RateMoji PiyapongBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Digital Communications: Bernadeth B. Zari, PeceDokumen18 halamanIntroduction To Digital Communications: Bernadeth B. Zari, PeceJOHN RYAN GUINANAOBelum ada peringkat
- MScThesis Jagdish Pandey FinalDokumen97 halamanMScThesis Jagdish Pandey FinaljaragumuraBelum ada peringkat
- ReadmeDokumen9 halamanReadmenarendraBelum ada peringkat
- Review of Wayne Tomasi's "Electronic Communications SystemDokumen16 halamanReview of Wayne Tomasi's "Electronic Communications Systemtsk2230Belum ada peringkat
- Komdat 3Dokumen8 halamanKomdat 3Khusnil MujibBelum ada peringkat
- Bit Loading and Channel SimulationDokumen13 halamanBit Loading and Channel SimulationSimon KepchabeBelum ada peringkat
- DTT Principles: N. Jethi, Dir (E) DDK, BhubaneswarDokumen34 halamanDTT Principles: N. Jethi, Dir (E) DDK, BhubaneswarShishir GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Bit Error Rate Evaluation of IEEE 802.16 in OFDM SystemDokumen4 halamanBit Error Rate Evaluation of IEEE 802.16 in OFDM Systemabhi_rules08Belum ada peringkat
- LECT - 15&16. Signal DesignDokumen46 halamanLECT - 15&16. Signal DesigntevredeBelum ada peringkat
- TCM ApplicationsDokumen50 halamanTCM ApplicationsPhúc Hòa PtitBelum ada peringkat
- Ofdma: LTE Air Interface CourseDokumen63 halamanOfdma: LTE Air Interface CourseAkhtar KhanBelum ada peringkat
- EC6501 - Digital Communications Lecture Notes Chapter 1 IntroductionDokumen75 halamanEC6501 - Digital Communications Lecture Notes Chapter 1 IntroductionsangeetaBelum ada peringkat
- Visible Light Communication ProjectsDokumen242 halamanVisible Light Communication ProjectsHarry RamzaBelum ada peringkat
- CCNA: 3 in 1- Beginner's Guide+ Tips on Taking the Exam+ Simple and Effective Strategies to Learn About CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Routing And Switching CertificationDari EverandCCNA: 3 in 1- Beginner's Guide+ Tips on Taking the Exam+ Simple and Effective Strategies to Learn About CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Routing And Switching CertificationBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Dari EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (4)
- The Ultimate Kali Linux Book - Second Edition: Perform advanced penetration testing using Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, and EmpireDari EverandThe Ultimate Kali Linux Book - Second Edition: Perform advanced penetration testing using Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, and EmpireBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Antenna Systems for 5G Network Deployments: Bridging the Gap Between Theory and PracticeDari EverandAdvanced Antenna Systems for 5G Network Deployments: Bridging the Gap Between Theory and PracticePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersDari EverandAmazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityDari EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (13)
- CEH Certified Ethical Hacker Practice Exams, Third EditionDari EverandCEH Certified Ethical Hacker Practice Exams, Third EditionBelum ada peringkat
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamDari EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Hacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxDari EverandHacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (67)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamDari EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamBelum ada peringkat
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionDari EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)Dari EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)Belum ada peringkat
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsDari EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsBelum ada peringkat
- A Practical Guide Wireshark ForensicsDari EverandA Practical Guide Wireshark ForensicsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- Networking Fundamentals: Develop the networking skills required to pass the Microsoft MTA Networking Fundamentals Exam 98-366Dari EverandNetworking Fundamentals: Develop the networking skills required to pass the Microsoft MTA Networking Fundamentals Exam 98-366Belum ada peringkat
- Cybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringDari EverandCybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (40)
- Introduction to Cyber-Warfare: A Multidisciplinary ApproachDari EverandIntroduction to Cyber-Warfare: A Multidisciplinary ApproachPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- CCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamDari EverandCCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamBelum ada peringkat
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsDari EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsBelum ada peringkat
- ITIL® 4 Direct, Plan and Improve (DPI): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional and Strategic Leader DPI certificationDari EverandITIL® 4 Direct, Plan and Improve (DPI): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional and Strategic Leader DPI certificationBelum ada peringkat
- Mastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionDari EverandMastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionBelum ada peringkat