42, Wang, 2000 English
Diunggah oleh
Nur Sidiq Agung SDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
42, Wang, 2000 English
Diunggah oleh
Nur Sidiq Agung SHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
The Chinese Journal of Burns Wounds and Surface Ulcers 2000, 12(2): 29~30.
III phase clinical trial of MEBO report for treating burns
Wang Wen-song, Wang Hong
Dalian Burn Center, Dalian 4th Peoples Hospital, Dalian, Liaoning 116031, China
INTRODUCTION From January of 1997 to March of 1999 Dalian Burn Center carried out a phase III clinical trial on MEBO, in which 100 burn patients in therapeutic group were treated with moist exposed burn ointment (MEBO), and 50 cases were treated with silver sulfadiazine (SD-Ag) as control. GENERAL INFORMATION: Gender: Among 150 patients, there are 128 male and 22 female (Table 1).
Table 1. Ratio of both sexes in the 2 groups
Groups (Number) MEBO (100) SD-Ag (50)
Male (%) 85.0 86.0
Female (%) 15.0 10.0
2
Male/Female 5.7/1 6.1/1
There was no significant difference between groups: <1, P>0.05
Age: Patients in the trial aged from 1~65 and details were showed in Table 2.
Table 2. Distribution of ages
Groups (Number) MEBO (100) SD-Ag (50)
1~18 (%) 18.0 20.0
18~35 (%) 48.0 50.0
36~50 (%) 22.0 18.0
2
51~60 (%) 12.0 12.0
The case-age structure of patients in two groups is very similar: <1, P>0.05
Burn severity: Table 3 showed the comparison of burn severity in two groups.
Table 3. Comparison of burn severity in two groups
Groups (Number) MEBO (100) SD-Ag (50)
2
Mild (%) 54.0 56.0
Moderate (%) 30.0 34.0
Severe (%) 16.0 14.0
Compared between two groups: <1, P>0.05
-1-
The Chinese Journal of Burns Wounds and Surface Ulcers 2000, 12(2): 29~30.
Causes of burn: The percentage distribution of burn causes in two groups was list in Table 4.
Table 4. Causes of burns in two groups (%)
Groups (Number) MEBO (100)
Hot Liquid 58.0
Flame 30.0
Hot solid 5.0
Acid/ Alkaline 3.0 4.0
Electricity 3.0 4.0
Radiation 1.0
Others 0 0
SD-Ag 54.0 34.0 6.0 (50) Compared between two groups: 2<1, P>0.05
1.0
Distribution of burn regions: Table 5 showed distribution of burn regions in two groups.
Table 5. Distribution of burn regions
Groups (Number) MEBO (100) SD-Ag (50)
Head & face (%) 53.0 52.0
2
Trunk (%) 42.0 46.0
Extremities (%) 66.0 58.0
Compared between two groups: <1, P>0.05
Laboratory test: Table 6 demonstrated the changes of white blood cells (WBC) after treatment in both groups. Though there was no difference in the incidence of abnormality between two groups (P>0.05), the significant test by Four-fold Table verified that the decrease of WBC in SD-Ag group had obviously higher.
Table 6. Changes of WBC after treatment in both groups (%)
Groups (Number) MEBO (100) SD-Ag (50)
Normal 60.0 90.0
Increase 10.00 2.00
9
Decrease 0 8.0 *
9
Abnormality 10 10
Note: Increase was marked as WBC>1010 /L; Decrease as WBC<410 /L Compared between two groups: * P<0.05
The above information revealed that there was no significant difference of two groups regarding sex, age, burn severity, burn regions and incidence of WBC abnormality, indicating two groups are comparable. RESULTS
-2-
The Chinese Journal of Burns Wounds and Surface Ulcers 2000, 12(2): 29~30.
Average wound healing time: Table 7 displayed comparison of wound healing time without skin-grafting in two groups. It was showed that the extremely significant differences in comparison of healing time for superficial II, deep II and III degree wounds (P<0.01), disclosing the average wound healing time in MEBO treating group was superior to that in SD-Ag control group.
Table 7. Comparison of wound healing time without skin grafting in two groups (Days, xs)
Groups (Number) MEBO (100) SD-Ag (50)
Superficial II degree 9.02.5 13.02.3 **
Deep II degree 15.33.6 18.03.0 **
III degree 304.5 Skin grafting
Compared with MEBO treating group: ** P<0.01
Analgesic effect: Table 8.
Table 8. Analgesic effect in both groups (%)
Groups (Number) MEBO (100) SD-Ag (50)
Excellent 70.0 10.0 **
2
Good 23.0 36.0 **
Fair 7.0 50.0
Poor 0 4.0
Very poor 0 0
Compared with MEBO treating group: =42.001, ** P<0.01
Incidence of scar formation: Comparison of incidences of scar formation in two groups after treatment was described in Table 9. Extremely significant difference was showed in the incidence of scar formation for deep II degree burns between two groups (P<0.01). It was verified no significant difference regarding the incidence of scar formation for III degree burns between two groups according to Abnormality Test of Four-fold Table (P>0.05).
Table 9. Comparison of incidences of scar formation in two groups
Groups (Number) MEBO (100) SD-Ag (50)
Superficial II degree 0 0
2
Deep II degree 18/56 18/21 **
III degree 19/21 15/15 (skin grafting)
Compared with MEBO treating group: =17.606, ** P<0.01
Wound infection: Either in cases of deep II degree or III degree wounds, there showed no significant difference in two groups concerning the incidence of wound infection (P>0.05).
Table 10. Comparison of wound infection
-3-
The Chinese Journal of Burns Wounds and Surface Ulcers 2000, 12(2): 29~30.
Groups (Number) MEBO (100) SD-Ag (50)
Superficial II degree 0 0
Deep II degree 2/56 1/21
III degree 3/21 2/15
Safety assessment: Of all patients in MEBO treating group, only two developed skin rash during the drug application, which disappeared after discontinuation of ointment application. No irritation to surrounding normal skin or other side effect was observed in the trial. The laboratory test also found no side effect of MEBO ointment to routine test of blood and urine, liver function or renal function. DISCUSSION As a drug for topical use, the results of this clinical trial revealed that MEBO ointment had excellent analgesic effects, accelerated wound healing, prevented or decreased scar formation. It was considered mainly to be used for burns and scalds inflicted by various causes and best therapeutic results could be achieved for treating the superficial and deep II degree burn wounds. The superficial III degree burn wound involving whole dermis but subcutaneous fat layer could also healed spontaneously. The clinical observation showed that MEBO ointment was remarkably superior to SD-Ag in the respects of analgesic effect, accelerating wound healing and alleviating scar formation. Both groups had similar effects in anti-infection. It was agreed that MEBO ointment is an ideal medicine for burn management.
-4-
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Headache Types and CausesDokumen17 halamanHeadache Types and CausesNur Sidiq Agung SBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 2Dokumen1 halamanPresentation 2Nur Sidiq Agung SBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 2Dokumen1 halamanPresentation 2Nur Sidiq Agung SBelum ada peringkat
- TwentyDokumen4 halamanTwentyNur Sidiq Agung SBelum ada peringkat
- A New Approach To Local Burn Wound Care: Moist Exposed Therapy. A Multiphase, Multicenter StudyDokumen9 halamanA New Approach To Local Burn Wound Care: Moist Exposed Therapy. A Multiphase, Multicenter StudyNur Sidiq Agung SBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 2Dokumen1 halamanPresentation 2Nur Sidiq Agung SBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar Pustaka Neuro Hnp2 ZalDokumen1 halamanDaftar Pustaka Neuro Hnp2 ZalNur Sidiq Agung SBelum ada peringkat
- 158 Ioannovich 1 2000Dokumen6 halaman158 Ioannovich 1 2000Nur Sidiq Agung SBelum ada peringkat
- 162 Dham 8 1999Dokumen6 halaman162 Dham 8 1999Nur Sidiq Agung SBelum ada peringkat
- 39 MulticenterDokumen10 halaman39 MulticenterNur Sidiq Agung SBelum ada peringkat
- 39 MulticenterDokumen10 halaman39 MulticenterNur Sidiq Agung SBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Art Therapy AssessmentDokumen7 halamanArt Therapy Assessmentreighn_21100% (4)
- Michael Mahoney A RetrospectiveDokumen17 halamanMichael Mahoney A RetrospectiveJonathon Bender100% (1)
- Clinical Audit: Pain Management in Total Knee Replacement Aadhar Hospital January - July 2018Dokumen29 halamanClinical Audit: Pain Management in Total Knee Replacement Aadhar Hospital January - July 2018Relacy Healthcare100% (2)
- Chest Pain Investigation, Diagnosis and TreatmentDokumen4 halamanChest Pain Investigation, Diagnosis and TreatmentHadsabsaBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine NursingDokumen2 halamanEndocrine NursingUnclePorkchop94% (34)
- PCAP - SummaryDokumen4 halamanPCAP - SummaryNani TumlosBelum ada peringkat
- Dental Trauma LectureDokumen10 halamanDental Trauma Lectureasop06Belum ada peringkat
- Emotion Focused Therapy - Greenberg 2004 PDFDokumen14 halamanEmotion Focused Therapy - Greenberg 2004 PDFiprates2Belum ada peringkat
- Edema Paru Kardiogenik Akut Kak TiaraDokumen8 halamanEdema Paru Kardiogenik Akut Kak TiaraTyara LarisaBelum ada peringkat
- Rectal bleeding causes and treatment optionsDokumen21 halamanRectal bleeding causes and treatment optionslinaleen67% (3)
- Structured Interview Guide For The Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (SIGH-D)Dokumen16 halamanStructured Interview Guide For The Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (SIGH-D)Gemma GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Maquet Servo 900c - User ManualDokumen105 halamanMaquet Servo 900c - User Manualpaola_96Belum ada peringkat
- Yoga Client Intake Form PDFDokumen2 halamanYoga Client Intake Form PDFΑντώνιος Σακελλάρης0% (1)
- Management of PreeclampsiaDokumen11 halamanManagement of PreeclampsiaDanBelum ada peringkat
- Bioeffects of UltrasoundDokumen35 halamanBioeffects of UltrasoundAlexandra Nicoleta Teisi0% (1)
- Aged Care and CounsellingDokumen2 halamanAged Care and CounsellingBildAndhraPradeshBelum ada peringkat
- Attachment and InterventionDokumen13 halamanAttachment and InterventioneducacionchileBelum ada peringkat
- Medicinal Plants: Benefits of LagundiDokumen18 halamanMedicinal Plants: Benefits of LagundiRugi Vicente RubiBelum ada peringkat
- Ocular Manifestations of Systemic DiseaseDokumen85 halamanOcular Manifestations of Systemic Diseaseapi-3705408100% (2)
- Kansas State Drug Mortality Statistics by CountyDokumen7 halamanKansas State Drug Mortality Statistics by CountyGet TreatmentBelum ada peringkat
- Model Curriculum Handbook RadiotDokumen157 halamanModel Curriculum Handbook RadiotYuda FhunkshyangBelum ada peringkat
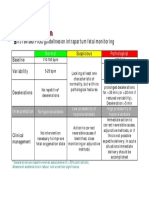
- CTG classification 2015 FIGO guidelines fetal monitoringDokumen1 halamanCTG classification 2015 FIGO guidelines fetal monitoringHerry SasukeBelum ada peringkat
- Management For Challenged ChildrenDokumen7 halamanManagement For Challenged ChildrenUday Kumar50% (2)
- FarmasiDokumen24 halamanFarmasiAulia Suci WulandariBelum ada peringkat
- Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding and Dysmenorrhea GuideDokumen44 halamanDysfunctional Uterine Bleeding and Dysmenorrhea GuideonijinoBelum ada peringkat
- OCB Cataract Surgery QA BookletDokumen36 halamanOCB Cataract Surgery QA BookletSurendar KesavanBelum ada peringkat
- Allergic Contact Terhadap LipstikDokumen4 halamanAllergic Contact Terhadap LipstikKlinik Cempaka PutihBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Case PresentationDokumen25 halamanClinical Case Presentationapi-246186340Belum ada peringkat
- Northern Cancer Control Strategy Final Report March 3Dokumen74 halamanNorthern Cancer Control Strategy Final Report March 3AndrewBelum ada peringkat
- Cabg Case Study FormDokumen9 halamanCabg Case Study FormVlad ConstantinBelum ada peringkat