Acls Nwmnics
Diunggah oleh
krishnaprasadm70 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
120 tayangan2 halamanPrimary survey ABCDs: Assess responsiveness, look, listen, and feel for breathing. If pulseless, begin chest compressions at 100 / min (15:2 ratio with unprotected airway) Consider precordial thump in witnessed arrest with no defibrillator immediately available.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
acls nwmnics
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniPrimary survey ABCDs: Assess responsiveness, look, listen, and feel for breathing. If pulseless, begin chest compressions at 100 / min (15:2 ratio with unprotected airway) Consider precordial thump in witnessed arrest with no defibrillator immediately available.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
120 tayangan2 halamanAcls Nwmnics
Diunggah oleh
krishnaprasadm7Primary survey ABCDs: Assess responsiveness, look, listen, and feel for breathing. If pulseless, begin chest compressions at 100 / min (15:2 ratio with unprotected airway) Consider precordial thump in witnessed arrest with no defibrillator immediately available.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
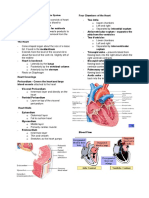
Universal Algorithm for Adult Emergency Cardiac Care
and Primary Survey ABCDs (Excerpt)
Assess responsiveness by speaking loudly, or gently shaking the patient if there are no signs of
trauma.
Call for help/crash cart if the patient is unresponsive.
A Airway: Open airway, look, listen, and feel for breathing.
B Breathing: If not breathing, slowly give 2 rescue breaths.
C Circulation: Check pulse. If pulseless, begin chest compressions at 100/min (15:2 ratio with
unprotected airway). Consider precordial thump in witnessed arrest with no defibrillator
immediately available.
D Defibrillation: Attach monitor/AED. Assess rhythm. Search for and Shock VF/PVT up to 3
times if needed.
——————————————————————————-
Secondary Survey ABCDs (Excerpt)
A Airway: Establish and secure an airway device.
B Breathing: Ventilate with 100% O2. Confirm airway device placement by exam, end-tidal
CO2 monitor, and O2 saturation monitor.
C Circulation: Evaluate rhythm, check pulse, if pulseless continue chest compressions (5:1 ratio
with protected airway), obtain IV access, give rhythm-appropriate medications.
D Differential Diagnosis: Attempt to identify and treat reversible causes.
——————————————————————————–
Asystole Algorithm
Asystole may be discovered during the primary ABCD survey after attaching a monitor, or it
may develop in a previously monitored patient. In either case, it is essential that asystole be
confirmed in another lead with properly functioning equipment. If the patient is in true asystole
and is a candidate for resuscitation, then proceed with the secondary ABCD survey.
Interventions for asystole are guided by the instructive phrase and acronym,
“Asystole ….. Check me in another lead,
then let’s have a cup of TEA.”
Acronym – Intervention – Comments/Dose
T Transcutaneous Pacing (TCP) Only effective with early implementation
along with appropriate interventions and medications.
NOTE: Not effective with prolonged down time.
E Epinephrine 1 mg IV q3-5 min.
A Atropine 1 mg IV q3-5 min. (max. dose 0.04 mg/kg)
Consider termination of efforts if asystole persists despite appropriate interventions.
———————————————————————————–
Bradycardia Algorithm
Treatments for absolute bradycardia (
“All Trained Dogs Eat Iams”
NOTE:(The sequence reflects interventions for increasingly severe bradycardia)
Mnemonic – Intervention – Comments/Dose
All – Atropine – 0.5-1.0 mg IV push q 3-5 min. (max. dose 0.03-0.04 mg/kg)
Trained - TCP – Use Transcutaneous Pacing (TCP) immediately with severely symptomatic
patients.
Dogs - Dopamine 5-20 µg/kg/min.
Eat – Epinephrine 2-10 µg/min.
Iams – Isoproterenol 2-10 µg/min.
——————————————————————————-
PEA Algorithm
Pulseless Electrical Activity may be discovered during the primary ABCD survey when a
monitor is attached to a pulseless patient and a rhythm is shown. As part of the secondary ABCD
survey, a doppler should be used to confirm pulselessness.
Interventions for pulseless electrical activity are guided by the letters
“P-E-A”
Intervention – Comments/Dose
Problem – Search for the probable cause and intervene accordingly. (see PEA Problem Table )
[Pulmonary Embolism] – No pulse w/ CPR, JVD – Thrombolytics, surgery
[Acidosis] – (preexisting) Diabetic/renal patient, ABGs -Sodium bicarbonate,
hyperventilation
[Tension pneumothorax] – No pulse w/ CPR, JVD, tracheal deviation – Needle thoracostomy
[Cardaic Tamponade] – No pulse w/ CPR, JVD, narrow pulse pressure prior to arrest –
Pericardiocentesis
[Hyperkalemia] – (preexisting) Renal patient, EKG, serum K level – Sodium bicarbonate,
calcium chloride, albuterol nebulizer, insulin/glucose, dialysis, diuresis, kayexalate
[Hypothermia] – Core temperature – Hypothermia Algorithm
[Hypovolemia] – Collapsed vasculature – Fluids
[Hypoxia] – Airway, cyanosis, ABGs – Oxygen, ventilation
[Massive MI] – History, EKG – Acute Coronary Syndrome algorithm
[Drug Overdose] – Medications, illicit drug use – Treat accordingly
Epinephrine – 1 mg IV q3-5 min.
Atropine – With slow heart rate, 1 mg IV q3-5 min. (max. dose 0.04 mg/kg)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Pediatric Nursing: Prepared By: ProfDokumen4 halamanPediatric Nursing: Prepared By: ProfAllyza Jane SartigaBelum ada peringkat
- ACHALASIADokumen2 halamanACHALASIAMaster ChiefBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary SystemDokumen9 halamanUrinary SystemCailah Sofia SelausoBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Surgery Seq 1Dokumen2 halamanAssignment Surgery Seq 1Maryam ishaqBelum ada peringkat
- Box Hijau Box Bahan AnesDokumen6 halamanBox Hijau Box Bahan Anesredy pristantoBelum ada peringkat
- Pricon BroDokumen41 halamanPricon Broophtho india inc100% (1)
- NP3 PreboardDokumen128 halamanNP3 PreboardKris Nielsen AmantilloBelum ada peringkat
- WINFOCUS USLS BL1 Provider CourseProgram 2d en Template 2012 Adult1Dokumen8 halamanWINFOCUS USLS BL1 Provider CourseProgram 2d en Template 2012 Adult1TNCinthBelum ada peringkat
- Imaging Evaluation of Tracheobronchial InjuriesDokumen14 halamanImaging Evaluation of Tracheobronchial InjuriesSantiago TapiaBelum ada peringkat
- MS NeurologyDokumen30 halamanMS NeurologyAu CassieBelum ada peringkat
- Uterine MYOMADokumen5 halamanUterine MYOMARoss Manalang100% (2)
- Developmental Dysplasia of The HipDokumen16 halamanDevelopmental Dysplasia of The Hipjonathan_alvaBelum ada peringkat
- IMU Surgery History: Name: Audrey Gan Mei Xin ID: 00000023725 Cohort: DT117Dokumen3 halamanIMU Surgery History: Name: Audrey Gan Mei Xin ID: 00000023725 Cohort: DT117Audrey GanBelum ada peringkat
- CSF LeaksDokumen11 halamanCSF Leakssudheer joelBelum ada peringkat
- Review FrenectomyDokumen6 halamanReview FrenectomyNyitnyit KunyitBelum ada peringkat
- NCP: Nursing Care Plan For Bone FracturesDokumen8 halamanNCP: Nursing Care Plan For Bone FracturesElham TabaoBelum ada peringkat
- Humerus Anterolateral ApproachDokumen15 halamanHumerus Anterolateral ApproachHussein SamhatBelum ada peringkat
- Biology NMAT Notes AnatomyCirculatory and RespiratoryDokumen13 halamanBiology NMAT Notes AnatomyCirculatory and RespiratoryMa. Teresa M. AbainzaBelum ada peringkat
- Prof. Dr. Hamdi Karakayalı CVDokumen3 halamanProf. Dr. Hamdi Karakayalı CVyousra charaouiBelum ada peringkat
- Fetal DistressDokumen32 halamanFetal DistressMadhu Sudhan PandeyaBelum ada peringkat
- Manajemen Airway & Breathing: NO. Alat & BahanDokumen7 halamanManajemen Airway & Breathing: NO. Alat & BahanHafiz Putra Mega NasutionBelum ada peringkat
- Abstract Book PVSM2021 FinalDokumen374 halamanAbstract Book PVSM2021 FinalnitaBelum ada peringkat
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus - Most Common Congenital Heart Defect Symptoms DependDokumen5 halamanPatent Ductus Arteriosus - Most Common Congenital Heart Defect Symptoms DependANNEBelum ada peringkat
- Fasting Times PresentationDokumen15 halamanFasting Times PresentationumeshBelum ada peringkat
- Anorectal Malformations HandoutDokumen4 halamanAnorectal Malformations HandoutShikha Acharya100% (1)
- Presentation - Expert Testimony Case StudiesDokumen21 halamanPresentation - Expert Testimony Case StudiesThik ThakBelum ada peringkat
- Cardio. Vascular System (The Circulatory System) : Blood 2' HeartDokumen12 halamanCardio. Vascular System (The Circulatory System) : Blood 2' Heartعزوز الراويBelum ada peringkat
- Subgaleal Haemorrhage Detection and Management in The NewbornDokumen9 halamanSubgaleal Haemorrhage Detection and Management in The NewbornVengky UtamiBelum ada peringkat
- Stanford CA-1 Tutorial Textbook 7-12-2022 FINALDokumen108 halamanStanford CA-1 Tutorial Textbook 7-12-2022 FINALTudor Ghiara100% (3)
- DiseaseDokumen3 halamanDiseaseTyron KristianBelum ada peringkat