Bronchial Asthma Pulmonary Oedema (Cardiac Asthma) : Avoid .Avoid
Diunggah oleh
jincymariyamJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Bronchial Asthma Pulmonary Oedema (Cardiac Asthma) : Avoid .Avoid
Diunggah oleh
jincymariyamHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Bronchial asthma
1. Usually long duration of recurrent episodes of cough, wheeze and breathlessness 2. History to suggest hyperirritable airways present ". #cute breathlessness is often precipitated by respiratory infection, e posure to cold, dust, pollen, emotional upset, or e ertion /. 0ast history of bronchial asthma 1. 2lood pressure3 Usually normal &but reactive hypertension can %$cur. $an be differentiated by absence of end organ damage and return to normal 20 when asthma is controlled, 4. Usually tachycardia only. No arrhythmia
Pulmonary oedema (cardiac asthma)
1. Relatively short duration, recurrent episodes are not as common as in asthma 2. No such history e cept when both diseases co! e ist ". $an be precipitated by emotional upset or e ertion. %ften preceding chest pain &'H(!)*+, and palpitation present &e.g. 'H(!)*+ and -. with pulmonary oedema, /. 0ast history of angina, infarction, hypertension, rheumatic heart disease, other cardiac problems 1. High 20 or hypotension favours diagnosis of pulmonary oedema
4. #rrhythmias li5e #+, ventricular ectopics, complete heart bloc5, and ventricular tachycardia favours pulmonary oedema 6. 8levated 7*0 if present favours diagnosis 9. $ardiomegaly, presence of ." or murmurs and muffled heart sounds favour pulmonary oedema :. $repitation more than rhonchi. $repitations more at the base &Ronchi alone can occur sometimes in early pulmonary oedema, 1;. 8$< ! 8vidence of 'H(, )*H or left atrial enlargement favour cardiac asthma
6. Normal 7*0 9. No cardiomegaly, heart sounds normal. .ometimes difficult to ma5e out heart .ounds due to the rhonchi :. Rhonchi only or Rhonchi more than crepitations. Rhonchi are uniformly heard all over the chest 1;. . 8$< ! Normal, unless there is coe isting 'H(
Note3 'n patients with acute breathlessness, when there is difficulty in differentiating between bronchial asthma and acute pulmonary oedema ''' when both co!e ist the following guidelines will help. =his problem is vory common in elderly individuals with acute breathlessness. )ate onset asthma is common in the elderly and lac5s typical features li5e atopic tendency <'*8 drugs useful in both, e.g.3 #minophyllin and % ygen Use drugs, which are indicated in one condition but not contraindicated in the other li5e ! isosorbide dinitrate, frusemide, steroid, digo in and de trose when indicated #*%'( drugs contraindicated in pulmonary oedema and 2ronchial asthma &e.g.3 avoid #drenaline, .albutamol, =erbutaline, and Normal saline which are contraindicated in pulmonary oedema and -orphine which is contraindicated in asthma,
.avoid
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtDari EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Chorea Continuum 2019Dokumen35 halamanChorea Continuum 2019nicolasBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac AsthmaDokumen12 halamanCardiac AsthmaNeupane KsabBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory Acidosis: Prepared By: Riezel Umaming Kathleen Testado Hazel AlarillaDokumen16 halamanRespiratory Acidosis: Prepared By: Riezel Umaming Kathleen Testado Hazel AlarillaDareRaymond100% (2)
- Asthma and CopdDokumen44 halamanAsthma and CopdBeer Dilacshe100% (1)
- Pulmonary HypertensionDokumen35 halamanPulmonary HypertensionKea Keleste DetablanBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to ImmunohematologyDokumen16 halamanIntroduction to ImmunohematologyJoshua TrinidadBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory Dysfunction GuideDokumen42 halamanRespiratory Dysfunction GuideHassan DayaxBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical InfectionsDokumen310 halamanSurgical InfectionsOmar Ed ChavezBelum ada peringkat
- The Main Principles:: A B C D EDokumen4 halamanThe Main Principles:: A B C D EHatem FaroukBelum ada peringkat
- Hematology - Oncology - PREP 2021Dokumen46 halamanHematology - Oncology - PREP 2021drthanalla100% (1)
- Respiratory System Assessment: Other SystemsDokumen4 halamanRespiratory System Assessment: Other SystemsChetan KumarBelum ada peringkat
- CVS PDFDokumen102 halamanCVS PDFmalik003Belum ada peringkat
- Dyspnea: Ahammed Naseem Roll No: 3 Second Year BSC Nursing Al-Mas College of NursingDokumen19 halamanDyspnea: Ahammed Naseem Roll No: 3 Second Year BSC Nursing Al-Mas College of NursingNaseem Bin YoosafBelum ada peringkat
- A Simple Guide to the Asthma and Lung DiseasesDari EverandA Simple Guide to the Asthma and Lung DiseasesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Dyspnea PresentationDokumen37 halamanDyspnea PresentationamgoperaBelum ada peringkat
- Treat Your Asthma Naturally - How To Use Natural, Drug Free Ways To Treat Your AsthmaDari EverandTreat Your Asthma Naturally - How To Use Natural, Drug Free Ways To Treat Your AsthmaBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Semiology ReviewDokumen15 halamanMedical Semiology Reviewdjxela89100% (5)
- Bronchial Asthma & Cardiac AsthmaDokumen7 halamanBronchial Asthma & Cardiac AsthmaAbraham Chiu100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory FailureDokumen8 halamanAcute Respiratory FailureCayunk NorlianaBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To The Patient With Cough and Hemoptysis 15 11 13Dokumen34 halamanApproach To The Patient With Cough and Hemoptysis 15 11 13Sanchit PeriwalBelum ada peringkat
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDokumen1 halamanImpaired Gas Exchange NCPCj AlconabaBelum ada peringkat
- pg42-44 Aesthetic Layering PDFDokumen2 halamanpg42-44 Aesthetic Layering PDFAing MaungBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Intrapartum and Newborn Care (EINC) Bulletin 1Dokumen10 halamanEssential Intrapartum and Newborn Care (EINC) Bulletin 1maxicap7386% (7)
- Assessment of Breathlessness Clinical Pathway Assessment HandoutDokumen8 halamanAssessment of Breathlessness Clinical Pathway Assessment HandoutShivaniBelum ada peringkat
- Sypmtoms and Signs of Respiratory DiseasesDokumen22 halamanSypmtoms and Signs of Respiratory DiseasesPrincewill SeiyefaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 The History and Smmptoms Iovascular Disease: ObjectivesDokumen9 halamanUnit 1 The History and Smmptoms Iovascular Disease: ObjectivesbtaleraBelum ada peringkat
- Differential Diagnosis of Respiratory DistressDokumen2 halamanDifferential Diagnosis of Respiratory DistressditaBelum ada peringkat
- Lectura CardiologiaDokumen8 halamanLectura CardiologiaNatalia Castellanos CoteBelum ada peringkat
- The Next Sequel: Scarring My HeartDokumen56 halamanThe Next Sequel: Scarring My Heartshmily_0810Belum ada peringkat
- 2 - Dyspnea 讲课稿 2020Dokumen16 halaman2 - Dyspnea 讲课稿 2020mirabel IvanaliBelum ada peringkat
- Symtoms and Signs of The Respiratory SystemDokumen33 halamanSymtoms and Signs of The Respiratory SystemmohammedBelum ada peringkat
- 5) AssessmentDokumen35 halaman5) Assessmentbikedet268Belum ada peringkat
- Acute Heart FailureDokumen9 halamanAcute Heart FailureChen Briones100% (1)
- Merged 37Dokumen21 halamanMerged 37abdulkreemsalem4Belum ada peringkat
- COPD and Pulmonary Hypertension Cause Right Heart FailureDokumen19 halamanCOPD and Pulmonary Hypertension Cause Right Heart FailureIka Lukita SariBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Pulmonary EdemaDokumen5 halamanAcute Pulmonary Edemaoctaviana_simbolonBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On History Taking in The Cardiovascular SystemDokumen10 halamanNotes On History Taking in The Cardiovascular Systemmdjohar72Belum ada peringkat
- Disorders Related To Respiration & CirculationDokumen19 halamanDisorders Related To Respiration & Circulationsamria 2005Belum ada peringkat
- Congenital Heart Diseases ExplainedDokumen27 halamanCongenital Heart Diseases ExplainedShreyas KotadiyaBelum ada peringkat
- COPD and Chronic Cor PulmonaleDokumen6 halamanCOPD and Chronic Cor PulmonaleMiranty Aditya HadiniBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluation of DyspneaDokumen11 halamanEvaluation of DyspneaNeil AlviarBelum ada peringkat
- Case Report on Primary Pulmonary HypertensionDokumen4 halamanCase Report on Primary Pulmonary HypertensionaknbdgBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Aspects of Medical Chest Disease: "Asthma": by Dr. Sana Bashir DPT, MS-CPPTDokumen21 halamanClinical Aspects of Medical Chest Disease: "Asthma": by Dr. Sana Bashir DPT, MS-CPPTbkdfiesefllBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory System History Taking: Dr. Aiman Al ShareiDokumen20 halamanRespiratory System History Taking: Dr. Aiman Al ShareiQusai IbraheemBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Major Chronic Illnesses of Older AdultsDokumen21 halamanUnderstanding Major Chronic Illnesses of Older AdultsSteffiBelum ada peringkat
- Heart FailureDokumen20 halamanHeart Failurelancer 89100% (1)
- Cor PulmonaleDokumen14 halamanCor PulmonaleEvangelin MelvinBelum ada peringkat
- ARDSDokumen23 halamanARDSDumora FatmaBelum ada peringkat
- Respirati On ExamDokumen7 halamanRespirati On ExamShum Wing Hei JoanneBelum ada peringkat
- Emphysema Fall 2019Dokumen3 halamanEmphysema Fall 2019Mary MarshBelum ada peringkat
- Asthma: Chronic Inflammation of The Airways. The Hyper-Responsive Airways Typical of AsthmaDokumen7 halamanAsthma: Chronic Inflammation of The Airways. The Hyper-Responsive Airways Typical of AsthmaRaj PaulBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Emphysema: EpidemiologyDokumen4 halamanPulmonary Emphysema: EpidemiologyAnonymous 835s2sxBelum ada peringkat
- Cor Pulmonale - Introduction To Cor Pulmonale, Etiology and Pathophysiology of Cor Pulmonale, Epidemiology of Cor PulmonaleDokumen18 halamanCor Pulmonale - Introduction To Cor Pulmonale, Etiology and Pathophysiology of Cor Pulmonale, Epidemiology of Cor PulmonaleRicky SpideyBelum ada peringkat
- Cor Pulmonale GuideDokumen9 halamanCor Pulmonale GuideMaríaDelPilarAguilarBelum ada peringkat
- BronchitisDokumen22 halamanBronchitisEvita AdiningtyasBelum ada peringkat
- Second Week Round Notes PDFDokumen9 halamanSecond Week Round Notes PDFNAIBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary PathoPhysiologyDokumen45 halamanPulmonary PathoPhysiologySuliman Garalleh100% (1)
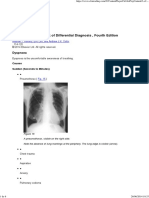
- Churchill's Pocketbook of Differential Diagnosis, Fourth EditionDokumen6 halamanChurchill's Pocketbook of Differential Diagnosis, Fourth EditionalexisBelum ada peringkat
- Canine Chronic Bronchitis 2019Dokumen12 halamanCanine Chronic Bronchitis 2019Carolina Duque RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- CPR Final DRAFTDokumen27 halamanCPR Final DRAFTKarlBalmeraBelum ada peringkat
- AEBA QUESTIONS-WPS OfficeDokumen2 halamanAEBA QUESTIONS-WPS OfficeMarj Castor LisondraBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Heart Disease Causes Right Ventricle EnlargementDokumen24 halamanPulmonary Heart Disease Causes Right Ventricle EnlargementGungdeprawira NegaraBelum ada peringkat
- Disorders Related To Respiration & CirculationDokumen18 halamanDisorders Related To Respiration & Circulationsamria 2005Belum ada peringkat
- Vestil - Case Study On AsthmaDokumen7 halamanVestil - Case Study On Asthmaninachristenevestil25Belum ada peringkat
- Definition of Heart FaillureDokumen15 halamanDefinition of Heart FaillureAsma FerabilBelum ada peringkat
- A Simple Guide to Pulmonary Infarction, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDari EverandA Simple Guide to Pulmonary Infarction, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Glaucoma in Eyes With Shallow Anterior ChamberDokumen11 halamanStudy of Glaucoma in Eyes With Shallow Anterior ChamberjincymariyamBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluation of Partogram in 50 Cases Each of Primigravida & Multigravida With Neonatal Outcome in Labour.Dokumen7 halamanEvaluation of Partogram in 50 Cases Each of Primigravida & Multigravida With Neonatal Outcome in Labour.jincymariyamBelum ada peringkat
- Role of Color-Assisted Duplex Sonography in Evaluation of Thyroid DiseasesDokumen6 halamanRole of Color-Assisted Duplex Sonography in Evaluation of Thyroid DiseasesjincymariyamBelum ada peringkat
- A Study of C-Reactive Protein in Acute Ischemic StrokeDokumen26 halamanA Study of C-Reactive Protein in Acute Ischemic StrokejincymariyamBelum ada peringkat
- 01 - M009 - 16a Clinical Study and Management of Varicose Veins in Lower Limbs.Dokumen13 halaman01 - M009 - 16a Clinical Study and Management of Varicose Veins in Lower Limbs.jincymariyamBelum ada peringkat
- ShortDokumen15 halamanShortIroet MarteniBelum ada peringkat
- 01 - M009 - 16a Clinical Study and Management of Varicose Veins in Lower Limbs.Dokumen13 halaman01 - M009 - 16a Clinical Study and Management of Varicose Veins in Lower Limbs.jincymariyamBelum ada peringkat
- Mothers' Knowledge on Preventing Childhood GastroenteritisDokumen16 halamanMothers' Knowledge on Preventing Childhood GastroenteritisjincymariyamBelum ada peringkat
- A Study On Prediction of Difficult Intubations Using Conventional Indicators and The Effect of Rapid Sequence Intubation On Ease of IntubationsDokumen10 halamanA Study On Prediction of Difficult Intubations Using Conventional Indicators and The Effect of Rapid Sequence Intubation On Ease of IntubationsjincymariyamBelum ada peringkat
- Precision Attachment: Retained OverdentureDokumen4 halamanPrecision Attachment: Retained OverdentureSudhanshu Kumar KashyapBelum ada peringkat
- Fever and Rash: Dr. Karwan Hawez Sulaiman MBCHB, Ficms, FM Family Medicine Specialist College of MedicineDokumen20 halamanFever and Rash: Dr. Karwan Hawez Sulaiman MBCHB, Ficms, FM Family Medicine Specialist College of MedicinesamiBelum ada peringkat
- Efficacy and Safety of Rabeprazole in Children.20Dokumen10 halamanEfficacy and Safety of Rabeprazole in Children.20Ismy HoiriyahBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Orientation To PharmacologyDokumen4 halamanChapter 1 - Orientation To Pharmacologydlneisha61Belum ada peringkat
- Vaccine Research StatusDokumen112 halamanVaccine Research StatusJunko Tsukuda100% (1)
- The Use of Contraceptives in Nigeria: Benefits, Challenges and Probable SolutionsDokumen13 halamanThe Use of Contraceptives in Nigeria: Benefits, Challenges and Probable SolutionsShaguolo O. JosephBelum ada peringkat
- Literature Review On Premature BabiesDokumen4 halamanLiterature Review On Premature Babiesc5eakf6z100% (1)
- Act 1. PhobiasDokumen2 halamanAct 1. PhobiasRoxanne CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- Expanding Consensus in Portal HypertensionDokumen29 halamanExpanding Consensus in Portal HypertensionJosé Pepo Apey Reinoso100% (1)
- The Stuart Stress Adaptation Model of Psychiatric Nursing CareDokumen3 halamanThe Stuart Stress Adaptation Model of Psychiatric Nursing CareScott PuckettBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 026 CoagulationDokumen7 halamanChapter 026 Coagulationthubtendrolma100% (3)
- GERD Nursing CareDokumen9 halamanGERD Nursing CareTrisha ArizalaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4: Medical EmergenciesDokumen44 halamanUnit 4: Medical EmergenciesMR々๛ AKMツBelum ada peringkat
- NS Compounding Set 4 PDFDokumen24 halamanNS Compounding Set 4 PDFJulia BottiniBelum ada peringkat
- ĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN THI MÔN TIẾNG ANHDokumen18 halamanĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN THI MÔN TIẾNG ANHBee LeeBelum ada peringkat
- ScizopheniaDokumen20 halamanScizopheniaGogea GabrielaBelum ada peringkat
- Fetal Assessment DRDokumen1 halamanFetal Assessment DRMicah Lou CalambaBelum ada peringkat
- EMT Training at Mansion Mandiri HotelDokumen4 halamanEMT Training at Mansion Mandiri Hotelyuna triazBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 24 - Arthritis - Osteoarthritis, Gout, & Amp Rheumatoid ArthritisDokumen23 halamanChapter 24 - Arthritis - Osteoarthritis, Gout, & Amp Rheumatoid ArthritisHarris GhifaryBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Epidemiology of Infection Diseases PDFDokumen17 halamanIntroduction To Epidemiology of Infection Diseases PDFRovaidKhanBelum ada peringkat
- MD AANOADokumen21 halamanMD AANOARizka Dany AfinaBelum ada peringkat
- Preoperative Assessment ChecklistDokumen27 halamanPreoperative Assessment ChecklistHairina MazlanBelum ada peringkat