Cholelithiasis: Clinical Manifestation
Diunggah oleh
thomasfinley44Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Cholelithiasis: Clinical Manifestation
Diunggah oleh
thomasfinley44Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
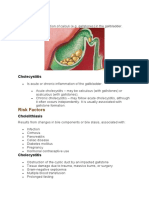
Cholelithiasis
Calculi, or gallstones, usually form in the gallbladder from the solid constituents of bile
Clinical Manifestation: Epigastric distress, such as fullness, abdominal distention, and vague pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, may occur. This distress may follow a meal rich in fried or fatty foods. Biliary colic with excruciating upper right abdominal pain that radiates to the back or right shoulder, is usually associated with nausea and vomiting, and is noticeable several hours after a heavy meal. Jaundice Dark Urine Color Putty or grey feces
Nursing Responsibilities: Cholescystectomy Preoperative Instruct the patient about the need to avoid smoking to enhance pulmonary recovery postoperatively and to avoid respiratory complications. Instruct the patient to avoid the use of aspirin and other agents (over-the-counter medications and herbal remedies) that can alter coagulation and other biochemical processes. Assessment should focus on the patients respiratory status. If a traditional surgical approach is planned, the high abdominal incision required during surgery may interfere with full respiratory excursion. The note history of smoking, previous respiratory problems, shallow respirations, a persistent or ineffective cough, and the presence of adventitious breath sounds. Nutritional status is evaluated through a dietary history and general examination performed at the time of preadmission testing. The nurse also reviews previously obtained laboratory results to obtain information about the patients nutritional status.
Postoperative
Place the patient in the low Fowlers position. Intravenous fluids may be given as ordered Nasogastric suction (a nasogastric tube was probably inserted immediately before surgery for a nonlaparoscopic procedure) may be instituted to relieve abdominal distention as Ordered. Water and other fluids are given in about 24 hours Soft diet is started when bowel sounds return. Tell patient to avoid turning and moving, to splint the affected site, and to take shallow breaths to prevent pain Reminds patients to take deep breaths and cough every hour to expand the lungs fully and prevent atelectasis. Fasten tubing to the dressings or to the patients gown, with enough leeway for the patient to move without dislodging or kinking it. Because jaundice may result, the nurse should be particularly observant of the color of the sclerae. The nurse should also note and report right upper quadrant abdominalpain, nausea and vomiting, bile drainage around any drainage tube, clay-colored stools, and a change in vital signs.
Closely monitor vital signs and inspects the surgical incisions and drains, if in place, for evidence of bleeding. Periodically assess the patient for increased tenderness and rigidity of the abdomen. Assess the patient for loss of appetite, vomiting, pain, distention of the abdomen, and temperature elevation. These may indicate infection or disruption of the gastrointestinal tract and should be reported to the surgeon promptly. Encourage the patient to eat a diet low in fats and high in carbohydrates and proteins immediately after surgery.
Appendicitis
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Rules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesDari EverandRules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesBelum ada peringkat
- Endoscopic Procedure (Nursing Responsibilities)Dokumen4 halamanEndoscopic Procedure (Nursing Responsibilities)YessaminBelum ada peringkat
- CholecystectomyDokumen19 halamanCholecystectomyAlyssa Quilban MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Risk Factors: CholelithiasisDokumen10 halamanRisk Factors: CholelithiasisRoyster CabralBelum ada peringkat
- Peritoneal DialysisDokumen37 halamanPeritoneal Dialysisger668Belum ada peringkat
- Intestinal Obstraction MajDokumen44 halamanIntestinal Obstraction MajHamss AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- GI Diagnostic TestsDokumen7 halamanGI Diagnostic TestspatzieBelum ada peringkat
- Chole CystitisDokumen31 halamanChole CystitisPrincess YesenBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care For Patient Undergoing TAHBSO For Ovarian GrowthDokumen4 halamanNursing Care For Patient Undergoing TAHBSO For Ovarian GrowthAyaBasilio100% (2)
- APPENDECITISDokumen5 halamanAPPENDECITISfxbukenyaBelum ada peringkat
- CASE STUDIES L3 A Group 3Dokumen10 halamanCASE STUDIES L3 A Group 3Doneva Lyn MedinaBelum ada peringkat
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Post-OperativeDokumen2 halamanTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Post-OperativeMiar QuestBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostics Serum Lab Studies:: 105 - Module G GastrointestinalDokumen17 halamanDiagnostics Serum Lab Studies:: 105 - Module G Gastrointestinalamanda081106Belum ada peringkat
- Cholecystectomy and Nursing Care PlanDokumen8 halamanCholecystectomy and Nursing Care PlanLara GatbontonBelum ada peringkat
- Intestinal ObstructionDokumen9 halamanIntestinal ObstructionHamss AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Raptured Appendicitis - VMCDokumen6 halamanAcute Raptured Appendicitis - VMCMicahMananguitBelum ada peringkat
- ColonosDokumen5 halamanColonosMa. Aira Jean PedroBelum ada peringkat
- Assess and Evaluate PatientDokumen3 halamanAssess and Evaluate PatientCindy Babsa-ay MaslagBelum ada peringkat
- Hiatal HerniaDokumen6 halamanHiatal HerniaMaria Donabella OngueBelum ada peringkat
- ParacentesisDokumen13 halamanParacentesisroger100% (2)
- Abdominal Distention: Emergency ActionsDokumen1 halamanAbdominal Distention: Emergency ActionschoobiBelum ada peringkat
- Vovulusoriginal Copy 121028055752 Phpapp01Dokumen37 halamanVovulusoriginal Copy 121028055752 Phpapp01Bheru LalBelum ada peringkat
- Appendectomy Possible NCPDokumen6 halamanAppendectomy Possible NCPIrish Nicole DC100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal Treatment Modalties 1Dokumen28 halamanGastrointestinal Treatment Modalties 1AndreBelum ada peringkat
- IntussusceptionDokumen1 halamanIntussusceptionJune DumdumayaBelum ada peringkat
- ColonosDokumen20 halamanColonosCarl miguel LoretoBelum ada peringkat
- CholecystitisDokumen4 halamanCholecystitisAmik, Aila H.Belum ada peringkat
- 4 Appendectomy Nursing Care PlansDokumen8 halaman4 Appendectomy Nursing Care PlansMarin Andrei100% (1)
- Colonoscopy / Page ofDokumen4 halamanColonoscopy / Page offallenangelleBelum ada peringkat
- July 27, 2009 Exploratory Laparotomy and Transverse Loop Colostomy 1.Dokumen8 halamanJuly 27, 2009 Exploratory Laparotomy and Transverse Loop Colostomy 1.MaRVBelum ada peringkat
- Sources of Stress As Per: Student's Academic Performance Effects of StressDokumen14 halamanSources of Stress As Per: Student's Academic Performance Effects of StressMacrina PatocBelum ada peringkat
- Peforated Peptic UlcerDokumen19 halamanPeforated Peptic Ulcertecklor SiakamwiBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen5 halamanNursing Care PlanAnju Luchmun100% (2)
- Nursing Care For Patient Undergoing TAHBSO For Ovarian GrowthDokumen4 halamanNursing Care For Patient Undergoing TAHBSO For Ovarian Growthsugarmontejo83% (6)
- CholecytitisDokumen28 halamanCholecytitisواحة الأمل100% (1)
- Abruptio PlacentaDokumen11 halamanAbruptio PlacentaAlynna ValbuenaBelum ada peringkat
- Cholecystitis Viva TopicDokumen4 halamanCholecystitis Viva TopicSalma NazarBelum ada peringkat
- Endoscopic Retrograde CholangiopancreatographyDokumen3 halamanEndoscopic Retrograde CholangiopancreatographyLoBelum ada peringkat
- Polycystic Kidney: Formation of Cysts in The Cortex and MedullaDokumen6 halamanPolycystic Kidney: Formation of Cysts in The Cortex and MedullaEileen OoiBelum ada peringkat
- RLE - Hiatal Hernia - ReportDokumen4 halamanRLE - Hiatal Hernia - ReportKaguraBelum ada peringkat
- Biliary DisoderDokumen50 halamanBiliary DisoderZanida ZainonBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing InterventionsDokumen3 halamanNursing InterventionsJemiah Lyn C. BragadoBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Surgical Nursing Module 1 Lesson 1 Upper Gastrointestinal DisordersDokumen34 halamanMedical Surgical Nursing Module 1 Lesson 1 Upper Gastrointestinal DisordersRomelyn Ordillas100% (2)
- PERITONITISDokumen12 halamanPERITONITISHayat AL AKOUM100% (1)
- ColonosDokumen22 halamanColonosJulienne Sanchez-Salazar100% (1)
- Inbound 1258778318981503831Dokumen59 halamanInbound 1258778318981503831Novelyn OlidanBelum ada peringkat
- 2.large Bowel ObstructionDokumen13 halaman2.large Bowel Obstructionurmila prajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Cholecystectom Y: Pilorin, Pingen, Pinto, Pira, PradesDokumen48 halamanCholecystectom Y: Pilorin, Pingen, Pinto, Pira, PradesKathleen Joy PingenBelum ada peringkat
- Definition of The Disease: Risk FactorsDokumen13 halamanDefinition of The Disease: Risk FactorsDivine Ballesteros Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- APPENDICITISDokumen32 halamanAPPENDICITISpaul kaundaBelum ada peringkat
- © 2021 Lippincott Advisor - Treatments - HysterectomyDokumen5 halaman© 2021 Lippincott Advisor - Treatments - HysterectomyJoyJoy Tabada CalunsagBelum ada peringkat
- Doc1 Obstractive JaundiceDokumen7 halamanDoc1 Obstractive JaundiceZhy CaluzaBelum ada peringkat
- استئصال المرارهDokumen16 halamanاستئصال المرارهsq_gBelum ada peringkat
- Intestinal ObstructionDokumen12 halamanIntestinal ObstructionwanyBelum ada peringkat
- NCP StrokeDokumen2 halamanNCP StrokeMichael John F. NatividadBelum ada peringkat
- Hiatal HerniaDokumen13 halamanHiatal HerniaDerrick SHEMABelum ada peringkat
- Gastro IntestineDokumen74 halamanGastro IntestineRhea Liza Comendador-TjernmoenBelum ada peringkat
- NCPsDokumen13 halamanNCPsRocel DevillesBelum ada peringkat
- Intestinal Obstruction 2Dokumen46 halamanIntestinal Obstruction 2Lawrence WanderiBelum ada peringkat
- Data Gathered in BatanesDokumen1 halamanData Gathered in Batanesthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Assistive Devices For WalkingDokumen4 halamanAssistive Devices For Walkingthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Seasons of LoveDokumen1 halamanSeasons of LoveMicah VirreyBelum ada peringkat
- Dying and DeathDokumen3 halamanDying and Deaththomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Oncology Nursing and ChemotherapeuticsDokumen4 halamanOncology Nursing and Chemotherapeuticsthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Nurses Monthly ScheduleDokumen20 halamanNurses Monthly Schedulethomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Esoteric MedicineDokumen6 halamanEsoteric Medicinethomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Memory Notebook of Nursing Vol. 1 Table of ContentDokumen6 halamanMemory Notebook of Nursing Vol. 1 Table of ContentMikaGieJergoLariza38% (21)
- PRC New2Dokumen6 halamanPRC New2thomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Postmaturity Is The Condition of A Baby That Has Not Yet Been Born After 42 Weeks ofDokumen4 halamanPostmaturity Is The Condition of A Baby That Has Not Yet Been Born After 42 Weeks ofthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- StaffofSerapis Excerpt Trade PBKDokumen6 halamanStaffofSerapis Excerpt Trade PBKthomasfinley4445% (11)
- PRC New TemplatesDokumen8 halamanPRC New Templatesthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- HelloDokumen1 halamanHellothomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia: Nursing ResponsibilityDokumen2 halamanPediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia: Nursing Responsibilitythomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Head Nursing: Pines City Colleges Magsaysay Avenue Baguio City College of NursingDokumen2 halamanHead Nursing: Pines City Colleges Magsaysay Avenue Baguio City College of Nursingthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- I.Family Background:: Personal DataDokumen4 halamanI.Family Background:: Personal Datathomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- A Comprehensive Review On Salt and Health and Current Experience of Worldwide Salt Reduction ProgrammesDokumen2 halamanA Comprehensive Review On Salt and Health and Current Experience of Worldwide Salt Reduction Programmesthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- PRC New TemplatesDokumen8 halamanPRC New Templatesthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Musculoskeletal System OverviewDokumen1 halamanMusculoskeletal System Overviewthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Interventions For CAPDokumen5 halamanNursing Interventions For CAPthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Ms CertDokumen117 halamanMs Certthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- AttendanceDokumen1 halamanAttendancethomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- What Causes SchizophreniaDokumen2 halamanWhat Causes Schizophreniathomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Childhood Asthma Linked To Risk of COPDDokumen1 halamanChildhood Asthma Linked To Risk of COPDthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Plan of Activities DRDokumen3 halamanPlan of Activities DRthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Different Case in The Surgical WardDokumen5 halamanDifferent Case in The Surgical Wardthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Or Write Up (Appendectomy) : Pines City Colleges College of NursingDokumen9 halamanOr Write Up (Appendectomy) : Pines City Colleges College of Nursingthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Doctors Order Drug Classification Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationDokumen3 halamanDoctors Order Drug Classification Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing Considerationthomasfinley44Belum ada peringkat
- Colgate Space Dentistry1Dokumen9 halamanColgate Space Dentistry1ShrishtiChokhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Culture Based Beliefs and Practices On Pregnancy and Childbirth Among Sorsoguenos Philippines PDFDokumen11 halamanCulture Based Beliefs and Practices On Pregnancy and Childbirth Among Sorsoguenos Philippines PDFRazaCreciaLastrillaMenesesBelum ada peringkat
- CARE Checklist English 2013 PDFDokumen1 halamanCARE Checklist English 2013 PDFNithin NairBelum ada peringkat
- Teste Examen Anul III ENGDokumen84 halamanTeste Examen Anul III ENGdianaBelum ada peringkat
- NeurologistDokumen3 halamanNeurologistnorlelaoBelum ada peringkat
- "Comparative Evaluation of Rate of Canine Retraction in Corticotomy Facilitated Orthodontics and Piezocision Technique in Adult Population" - Protocol For A in Vivo StudyDokumen7 halaman"Comparative Evaluation of Rate of Canine Retraction in Corticotomy Facilitated Orthodontics and Piezocision Technique in Adult Population" - Protocol For A in Vivo StudyAly OsmanBelum ada peringkat
- Regeneración Periodontal de Defectos Infraóseos HumanosDokumen7 halamanRegeneración Periodontal de Defectos Infraóseos HumanosAgustin BuryakBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Oral Supplementation Criteria For WebDokumen3 halamanPediatric Oral Supplementation Criteria For WebDHARA MODIBelum ada peringkat
- Acute PainDokumen2 halamanAcute PainNicole Genevie MallariBelum ada peringkat
- Health InsuranceDokumen40 halamanHealth InsuranceSubhadeep SahaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug STUDY CefotaximeDokumen5 halamanDrug STUDY CefotaximeJeffrey Calicdan Bucala75% (8)
- Niosh Training ScheduleDokumen20 halamanNiosh Training Scheduleakula100% (2)
- Adoc - Pub - Daftar Pustaka Arikunto S 2010 Prosedur PenelitianDokumen6 halamanAdoc - Pub - Daftar Pustaka Arikunto S 2010 Prosedur PenelitianmaulinaaBelum ada peringkat
- Soft Skills For Pharmacist 2Dokumen5 halamanSoft Skills For Pharmacist 2shailendra patilBelum ada peringkat
- The Steps For Applying For The DHCA Prometric ExaminationDokumen1 halamanThe Steps For Applying For The DHCA Prometric ExaminationLentoOt EksDiiBelum ada peringkat
- Sanjivani Psychosocial Rehabilitation Centre, Nedumkunnam, Kottayam DT., KeralaDokumen3 halamanSanjivani Psychosocial Rehabilitation Centre, Nedumkunnam, Kottayam DT., KeralaJSM MKZYBelum ada peringkat
- Neffati Mehdi: ExperienceDokumen2 halamanNeffati Mehdi: ExperienceMehdi NeffatiBelum ada peringkat
- HDSS-Matlab Annual Report 2017 - Final VersionDokumen80 halamanHDSS-Matlab Annual Report 2017 - Final VersionFoiz NomanBelum ada peringkat
- Post Test On Food and Water Borne DiseasesDokumen4 halamanPost Test On Food and Water Borne DiseasesMardie ArcesBelum ada peringkat
- IUI Procedure Success Rates MIRACLE FERTILITYDokumen3 halamanIUI Procedure Success Rates MIRACLE FERTILITYKweku BaahBelum ada peringkat
- Behavior and Social SciencesDokumen11 halamanBehavior and Social SciencesRoxana Alexandra BogosBelum ada peringkat
- World Health Awareness DaysDokumen4 halamanWorld Health Awareness Daysbnrajeeva3344Belum ada peringkat
- Patient Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis (In Priority Order) Patient-Centered Goals Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen3 halamanPatient Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis (In Priority Order) Patient-Centered Goals Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationmp1757Belum ada peringkat
- Healthcare - Gov/sbc-Glossary: Important Questions Answers Why This MattersDokumen9 halamanHealthcare - Gov/sbc-Glossary: Important Questions Answers Why This Mattersapi-252555369Belum ada peringkat
- 2005 Pedi Regional - HandoutDokumen44 halaman2005 Pedi Regional - HandoutSandhi Prabowo100% (1)
- NEJMHSVDokumen10 halamanNEJMHSVhenkBelum ada peringkat
- Prosthodontics Q&a (CDD)Dokumen121 halamanProsthodontics Q&a (CDD)Tara Lingating100% (1)
- Bautista, 2020. Health Literacy Education and Research in The Philippines: An Agenda For Filipino Information Professionals During and After COVID-19Dokumen7 halamanBautista, 2020. Health Literacy Education and Research in The Philippines: An Agenda For Filipino Information Professionals During and After COVID-19kelseyBelum ada peringkat
- Pregnancy - Preparing To Be A MomDokumen16 halamanPregnancy - Preparing To Be A MomTes B FourieBelum ada peringkat
- Nutrition Recommendations in Pregnancy and LactationDokumen17 halamanNutrition Recommendations in Pregnancy and LactationDodi TambunBelum ada peringkat