Concept Testing: Seven Step Method For Testing Product Concepts
Diunggah oleh
Ankit saxenaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Concept Testing: Seven Step Method For Testing Product Concepts
Diunggah oleh
Ankit saxenaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CONCEPT TESTING
This type of testing may be used to select which of two or more concepts should be pursued, to gather information from potential customers on how to improve a concept, and to estimate the sales potential of the product. Concept testing is closely related to prototyping because concept testing invariably involves some kind of representation of product concept. One of the end results of a concept test may be an estimate of units of product the company is likely to sell.
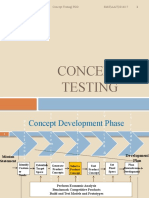
Identify customer needs
Establish target specifications
Generate product concept
Select product concept(s)
Test Product concept(s)
Set Final Specifications
Plan Downstream Development
Perform Economic Analysis Benchmark Competitive Products Build and test models and prototypes
Fig.1 Concept testing in relation to other concept development activities.
Seven step method for testing product concepts:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Define the purpose of the concept test. Choose a survey population. Choose a survey format. Communicate the concept. Measure customer response. Interpret the result. Reflect on the results and the process.
1|Page
STEP1: DEFINE THE PURPOSE OF THE CONCEPT TEST The primary questions addressed in concept testing are typically: Which of several alternative concepts should be pursued? How can the concept be improved to better meet customer needs? Approximately how many units are likely to be sold? Should development be continued?
STEP2: CHOOSE A SURVEY POPULATION The team should choose a survey population that mirrors the target market in as many ways as possible. The sample size of the survey should be large enough that the team`s confidence in the results is high enough to guide decision making. STEP3: CHOOSE A SURVEY FORMAT The following formats are commonly used in concept testing: Face to-face interaction Telephone Postal Mail Electronic Mail Internet
STEP4: COMMUNICATE THE CONCEPT Concepts can be communicated in any of the following ways, listed in order of increasing richness of description. Verbal description Sketch Photos and renderings Storyboard Video Simulation Interactive multimedia Physical appearance models Working prototype
2|Page
STEP5: MEASURE CUSTOMER RESPONSE The most commonly used purchase-intent scale has five response categories: Definitely would buy. Probably would buy. Might or might not buy. Probably would not buy. Definitely would not buy.
STEP6: INTERPRET THE RESULT If the team is simply interested in comparing two or more concepts, interpretation of the result is straight-forward. If one concept dominates the others and the team is confident that the respondents understood the key differences among concepts, then the team can choose the preferred concept. If the results are not conclusive, the team may decide to choose a concept based on cost considerations. Some of the factors that can cause actual purchase patterns to differ from the purchase intentions expressed in surveys include: a. Importance of word-of-mouth b. Pricing c. Level of promotion
STEP7: REFLECT ON THE RESULTS AND THE PROCESS The Team benefits from thinking about the impact of the three key variables in the forecasting model: The overall size of the market. The availability and awareness of the product. The fraction of the customers who are likely to purchase.
3|Page
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- New Product Development A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDari EverandNew Product Development A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Marketing Trends and Prospects: Develop an effective Digital Marketing strategy with SEO, SEM, PPC, Digital Display Ads & Email Marketing techniques. (English Edition)Dari EverandDigital Marketing Trends and Prospects: Develop an effective Digital Marketing strategy with SEO, SEM, PPC, Digital Display Ads & Email Marketing techniques. (English Edition)Belum ada peringkat
- Product StrategyDokumen4 halamanProduct StrategyShaira SalandaBelum ada peringkat
- Jom 05 04 050 PDFDokumen16 halamanJom 05 04 050 PDFLanie Aler Delos SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Samsung Electronics' Innovation DilemmaDokumen8 halamanSamsung Electronics' Innovation DilemmaJames JungBelum ada peringkat
- Huỳnh Nguyễn Nam Phương - Individual Reflective Assignment - Consumer Behavior-T22324PWB-1Dokumen29 halamanHuỳnh Nguyễn Nam Phương - Individual Reflective Assignment - Consumer Behavior-T22324PWB-1huynhharmony5Belum ada peringkat
- Trade marketing -Hướng dẫn tiểu luận cuối kỳ chính thức (17.05.2023)Dokumen15 halamanTrade marketing -Hướng dẫn tiểu luận cuối kỳ chính thức (17.05.2023)Liêm BéBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study - Besa1Dokumen27 halamanCase Study - Besa1Sneha Joshi100% (1)
- Marketing Aptitude Book For SBIDokumen49 halamanMarketing Aptitude Book For SBIPankaj SinghBelum ada peringkat
- How Do I Conduct A Concept TestDokumen3 halamanHow Do I Conduct A Concept TestSalim H.Belum ada peringkat
- Week 2 4 Mgt5strDokumen38 halamanWeek 2 4 Mgt5strSơn BadGuyBelum ada peringkat
- Marketing Plan - 15782988 and 15781144Dokumen21 halamanMarketing Plan - 15782988 and 15781144Khoilinh PhamBelum ada peringkat
- The Effect of Viral Marketing in The Decision Making of The CustomersDokumen18 halamanThe Effect of Viral Marketing in The Decision Making of The CustomersGeorgette GalesBelum ada peringkat
- Creating Customer Relationships and Value Through MarketingDokumen2 halamanCreating Customer Relationships and Value Through MarketingCuriousPanda66100% (1)
- Paper: Assignment Style: Harvard Pages: 27 Sources: 10 Level: MaterDokumen27 halamanPaper: Assignment Style: Harvard Pages: 27 Sources: 10 Level: MaterAlice AliceBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Decision Making and Diffusion of InnovationDokumen23 halamanConsumer Decision Making and Diffusion of InnovationArham WaseemBelum ada peringkat
- You Work For Nokia in Its Global Cell Phone GroupDokumen1 halamanYou Work For Nokia in Its Global Cell Phone GroupAmit PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Dove Men+ Care PresentationDokumen30 halamanDove Men+ Care PresentationEric CamardelleBelum ada peringkat
- B2B Mid Term 2Dokumen5 halamanB2B Mid Term 2Rashmi SuryaBelum ada peringkat
- 인터넷과 전자상거래 조교 김현모의 비즈니스 시뮬레이션 게임 설명Dokumen31 halaman인터넷과 전자상거래 조교 김현모의 비즈니스 시뮬레이션 게임 설명Manju HanBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study On Du Pont PDFDokumen54 halamanCase Study On Du Pont PDFAnonymous a2SDmQl30Belum ada peringkat
- Advertisement AnalysisDokumen4 halamanAdvertisement AnalysisbhavaniBelum ada peringkat
- Marketing Stimuli - GilletteDokumen11 halamanMarketing Stimuli - GilletteAfsheen Danish NaqviBelum ada peringkat
- Sampling Methods in Quantitative, Qualitative, and Mixed ResearchDokumen3 halamanSampling Methods in Quantitative, Qualitative, and Mixed ResearchMuhammad Kashif AzharBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment #5Dokumen2 halamanAssignment #5COREY DAVISBelum ada peringkat
- Marketing Plan of MoisturizersDokumen11 halamanMarketing Plan of MoisturizersPankaj MehrotraBelum ada peringkat
- Everything You Need to Know About the Whirlpool Duet Washer and DryerDokumen14 halamanEverything You Need to Know About the Whirlpool Duet Washer and DryercassrynneBelum ada peringkat
- Concept TestingDokumen17 halamanConcept TestingHailemariam WeldegebralBelum ada peringkat
- 486- Assignment 2 Frontsheet -đã chuyển đổiDokumen14 halaman486- Assignment 2 Frontsheet -đã chuyển đổiPhạm Hải100% (1)
- IMC A1 Mâu 1Dokumen15 halamanIMC A1 Mâu 1Dulcie NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 (Dokumen16 halamanAssignment 1 (Hoang HaBelum ada peringkat
- Measure IMC Effectiveness with MetricsDokumen32 halamanMeasure IMC Effectiveness with MetricsPhan Công ThànhBelum ada peringkat
- Marketing Report on OMO Liquid DetergentDokumen23 halamanMarketing Report on OMO Liquid DetergentTra MyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter One An Overview of Marketing and Marketing ManagementDokumen57 halamanChapter One An Overview of Marketing and Marketing ManagementVijayakumar ManiBelum ada peringkat
- CONCEPT TESTING ELECTRIC SCOOTERDokumen26 halamanCONCEPT TESTING ELECTRIC SCOOTERkushal pramanickBelum ada peringkat
- Swot of ConverseDokumen6 halamanSwot of Conversekhanh LongBelum ada peringkat
- Red Bull IMCDokumen24 halamanRed Bull IMCfazali57399Belum ada peringkat
- Semester: 113 - Fall 2011Dokumen7 halamanSemester: 113 - Fall 2011Manju MohanBelum ada peringkat
- Research ProposalDokumen14 halamanResearch ProposalshuvoBelum ada peringkat
- Speaking For Enm301 - RevisionDokumen16 halamanSpeaking For Enm301 - RevisionThành NhânBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Strategy of TNC Canon VietnamDokumen32 halamanAnalysis of Strategy of TNC Canon VietnamHà Bành100% (1)
- Case 7-1 PDFDokumen3 halamanCase 7-1 PDFasdfBelum ada peringkat
- 486 Assignment 3 FrontsheetDokumen22 halaman486 Assignment 3 FrontsheetNguyen Viet Duy (FGW HN)Belum ada peringkat
- Strategic Management Journal Resource-Based View of the FirmDokumen10 halamanStrategic Management Journal Resource-Based View of the FirmWallacyyyBelum ada peringkat
- Marketing Advantages of Strong BrandsDokumen26 halamanMarketing Advantages of Strong BrandsGizem GündayBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Goods ClassificationDokumen5 halamanConsumer Goods ClassificationfdiolosaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 17 Evans BermanDokumen27 halamanChapter 17 Evans BermanthesimpleBelum ada peringkat
- Implantation of Global Brand Equity Measurement SystemDokumen29 halamanImplantation of Global Brand Equity Measurement SystemRaj Kishore GoswamiBelum ada peringkat
- Product Planning and DevelopmentDokumen38 halamanProduct Planning and DevelopmentLapi Boy Mics100% (1)
- BitisDokumen3 halamanBitisDanicaBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank: 2.which Technologies Influence Strategic CRM, On Both The Consumer and The Company Sides?Dokumen23 halamanTest Bank: 2.which Technologies Influence Strategic CRM, On Both The Consumer and The Company Sides?Tấn Nguyễn Thị KimBelum ada peringkat
- Keller's Brand Equity ModelDokumen7 halamanKeller's Brand Equity ModelVM100% (1)
- Does Gamification Affect Brand Engagement and Equity - 2020 - Journal of Busin PDFDokumen12 halamanDoes Gamification Affect Brand Engagement and Equity - 2020 - Journal of Busin PDFIustina TudorBelum ada peringkat
- Managing Starwood's Loyalty Program for Customer PrivacyDokumen2 halamanManaging Starwood's Loyalty Program for Customer PrivacyShreya JainBelum ada peringkat
- Concept Testing in Product DesignDokumen28 halamanConcept Testing in Product Designvenkatesh prasadBelum ada peringkat
- Reasons MNCs Seek Raw Materials, Markets, Lower CostsDokumen2 halamanReasons MNCs Seek Raw Materials, Markets, Lower CostsNafisa Afsana Taskia100% (1)
- Diana Cool Fresh Case StudyDokumen41 halamanDiana Cool Fresh Case StudyDung VũBelum ada peringkat
- Competitive advantage A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDari EverandCompetitive advantage A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Acceptance Speech by Dr. E. Sreedharan at Cochin University of Science and TechnologyDokumen3 halamanAcceptance Speech by Dr. E. Sreedharan at Cochin University of Science and TechnologyAnkit saxenaBelum ada peringkat
- On JIT (Just-In-Time) by Ankit SaxenaDokumen48 halamanOn JIT (Just-In-Time) by Ankit SaxenaAnkit saxenaBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial DesignDokumen5 halamanIndustrial DesignAnkit saxenaBelum ada peringkat
- Microprocessor and It's ArchitectureDokumen22 halamanMicroprocessor and It's ArchitectureAnkit saxenaBelum ada peringkat
- (Signal To Noise Ratio) PDFDokumen24 halaman(Signal To Noise Ratio) PDFAnkit saxena100% (1)
- Design of Exhaust Gas Heat ExchangerDokumen56 halamanDesign of Exhaust Gas Heat ExchangerAnkit saxena100% (11)
- of Design of Exhaust Gas Heat ExchangerDokumen21 halamanof Design of Exhaust Gas Heat ExchangerAnkit saxenaBelum ada peringkat
- Kuliah Statistik Inferensial Ke4: Simple Linear RegressionDokumen74 halamanKuliah Statistik Inferensial Ke4: Simple Linear Regressionvivian indrioktaBelum ada peringkat
- Managing operations service problemsDokumen2 halamanManaging operations service problemsJoel Christian Mascariña0% (1)
- Responsibility Centres: Nature of Responsibility CentersDokumen13 halamanResponsibility Centres: Nature of Responsibility Centersmahesh19689Belum ada peringkat
- nrcs143 009445Dokumen4 halamannrcs143 009445mdsaleemullaBelum ada peringkat
- Draft of The English Literature ProjectDokumen9 halamanDraft of The English Literature ProjectHarshika Verma100% (1)
- Easyjet Group6Dokumen11 halamanEasyjet Group6Rishabh RakhechaBelum ada peringkat
- Uniform Bonding Code (Part 2)Dokumen18 halamanUniform Bonding Code (Part 2)Paschal James BloiseBelum ada peringkat
- Ultrasonic Examination of Heavy Steel Forgings: Standard Practice ForDokumen7 halamanUltrasonic Examination of Heavy Steel Forgings: Standard Practice ForbatataBelum ada peringkat
- December 2018: Russian Journal of Agricultural and Socio-Economic SciencesDokumen339 halamanDecember 2018: Russian Journal of Agricultural and Socio-Economic Sciencesnahla saviraBelum ada peringkat
- ThesisDokumen18 halamanThesisapi-29776055293% (15)
- Rejoinder To Adom Ochere's Misrepresentation - FinalDokumen3 halamanRejoinder To Adom Ochere's Misrepresentation - FinalFuaad DodooBelum ada peringkat
- Books 2738 0Dokumen12 halamanBooks 2738 0vinoohmBelum ada peringkat
- Youtube AlgorithmDokumen27 halamanYoutube AlgorithmShubham FarakateBelum ada peringkat
- Sap Fi/Co: Transaction CodesDokumen51 halamanSap Fi/Co: Transaction CodesReddaveni NagarajuBelum ada peringkat
- Maximizing Revenue of IT Project DevelopmentDokumen4 halamanMaximizing Revenue of IT Project DevelopmentJulius Mark CerrudoBelum ada peringkat
- Diagram of Thermal RunawayDokumen9 halamanDiagram of Thermal RunawayVeera ManiBelum ada peringkat
- Lea 201 Coverage Topics in Midterm ExamDokumen40 halamanLea 201 Coverage Topics in Midterm Examshielladelarosa26Belum ada peringkat
- 04 Activity 2Dokumen2 halaman04 Activity 2Jhon arvie MalipolBelum ada peringkat
- Enhancing reliability of CRA piping welds with PAUTDokumen10 halamanEnhancing reliability of CRA piping welds with PAUTMohsin IamBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 2 ReportDokumen9 halamanLab 2 Reportsherub wangdiBelum ada peringkat
- University Assignment Report CT7098Dokumen16 halamanUniversity Assignment Report CT7098Shakeel ShahidBelum ada peringkat
- Management Reporter Integration Guide For Microsoft Dynamics® SLDokumen22 halamanManagement Reporter Integration Guide For Microsoft Dynamics® SLobad2011Belum ada peringkat
- WEEK 8 HW WS - B - Graphs & ChartsDokumen6 halamanWEEK 8 HW WS - B - Graphs & Chartsangela trioBelum ada peringkat
- Process ValidationDokumen116 halamanProcess ValidationsamirneseemBelum ada peringkat
- STS Chapter 5Dokumen2 halamanSTS Chapter 5Cristine Laluna92% (38)
- Exercise No. 7: AIM: To Prepare STATE CHART DIAGRAM For Weather Forecasting System. Requirements: Hardware InterfacesDokumen4 halamanExercise No. 7: AIM: To Prepare STATE CHART DIAGRAM For Weather Forecasting System. Requirements: Hardware InterfacesPriyanshu SinghalBelum ada peringkat
- IBM TS3500 Command Line Interface (CLI) ExamplesDokumen6 halamanIBM TS3500 Command Line Interface (CLI) ExamplesMustafa BenmaghaBelum ada peringkat
- A Dream Takes FlightDokumen3 halamanA Dream Takes FlightHafiq AmsyarBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 13 AminesDokumen3 halamanUnit 13 AminesArinath DeepaBelum ada peringkat
- Domestic Water Consumption in ChennaiDokumen18 halamanDomestic Water Consumption in Chennaimaaz0% (1)