10 IGCSE Physics Study Stack - Forces & Motion
Diunggah oleh
pixelhoboDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
10 IGCSE Physics Study Stack - Forces & Motion
Diunggah oleh
pixelhoboHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Forces & Motion
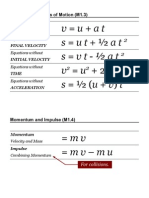
10 IGCSE Physics Revision Topic 9.10 Mechanics Statement Response Comment Units are metres per second ( m/s ) The steeper the slope the faster the speed. It hasn't gone anywhere! It travels equal distances in equal times. Velocity is a VECTOR quantity. Not the same as a distance-time graph.
For an object moving at steady speed in a straight line, SPEED DISTANCE / TIME = If an object moves in a straight line, its distance from a certain a distance-time graph point can be represented by . . . When a body is at rest (stationary) its distance-time graph is a . . . horizontal straight line.
When a body is moving with constant speed its distance-time diagonal straight line. graph is a . . . The VELOCITY of an object is . its SPEED in a given .. DIRECTION The motion of a body can be represented by a . . . On a velocity-time graph, a horizontal straight line represents a body which is . . . VELOCITY-TIME graph
We also need to know moving with constant speed its direction e.g. left to in a straight line. right. Its velocity is increasing if the slope is positive. It could be increasing or decreasing the rate at which its velocity is changing. Think what a rocket does. Units are metres per second squared ( m/s^2) Steeper gradient = higher speed. Steeper gradient = greater acceleration.
On a velocity-time graph, a diagonal straight line represents constant acceleration. a body moving with . . . If a velocity-time graph shows a changing its acceleration. curved line then the body is . . . The steeper the slope of a velocity-time graph . . . the greater the acceleration.
For an object moving in a change in velocity / time straight line with a steady taken for change acceleration, ACCELERATION= The gradient of a distance-time graph represents the . . . The gradient of a velocity-time graph represents the . . . speed of a body. acceleration of a body.
The distance travelled by a body AREA underneath a can be found by working out the velocity-time graph. ... When the forces acting on an object cancel each other out (balance) the object is in . . . When an object rests on a surface its weight exerts a downwards force on the surface. The surface will . . . Whenever two bodies interact, the forces they exert on each other are . . .
This is a very useful way to find the distance travelled, especially if the velocity is not constant. It cannot speed up or slow down.
EQUILIBRIUM
The size of the two exert an equal and opposite forces is the same force on the object. they balance. EQUAL and OPPOSITE This is Newton's 3rd law.
remain stationary or if it is Balanced forces have no effect already moving, it will This is Newton's 1st on the movement of an object. It continue to move at law. will either . . . constant speed in a straight line in the same direction. If the forces acting on an object do not cancel out, an ACCELERATE unbalanced force will act. This will cause the object to . . . Force, mass and acceleration are related by the equation, FORCE = The unit of FORCE (appropriately) is the . . . If the unbalanced force which acts on a body is kept constant but the mass of the body is increased, the acceleration will be . . . mass x acceleration NEWTON This is Newton's 2nd law. This is the usual form of Newton's 2nd law. 1N gives 1kg an acceleration of 1m/s^2 acceleration is inversely proportional to mass
decreased.
If the mass of a body is constant but the resultant external force increase. increases, the acceleration will . .. If a force of friction acts on a body, the external force needed greater. to give it a particular acceleration will be . . . The direction in which a in the opposite direction to frictional force acts is always . . . the motion of a body.
Acceleration is directly proportional to resultant force. It is necessary to apply a larger force to overcome the effect of the frictional force. Friction acts to reduce the speed of a body.
A force of friction is needed otherwise the tyres would when a car accelerates because not grip the road. ... Air resistance is a form of friction (drag) which limits the top speed of a racing car because . . . A sky-diver experiences a frictional drag which increases as his speed increases. The result of this is . . .
The tyre pushes against the road, which pushes back by Newton's 3rd law.
when the driving force is The car has reached equal to the friction force, TERMINAL VELOCITY the two forces are balanced. he reaches a terminal velocity and no longer accelerates.
Newton's 1st law again If forces are balanced, acceleration is zero. Also called DRAG Can be reduced by lubricating with oil or graphite. Friction between brake pads and wheel drum ( or disks) creates a lot of excess heat energy. To stop it within a given distance. Stopping distance increases dramatically with increasing speed. Because the wheels will lock and the tyres will slide against the road surface. If he has taken drugs or alcohol, his reactions will be slower. If there is water or ice on the road, the car may skid. Put your hand out of a moving car window (take care!) and feel the force.
Terminal velocity occurs when there is no resultant force ... acting on a body. A force of friction acts when an object moves . . . Friction causes objects to . . . Friction is used to slow down and stop moving vehicles by applying . . . through air or water. heat up and wear away.
the BRAKES!
In order to stop a vehicle moving at high speed we need . a larger braking force. .. For a given braking force, if a travels further before vehicle moves at a higher speed stopping. it . . . If too great a braking force is applied, the vehicle may . . . SKID
Stopping distance also depends the driver's reaction time. on . . . The braking distance depends on . . . the speed and road conditions.
The faster an object moves through a gas or liquid (fluid) the friction or drag acting on it. greater the . . .
When a body falls, it accelerates GRAVITY initially due to the force of . . . When a car has a steady speed, driving force produced by the frictional forces balance the . the engine. .. When a sky diver pulls the ripcord he slows down because upward force. the parachute exerts a large . . .
All bodies accelerate at approximately 10 m/s^2 on Earth. A bigger engine gives a bigger top speed. Initially - but as he slows down this force decreases until it equals his weight.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsDari EverandA Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Physics - DefinitionsDokumen24 halamanIGCSE Physics - DefinitionsBala Malaivendan100% (1)
- Measurement (Answers)Dokumen16 halamanMeasurement (Answers)keyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Physics Revision Guide Chapter 1Dokumen18 halamanIGCSE Physics Revision Guide Chapter 1Izatul NadiaBelum ada peringkat
- HeinemannIGCSE Physics Chapter1Dokumen11 halamanHeinemannIGCSE Physics Chapter1Mohamed Zein HendawyBelum ada peringkat
- Igcse 52 Solidsliquids&GasesDokumen39 halamanIgcse 52 Solidsliquids&GasesHany ElGezawy100% (1)
- Handout For Physics IGCSEDokumen28 halamanHandout For Physics IGCSEDewi Niken Ariyanti100% (1)
- IGCSE Chemistry Note - States of MatterDokumen8 halamanIGCSE Chemistry Note - States of MatterZahir Sher100% (2)
- IGCSE Chemistry DefinitionsDokumen5 halamanIGCSE Chemistry DefinitionsTanmay Karur100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Turning Effect of Forces (E-Learning)Dokumen32 halamanChapter 5 - Turning Effect of Forces (E-Learning)gayBelum ada peringkat
- Preliminary Exam 2012: Physics and Chemistry MCQsDokumen9 halamanPreliminary Exam 2012: Physics and Chemistry MCQsYee Kai TanBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 1 - Length and TimeDokumen43 halamanPhysics 1 - Length and TimeHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Important Equation in Physics2Dokumen5 halamanImportant Equation in Physics2Ghazi DallyBelum ada peringkat
- 9701 s09 QP 5Dokumen12 halaman9701 s09 QP 5Hubbak KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Skate Park WorksheetDokumen4 halamanEnergy Skate Park WorksheetKiLlmEEEplz XD100% (1)
- Pure Physics Definitions o LevelDokumen7 halamanPure Physics Definitions o LevelDesiree ChenBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Fission and ParticlesDokumen29 halamanNuclear Fission and ParticlesHany ElGezawy100% (2)
- Rate of Reaction 2 QP (Tomek)Dokumen9 halamanRate of Reaction 2 QP (Tomek)Tomasz OstrowskiBelum ada peringkat
- Redox Reactions ExplainedDokumen7 halamanRedox Reactions ExplainedShaikh IradBelum ada peringkat
- Caie Igcse Physics 0625 Theory v2Dokumen22 halamanCaie Igcse Physics 0625 Theory v2Itz MeBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Igcse SummaryDokumen86 halamanBiology Igcse SummaryTarun PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Overcoming Sectarian Divisions in Northern IrelandDokumen3 halamanOvercoming Sectarian Divisions in Northern Irelanddavid peiBelum ada peringkat
- Summary Notes - Topic 1 Forces and Motion - Edexcel Physics IGCSEDokumen5 halamanSummary Notes - Topic 1 Forces and Motion - Edexcel Physics IGCSEEric TTLBelum ada peringkat
- Measurements and Motions in PhysicsDokumen87 halamanMeasurements and Motions in PhysicsJerry Pan100% (1)
- Turning ForcesDokumen42 halamanTurning ForcesNaomi Millidine100% (1)
- Igcse Chemistry NotesDokumen46 halamanIgcse Chemistry Notesapi-1811760180% (1)
- Udgam School For Children: SUBJECT: Science Worksheet CH-13Dokumen10 halamanUdgam School For Children: SUBJECT: Science Worksheet CH-13YASHVI MODIBelum ada peringkat
- Igcse 72 Radiation&HalflifeDokumen32 halamanIgcse 72 Radiation&HalflifeHany ElGezawy50% (2)
- IGCSE Excretion in HumansDokumen15 halamanIGCSE Excretion in HumansYashodhaBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Grade 10 IGCSEDokumen9 halamanEnergy Grade 10 IGCSEsamiksha dudejaBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics M1 EDEXCELDokumen10 halamanMathematics M1 EDEXCELballpoint96Belum ada peringkat
- Physics: Students Should: GuidanceDokumen19 halamanPhysics: Students Should: GuidanceArun MosesBelum ada peringkat
- Phy Unit 2 Notes: Mains ElectricityDokumen9 halamanPhy Unit 2 Notes: Mains Electricityarin ahmedBelum ada peringkat
- St. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 4E Science (Physics) Chapter 14 Sound NotesDokumen6 halamanSt. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 4E Science (Physics) Chapter 14 Sound NotesMsLiewBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter08 Deformation of Solids SsDokumen6 halamanChapter08 Deformation of Solids SseltytanBelum ada peringkat
- MagnetismDokumen3 halamanMagnetismalvin talaveraBelum ada peringkat
- Igcse 12 Forces&ShapeDokumen34 halamanIgcse 12 Forces&ShapeHany ElGezawy0% (1)
- Chapter 14 OscillationsDokumen54 halamanChapter 14 OscillationsPathmanathan Nadeson100% (1)
- Igcse 23 Current&VoltageincircuitsDokumen32 halamanIgcse 23 Current&VoltageincircuitsHany ElGezawy100% (1)
- 1993 - Paper1 PHYSICSDokumen11 halaman1993 - Paper1 PHYSICSNalini Rooplal100% (1)
- Igcse 13 Forces&MovementDokumen26 halamanIgcse 13 Forces&MovementHany ElGezawyBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring AC Voltages and Frequencies Using an OscilloscopeDokumen15 halamanMeasuring AC Voltages and Frequencies Using an OscilloscopeUcok PandapotanBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Reactions and Equations FinalDokumen29 halamanChemical Reactions and Equations FinalRenemartin RebambaBelum ada peringkat
- A Level PhysicsDokumen25 halamanA Level PhysicsAnonymous rn5Te9MwkBelum ada peringkat
- Equations of Motion - Summative Quiz - IB 11 HLDokumen5 halamanEquations of Motion - Summative Quiz - IB 11 HLpixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- AS Level Physics Revision NotesDokumen39 halamanAS Level Physics Revision NotesjoshuaBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Physics - ElectricityDokumen3 halamanIGCSE Physics - ElectricityHyun Jung HongBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Physics Chapter 6 PDFDokumen17 halamanIGCSE Physics Chapter 6 PDFtasmiah100% (2)
- Cie Igcse Physics Chapter 3 2023 OnwDokumen14 halamanCie Igcse Physics Chapter 3 2023 OnwZeinab ElkholyBelum ada peringkat
- Waves - Worksheet Transverse and LongitudinalDokumen2 halamanWaves - Worksheet Transverse and Longitudinalschlemielz100% (1)
- H2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersDokumen12 halamanH2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersKaitlyn HoBelum ada peringkat
- Waves Revision Notes (IGCSE PHYSICS)Dokumen12 halamanWaves Revision Notes (IGCSE PHYSICS)Khushi MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- Notes 5.turning Effects of ForcesDokumen10 halamanNotes 5.turning Effects of ForcesNg Yong Hui Melvin69% (13)
- Igcse 73 ApplicationsofradioactivityDokumen27 halamanIgcse 73 ApplicationsofradioactivityHany ElGezawy100% (1)
- 12 SACE Start of Year Revision SOLUTIONSDokumen6 halaman12 SACE Start of Year Revision SOLUTIONSLydia LamBelum ada peringkat
- Sec 4 MYE Study Notes 2011Dokumen23 halamanSec 4 MYE Study Notes 2011Allyson Tan75% (4)
- Specimen Paper 1 PhyDokumen23 halamanSpecimen Paper 1 Phynewtonian_physicsBelum ada peringkat
- Forces and MotionDokumen29 halamanForces and MotionMoeez Ahmad100% (1)
- 4.5 Standing WavesDokumen2 halaman4.5 Standing WavespixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- U6 Work Energy Power Topic Test ADokumen14 halamanU6 Work Energy Power Topic Test ApixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- A Level Physics PracticalsDokumen89 halamanA Level Physics Practicalspixelhobo50% (2)
- Difficulties With Motion and Energy Problems PDFDokumen2 halamanDifficulties With Motion and Energy Problems PDFpixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- Food Tests InvestigationDokumen3 halamanFood Tests Investigationpixelhobo0% (1)
- Year 10 End Term 3 Sample TestsDokumen6 halamanYear 10 End Term 3 Sample TestspixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- 0654 2019 Specimen Paper Labs 6 & 7Dokumen5 halaman0654 2019 Specimen Paper Labs 6 & 7pixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- Measure Speed & Acceleration with Hands-On ExperimentsDokumen1 halamanMeasure Speed & Acceleration with Hands-On ExperimentspixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple Choice & Paper Questions 1-23Dokumen15 halamanMultiple Choice & Paper Questions 1-23pixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- 9702 s12 QP 31Dokumen12 halaman9702 s12 QP 31pixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Osmosis & Diffusion with Hands-On ExperimentsDokumen4 halamanUnderstanding Osmosis & Diffusion with Hands-On ExperimentspixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- As Physics Lab - Upthrust of Partly Immersed ObjectDokumen5 halamanAs Physics Lab - Upthrust of Partly Immersed ObjectpixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- Year 10 End Term 3 Sample TestsDokumen6 halamanYear 10 End Term 3 Sample TestspixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- Igcse Physics p1 MCQ SehDokumen64 halamanIgcse Physics p1 MCQ SehpixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- 7G WorksheetsDokumen6 halaman7G Worksheetspixelhobo0% (1)
- Grade 6 Revision Test AnswersDokumen9 halamanGrade 6 Revision Test AnswerspixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- G6 Eath Sun Moon Topic Test PDFDokumen11 halamanG6 Eath Sun Moon Topic Test PDFpixelhobo100% (1)
- G6 Magnets & Magnetism Questions: Q1. (A) Which Statements About A Magnet Are True?Dokumen2 halamanG6 Magnets & Magnetism Questions: Q1. (A) Which Statements About A Magnet Are True?pixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- G6 Eath Sun Moon Topic Test PDFDokumen11 halamanG6 Eath Sun Moon Topic Test PDFpixelhobo100% (1)
- Reactivity Topic TestDokumen5 halamanReactivity Topic TestpixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- 9702 Data SheetDokumen2 halaman9702 Data SheetpixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- G8 Reactivity Topic TestDokumen2 halamanG8 Reactivity Topic TestpixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- Food Test 1Dokumen2 halamanFood Test 1pixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- G7 Midsemester 2 ExamDokumen6 halamanG7 Midsemester 2 ExampixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- Salt On The Roads Investigation (Scan)Dokumen1 halamanSalt On The Roads Investigation (Scan)pixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 8 Plants Progress Test ReviewDokumen16 halamanGrade 8 Plants Progress Test Reviewpixelhobo100% (1)
- A Level Physics Topic 1 Mechanics TestDokumen12 halamanA Level Physics Topic 1 Mechanics Testpixelhobo0% (1)
- Reactivity and The Reactions of Metals Worksheet 4Dokumen2 halamanReactivity and The Reactions of Metals Worksheet 4pixelhobo100% (1)
- Work Power Energy Vocab SheetDokumen1 halamanWork Power Energy Vocab SheetpixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 6 Progress Test - Energy, Work & Power: Student Name: - ClassDokumen11 halamanGrade 6 Progress Test - Energy, Work & Power: Student Name: - ClasspixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Lifting Machines MyDokumen14 halamanSimple Lifting Machines MyAkash SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Comment On "The One-Dimensional Harmonic Oscillator PDFDokumen2 halamanComment On "The One-Dimensional Harmonic Oscillator PDFJosé HoyosBelum ada peringkat
- Newtons Second LawDokumen2 halamanNewtons Second LawTalina FlowerBelum ada peringkat
- MARK SCHEME For The June 2005 Question PaperDokumen6 halamanMARK SCHEME For The June 2005 Question PaperUmer AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 28th June Shift-2Dokumen20 halamanPhysics 28th June Shift-2Suman KumariBelum ada peringkat
- MTU 4R0120 DS125: Diesel Generator SetDokumen4 halamanMTU 4R0120 DS125: Diesel Generator Setsaneesh81Belum ada peringkat
- Ref. - No.: 261 - Ruston Gas Turbine Power Generation PackagesDokumen8 halamanRef. - No.: 261 - Ruston Gas Turbine Power Generation Packagesscribdkhatn0% (1)
- Co2 Removal Membrane TechnologyDokumen32 halamanCo2 Removal Membrane TechnologyhecalsieBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Pressure Measurement TechniquesDokumen52 halamanFluid Pressure Measurement Techniquesrohit sharma100% (1)
- POLARONS: Electron-Phonon Interactions in Polar CrystalsDokumen31 halamanPOLARONS: Electron-Phonon Interactions in Polar CrystalscaccaBelum ada peringkat
- Monninghoff 546 - DatasheetDokumen11 halamanMonninghoff 546 - DatasheetirfannadineBelum ada peringkat
- Extraction in Chemical Technology PrincipleDokumen24 halamanExtraction in Chemical Technology PrincipleFatima ZaharaBelum ada peringkat
- Weather CardDokumen2 halamanWeather Cardmekstone100% (1)
- Adsorption Tank Specification SheetDokumen16 halamanAdsorption Tank Specification SheetKristine AmbasBelum ada peringkat
- PDU Assignment 3 TitleDokumen15 halamanPDU Assignment 3 Titleaqib rizwanBelum ada peringkat
- Why Phase Information Is Important For Diagnosing Machinery ProblemsDokumen3 halamanWhy Phase Information Is Important For Diagnosing Machinery ProblemsdinhdtBelum ada peringkat
- Where Is There Light in This Room?Dokumen18 halamanWhere Is There Light in This Room?Casmara LyBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-1 Semiconductor Diodes PDFDokumen103 halamanUnit-1 Semiconductor Diodes PDFRajarao MandaBelum ada peringkat
- Muhammad Imran YousufDokumen1 halamanMuhammad Imran YousufMuhammad Irfan YousufBelum ada peringkat
- William Tell LiteracyDokumen29 halamanWilliam Tell LiteracyAndrés Romero SeguraBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Cold Formed Steel Members 2003 LibroDokumen246 halamanDesign of Cold Formed Steel Members 2003 LibroFelipeBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Report Total Internal Reflection - EditedDokumen10 halamanPhysics Report Total Internal Reflection - EditedJASMSJS SkskdjBelum ada peringkat
- Research Paper in MicrowavesDokumen10 halamanResearch Paper in MicrowavesManoling PanopioBelum ada peringkat
- Ei8553 Process Control Question BankDokumen127 halamanEi8553 Process Control Question BankumamaheswariBelum ada peringkat
- Frequency, Energy, Wavelength Activity C12!2!01Dokumen7 halamanFrequency, Energy, Wavelength Activity C12!2!01Niko BrocesBelum ada peringkat
- Sales Bulletin American Meter 4510Dokumen12 halamanSales Bulletin American Meter 4510rieza_fBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamic IEEE Test Systems for Transient AnalysisDokumen10 halamanDynamic IEEE Test Systems for Transient AnalysisSlobdanBelum ada peringkat
- The Circle and Its Parts: NameDokumen4 halamanThe Circle and Its Parts: NameDaniel DubeBelum ada peringkat
- Lm331 AppnoteDokumen8 halamanLm331 AppnoteEward KenBelum ada peringkat