Advanced Thermodynamics: Outline
Diunggah oleh
xx_aleksa_hrvatska_xxDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Advanced Thermodynamics: Outline
Diunggah oleh
xx_aleksa_hrvatska_xxHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1
Centre for Energy
1
Advanced Thermodynamics
Phase Behaviour of Fluid Mixtures
Lecture 1, 26
th
February 2014
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
2
Outline
1. Course Administration
Introduction, Expectations & Outline
2. Phase Behaviour of Pure Substances
3. Phase Behaviour of Fluid Mixtures
4. Solving the Standard Flash Problem
2
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
3
Introduction & Expectations
About the lecturers
Goal of Education:
The creation of independent, autonomous students
who assume responsibility for their own learning
Why is this unit relevant?
Need to know about:
How fluids behave
Why they behave that way
How we predict that behaviour
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
4
Unit Outline
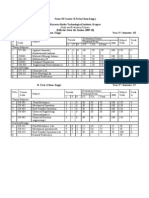
CHPR4404 Advanced Thermodynami cs
Outl i ne Week Date Tutori al
Topi c Ti tl e Lectures
Wed
11:00 -
12:30
17:30 -
18:15
18:25 -
19:10
19:20 -
20:05
A Phase behaviour & thermodynamics 3 1 26-Feb-14 1-A 2-A 3-A
B Fundamentals of Statistical Mechanics 2 2 5-Mar-14 MultiFlash 4-B 5-B 6-C
C The Perfect Molecular Gas 2 3 12-Mar-14 A,B 7-C 8-D 9-D
D Intermolecular Potential and Virial EOS 3 4 19-Mar-14 C,D 10-D 11-E 12-E
E Corresponding States 2 5 26-Mar-14 D,E Qui z 13-F 14-F
F Equations of State 4 6 2-Apr-14 E,F 15-F 16-F 17-G
G Flash Calculations 3 7 9-Apr-14 F 18-G 19-G 20-H
H Activity Coefficients & Liquid Solutions 2 8 16-Apr-14 G Qui z 21-H 22-I
I Solubility of Solids in Liquids 2 NT 23-Apr-14 Non teach
J Gas Hydrates 2 9 30-Apr-14 H 23-I 24-J 25-J
K Interfaces & Petroleum Fluid Characterisation 2 10 7-May-14 I,J Qui z 26-K 27-K
L Introduction to Transport Properties 2 11 14-May-14 J ,K 28-L 29-L 30-M
M Viscosity Models 2 12 21-May-14 L,M 31-M Mock Exam
31 13 28-May-14 Review Qui z Mock Exam
Semester 1 2014 - Ti mel i ne summary
Lecture/Qui z
3
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
5
Unit Assessment & Contacts
3 hour final exam: 60 % or 70 %
4 quizzes based on tutorials & lectures: 40% or 30%
Exam weighting adjusted to give student best result
Lecturer & Co-ordinator
Prof Eric F May
Rm 2.50
Eric.May@uwa.edu.au
On sabbatical until April 21st
Lecturers
Dr Thomas Hughes
Rm 2.47B
thomas.hughes@uwa.edu.au
Dr Zachary Aman
Rm 2.49B
zachary.aman@uwa.edu.au
Consultation by appointment (arrange
through email) or during tutorials.
Recommended texts (short-hand author reference in bold)
1) Assael, Trusler & Tsolakis. "Thermophysical Properties
of Fluids: An Introduction to their Prediction"
2) Prausnitz, Lichtenthaler, de Azevedo. "Molecular
Thermodynamics of Fluid-Phase Equilibria"
3) Kyle. "Chemical and Process Thermodynamics"
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
6
1. Choose your response from the
keypad buttons.
2. The light will go GREEN to confirm
your response has been received.
3. You can change your answer by
simply keying in your new choice.
(The system will only count the last vote)
HOW TO USE THE KEYPADS
NOTE:
Please DO NOT press the GO button, this is
a functionality for break-out sessions only.
4
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
7
What is a Phase?
A phase is a homogenous region in space where
the intensive properties are the same.
i.e. uniform properties throughout
A heterogenous system is made up of two or
more phases (homogenous systems).
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
8
PVT Surface for a Pure Substance
a b c d e
5
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
9
Terminology
Triple Line
Triple Point
Sublimation line
Saturation curve
Dew-point curve
Phase Envelope
What would be the shape of the
PVT surface for an ideal gas?
Critical Point
Melting line
Vapour-pressure curve
Bubble-point curve
Two-phase region
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
10
A non-simple
substance: H
2
O
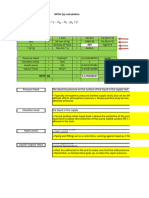
Clapeyron Equation
T v
L
T v v
h h
dT
dP
o|
o|
| o
| o
A
=
=
) (
For ALL pure substances:
i.e. Slope in P-T plane of
boundary between phases
o and| in terms of latent
heat and change in volume
(per unit mole or mass).
6
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
11
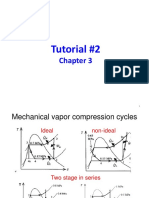
Phase Behaviour of Fluid Mixture
2 or more components
2 phase region of
PVT surface not flat
(Quality lines)
Exercise: P-V
projection for a
fluid mixture?
Upper dew point (for isotherm)
Lower dew point
(for isotherm)
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
12
Retrograde Behaviour
At point d, there are 2 competing processes
1. Molecules compressed together, start to
associate & form liquid phase
Normal behaviour: P |, liquid volume |
2. Small molecules remaining in gas phase
behave as a solvent for the large molecules
in condensate phase
Retrograde behaviour: P |, liquid volume +
Can be thought of in terms of a supercritical solvent
7
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
13
Typical Hydrocarbon Mixtures
C
n
notation & plus fraction
Phase envelope completely determined by
composition. Why?
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
14
Phase Envelopes for Reservoir Fluids
8
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
15
Issues for Engineers
Evaluate reserves & production strategy
Facilities Sizing
Gas-Oil Ratio GOR & CGR
Condensate drop-out and Gas Recycling
Pipeline specifications: HC dew point
Location of dew point curve VERY
sensitive to (small) amounts of heavy HCs
Dew points key parameter for measurement
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
16
N components, 2 phases:
Compositions: Bulk - z
i
, Vap - y
i
, Liq - x
i
, i =1 to N
Molar Flow Rates or Quality Specification:
F
feed
, F
vap
, F
liq
amounts of substance
Phase Behaviour Problem
Vectors length N
The Standard Flash Problem
9
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
17
Specify F
feed
, z
i
, and two of {T, P, F
liq
}
2N+2 unknowns: x
i
, y
i
, F
vap
& one of {T, P, F
liq
}
N+2 material balance equations:
1
1
=
=
N
i
i
x 1
1
=
=
N
i
i
y
2 normalisation eqns
feed vap liq
F F F = +
feed i vap i liq i
F z F y F x = +
N eqns
Solving the Standard Flash Problem
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
18
Remaining Equations?
Where do we get the remaining N equations?
ANSWER:
Chemical Thermodynamics gives us N equations
in algebraic form:
i
(v)
=
i
(l)
Models of microscopic nature of matter gives us
the numerical values needed to solve them
So we must start with the armoury of
Classical Thermodynamics
10
Advanced Thermodynamics
Centre for Energy
19
Lecture 1: Core Ideas
1. Phase Behaviour of Pure Substances
PVT Surface, PT & PV Planar Projections, Terminology,
ClapeyronEquation
2. Phase Behaviour of Fluid Mixtures
2-phase AREA in PT plane, Terminology
Retrograde Condensation
3. Typical Reservoir Fluids
Compositions, Phase Behaviour, Critical Points, Issues for
Engineers
4. Solving the Standard Flash Problem
Material balance +Thermodynamics +Model of microscopic world
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Partial Differential Equations: An Introduction to Theory and ApplicationsDari EverandPartial Differential Equations: An Introduction to Theory and ApplicationsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2)
- Advanced Heat and MassDokumen58 halamanAdvanced Heat and MassJonathan LokeBelum ada peringkat
- Course Outline ENCH 427 F2010Dokumen3 halamanCourse Outline ENCH 427 F2010Bessem BelliliBelum ada peringkat
- 2-Real Gases LectureDokumen38 halaman2-Real Gases Lecturemahmoud50% (2)
- Transport Processes in Petroleum Production: PETE 314Dokumen4 halamanTransport Processes in Petroleum Production: PETE 314Bharat BhattaraiBelum ada peringkat
- Me MtechDokumen43 halamanMe MtechStanly KurianBelum ada peringkat
- M.tech Syllabus PDFDokumen51 halamanM.tech Syllabus PDFAnonymous MR8PLYBelum ada peringkat
- Thermo Lesson Plan 2018Dokumen6 halamanThermo Lesson Plan 2018kap42Belum ada peringkat
- KTU Thermal Science Mtech Draft SyllabusDokumen82 halamanKTU Thermal Science Mtech Draft SyllabusFennBelum ada peringkat
- ChE Templates PDFDokumen61 halamanChE Templates PDFCuriousBelum ada peringkat
- ChE 2O04 Course Outline Winter 2014 - R4Dokumen6 halamanChE 2O04 Course Outline Winter 2014 - R4cesaggBelum ada peringkat
- Transport 252525252BPhenomena 252525252B 252525252B 252525252BIntroDokumen54 halamanTransport 252525252BPhenomena 252525252B 252525252B 252525252BIntrocoolkanna100% (1)
- Thermo Course OutlineDokumen4 halamanThermo Course OutlineKhDaniBelum ada peringkat
- BSC Hs Physics Semester I To Vi CbcegsDokumen43 halamanBSC Hs Physics Semester I To Vi CbcegsGerald BrightBelum ada peringkat
- Mat201 Complex Variables and Partial Differential Equations TH 1.20 Ac26Dokumen2 halamanMat201 Complex Variables and Partial Differential Equations TH 1.20 Ac26NiketGhelaniBelum ada peringkat
- M.E.Mech. HEAT POWERDokumen37 halamanM.E.Mech. HEAT POWERKapil KotangaleBelum ada peringkat
- Course Outline ELEC 1002 Electrical Principles IDokumen4 halamanCourse Outline ELEC 1002 Electrical Principles IFiveCent NickelBelum ada peringkat
- ME10 - Heat and Flow 1 - Module DescDokumen2 halamanME10 - Heat and Flow 1 - Module DescSridhar TholasingamBelum ada peringkat
- FFTMHDokumen3 halamanFFTMHHarmanpreet Singh RandhawaBelum ada peringkat
- MENG1003 Course Descriptor (1) - 54645703Dokumen7 halamanMENG1003 Course Descriptor (1) - 54645703Gregory CameraBelum ada peringkat
- Computational Fluid Dynamics IDokumen3 halamanComputational Fluid Dynamics Iapi-296698256Belum ada peringkat
- Che1003 Process-Engineering-Thermodynamics Eth 1.1 47 Che1003Dokumen2 halamanChe1003 Process-Engineering-Thermodynamics Eth 1.1 47 Che1003kiranchemenggBelum ada peringkat
- Ismael Mohammed Merie - CHEM410Dokumen9 halamanIsmael Mohammed Merie - CHEM410ismailop079Belum ada peringkat
- ChE SyllabusDokumen30 halamanChE SyllabusRavindra Kumar NiranjanBelum ada peringkat
- Gujarat Technological University Metallurgy EngineeringDokumen3 halamanGujarat Technological University Metallurgy EngineeringSankar SabarishBelum ada peringkat
- Course Outline PHY-111 (6) SP2024Dokumen5 halamanCourse Outline PHY-111 (6) SP2024shibly.nomany.khanBelum ada peringkat
- ChE 303 Introduction and VLEDokumen21 halamanChE 303 Introduction and VLEMahmood UllahBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics R 18Dokumen31 halamanMathematics R 18VigneshBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 - IntroductionDokumen42 halamanLecture 1 - IntroductionWillie MojataleBelum ada peringkat
- ECSE-6230 Semiconductor Devices and Models I: Prof. Shayla SawyerDokumen31 halamanECSE-6230 Semiconductor Devices and Models I: Prof. Shayla Sawyerprabhat1_16082Belum ada peringkat
- Study Guide Th2!18!19Dokumen23 halamanStudy Guide Th2!18!19Anonymous bTx6sLrSFBelum ada peringkat
- Format For Course Curriculum: Annexure CD - 01'Dokumen4 halamanFormat For Course Curriculum: Annexure CD - 01'Sudeb SarkarBelum ada peringkat
- 3340 Fall16 SyllabusDokumen3 halaman3340 Fall16 SyllabusJoseBelum ada peringkat
- Aeronautical Syllabus-Shivaji University - R.H.B. RamamurthyDokumen36 halamanAeronautical Syllabus-Shivaji University - R.H.B. RamamurthyZachary GuerraBelum ada peringkat
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Pilani Campus Instruction DivisionDokumen6 halamanBirla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Pilani Campus Instruction DivisionSijo VMBelum ada peringkat
- ChE SyllabusDokumen30 halamanChE SyllabusSubodh DwivediBelum ada peringkat
- ECE Syllabus and SructureDokumen82 halamanECE Syllabus and SructureMohit JindalBelum ada peringkat
- M.E. ENERGY ENGINEERING SyllabusDokumen44 halamanM.E. ENERGY ENGINEERING SyllabusJoswa CaxtonBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid HydraulicDokumen362 halamanFluid HydraulicLaw Jia WeiBelum ada peringkat
- Elective Module:: CE4-33 Molecular Modelling of FluidsDokumen11 halamanElective Module:: CE4-33 Molecular Modelling of FluidsYolanda Winarny Eviphanie HutabaratBelum ada peringkat
- AE SyllabusDokumen158 halamanAE Syllabusuzma takkalkiBelum ada peringkat
- Computational Fluid Dynamics : February 4Dokumen30 halamanComputational Fluid Dynamics : February 4Frik van der MerweBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Engineering SyllabusDokumen49 halamanEnergy Engineering SyllabusKarthiik88Belum ada peringkat
- B.TECH SECOND YEAR SYLLABUS CHEMICAL ENGINEERING 2022 Batch 20-07-2023 V1Dokumen19 halamanB.TECH SECOND YEAR SYLLABUS CHEMICAL ENGINEERING 2022 Batch 20-07-2023 V1nandanitiwari2004Belum ada peringkat
- Thermal and Fluids - Engineering Syllabus M. TechDokumen59 halamanThermal and Fluids - Engineering Syllabus M. TechDamodar S PrabhuBelum ada peringkat
- MSC Physics Sem 1Dokumen10 halamanMSC Physics Sem 1Trilok AkhaniBelum ada peringkat
- ChemistryDokumen666 halamanChemistryBinary Bark100% (1)
- JKLDokumen9 halamanJKLanon_314301380Belum ada peringkat
- Pharma Iii To Viii PDFDokumen57 halamanPharma Iii To Viii PDFRaja PrabhuBelum ada peringkat
- Course Outline Me6510 Au2016Dokumen4 halamanCourse Outline Me6510 Au2016Atieh YousefiBelum ada peringkat
- Te Autonbomous SyllabusDokumen36 halamanTe Autonbomous SyllabusRama Manikanta DondapatiBelum ada peringkat
- IC EngineDokumen52 halamanIC EngineShreepal ChilaBelum ada peringkat
- APL 106: Fluid Mechanics (3-1-0) Lecture Time: 11 Am-12 PM, T TH F Slot-F (LH 310) Tutorial Time: TBDDokumen3 halamanAPL 106: Fluid Mechanics (3-1-0) Lecture Time: 11 Am-12 PM, T TH F Slot-F (LH 310) Tutorial Time: TBDakanksh sandeepsaxenaBelum ada peringkat
- Mumbai University Me Thermal SyllabusDokumen38 halamanMumbai University Me Thermal SyllabusbroninBelum ada peringkat
- M.Tech. ME HPEDokumen32 halamanM.Tech. ME HPEKarthikeyanBelum ada peringkat
- M.Tech. ME HPE PDFDokumen32 halamanM.Tech. ME HPE PDFMalla VasanthaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Thermodynamics: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Conference on Chemical Thermodynamics Université des Sciences et Techniques de Languedoc, Montpellier, France 26–30 August 1975Dari EverandChemical Thermodynamics: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Conference on Chemical Thermodynamics Université des Sciences et Techniques de Languedoc, Montpellier, France 26–30 August 1975J. RouquerolBelum ada peringkat
- High-Pressure Fluid Phase Equilibria: Phenomenology and ComputationDari EverandHigh-Pressure Fluid Phase Equilibria: Phenomenology and ComputationBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamic Models for Chemical Engineering: Design, Develop, Analyse and OptimizeDari EverandThermodynamic Models for Chemical Engineering: Design, Develop, Analyse and OptimizeBelum ada peringkat
- GENG5505 Lecture 01Dokumen30 halamanGENG5505 Lecture 01xx_aleksa_hrvatska_xxBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To Sustainability Applied To Projects & Project Management Raw Project Management: An Agile and Adaptable Body of KnowledgeDokumen25 halamanAn Introduction To Sustainability Applied To Projects & Project Management Raw Project Management: An Agile and Adaptable Body of Knowledgexx_aleksa_hrvatska_xxBelum ada peringkat
- Sample ResumeDokumen2 halamanSample ResumeElena TodorovskaBelum ada peringkat
- Cover Letter SampleDokumen1 halamanCover Letter Samplexx_aleksa_hrvatska_xxBelum ada peringkat
- DT DP RT R: Constant-Volume Batch ReactorDokumen20 halamanDT DP RT R: Constant-Volume Batch Reactorxx_aleksa_hrvatska_xxBelum ada peringkat
- CHPR4406 Reactions Lecture 1Dokumen16 halamanCHPR4406 Reactions Lecture 1xx_aleksa_hrvatska_xxBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Thermodynamics: OutlineDokumen7 halamanAdvanced Thermodynamics: Outlinexx_aleksa_hrvatska_xxBelum ada peringkat
- Enron Annual Report 2000Dokumen60 halamanEnron Annual Report 2000Hassan RazaBelum ada peringkat
- '1812 Overture': The '1812 Overture' of Peter TchaikovskyDokumen4 halaman'1812 Overture': The '1812 Overture' of Peter Tchaikovskyxx_aleksa_hrvatska_xx0% (1)
- Advanced Thermodynamics: OutlineDokumen7 halamanAdvanced Thermodynamics: Outlinexx_aleksa_hrvatska_xxBelum ada peringkat
- The State of The Cubic Equations of State, ValderramaDokumen16 halamanThe State of The Cubic Equations of State, Valderramaxx_aleksa_hrvatska_xxBelum ada peringkat
- They Knew and Failed ToDokumen33 halamanThey Knew and Failed Toxx_aleksa_hrvatska_xxBelum ada peringkat
- Global Corruption BarometerDokumen48 halamanGlobal Corruption BarometerTProyecta: Emprendimiento Cultural de VanguardiaBelum ada peringkat
- CH126P.B22.M1Exam (M1.Exam.P2)Dokumen2 halamanCH126P.B22.M1Exam (M1.Exam.P2)Luis Alfonso DañezBelum ada peringkat
- Data Book: Specify Chart For Top Performance In..Dokumen58 halamanData Book: Specify Chart For Top Performance In..Kelvin RomeroBelum ada peringkat
- Lec.1 Introduction To TurbomachineryDokumen37 halamanLec.1 Introduction To TurbomachineryMechanical EngineeringBelum ada peringkat
- Lab No.: 1 Flowmeter Measurement Apparatus Topic: Mark: Date: Participant Course: CHE 241 Semester: 3 Group: EH110 - 3C No. Name Matrix No. SignatureDokumen5 halamanLab No.: 1 Flowmeter Measurement Apparatus Topic: Mark: Date: Participant Course: CHE 241 Semester: 3 Group: EH110 - 3C No. Name Matrix No. SignatureMohd RafiqBelum ada peringkat
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 88Dokumen1 halamanLecturesNotes (MEE122) 88mhd slmnBelum ada peringkat
- Pressure Measurement - CHL207Dokumen28 halamanPressure Measurement - CHL207Sakthi SBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Vacuum Technology: 00.200.02 Kat.-Nr. 199 90Dokumen199 halamanFundamentals of Vacuum Technology: 00.200.02 Kat.-Nr. 199 90GOWTHAMBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Flow MeasurementDokumen56 halamanGas Flow MeasurementIda Nurdiyana Mohd Yunus100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Selected SolutionsDokumen32 halamanChapter 6 Selected SolutionsEyüp MetinBelum ada peringkat
- Nick Laws: Turbulent Boundary Layer SeparationDokumen36 halamanNick Laws: Turbulent Boundary Layer SeparationkimjimBelum ada peringkat
- CE8394 Fluid Mechanics 01 - by LearnEngineering - inDokumen213 halamanCE8394 Fluid Mechanics 01 - by LearnEngineering - inpriya dharshini100% (2)
- SMJC 2253 Lecture Note 7 Free ConvectionDokumen29 halamanSMJC 2253 Lecture Note 7 Free ConvectionHoongBelum ada peringkat
- CH 1Dokumen29 halamanCH 1Anteneh TarikuBelum ada peringkat
- For Exchanger Tube Rupture PDFDokumen3 halamanFor Exchanger Tube Rupture PDFNikhil DivateBelum ada peringkat
- 1.2 Moles, Molar Volume & Gas LawsDokumen14 halaman1.2 Moles, Molar Volume & Gas LawsShyamal DlrBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Chemistry Practical File: DR B.R. Ambedkar National Institute of Technology JalandharDokumen9 halamanApplied Chemistry Practical File: DR B.R. Ambedkar National Institute of Technology JalandharPRATHAM KHANDELWALBelum ada peringkat
- Projet Proposal For The Construction of A Marcet BoilerDokumen5 halamanProjet Proposal For The Construction of A Marcet BoilerOjiSofttouchCharlesBelum ada peringkat
- Solution of Assignment 2Dokumen9 halamanSolution of Assignment 2Mahmoud AbdelghfarBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - MBE Solution Gas Drive Below Bubble Point Pressure - 15879Dokumen2 halaman1 - MBE Solution Gas Drive Below Bubble Point Pressure - 15879Wan Muhammad ZamyrBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulics Engineering I: Properties of FluidDokumen30 halamanHydraulics Engineering I: Properties of FluidJhoreene JulianBelum ada peringkat
- Dalton's Law (Law of Partial Pressures)Dokumen3 halamanDalton's Law (Law of Partial Pressures)Luyando LikubangwaBelum ada peringkat
- ChokesDokumen3 halamanChokesNaief JavaheriBelum ada peringkat
- Dew PointDokumen1 halamanDew PointSaeed Ahmed Shaikh100% (2)
- ME44001 17 18 S2 Tutorial 2Dokumen48 halamanME44001 17 18 S2 Tutorial 2Tsz Chun YuBelum ada peringkat
- Main Canal List of StructuresDokumen12 halamanMain Canal List of StructuresItaliya ChintanBelum ada peringkat
- Knudsen EffusionDokumen9 halamanKnudsen EffusionMohammadBelum ada peringkat
- Liquefaction Cycles 00Dokumen30 halamanLiquefaction Cycles 00Wael_Barakat_3179100% (1)
- NPSH CalculationDokumen10 halamanNPSH CalculationBalamuruganBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics Handout 2Dokumen4 halamanThermodynamics Handout 2Demetrio C. Villanueva IIIBelum ada peringkat