EML 6451 Midterm Exam Info
Diunggah oleh
medlyncJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EML 6451 Midterm Exam Info
Diunggah oleh
medlyncHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EML 6451 Mid-Term Exam Information Time and Place : Feb 28, 2014, 3:00-5:00 pm in CISE Building E118.
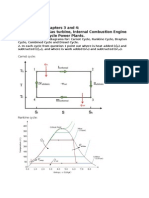
Open book and Notes. All the thermal properties needed in the problem solving will be provided, so you do not need to include any tables, charts, and figures in your books and notes. You need to bring a scientific and engineering calculator. No computer and cell phone Materials covered : the exam will include all the materials covered in classes up to the Wednesday, February 26 lecture (Lecture 1 to lecture 22). Only the topics included in class and in homeworks will be in the exam. Exam Format Part A : 40% five questions aiming at the fundamental understanding of the physics and engineering principles. Sample review questions are given next. Part B : 60%, three problem comparable to your HW problems. They will involve setting up the solution methods and perform simple calculations to obtain numerical answers. Review questions for Part A : 1. The thermal energy has both quantity and quality issues. How do you assess the quality aspect of energy ? You may give a simple example to show your point. 2. First, discuss the factors that control the power density (volumetric heat generation rate) in a nuclear reactor core. Can we design the power density as high as we want ? If not what are the factors that limit the power density and which one is the most significant one ? 3. Please explain the physics of a fast nuclear reactor. Most of the time a fast nuclear reactor is designed to be a breeder reactor. Describe how the breeding is achieved and also define the breeding ratio. What the breeding ratio should be for a breeder reactor ? 4. For a combined Brayton-Rankine cycle, explain how the two subsystems are coupled and what are the limitations. Explain why a combined system enhances the overall efficiency. 5. In a Brayton cycle system with regeneration, discuss under what conditions regeneration would be more beneficial ? Also explain why there are situations regeneration actually results in lower efficiency than that without regeneration.
6. For a Brayton cycle gas turbine system, please explain when you decrease the scale of the compressor and turbine, mainly what will be affected and why ? 7. For an ideal Brayton cycle, when you add the intercooling and reheating only what always happen to the back work ratio and thermal efficiency ? Why ? 8. For an ideal Brayton cycle, when you add only the regeneration what always happen to the back work ratio and thermal efficiency ? Why ?
9. For an ideal Brayton cycle, when you add the intercooling, reheating and also regeneration what always happen to the back work ratio and thermal efficiency ? Why ? 10. Between a typical Rankine cycle and a typical Brayton cycle, explain why the Brayton cycle has a very large back work ratio, but it still manages to have a relatively higher thermal efficiency ? 11. What are the major advantages for the Rankine and Brayton cycles respectively ? 12. Please outline the general concept for optimizing a Brayton cycle ? 13. For absorption refrigeration, it actually involves two cycles working together to achieve the cooling effects. Please draw a diagram to show this combination. 14. Explain in general, why a co-gen plant releases less CO 2 than the sum of CO 2 releases from the two stand alone systems ? 15. What are the three groups of fission energy materials and their respective definitions ? Please explain why most nuclear power plants are based on thermal reactors and fast reactors are usually associated with breeding functions rather than producing power ?
Please note the above are sample questions that guide your preparation. Do not assume that all five Part A questions will come from the above.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Combined Cooling, Heating, and Power Systems: Modeling, Optimization, and OperationDari EverandCombined Cooling, Heating, and Power Systems: Modeling, Optimization, and OperationBelum ada peringkat
- MP3801 Assignment 2020Dokumen3 halamanMP3801 Assignment 2020Abeyaantrix onlineBelum ada peringkat
- Process System Value and Exergoeconomic Performance of Captive Power PlantsDari EverandProcess System Value and Exergoeconomic Performance of Captive Power PlantsBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen3 halamanUntitledChad AndersonBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Engineering Science: In SI UnitsDari EverandMechanical Engineering Science: In SI UnitsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- ME 325 Final Project Combined Cycle Efficiency OptimizationDokumen3 halamanME 325 Final Project Combined Cycle Efficiency Optimizationazeem sheikhBelum ada peringkat
- CHE 372 Project ReportDokumen12 halamanCHE 372 Project ReportGonzalo Jose SequeiraBelum ada peringkat
- Cracker SimulationDokumen6 halamanCracker Simulationadav1232887Belum ada peringkat
- Basic Thermodynamics (BTME-305-18)Dokumen14 halamanBasic Thermodynamics (BTME-305-18)Surjit Kumar GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal Power Plant Exergy AnalysisDokumen6 halamanThermal Power Plant Exergy AnalysisEmilio Joaquin FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Solucionario de Los Problemas de StoneDokumen192 halamanSolucionario de Los Problemas de StoneCarlosDeLaMataBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Systems - Fuel CellDokumen15 halamanEnergy Systems - Fuel Celleoghan mulliganBelum ada peringkat
- Hababneh@zu Edu JoDokumen3 halamanHababneh@zu Edu JoRaed IzzatBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 4-Activity StatementDokumen3 halamanActivity 4-Activity StatementSalman JalaliBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank: Name of Faculty: Prof. Chetan O Yadav Sem: 8 Subject: Renewable Energy Engineering Subject Code: 2181910Dokumen4 halamanQuestion Bank: Name of Faculty: Prof. Chetan O Yadav Sem: 8 Subject: Renewable Energy Engineering Subject Code: 2181910avinashBelum ada peringkat
- Engines Teaching ManualDokumen177 halamanEngines Teaching ManualSteve FoleyBelum ada peringkat
- Lovely Professional University, Punjab: Internal Combustion Engines V. Ganesan, Pub.-Tata Mcgraw-HillDokumen10 halamanLovely Professional University, Punjab: Internal Combustion Engines V. Ganesan, Pub.-Tata Mcgraw-HillVikas PoddarBelum ada peringkat
- Gujarat Technological University: Bachelor of Engineering Subject Code: 3130109Dokumen3 halamanGujarat Technological University: Bachelor of Engineering Subject Code: 3130109Nisarg ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Dar Es Salaam Maritime Institute: Department of Marine EngineeringDokumen3 halamanDar Es Salaam Maritime Institute: Department of Marine EngineeringellyBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Simulation3-Final - 2023 - 230804 - 103255Dokumen20 halaman1 - Simulation3-Final - 2023 - 230804 - 103255akshair03Belum ada peringkat
- Mechanical and Electrical Systems in Buildings: Online Instructor's ManualDokumen28 halamanMechanical and Electrical Systems in Buildings: Online Instructor's ManualAltheo Mateo0% (2)
- A Simplified Model of The Internal Combustion EngineDokumen14 halamanA Simplified Model of The Internal Combustion EnginezaranrajputBelum ada peringkat
- PEM FinalDokumen9 halamanPEM FinalAlejandro BarreraBelum ada peringkat
- 吴宇峰 Thermodynamics PaperDokumen10 halaman吴宇峰 Thermodynamics PaperPalmBelum ada peringkat
- SCE Questions For Chapters 3 and 4Dokumen6 halamanSCE Questions For Chapters 3 and 4Luis Fernando LunaBelum ada peringkat
- SECTION-A (5 X 4 20)Dokumen3 halamanSECTION-A (5 X 4 20)seshatsBelum ada peringkat
- Term Assignment - IAFT 19bme112Dokumen49 halamanTerm Assignment - IAFT 19bme112Rohan PatelBelum ada peringkat
- BMM2523_Chapter 2 thermodynamics9-13 An air-standard cycle executed in a piston-cylinder system is composed of three specified processes. The cycle is to besketcehed on the P - v and T - s diagrams and the back work ratio are to be determined. Assumptions 1 The air-standard assumptions are applicable. 2 Kinetic and potential energy changes are negligible. 3 Air isan ideal gas with constant specific heats. Properties The properties of air are given as R = 0.287 kPa·m 3 /kg·K, c p = 1.005 kJ/kg·K, c v = 0.718 kJ/kg·K, and k =1.4. Analysis (a) The P - v and T - s diagrams of the cycle are shown in the figures.(b) Process 1-2: Isentropic compression )( 12,21 T T mcw in −= − v s T 321 v P 321 11212 =⎟⎟ ⎠⎜⎜⎝ = r T T T v 11 −− ⎞⎛ k k v rocess 2-3: Constant pressure heat addition T T mRP −=−= V V v he back wrk ratio isP 2,32 Pd w out = ∫ − )()( 232323 To )()( 2312,32,21 T T mRT TDokumen11 halamanBMM2523_Chapter 2 thermodynamics9-13 An air-standard cycle executed in a piston-cylinder system is composed of three specified processes. The cycle is to besketcehed on the P - v and T - s diagrams and the back work ratio are to be determined. Assumptions 1 The air-standard assumptions are applicable. 2 Kinetic and potential energy changes are negligible. 3 Air isan ideal gas with constant specific heats. Properties The properties of air are given as R = 0.287 kPa·m 3 /kg·K, c p = 1.005 kJ/kg·K, c v = 0.718 kJ/kg·K, and k =1.4. Analysis (a) The P - v and T - s diagrams of the cycle are shown in the figures.(b) Process 1-2: Isentropic compression )( 12,21 T T mcw in −= − v s T 321 v P 321 11212 =⎟⎟ ⎠⎜⎜⎝ = r T T T v 11 −− ⎞⎛ k k v rocess 2-3: Constant pressure heat addition T T mRP −=−= V V v he back wrk ratio isP 2,32 Pd w out = ∫ − )()( 232323 To )()( 2312,32,21 T T mRT Tmh13001Belum ada peringkat
- Thermal Engineering SyllabusDokumen144 halamanThermal Engineering SyllabusVpr NaturalsBelum ada peringkat
- AE 315 - Finals - Learning Module No. 05Dokumen40 halamanAE 315 - Finals - Learning Module No. 05Saleh Adam OsmanBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Thermodynamics Course DetailsDokumen4 halamanApplied Thermodynamics Course DetailsSaurav DattaBelum ada peringkat
- PPE 16m PDFDokumen7 halamanPPE 16m PDFMariappan VBelum ada peringkat
- Weber Patrick Rep TDokumen14 halamanWeber Patrick Rep TAkindolu DadaBelum ada peringkat
- Power Plant Engineering Question Bank For EEEDokumen7 halamanPower Plant Engineering Question Bank For EEEJOHN PAUL V100% (1)
- Termodinamika Technique Jilid 1 Edition 4Dokumen5 halamanTermodinamika Technique Jilid 1 Edition 4NholisbarberBelum ada peringkat
- Final Technical Report: Development of Low-Irreversibility EnginesDokumen40 halamanFinal Technical Report: Development of Low-Irreversibility EnginesProgyBelum ada peringkat
- Research Paper On Stirling Engine PDFDokumen7 halamanResearch Paper On Stirling Engine PDFfyrgevs3100% (1)
- Journal of Power Sources: Martin Lenz, Tobias Hoehl, Lukas Zanger, Stefan PischingerDokumen12 halamanJournal of Power Sources: Martin Lenz, Tobias Hoehl, Lukas Zanger, Stefan PischingerpolkafBelum ada peringkat
- (M. Rasul) Thermal Power PlantsDokumen274 halaman(M. Rasul) Thermal Power Plantsgoyal.167009100% (1)
- Me8792 - Power Plant EngineeringDokumen48 halamanMe8792 - Power Plant EngineeringPalanivel Rajan A RBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Conservation in CCPPDokumen25 halamanEnergy Conservation in CCPPHoozefa J. Shaikh100% (1)
- Process Design and Simulation: Submission Deadline: TBCDokumen24 halamanProcess Design and Simulation: Submission Deadline: TBCBrajesh ChandraBelum ada peringkat
- Hybrid Fuel Cell Gas Turbine SystemsDokumen32 halamanHybrid Fuel Cell Gas Turbine Systemsİsmail Cem OktayBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics Analysis of Reciprocating Machines and CyclesDokumen13 halamanThermodynamics Analysis of Reciprocating Machines and CyclesVictoriaBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Rankine Cycle in Steam TurbineDokumen26 halamanAnalysis of Rankine Cycle in Steam Turbinemanshulakesh59Belum ada peringkat
- Guide to Cogeneration SystemsDokumen76 halamanGuide to Cogeneration SystemsBo Cu BinBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 32Dokumen19 halamanLec 32arjun SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Turbine Exam Solutions Aug 2016Dokumen4 halamanGas Turbine Exam Solutions Aug 2016Krishna GummadiBelum ada peringkat
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Power Plant TechnologyDokumen9 halamanUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Power Plant TechnologyMaryBelum ada peringkat
- ProposalDokumen8 halamanProposalMontaser KassemBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Brief 2 Energy Efficiency ManagementDokumen5 halamanAssignment Brief 2 Energy Efficiency ManagementLooqman Al-HarahshehBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Design and Exergy Analyses For Combustion Gas Turbine Based Power Generation SystemDokumen23 halamanEngineering Design and Exergy Analyses For Combustion Gas Turbine Based Power Generation SystemInemie-ebi NiweighaBelum ada peringkat
- New and Advanced Conversion TechnologiesDokumen155 halamanNew and Advanced Conversion TechnologiesRudra MurthyBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Review On Thermal ManagementDokumen11 halamanDetailed Review On Thermal Managementvinay shimpiBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Objectives:: MECH 337 Thermodynamics Class Notes - Page: 1 Gas Power Systems Text Reading: Ch. 9Dokumen18 halamanTechnical Objectives:: MECH 337 Thermodynamics Class Notes - Page: 1 Gas Power Systems Text Reading: Ch. 9RAJABelum ada peringkat
- Morini Lorenzo Tesis Thermal Management PhevDokumen119 halamanMorini Lorenzo Tesis Thermal Management PhevSantiago MolinaBelum ada peringkat
- ME6301-SCAD-MSM - by WWW - LearnEngineering.in PDFDokumen167 halamanME6301-SCAD-MSM - by WWW - LearnEngineering.in PDFMohsin EngrBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis On Ic EnginesDokumen6 halamanThesis On Ic EnginesNicole Adams100% (2)
- HW3 AssignmentDokumen1 halamanHW3 AssignmentmedlyncBelum ada peringkat
- Cs Ce: Errors in 7 EditionDokumen1 halamanCs Ce: Errors in 7 EditionmedlyncBelum ada peringkat
- Separations+Homework+ 1Dokumen1 halamanSeparations+Homework+ 1medlyncBelum ada peringkat
- GM 6431Dokumen4 halamanGM 6431medlyncBelum ada peringkat
- Upload ClinicDokumen1 halamanUpload ClinicmedlyncBelum ada peringkat
- Ech 4403Dokumen5 halamanEch 4403medlyncBelum ada peringkat
- Diaphragm Design PDFDokumen50 halamanDiaphragm Design PDFManoj JaiswalBelum ada peringkat
- High-Efficiency Solar Inverter Test Report SummaryDokumen17 halamanHigh-Efficiency Solar Inverter Test Report Summarybharath prabhuBelum ada peringkat
- Stepper Motor Driven Solar Tracker SystemDokumen4 halamanStepper Motor Driven Solar Tracker SystemFAHMY RINANDA SAPUTRI (066629)Belum ada peringkat
- Pelton TurbineDokumen18 halamanPelton Turbinetiwarishbhm0% (1)
- Schlumberger Log Interpretation ChatsDokumen287 halamanSchlumberger Log Interpretation ChatsSabrianto AswadBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Wood Bending PropertiesDokumen11 halamanAnalysis of Wood Bending Propertiesprasanna020391100% (1)
- POLYMERIZATION PROCESSESDokumen0 halamanPOLYMERIZATION PROCESSESmajesticdharma1985Belum ada peringkat
- Atomic TheoryDokumen2 halamanAtomic TheorybabeBelum ada peringkat
- Column Design PDFDokumen2 halamanColumn Design PDFRobin0% (1)
- Clarke and Park TransfomationDokumen9 halamanClarke and Park TransfomationGREATJUSTGREATBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration Case HistoriesDokumen56 halamanVibration Case HistoriesanuprajaBelum ada peringkat
- Plate Bending Element Formulation and Stiffness Matrix DevelopmentDokumen6 halamanPlate Bending Element Formulation and Stiffness Matrix DevelopmentSeyhan ÖzenBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 Forces & PressureDokumen25 halamanPhysics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 Forces & PressureMisratul A'la Mahyuddin100% (2)
- (Architecture Ebook) Alvar Aalto, Alvar Aalto and The Bio-ArchitectureDokumen5 halaman(Architecture Ebook) Alvar Aalto, Alvar Aalto and The Bio-Architecturepooh86poohBelum ada peringkat
- SosthenesDokumen396 halamanSosthenesAthiesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Tuning Equation of State ModelsDokumen34 halamanTuning Equation of State Modelswelltest vspBelum ada peringkat
- CPM cc1 - CH 2 VocabularyDokumen3 halamanCPM cc1 - CH 2 Vocabularyapi-252110147Belum ada peringkat
- Group Theory PDFDokumen280 halamanGroup Theory PDFLuis Cancino Arancibia100% (1)
- Martin Hermann, Masoud Saravi - Nonlinear Ordinary Differential Equations - Analytical Approximation and Numerical Methods-Springer (2016) PDFDokumen320 halamanMartin Hermann, Masoud Saravi - Nonlinear Ordinary Differential Equations - Analytical Approximation and Numerical Methods-Springer (2016) PDFHugo Mayorga100% (1)
- Alloy ZN Ni PDFDokumen8 halamanAlloy ZN Ni PDFElenaBelum ada peringkat
- Separation and Purification of Triacylglycerols From Nyamplung (Calophyllum Inophyllum) Oil by Batchwise Solvent ExtractionDokumen24 halamanSeparation and Purification of Triacylglycerols From Nyamplung (Calophyllum Inophyllum) Oil by Batchwise Solvent ExtractionAfifatul JannahBelum ada peringkat
- How retinal adaptation maintains visual perception despite illumination changesDokumen1 halamanHow retinal adaptation maintains visual perception despite illumination changesAkicaBelum ada peringkat
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Dokumen3 halamanGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19SURAJ NAKUMBelum ada peringkat
- Refraction Through Spherical Surfaces and LensesDokumen2 halamanRefraction Through Spherical Surfaces and LensesOrbit MBBS PreparationBelum ada peringkat
- Crisfield M A Vol 2 Non-Linear Finite Element Analysis of Solids and Structures Advanced TopicsDokumen509 halamanCrisfield M A Vol 2 Non-Linear Finite Element Analysis of Solids and Structures Advanced TopicsIffat Siddqiue0% (1)
- WBUT Btech 2nd Sem 2011 ThemodynamicsDokumen7 halamanWBUT Btech 2nd Sem 2011 ThemodynamicsBapi SarkarBelum ada peringkat
- Equilibrium Stage Processes - Docx CetDokumen25 halamanEquilibrium Stage Processes - Docx CetPortia ShilengeBelum ada peringkat
- Mec 424 - Laboratory Report: Free Vibration Experiment - Natural Frequency of Spring Mass System Without DampingDokumen24 halamanMec 424 - Laboratory Report: Free Vibration Experiment - Natural Frequency of Spring Mass System Without DampingWan AimanBelum ada peringkat
- Cylinders Shall Be Produced As Per IS 7285 and Approved by Chief Controller of ExplosiveDokumen1 halamanCylinders Shall Be Produced As Per IS 7285 and Approved by Chief Controller of ExplosiveAlanka Prasad100% (1)
- MCAT Formula SheetDokumen3 halamanMCAT Formula SheetYank AzharBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyDari EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (2)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyDari EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyBelum ada peringkat
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsDari EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Implementing an Integrated Management System (IMS): The strategic approachDari EverandImplementing an Integrated Management System (IMS): The strategic approachPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresDari EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresBelum ada peringkat
- The Grid: The Fraying Wires Between Americans and Our Energy FutureDari EverandThe Grid: The Fraying Wires Between Americans and Our Energy FuturePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (48)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDari EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesDari EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (21)
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesDari EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementDari EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementBelum ada peringkat
- Idaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentDari EverandIdaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (21)
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialDari EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialBelum ada peringkat
- The New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successDari EverandThe New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Build Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionDari EverandBuild Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Renewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionDari EverandRenewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (12)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressDari EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- OFF-GRID PROJECTS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learn All about OffGrid Living from A-Z and Live a Life of Self-SufficiencyDari EverandOFF-GRID PROJECTS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learn All about OffGrid Living from A-Z and Live a Life of Self-SufficiencyBelum ada peringkat
- Shorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridDari EverandShorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationDari EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemDari EverandHandbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Industrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualDari EverandIndustrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (7)
- Produced Water Treatment Field ManualDari EverandProduced Water Treatment Field ManualPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (5)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesDari EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (14)
- ISO 50001: A strategic guide to establishing an energy management systemDari EverandISO 50001: A strategic guide to establishing an energy management systemBelum ada peringkat
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersDari EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (12)
- Transmission Pipeline Calculations and Simulations ManualDari EverandTransmission Pipeline Calculations and Simulations ManualPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (10)