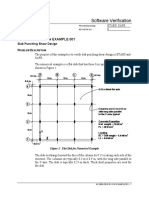
DSFGDSF
Diunggah oleh
Sam JonesJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
DSFGDSF
Diunggah oleh
Sam JonesHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
UNIT 2: STRUCTURE OF ATOM
Atom was earlier considered the most fundamental and indivisible unit of matter. Daltons Atomic Theory considered atom as the most fundamental unit of matter and thus believed it to be indivisible. But further on Sub atomic particles were discovered like electron, protons, neutrons, etc. Electrons were discovered in the Cathode Ray tube experiment. Adding to this J.J Thompson found out the charge to mass ratio of an electron. R.A Millikan found out the value of charge on an electron with his oil drop experiment, and using the ratio of J.J Thompson was able to find out the mass too. A simple modification of the cathode ray tubes lead to the discovery of canal rays, particles carrying positive charge, thus, protons were discovered. Eventually, due to the aspect of stabilizing the atom neutrons were discovered by Chadwick. Neutrons have a mass slightly higher than the protons and have no charge.
Now, since so many particles came up, thus there was a need to visualize how these particles were arranged in an atom, thus experimentalists started making atomic models, many came up with distinct ideas but had to face serious limitations and drawbacks. Lord Rutherford came up with an idea of the model like the solar system, and his model was also called the solar system model. To put limitations to his model James Clark Maxwell had already developed a theory known as the electromagnetic theory of Maxwell. Thus such models, though not perfect still helped the early scientists to work on their own model in a more comprehensive way, and also lead to the development of the Bohr model of atom, the two developments which played an important role in the formulation of Bohrs model were: 1. Dual character of electromagnetic radiation, which means radiation has both wave and particle nature. 2. Experiments on atomic spectra, and the quantization of energy levels. Sir James Clark Maxwell gave the theory on wave nature of electromagnetic radiation; by this he was able to explain the phenomenon of charged particles on macroscopic level. He explained that if a charge particle is accelerated then it emits electromagnetic radiation, which is in fact a form of energy. Maxwell also proved that light itself is an electromagnetic wave. Many phenomenon like diffraction, interference etc. could be explained by Maxwells theory, but certain phenomenon seem to deviate from Maxwells electromagnetic theory. Some of those phenomenon are:
1. Nature of emission of radiation: Black Body radiation.
2. Ejection of electrons when radiation strikes the metal: The Photoelectric effect. 3. Variation of heat capacity of solids as a function of temperature. 4. Line Spectra of atoms, with special reference to hydrogen. Thus, to overcome this problem a theory was put forward by Max Plank, the main and basic idea of his theory was that atoms and molecules could emit or absorb energy(light) only in discrete amounts and not in a continuous manner, thus to the smallest quantity of energy Plank gave the name Quantum.
UNIT 2: STRUCTURE OF ATOM
Atom was earlier considered the most fundamental and indivisible unit of matter. Daltons Atomic Theory considered atom as the most fundamental unit of matter and thus believed it to be indivisible. But further on Sub atomic particles were discovered like electron, protons, neutrons, etc.
Electrons were discovered in the Cathode Ray tube experiment. Adding to this J.J Thompson found out the charge to mass ratio of an electron. R.A Millikan found out the value of charge on an electron with his oil drop experiment, and using the ratio of J.J Thompson was able to find out the mass too. A simple modification of the cathode ray tubes lead to the discovery of canal rays, particles carrying positive charge, thus, protons were discovered. Eventually, due to the aspect of stabilizing the atom neutrons were discovered by Chadwick. Neutrons have a mass slightly higher than the protons and have no charge. Now, since so many particles came up, thus there was a need to visualize how these particles were arranged in an atom, thus experimentalists started making atomic models, many came up with distinct ideas but had to face serious limitations and drawbacks. Lord Rutherford came up with an idea of the model like the solar system, and his model was also called the solar system model. To put limitations to his model James Clark Maxwell had already developed a theory known as the electromagnetic theory of Maxwell. Thus such models, though not perfect still helped the early scientists to work on their own model in a more comprehensive way, and also lead to the development of the Bohr model of atom, the two developments which played an important role in the formulation of Bohrs model were: 1. Dual character of electromagnetic radiation, which means radiation has both wave and particle nature. 2. Experiments on atomic spectra, and the quantization of energy levels.
Sir James Clark Maxwell gave the theory on wave nature of electromagnetic radiation; by this he was able to explain the phenomenon of charged particles on macroscopic level. He explained that if a charge particle is accelerated then it emits electromagnetic radiation, which is in fact a form of energy. Maxwell also proved that light itself is an electromagnetic wave. Many phenomenon like diffraction, interference etc. could be explained by Maxwells theory, but certain phenomenon seem to deexperimentalists started making atomic models, many came up with distinct ideas but had to face serious limitations and drawbacks. Lord Rutherford came up with an idea of the model like the solar system, and his model was also called the solar system model. To put limitations to his model James Clark Maxwell had already developed a theory known as the electromagnetic theory of Maxwell. Thus such models, though not perfect still helped the early scientists to work on their own model in a more comprehensive way, and also lead to the development of the Bohr model of atom, the two developments which played an important role in the formulation of Bohrs model were: 1. Dual character of electromagnetic radiation, which means radiation has both wave and particle nature. 2. Experiments on atomic spectra, and the quantization of energy levels. Sir James Clark Maxwell gave the theory on wave nature of electromagnetic radiation; by this he was able to explain the phenomenon of charged particles on macroscopic level. He explained that if a charge particle is accelerated then it emits electromagnetic radiation, which is in fact a form of energy. Maxwell also proved that light itself is an electromagnetic wave. Many phenomenon like diffraction, interference etc. could be explained by Maxwells theory, but certain phenomenon seem to deviate from Maxwells electromagnetic theory. Some of those phenomenon are:
1. Nature of emission of radiation: Black Body radiation. 2. Ejection of electrons when radiation strikes the metal: The Photoelectric effect. 3. Variation of heat capacity of solids as a function of temperature. 4. Line Spectra of atoms, with special reference to hydrogen. Thus, to overcome this problem a theory was put forward by Max Plank, the main and basic idea of his theory was that atoms and molecules could emit or absorb energy(light) only in discrete amounts and not in a continuous manner, thus to the smallest quantity of energy Plank gave the name Quantum.
UNIT 2: STRUCTURE OF ATOM
Atom was earlier considered the most fundamental and indivisible unit of matter. Daltons Atomic Theory considered atom as the most fundamental unit of matter and thus believed it to be indivisible. But further on Sub atomic particles were discovered like electron, protons, neutrons, etc.
Electrons were discovered in the Cathode Ray tube experiment. Adding to this J.J Thompson found out the charge to mass ratio of an electron. R.A Millikan found out the value of charge on an electron with his oil drop experiment, and using the ratio of J.J Thompson was able to find out the mass too. A simple modification of the cathode ray tubes lead to the discovery of canal rays, particles carrying positive charge, thus, protons were discovered. Eventually, due to the aspect of stabilizing the atom neutrons were discovered by Chadwick. Neutrons have a mass slightly higher than the protons and have no charge. Now, since so many particles came up, thus there was a need to visualize how these particles were arranged in an atom, thus experimentalists started making atomic models, many came up with distinct ideas but had to face serious limitations and drawbacks. Lord Rutherford came up with an idea of the model like the solar system, and his model was also called the solar system model. To put limitations to his model James Clark Maxwell had already developed a theory known as the electromagnetic theory of Maxwell. Thus such models, though not perfect still helped the early scientists to work on their own model in a more comprehensive way, and also lead to the development of the Bohr model of atom, the two developments which played an important role in the formulation of Bohrs model were: 1. Dual character of electromagnetic radiation, which means radiation has both wave and particle nature. 2. Experiments on atomic spectra, and the quantization of energy levels.
Sir James Clark Maxwell gave the theory on wave nature of electromagnetic radiation; by this he was able to explain the phenomenon of charged particles on macroscopic level. He explained that if a charge particle is accelerated then it emits electromagnetic radiation, which is in fact a form of energy. Maxwell also proved that light itself is an electromagnetic wave. Many phenomenon like diffraction, interference etc. could be explained by Maxwells theory, but certain phenomenon seem to deexperimentalists started making atomic models, many came up with distinct ideas but had to face serious limitations and drawbacks. Lord Rutherford came up with an idea of the model like the solar system, and his model was also called the solar system model. To put limitations to his model James Clark Maxwell had already developed a theory known as the electromagnetic theory of Maxwell. Thus such models, though not perfect still helped the early scientists to work on their own model in a more comprehensive way, and also lead to the development of the Bohr model of atom, the two developments which played an important role in the formulation of Bohrs model were: 1. Dual character of electromagnetic radiation, which means radiation has both wave and particle nature. 2. Experiments on atomic spectra, and the quantization of energy levels. Sir James Clark Maxwell gave the theory on wave nature of electromagnetic radiation; by this he was able to explain the phenomenon of charged particles on macroscopic level. He explained that if a charge particle is accelerated then it emits electromagnetic radiation, which is in fact a form of energy. Maxwell also proved that light itself is an electromagnetic wave. Many phenomenon like diffraction, interference etc. could be explained by Maxwells theory, but certain phenomenon seem to deviate from Maxwells electromagnetic theory. Some of those phenomenon are:
1. Nature of emission of radiation: Black Body radiation. 2. Ejection of electrons when radiation strikes the metal: The Photoelectric effect. 3. Variation of heat capacity of solids as a function of temperature. 4. Line Spectra of atoms, with special reference to hydrogen. Thus, to overcome this problem a theory was put forward by Max Plank, the main and basic idea of his theory was that atoms and molecules could emit or absorb energy(light) only in discrete amounts and not in a continuous manner, thus to the smallest quantity of energy Plank gave the name Quantum.
UNIT 2: STRUCTURE OF ATOM
Atom was earlier considered the most fundamental and indivisible unit of matter. Daltons Atomic Theory considered atom as the most fundamental unit of matter and thus believed it to be indivisible. But further on Sub atomic particles were discovered like electron, protons, neutrons, etc.
Electrons were discovered in the Cathode Ray tube experiment. Adding to this J.J Thompson found out the charge to mass ratio of an electron. R.A Millikan found out the value of charge on an electron with his oil drop experiment, and using the ratio of J.J Thompson was able to find out the mass too. A simple modification of the cathode ray tubes lead to the discovery of canal rays, particles carrying positive charge, thus, protons were discovered. Eventually, due to the aspect of stabilizing the atom neutrons were discovered by Chadwick. Neutrons have a mass slightly higher than the protons and have no charge. Now, since so many particles came up, thus there was a need to visualize how these particles were arranged in an atom, thus experimentalists started making atomic models, many came up with distinct ideas but had to face serious limitations and drawbacks. Lord Rutherford came up with an idea of the model like the solar system, and his model was also called the solar system model. To put limitations to his model James Clark Maxwell had already developed a theory known as the electromagnetic theory of Maxwell. Thus such models, though not perfect still helped the early scientists to work on their own model in a more comprehensive way, and also lead to the development of the Bohr model of atom, the two developments which played an important role in the formulation of Bohrs model were: 1. Dual character of electromagnetic radiation, which means radiation has both wave and particle nature. 2. Experiments on atomic spectra, and the quantization of energy levels.
Sir James Clark Maxwell gave the theory on wave nature of electromagnetic radiation; by this he was able to explain the phenomenon of charged particles on macroscopic level. He explained that if a charge particle is accelerated then it emits electromagnetic radiation, which is in fact a form of energy. Maxwell also proved that light itself is an electromagnetic wave. Many phenomenon like diffraction, interference etc. could be explained by Maxwells theory, but certain phenomenon seem to deviate from Maxwells electromagnetic theory. Some of those phenomenon are:
1. Nature of emission of radiation: Black Body radiation. 2. Ejection of electrons when radiation strikes the metal: The Photoelectric effect. 3. Variation of heat capacity of solids as a function of temperature. 4. Line Spectra of atoms, with special reference to hydrogen. Thus, to overcome this problem a theory was put forward by Max Plank, the main and basic idea of his theory was that atoms and molecules could emit or absorb energy(light) only in discrete amounts and not in a continuous manner, thus to the smallest
quantity of energy Plank gave the name Quantum.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- AP Calculus AB Practice ExamDokumen21 halamanAP Calculus AB Practice ExamGaming 1 SportsBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- 33 As Statistics Unit 5 TestDokumen2 halaman33 As Statistics Unit 5 TestThomas BeerBelum ada peringkat
- Physic Ss2 2019Dokumen4 halamanPhysic Ss2 2019sulayajannyBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Form and DesignDokumen350 halamanPrinciples of Form and DesignNora Maloku100% (8)
- AS 3600-2018 RC-PN Example 001Dokumen4 halamanAS 3600-2018 RC-PN Example 001Aashu chaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 Slides PSK - QAMDokumen87 halamanUnit 3 Slides PSK - QAMSam JonesBelum ada peringkat
- Structure and Properties of Solids Helps Us To Make Solids of Desired PurposeDokumen37 halamanStructure and Properties of Solids Helps Us To Make Solids of Desired PurposeSam JonesBelum ada peringkat
- Us To Make Solids of Desired PurposeDokumen5 halamanUs To Make Solids of Desired PurposeSam JonesBelum ada peringkat
- Sturcture of AtomDokumen32 halamanSturcture of AtomSam JonesBelum ada peringkat
- Final UTS-1 PDFDokumen3 halamanFinal UTS-1 PDFKritika Yadav100% (1)
- Dynamics Tutorial 1Dokumen2 halamanDynamics Tutorial 1ethanBelum ada peringkat
- Latent Graph Diffusion A Unified Framework For Generation and Prediction On GraphsDokumen21 halamanLatent Graph Diffusion A Unified Framework For Generation and Prediction On GraphslinkzdBelum ada peringkat
- Numerical Methods PPT AYUSH MISHRADokumen11 halamanNumerical Methods PPT AYUSH MISHRAsubscribe.us100Belum ada peringkat
- G and M Programming For Mills ManualDokumen98 halamanG and M Programming For Mills ManualyendiBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Mathematics1 2015 PDFDokumen24 halamanEngineering Mathematics1 2015 PDFsenyonjo emmaBelum ada peringkat
- A Case Study in Ow Assurance of A Pipeline-Riser System Using OLGADokumen10 halamanA Case Study in Ow Assurance of A Pipeline-Riser System Using OLGAAhmed BedhiefBelum ada peringkat
- Aits 2021 FT Ix Jeem.Dokumen16 halamanAits 2021 FT Ix Jeem.Atharv AtoleBelum ada peringkat
- Small Satellite Thermal Design, Test and AnalysisDokumen12 halamanSmall Satellite Thermal Design, Test and AnalysisMihaela NastaseBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 (Laplace Transform)Dokumen14 halamanChapter 3 (Laplace Transform)EmmanuelBelum ada peringkat
- Ip AdaptorDokumen16 halamanIp Adaptorlaure9239Belum ada peringkat
- Virtual Work (Deflection)Dokumen46 halamanVirtual Work (Deflection)Rovic JayBelum ada peringkat
- Sek - Men.Keb. Tinggi Melaka (Malacca High School. Estd.1826)Dokumen19 halamanSek - Men.Keb. Tinggi Melaka (Malacca High School. Estd.1826)Lee Shi HockBelum ada peringkat
- Prototyping Approach To Neuro-Fuzzy Speed Control of Trapezoidal Brushless DC MotorDokumen6 halamanPrototyping Approach To Neuro-Fuzzy Speed Control of Trapezoidal Brushless DC MotorJournal of ComputingBelum ada peringkat
- Java Syntax Reference IDokumen14 halamanJava Syntax Reference ITom BertinBelum ada peringkat
- Package Survival': R Topics DocumentedDokumen185 halamanPackage Survival': R Topics DocumentedFlorencia FirenzeBelum ada peringkat
- The Impact of Firm Growth On Stock Returns of Nonfinancial Firms Listed On Egyptian Stock ExchangeDokumen17 halamanThe Impact of Firm Growth On Stock Returns of Nonfinancial Firms Listed On Egyptian Stock Exchangealma kalyaBelum ada peringkat
- Representation of Numeric Data in Computer-1Dokumen3 halamanRepresentation of Numeric Data in Computer-1Anthony LoñezBelum ada peringkat
- Open Set ProofDokumen2 halamanOpen Set Proofsagetbob43Belum ada peringkat
- Solved Problems - Continuous Random VariablesDokumen4 halamanSolved Problems - Continuous Random VariablesDahanyakage WickramathungaBelum ada peringkat
- PPT 6 Pms-Remaining Service LifeDokumen22 halamanPPT 6 Pms-Remaining Service LifeSwagata SarkarBelum ada peringkat
- Deflection Considerations in Two-Way Reinforced CoDokumen13 halamanDeflection Considerations in Two-Way Reinforced CoHamid HassanzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic ForcesDokumen6 halamanMagnetic ForcesJevaughn SmithBelum ada peringkat
- CE 14 Course SyllabusDokumen2 halamanCE 14 Course SyllabusChristian GalopeBelum ada peringkat
- Sabour & Poulin 2006Dokumen22 halamanSabour & Poulin 2006ali basyaBelum ada peringkat