FE Fluids Review - Notes and Problems113pdf
Diunggah oleh
Mahmoud HelmyDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
FE Fluids Review - Notes and Problems113pdf
Diunggah oleh
Mahmoud HelmyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
PPI
Fluid Mechanics FE Review
Carrie (CJ) McClelland, P.E. cmcclell@mines.edu
FERC
Fluid Mechanics FE Review
These slides contain some notes, thoughts about what to study, and some practice problems. The answers to the problems are given in the last slide. In the review session, we will be working some of these problems. Feel free to come to the session, or work the problems on your own. I am happy to answer your email questions or those that you bring to the session. Good luck!
FERC
PPI
Fluid Mechanics FE Review
MAJOR TOPICS Fluid Properties Fluid Statics Fluid Dynamics Fluid Measurements Dimensional Anaysis
FERC
Fluid Mechanics FE Review
It will be very helpful to memorize the following concepts and equations: Specific weight, density, and specific gravity Hydrostatics pressure equation / manometry Force magnitude and location due to hydrostatic pressure for horizontal and vertical plane walls Conservation of mass / continuity Conservation of energy / Bernoulli and Energy Eqn Darcy Eqn Relative roughness equation Drag equation How to use the Moody Diagram
Most equations and problems taken from Professional Publications, Inc. FERC Review Course Book
FERC
PPI
Fluid Mechanics
Properties
Fluids Substances in either the liquid or gas phase Cannot support shear
Make sure you use the ideal gas law when calculating properties for gasses!!
FERC
Fluid Mechanics
Properties
Property Density Specific Weight Specific Gravity Viscosity Symbol & Equation = = =
Definition
Etc.
density x gravity
Kinematic viscosity
Make sure you know the relationship between density, specific weight, and specific gravity!
FERC
PPI
Mass & Weight
1. 10.0 L of an incompressible liquid exert a force of 20 N at the earths surface. What force would 2.3 L of this liquid exert on the surface of the moon? The gravitational acceleration on the surface of the moon is 1.67 m/s2
(A) 0.39 N (B) 0.78 N (C) 3.4 N (D) 4.6 N
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Fluid Mechanics Fluid Properties
Property Definitions Vapor Pressure Symbol & Equation Definition
Pressure at which liquid and vapor are in equilibrium
Etc.
Used to predict cavitation (local pressure < vapor pressure
Bulk Modulus Speed of Sound
=
, = , =
Velocity of propegation of a small wave
k = Bulk modulus = 1.4
FERC
PPI
Mach Number
2. A jet aircraft is flying at a speed o f 1700 km/h. The air temperature is 20 C. The molecular weight of air is 29 g/mol. What is the Mach number of the aircraft?
(A) 0.979 (B) 1.38 (C) 1.92 (D) 5.28
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Fluid Mechanics Fluid Properties
Property Definitions Surface Tension Capillary Rise Symbol & Equation =
= 4
Definition
Etc.
Distance a liquid will rise (or fall) in a tube
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
PPI
Surface Tension
3. A 2 mm (inside diameter) glass tube is placed in a container of mercury. An angle of 40is measured as illustrated. The density and surface tension of mercury are 13550 kg/m3 and 37.5 x 10-2 N/m, respectively. How high will the mercury rise or be depressed in the tube as a result of capillary action?
(A) -4.3 mm (depression) (B) -1.6 mm (depression) (C) 4.2 mm (rise) (D) 6.4 mm (rise)
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Fluid Mechanics
Stresses and Viscosity
Shear Stress Normal Component: Tangential Component - For a Newtonian fluid: =
(v = velocity)
9-1b
- For a pseudoplastic or dilatant fluid: Absolute Viscosity = = Ratio of shear stress to rate of shear deformation
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
PPI
Viscosity
4. A sliding-plate viscometer is used to measure the viscosity of a Newtonian fluid. A force of 25 N is required to keep the top plate moving at a constant velocity of 5 m/s. What is the viscosity of the fluid?
(A) 0.005 N-s/m2 (B) 0.04 N-s/m2 (C) 0.2 N-s/m2 (D) 5.0 N-s/m2
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Fluid Statics
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
PPI
Manometry
5. An open water manometer is used to measure the pressure in a tank. The tank ifs half-filled with 50,000 kg of a liquid chemical that is not miscible in water. The manometer tube is filled with liquid chemical. What is the pressure in the tank relative to the atmospheric pressure?
(A) 1.4 kPa (B) 1.9 kPa (C) 2.4 kPa (D) 3.4 kPa
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Fluid Statics
Barometer
9-2c
Atmospheric Pressure
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
PPI
Fluid Statics
FERC
Hydrostatics
6. A 6m x 6m x 6m vented cubical tank is half-filled with water; the remaining space is filled with oil (SG=0.8). What is the total force on one side of the tank?
(A) 690 kN (B) 900 kN (C) 950 kN (D) 1.0 MN
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
PPI
Fluid Statics Examples
Example 1 (FEIM): The tank shown is filled with water. At what depth does the resultant force act?
9-2f1
The surface under pressure is a rectangle 1 m at the base and 2.31 m tall.
A = bh b3 h Iy = 12 4m Zc = = 4.618 m sin60
c
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Fluid Statics Examples
Using the moment of inertia for a rectangle given in the NCEES Handbook, z* = = Iy b3 h b2 = = AZc 12bhZc 12Zc
c
9-2f2
(2.31 m)2 = 0.0963 m (12)(4.618 m)
Rdepth = (Zc + z*) sin 60= (4.618 m + 0.0963 m) sin 60= 4.08 m
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
10
PPI
Fluid Statics Examples
Example 2 (FEIM): The rectangular gate shown is 3 m high and has a frictionless hinge at the bottom. The fluid has a density of 1600 kg/m3. The magnitude of the force F per meter of width to keep the gate closed is most nearly
9-2g
pave = gzave (1600
kg m 1 )(9.81 2 )( 2 )(3 m) m3 s
= 23544 Pa R = paveh = (23544 Pa)(3 m) = 70 662 N/m w F + Fh = R
R is one-third from the bottom (centroid of a triangle from the NCEES Handbook). Taking the moments about R, 2 F = Fh N 70,667 F 1 R m = = = 23.6 kN/m w 3 w 3 Therefore, (B) is correct.
(A) 0 kN/m (B) 24 kN/m (C) 71 kN/m (D) 370 kN/m
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Hydrostatics
6. A gravity dam has the cross section shown. What is the magnitude of the resultant water force (per meter of width) acting on the face of the dam?
(A) 7.85 MN/m (B) 12.3 MN/m (C) 14.6 MN/m (D) 20.2 MN/m
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
11
PPI
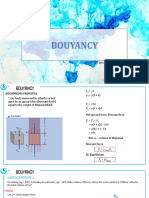
Buoyancy
Archimedes Principle and Buoyancy The buoyant force on a submerged or floating object is equal to the weight of the displaced fluid. A body floating at the interface between two fluids will have buoyant force equal to the weights of both fluids displaced.
Fbuoyant = waterVdisplaced
FERC
Buoyancy
8. A 35 cm diameter solid sphere ( = 4500 kg/m3) is suspended by a cable as shown. Half of the sphere is in one fluid ( = 1200 kg/m3) and the other half of the sphere is in another ( = 1500 kg/m3). What is the tension in the cable?
(A) 297 N (B) 593 N (C) 694 N (D) 826 N
=1200 kg/m3
=1500 kg/m3
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
12
PPI
Fluid Dynamics
(might be called the field eqn.)
FERC
Continuity Equation Example
Example (FEIM):
9-3c
The speed of an incompressible fluid is 4 m/s entering the 260 mm pipe. The speed in the 130 mm pipe is most nearly (A) 1 m/s (B) 2 m/s (C) 4 m/s (D) 16 m/s A1v1 = A2v 2
A1 = 4A2 m so v 2 = 4v 1 = 4 4 = 16 m/s s Therefore, (D) is correct.
()
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
13
PPI
Bernoulli Equation
9. The diameter of a water pipe gradually changes from 5 cm at point A to 15 cm at point B. Point A is 5 m lower than point B. The pressure is 700 kPa at point A and 664 kPa at point B. Friction between the water and the pipe walls is negligible. What is the rate of discharge at point B?
15 cm
(A) 0.0035 m3/s (B) 0.0064 m3/s (C) 0.010 m3/s (D) 0.018 m3/s
5m
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Bernoulli Flow from a Jet
10. A liquid with a specific gravity of 0.9 is stored in a pressurized, closed storage tank. The tank is cylindrical with a 10 m diameter. The absolute pressure in the tank above the liquid is 200 kPa. What is the initial velocity of a fluid jet when a 5 cm diameter orifice is opened at point A?
(A) 11.3 m/s (B) 18.0 m/s (C) 18.6 m/s (D) 23.9 m/s
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
14
PPI
Flow in Pipes Fluid Dynamics and Friction
Steady, Incompressible Flow
FERC
Reynolds Number
For a Newtonian fluid:
9-3g
D = hydraulic diameter = 4RH = kinematic viscosity = dynamic viscosity
For a pseudoplastic or dilatant fluid:
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
15
PPI
Fluid Dynamics and Friction
11. A steel pipe with an inside diameter of 25 mm is 20 m long and carries water at a rate of 4.5 m3/h. Assuming the specific roughness of the pipe is 0.00005 m, the water has an absolute viscosity of 1.00 x 10-3 Pa-s and a density of 1000 kg/m3, what is the friction factor?
(A) 0.023 (B) 0.030 (C) 0.026 (D) 0.028
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Non-Circular Conduits, Open Channel Flow, and Partially Full Pipes
FERC
16
PPI
Hydraulic Radius
12. What is the hydraulic radius of the trapezoidal irrigation canal shown?
(A) 1.63 m (B) 2.00 m (C) 2.13 m (D) 4.00 m
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Hydraulic Grade Line and Energy Grade Line Pump Power
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
17
PPI
Multi-path Pipelines
FERC
Multi-path pipelines
13. The Darcy friction factor for both of the pipes shown is 0.024. The total flow rate is 300 m3/h. What is the flow rate through the 250 mm pipe?
(A) 0.04 m3/s (B) 0.05 m3/s (C) 0.06 m3/s (D) 0.07 m3/s
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
18
PPI
Implulse-Momentum
Be sure to familiarize yourself with how this equation works for bends, enlargements, contractions, jet propulsion, fixed blades, moving blades, and impulse turbines.
FERC
Impulse-Momentum
9-6a
Pipe Bends, Enlargements, and Contractions
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
19
PPI
Impulse-Momentum
14. Water is flowing at 50 m/s through a 15 cm diameter pipe. The pipe makes a 90 degree bend, as shown. What is the reaction on the water in the z-direction at the bend?
(A) -44 kN (B) -33 kN (C) 14 kN (D) 44 kN
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Flow and Pressure Measurement
FERC
20
PPI
Fluid Mechanics
Fluid Measurements
Pitot Tube measures flow velocity
9-10a
The static pressure of the fluid at the depth of the pitot tube (p0) must be known. For incompressible fluids and compressible fluids with M 0.3,
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Flow and Pressure Measurement
15. The density of air flowing in a duct is 1.15 kg/m3. A pitot tube is placed in the duct as shown. The static pressure in the duct is measured with a wall tap and pressure gage. Use the gage readings to determine the velocity of the air.
(A) 42 m/s (B) 102 m/s (C) 110 m/s (D) 150 m/s
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
21
PPI
Fluid Mechanics
Fluid Measurements
Venturi Meters measures the flow rate in a pipe system The changes in pressure and elevation determine the flow rate. In this diagram, z1 = z2, so there is no change in height.
9-10c
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Fluid Mechanics
Fluid Measurements
Orifices
9-10e
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
22
PPI
Orifice Flow
16. Water flows out of a tank at 12.5 m/s from an orifice located 9m below the surface. The crosssectional area of the orifice is 0.002 m2, and the coefficient of discharge is 0.85. What is the diameter D, at the vena contracta?
(A) 4.2 cm (B) 4.5 cm (C) 4.7 cm (D) 4.8 cm
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Similitude
In other words Dimensionless parameters must be equal between the model and prototype (Each dimensionless parameter is a ratio of different types of forces being exerted on the fluid) For example: For completely submerged models/prototypes and pipe flow, the Reynolds numbers must be equal For Weirs, dams, ships, and open channels, the Froude numbers must be equal
FERC
23
PPI
Similitude Dimensionless Parameters
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
Similitude
17. A nuclear submarine is capable of a top underwater speed of 65 km/h. How fast would a 1/20 scale model of the submarine have to be moved through a testing pool filled with seawater for the forces on the submarine and model to be dimensionally similar?
(A) 0.90 m/s (B) 18 m/s (C) 180 m/s (D) 360 m/s
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
24
PPI
Drag
Typically these problems will be plug and chug Drag Coefficients for Spheres and Circular Flat Disks
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
ANSWERS!! 1. B 2. B 3. A 4. B 5. A 6. B 7. C 8. C 9. C 10. C 11. C 12. C 13. C 14. D 15. A 16. D 17. D
Professional Publications, Inc.
FERC
25
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Final Fe Fluid Practice ProblemsDokumen7 halamanFinal Fe Fluid Practice ProblemsHasen BebbaBelum ada peringkat
- Beam Deflection AssignmentDokumen4 halamanBeam Deflection AssignmentTalha KhanBelum ada peringkat
- BITS Pilani: Engineering Materials: ENGG ZC 232Dokumen49 halamanBITS Pilani: Engineering Materials: ENGG ZC 232Amit SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Renewable Energy Sources: Presented ByDokumen56 halamanRenewable Energy Sources: Presented Byjkl417Belum ada peringkat
- Quality Within Higher Education 2017 Summary ReportDokumen52 halamanQuality Within Higher Education 2017 Summary ReportCentras CentrasBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Materials by McalisterDokumen17 halamanEngineering Materials by McalisterHamza KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- PDF ViscosityDokumen18 halamanPDF ViscosityTobyBorlandBelum ada peringkat
- Parilla x30 Overhaul ManualDokumen38 halamanParilla x30 Overhaul ManualCarolina MatosBelum ada peringkat
- CHP 29Dokumen13 halamanCHP 29Abhiram Reddy100% (1)
- FE Environmental Air Quality and Control Workshop ProblemsDokumen69 halamanFE Environmental Air Quality and Control Workshop Problemsmiguel zambrano100% (1)
- Stream Function Solution of Navier Stokes EquationsDokumen16 halamanStream Function Solution of Navier Stokes EquationsSteven GoddardBelum ada peringkat
- E. Surface Area of 3D ShapesDokumen19 halamanE. Surface Area of 3D ShapesanjanamenonBelum ada peringkat
- FrictionDokumen9 halamanFrictionjarvis007Belum ada peringkat
- 1/27/2014 Hareesha N Gowda, Asst. Prof, Dsce, Blore-78 1Dokumen25 halaman1/27/2014 Hareesha N Gowda, Asst. Prof, Dsce, Blore-78 1Sameer SonuBelum ada peringkat
- 4 - Pipe Fitting LossesDokumen4 halaman4 - Pipe Fitting LossesstarykltBelum ada peringkat
- Workplace Hazard Analysis ProcedureDokumen12 halamanWorkplace Hazard Analysis ProcedureKent Nabz60% (5)
- ARG FMA-EMPDevelopment WhitePaperDokumen25 halamanARG FMA-EMPDevelopment WhitePaperJose AlfredoBelum ada peringkat
- Forces in Bridge MembersDokumen18 halamanForces in Bridge MembersSameer PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Double Digit Subtraction With Regrouping: by Amy Lemons Graphics Courtesy of Scrappin' DoodlesDokumen44 halamanDouble Digit Subtraction With Regrouping: by Amy Lemons Graphics Courtesy of Scrappin' DoodlesJohanna MaraBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 4: Indices and Logarithms: Jacques Text Book (Edition 4) : Section 2.3 & 2.4Dokumen22 halamanTopic 4: Indices and Logarithms: Jacques Text Book (Edition 4) : Section 2.3 & 2.4Ateef HatifaBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 1.1.5b Circuit Theory: SimulationDokumen4 halamanActivity 1.1.5b Circuit Theory: SimulationParkerBelum ada peringkat
- Week 1 - 2 Linear EquationsDokumen50 halamanWeek 1 - 2 Linear EquationsMichael De Vera100% (1)
- CH 13Dokumen61 halamanCH 13anon_273249445Belum ada peringkat
- An Evaluation of Life Cycle Cost Analysis of Airport Pavement PDFDokumen6 halamanAn Evaluation of Life Cycle Cost Analysis of Airport Pavement PDFariesBelum ada peringkat
- FE Fluids Review 2013Dokumen31 halamanFE Fluids Review 2013Mahmoud HelmyBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mech SlidesDokumen48 halamanFluid Mech Slidesvinoja29Belum ada peringkat
- Fe Review Fluids Practice Problems Spring 2013Dokumen12 halamanFe Review Fluids Practice Problems Spring 2013festsobi100% (6)
- PHPA As A Frictional Pressure Loss Reducer and Its Pressure Loss EstimationDokumen6 halamanPHPA As A Frictional Pressure Loss Reducer and Its Pressure Loss Estimationtariq82aliBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics NotesDokumen12 halamanFluid Mechanics Notessubha_aeroBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mech ModuleDokumen66 halamanFluid Mech ModuleVudayagirisivaBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank - FMDokumen14 halamanQuestion Bank - FMsrajapratyBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsDokumen24 halamanFluid Mechanics and Machinery - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsMohan Prasad.M94% (18)
- Drilling Fluids Flow BehaviorDokumen44 halamanDrilling Fluids Flow BehaviorIsmail IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- TRANSPORT MECHANICSDokumen19 halamanTRANSPORT MECHANICSMariAntonetteChangBelum ada peringkat
- IIT Bombay Transport Phenomena Assignment 3Dokumen5 halamanIIT Bombay Transport Phenomena Assignment 3jayBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics - Corrected ExercisesDokumen5 halamanFluid Mechanics - Corrected Exercisesug2319311Belum ada peringkat
- 2013 Fe Review WsuDokumen26 halaman2013 Fe Review WsuSai KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Homeworks 1-10 PDFDokumen95 halamanHomeworks 1-10 PDFWendy LinBelum ada peringkat
- 9A01304 Fluid MechanicsDokumen4 halaman9A01304 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- Model 1Dokumen68 halamanModel 1Prashanth Menon0% (1)
- GTU BE Sem-III Fluid Mechanics Remedial Exam March 2010 Question PaperDokumen2 halamanGTU BE Sem-III Fluid Mechanics Remedial Exam March 2010 Question Papersameer_m_daniBelum ada peringkat
- Scheme: TUTORIAL 1: (Answer: 40.77kg)Dokumen5 halamanScheme: TUTORIAL 1: (Answer: 40.77kg)Mohd AideelBelum ada peringkat
- TRANSPORTMECHANICSDokumen20 halamanTRANSPORTMECHANICSEfraim AbuelBelum ada peringkat
- FMFM Important QuestionsDokumen3 halamanFMFM Important QuestionsANANDKUMAR SBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics2Dokumen6 halamanFluid Mechanics2cemaliBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics Question BankDokumen8 halamanFluid Mechanics Question BankRameez FaroukBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Fluid MechanicsDokumen49 halamanChapter 1 Fluid MechanicsHunain AK100% (1)
- ME 2204 - FMM 2 Marks With AnswerDokumen22 halamanME 2204 - FMM 2 Marks With AnswerMohan Prasad.M100% (1)
- Yaqub 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 458 012078Dokumen10 halamanYaqub 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 458 012078Daniel MoraesBelum ada peringkat
- Centrifugal Pumps & Fluid Flow Practical Calculations: Pdhonline Course M388 (3 PDH)Dokumen53 halamanCentrifugal Pumps & Fluid Flow Practical Calculations: Pdhonline Course M388 (3 PDH)Prad1979100% (5)
- Screenshot 2023-10-09 at 3.54.38 AMDokumen5 halamanScreenshot 2023-10-09 at 3.54.38 AMhnsm9bwtqrBelum ada peringkat
- Me 6604 GDJP 2 Marks With AnswersDokumen16 halamanMe 6604 GDJP 2 Marks With AnswersKanagarajBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Flow PDFDokumen55 halamanFluid Flow PDFHarrrison100% (1)
- Rigonan A-1 HydraulicsDokumen13 halamanRigonan A-1 HydraulicsFrancis Angelo RigonanBelum ada peringkat
- E3. Friction Losses in Pipes and FittingsDokumen15 halamanE3. Friction Losses in Pipes and FittingsMuzammil IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- EI6603 - Industrial - Instrumentation - II - University - QP - Answer - KeyDokumen16 halamanEI6603 - Industrial - Instrumentation - II - University - QP - Answer - KeyMadhusudhanan Ramaiah100% (1)
- Fisika 1 - Kelas B - Grup 4Dokumen12 halamanFisika 1 - Kelas B - Grup 4faridBelum ada peringkat
- 10 FluidDynamicsDokumen39 halaman10 FluidDynamicsSyed Raheel AdeelBelum ada peringkat
- Correction of Pressure Drop in Boiler Performance TestsDokumen9 halamanCorrection of Pressure Drop in Boiler Performance TestsK P SBelum ada peringkat
- Application of The Transfer Matrix Method To The Analysis of Hydro-Mechanical Vibration of NPP PipingDokumen10 halamanApplication of The Transfer Matrix Method To The Analysis of Hydro-Mechanical Vibration of NPP PipingTopNameBelum ada peringkat
- Online Application & Engineering Education EvaluationDokumen7 halamanOnline Application & Engineering Education EvaluationMahmoud HelmyBelum ada peringkat
- Fe Review Fluids Practice Problems Spring 2013Dokumen12 halamanFe Review Fluids Practice Problems Spring 2013festsobi100% (6)
- Fe Review Fluids Practice Problems Spring 2013Dokumen12 halamanFe Review Fluids Practice Problems Spring 2013festsobi100% (6)
- Thermo ProblemsDokumen3 halamanThermo ProblemsHasen BebbaBelum ada peringkat
- Fe Practice Questions Spring 2014Dokumen7 halamanFe Practice Questions Spring 2014Mahmoud HelmyBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Statics 2014Dokumen8 halamanFluid Statics 2014Mahmoud HelmyBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Circuits ReviewDokumen14 halamanElectrical Circuits ReviewHasen BebbaBelum ada peringkat
- FE Fluids Review 2013Dokumen31 halamanFE Fluids Review 2013Mahmoud HelmyBelum ada peringkat
- Fe Math Review 2014Dokumen19 halamanFe Math Review 2014Mahmoud Helmy100% (1)
- BS en 13138-1-2014Dokumen34 halamanBS en 13138-1-2014aminBelum ada peringkat
- Composite Breakwater Design, 3-14-00Dokumen14 halamanComposite Breakwater Design, 3-14-00Uriel Alexander RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- REVIEWERIN MATH, SCIENCE, APAN & VALUES With ANSWER KEYDokumen34 halamanREVIEWERIN MATH, SCIENCE, APAN & VALUES With ANSWER KEYJean Rose GentizonBelum ada peringkat
- Questionnaire for mass, balance and volume calibrationDokumen3 halamanQuestionnaire for mass, balance and volume calibrationVAIBHAV INSTRUMENTATIONBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4 Guided NotesDokumen10 halamanUnit 4 Guided NotesflyingmsBelum ada peringkat
- Diving Physics ExplainedDokumen35 halamanDiving Physics ExplainedRaul LaggerBelum ada peringkat
- UNICEL Vertical Gas Flotation PDFDokumen2 halamanUNICEL Vertical Gas Flotation PDFJessika LópezBelum ada peringkat
- Pressure and Buoyancy CalculationsDokumen6 halamanPressure and Buoyancy CalculationsParmeshwarPaul100% (1)
- Flow Visualization ApparatusDokumen6 halamanFlow Visualization Apparatusasn90Belum ada peringkat
- Types of Gas Mass Flow MetersDokumen12 halamanTypes of Gas Mass Flow MetersFirmansyah Budhi SaputhraBelum ada peringkat
- Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing: ISSN 1643-1049 Index No. 32213XDokumen329 halamanPhysicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing: ISSN 1643-1049 Index No. 32213Xravibelavadi100% (1)
- Notes On Hydrostatic Pressure: Gérard C. NihousDokumen5 halamanNotes On Hydrostatic Pressure: Gérard C. NihousSahilBelum ada peringkat
- Buoyancy and Flotation ForcesDokumen13 halamanBuoyancy and Flotation ForcesDenzel Edward CariagaBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Grade 8Dokumen5 halamanPhysics Grade 8AshaBelum ada peringkat
- CSW 101 - SwimmingDokumen37 halamanCSW 101 - SwimmingRahmat ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Richard Fitzpatrick Theoretical Fluid Mechanics ContentsDokumen574 halamanRichard Fitzpatrick Theoretical Fluid Mechanics ContentsArvin SookramBelum ada peringkat
- Eseiform 3Dokumen46 halamanEseiform 3norhanisa100% (1)
- Seamanship 2 Trim, Stability and Stress 1: The Maritime Academy of Asia and The PacificDokumen130 halamanSeamanship 2 Trim, Stability and Stress 1: The Maritime Academy of Asia and The PacificSecret files100% (1)
- Pascal's Principle Explained: How Pressure is Transmitted Through FluidsDokumen43 halamanPascal's Principle Explained: How Pressure is Transmitted Through FluidsStar BitBelum ada peringkat
- Water Freedom For All - The Halliwick MethodDokumen10 halamanWater Freedom For All - The Halliwick MethodFiorella GBelum ada peringkat
- Structural Design and Cost Factors in Submersible Vehicle DevelopmentDokumen49 halamanStructural Design and Cost Factors in Submersible Vehicle DevelopmentMuhammad Rafi SiratBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid MechanicsDokumen2 halamanFluid MechanicsAnn Margarette MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- Matter and Energy Provider Guide - FINALDokumen1.108 halamanMatter and Energy Provider Guide - FINALJames OsterhoutBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)Dokumen32 halamanGastroretentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)Hely PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Motion of Particles Through Fluids 221Dokumen27 halamanMotion of Particles Through Fluids 221SAYEEBelum ada peringkat
- Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy LectureDokumen9 halamanPotential Energy and Conservation of Energy LectureJames SergeantBelum ada peringkat
- Philippines Technical-Vocational Schools Safety MatrixDokumen43 halamanPhilippines Technical-Vocational Schools Safety MatrixGideonCavidaBelum ada peringkat
- 04 Buoyancy and StabilityDokumen5 halaman04 Buoyancy and StabilityFalconer AldBelum ada peringkat
- Archimedes principle and buoyant force problemsDokumen7 halamanArchimedes principle and buoyant force problemsBillie Ian. Salamante JrBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of ship dimensionsDokumen33 halamanFundamentals of ship dimensionsgirishBelum ada peringkat