Nclex Eyes
Diunggah oleh
Yoke W KhooHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nclex Eyes
Diunggah oleh
Yoke W KhooHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
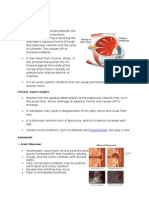
Straibismus lazy eye.
. There is a misalightnment of the pupils confirmed by the Hirschberg test where light is shone at the eyes one foot away and not reflected in the same area. Treatment includes covering up the good eye and forcing the weaker eye to focus, corrective lens, eye drops on the good eye and eye muscle exercises Cataracts are the clouding of the eyes- increasing opacities that usually happens with Age, but can happen with trauma, diabetes mellitus, UV light or inherited. Symptoms: - Distorted images and gradual loss of vision (Reduced Visual Acuity) - Clouding of the eyes / hazy vision diplopia - Glare from bright light - Discoloration of the pupils with green or yellow colors - Absence of red reflex - when the pen light is shone on an infants pupil, the normal result is the presence of red/orange colors in the pupils. The absence of this is diagnostic of Cataract due to inheritance. o Infants at 3 months are supposed to be able to follow moving objects. The inability to do that needs to be followed up on. - For elderly: Redness of the eyes and Eye Pain usually from aging indicate cataract is worsening Surgical Treatment Done with an extracapsular extraction called ECCE. It is when the front len is removed, and the posterior len stays in place. The len is then photoemulsified to correct the problem and then re-inserted back into the eye. (lens implantation) Intracapsular extraction is when the anterior and posterior lens are both removed surgically to rectify, and lens implantation is implemented Partial iridectomy- is when part of the iris is taken out to relieve pressure for Glaucoma Preoperative Medications that are used in this are: 1) Diamox (Acetazolamide)- to reduce intraocular pressure 2) Neo-Syephrine (mydiatrics) and Cyclogyl to paralyze muscles in the eyes 3) Versed- local anesthesia Post operative position- semi Fowlers position, no more than 30-40 degrees on the head of bed - Put eye patch on the operative side - Administer eye drops correctly (pull down lid, ask patient to look up and then administer drops) usually 2-3 times a day for 2-4 weeks. - Avoid straining and rubbing the eyes - Use side rails! - Prevent constipation because it strains the head - Excess tear drainage from the eye after the surgery should be cleaned with a sterile cotton tip - If the patient is given cataract glasses because lens were not implanted, let the patient be aware of the fact that the glasses are magnifying glasses so everything is going to appear closer. o The visual acuity will be better, but DEXTERITY (skills) isnt Before discharge: o ask patient to report any signs of bleeding, and signs of pain, and signs of bad vision (hazy, hollow). Tell patient to not let water get into the eye the best they can, and to wear the shield
GLAUCOMA- an increase in intraocular pressure and there are several types of glaucoma Normal ocular pressure is 10-21 mm/hg 1) Open Angle Glaucoma- it is the more common form of glaucoma and least dangerous. Open angle is when the aqueous humor outflow of the eye is decreased and hence an increase in intraocular pressure. The pressure under this circumstance is usually between 22-32 mm Hg Symptoms -painless, gradual, loss of peripheral vision- TUNNEL VISION -no pain -cloudiness -fatigue -seeing halos around eyes 2) Closed Angle Glaucoma- is the more dangerous form of Glaucoma that can lead to blindness. It is the sudden increase of intraocular pressure that exceeds over 30 mm Hg, due to the Sudden increase of aqueous humor production in the eyes. It is the form that consists of pain and can result in loss of vision. It also usually comes without warning. -dilation of pupils will cause increased intracranial pressure which can cause even worse problems. Ophthalmic epinephrine will cause this problem. Always assess for this condition prior to giving it. Emergency treatment is necessary for this! Symptoms: -pain around the eye area that is sudden -cloudy and halo vision - headache -n/v Treatment Surgical: This is usually reserved for patients who do not respond well to medications and have no other options. 1. Partial Iridectomy to allow for the aqueous humor to pass from posterior to anterior more easily 2. Trabectulectomy : the removal or partial removal of the Trabecular Network in the eyes to allow for less intraocular pressure. (create a better opening) Postoperatively; avoid taking aspirin, and to report severe eye pain. Report any signs of vision changes or hemorrhage . Medical Interventions 1) Miotic Eye drops are used to constrict to pupils to allow for easier flow. Isopto Carpine (pilocarpine HCL) 2) Beta blockers (timolol) and carbon analyase inhibitors (Diamox) decrease the production of aqueous humor-> lowering intraocular pressure 3) Osmotics (MAnnitol ) helps reduce intraocular pressure 4) patients should consult the doctor when taking OVER THE COUNTER medications- and should highly avoid them because they INCREASE INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE. - Visine can raise intraocular pressure - Atropine is also contraindicated with glaucoma -anti-cholinergics are contraindicated because of the increase in intraocular pressure. 5) always wear a medic alert bracelet
RETINAL DISORDERS 1) Hypertensive retinopathyHappens from unmanaged hypertension that leads to the build up of Cotton Wool Spots that are created from the occlusion of arterioles. may lead to loss of vision 2) Diabetic Retinopathy: Is retinal defects caused by diabetes mellitus due to the changes its entire vascular network. There are two kinds 1) background diabetic retinopathy: is when the blood vessels in the eyes bleed due to poor management, and aneurysms and hemorrhage happen 2) Proliferative diabetic retinopathy: is when new vessels are created that leak blood to its surrounding tissues Symptoms: -Change in vision from aneurysms -blindness may occur Macular Degeneration - Is the decreased central vision (macula). Decreased production of rods and cones. Dry: Aging can be a factor for this. Poor blood flow to the macula can cause ischema and necrosis of macula and hence decreased production of cones and rods. People with HTN, smokers are higher at risk for this to happen. Sx: gradual loss of vision, blurred vision Treatment: Diet high in antioxidants, carotenoids, leutein. Wet: When an exudate is build up under the epithelium of macula, separating them from each other. Presented with SUDDEN decrease in Vision. Sx: sudden loss of central vision Treatment for both Wet and Dry: Laser Surgery: to seal hemorrhagic blood vessels Retinal detachment = 3Fs - Occurs due to an accumulation of fluid between the retina and choroid leading to a detachment of retina. Partial detachment left untreated can become complete, and complete detachment= complete blindness Symptoms: 3 Fs Pain-free gradual loss of field vision, flashes of light, visual floaters and veil like loss of vision (shadows) Interventions: 1) Bed Rest
2) Covering both eyes with patches to reduce further retinal detachment 3) speak to client before approaching 4) do not jerk head or cause any strain Surgeries: purpose is to drain out fluid in between retina and choroid or to trigger the sclerosis of both components. Surgery is required since natural reattachment is very rare. 1) cryosurgery: placing a cold probe on the sclera to trigger an inflammatory response for adhesion 2) Diathermy: using heat to trigger an inflammatory response 3) Laser therapy: trigger an inflammatory response 4) sclera therapy: produce a sclera bulk 5) insertion of gas or oil Postoperative: If gas/oil been used, place the patient on the abdomen so the eyes are facing upwards maintained for several days . or if not on abdomen, the head is placed on overbed table - Maintain eye patches - Monitor for signs of hemorrhage: eye pain, nausea/vomiting - Refrain from jerky movements and limit reading (3-5 weeks) - Perform deep breathing but not coughing - Wear dark glasses - Do not bend head over Refractive Errors 1) Myopia- nearsightness can see in front 2) Hyperopia- farsightedness- can only see far 3) Presbyopia- lens losing elasticity -age related and making it difficult to see objects up close 4) Astigmatism- an uneven curvature of cornea lack of focus point- light rays are un-refracted unequally Surgeries to correct this Radial keratotomy- used to treat myopia by flattening out the cornea with 8-18 incisions on the cornea Photorefractive keratomy- to treat myopia and astigmatism- correction of cornea through ultraviolet light beam the surgery is done with one eye at a time, and the wait time between surgeries is 6 months Laser in situ surgery- correction of cornea through laser beam. Both eyes can be done at the same time. No pain, better than photorefractive keratomy Intacs corneal ring where the shape of the cornea is changed by the placement of rings at the corner of the corneas. These rings can be replaced and reversible. Replacement is available due to progressive worsening of vision. Hyphema is the damage of the anterior chamber due to physical trauma to the eyes. It usually resolves in 5-7 days by itself. Interventions1) Semi Fowlers position 2) no eye movements for 3-5 days 3) cycloplegic eyedrops- Cyclogyl 4) eyepatches to protect the eyes
5) limited television viewing Contusion- Bruising of the eyeball . treatment is to ice the affected area and elevating the clients head to 30-40 degrees. Foreign bodies- irritated the surface of the conjunctiva . Must be brought to the ER where two cups are placed over the eyes and saline is used to irrigate the eyes Lacerations and penetrating injuries- EMERGENCY- administration of IV antibiotics and surgery Snellen chart- visual acuity Ishihara chart- color vision Ansler grid- detect changes caused by macular degeneration Tonometry- changes in intraocular pressure (Glaucoma) Mydratics and Cycloplegics (anti-cholinergics)= dilation of eyes= increase in intraocular patients. Therefore contraindicated in people with glaucoma Examples are: Atropine (Isopto Atropine) Cyclopentolate (AK-Pentolate, Cyclogyl, Pentolair) Homatropine (Isopto Homatropine) Scopolamine (Isopto Hyoscine) Tropicamide (Mydriacyl, Tropicacyl, Opticyl) - are medications used for cataracts- they relax the ocular muscles -contraindicated in patients with DYSRTHMIA, cerebral artherosclerosis, glaucoma -side effects: conjunctivitis, tachycardia, photophobia (sensitive to light), dermatitis and higher BP Tell clients that you may feel a warm sensation when its instilled . Report pain or signs of hemorrhage Wear sunglasses until med wears off Atropine ToxicityTachycardia, blurred vision, DRY MouTH, heightened BP, photophobia, fever, urinary retention, headache, coma, confusion, hallucinations Miotics (cholinergics) used to constrict the pupils to allow for the outflow of aqueous humor from the insides of the eyes. This is mainly used for Glaucoma. However, because of the nature of the medication, it is contraindicated in people with RETINAL DETACHMENT because theres a build up of fluid between retina and choroid. It is also used to induce miosis in surgeries . Side effects: (opposite of mydratics) 1) Myopia 2) headache 3) tachycardia 4) decreased eye vision at night 5) eye pain Systemic: sweating, flushing of skin , gi upset - increase in saliva production
-Atropine Sulfate is an antidote Beta-adrenergic blockersDecrease intraocular pressure by decreasing signals of sympathetic impulses and also by decreasing the production of aqueous humor. Does not change the size of pupils. Due to less production of fluids; monitor for hypovolemia side effects: 1) bradycardia 2) hypotension 3) dizziness 4) bronchospasm Interventions: 1) do no administer if HR is less than 60, and systolic pressure is less than 90 mm Hg 2) shortness of breathe or respiratory depression must be monitored. If so, please notify physician. 3) I/O monitoring 4) cannot stop using meds abrupt 5) change position slowly= risk for orthostatic hypotension 6) over the counter meds should be consulted for approval Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor Decrease the production of carbonic acid which decreases the production of aqueous humor . it is a long term medication for Glaucoma Otitis Externa- inflammation on the most outer part of the ear that is usually caused by an irritant getting in contact with it. It is called the Swimmers ear and happens often in hot and humid weather. In rare cases the bacteria infection can spread to surrounding tissues. The obstruction (inflammation ) can lead to conductive hearing loss Symptoms: Pain in the ear Feeling some sort of plug in the ear Hard of hearing Redness and swelling Interventions 1) Analgesic therapy by applying heat to the area locally . administer Tylenol 2) bed rest 3) antibiotics (corticosteroids) 4) do not use cutips 5) ear plugs for swimming Otitis Media- it is the inflammation of the middle of the ear that is usually caused by H influenza It happens commonly in young children because their Estuchian tubes are longer and wider The tympanic membrane swells up, is painful and makes it hard to hear. The rupture of tympanic membrane usually provides relief, but too much of It happening can lead to loss of hearing. Symptoms:
1) tenderness, swelling, pain, redness, protrusion 2) fever (infection) 3) infectious symptoms: N/V, anorexia Interventions 1) provide heat or cold therapy to alleviate the pain administer acetaminophen and or aspirin can help with the pain 2) make sure the clients head is down towards the affected side 3) fluid intake is encouraged due to an infection 4) HYGEINE: make sure cleansing occurs frequently, and sterile swabs are being used to cleanse 5) antibiotics should be administered 6) avoid chewing 7) administer topic pain relief drops: - for a child younger than 3, pull down the ear lobe and pull back then administer - for anyone older than 3, pull up the pinna and then back Myringotomy is a surgical procedure that drains out the fluid from the tympanic membrane to alleviate the pain and infection. Tubes may also be inserted to allow for continued drainage Postoperative1) keep the ears dry 2) provide ear plugs 3) cleansing 4) no Valsalva maneuver 7-10 days after surgery 5) be aware of the tubes falling out. If they do its okay, just notify the physician 6) POSITION : head is flat with operative side facing up! Complications: Mastoiditis (inflammation of the mastoid, right behind the ear) Menieres disease inflammation of the insides of the ear. Due to the buildup of endolympathic fluid. Three symptoms that characterize the symptoms: they occur in attacks and can last for days 1) vertigo 2) tinnitus 3) loss of low tones hearing Usually allergies cause it and its an inflammatory reaction Intervention 1) safety measures- very important- due to the inability to see and hear well. prevent injury 2) provide bed rest 3) do not allow for the watching of TV 4) Administer niacin for its vasodilatory effects 5) FLUID AND SODIUM RESTRICTION to lower the endolympathic fluid LIMIT COFFEE AND SMOKING 6) administer anti-histamine, anti-emetic , antibiotics Surgical intervention- creation of a shunt to allow the endolympathic fluid to flow out of the ear Postoperative- 1) assess the dressing of the ear 2) make sure that the client is doing ok neurologically
3) MAINTAIN SAFETY IS A PRIORITY 4) after surgery the client will experience Vertigo, Nausea and vomiting for several days until he/she recovers Otosclerosis- the hardening of a bony prominence called stapes in the ear. The enlargement of this produces conductive hearing loss, diagnosed with a positive Swartz test (pink tympanic membrane) The enlargement of stapes causes lowered hearing ability and tinnitus. Symptoms: Tinnitus, Negative Rhinne Test, Positive Swartz test, loud sounds are heard when client is chewing, hearing loss, Treatment: Fenestration- it is the removal of stapes from the ear. Postoperatively: 1) inform the client that hearing may be worse due to swelling and buildup of fluid from surgery. However in a week or two, the fluid shall be absorbed and hearing will be better 2) do not cough with closed mouth- do not strain the head 3) provide side rails, ambulation assistance 4) ensure neurological integrity 5) be aware that tinnitus still occurs after surgery 6) move head slowly, no nose blowing 7) medications: antibiotics, anti-vertigo 8) avoid wetting the affected ear. Bath is better than shower 9) report signs of hemorrhage Presbycusis It is an AGING related disorder that occurs due to the lack of blood supply to the inner ear. Deficiencies in B9 and B 12 are also associated with this. This leads to SENSORIAl hearing loss . people with this problem cannot hear high frequency sounds and soft consonant sounds (t, s, th, ch, sh, b, f, p and pa) Symptoms: 1. gradual loss of hearing. Cannot understand what people are saying and think theyre mumbling 2. bilateral loss of hearing 3. claims nothing is wrong with the hearing 4. cannot hear soft consonant sounds Cerumen is removed at 98 degrees farenheight Acoustic Neuroma is the benign tumor of auditory nerve that may cause destruction to the cerebellum - May cause damage to facial tumors and sensations - Surgery is done to remove the tumor by performing craniotomy Symptoms: Tinnitus and sensorial hearing loss , damage to cranial nerves occur Cholesteatoma benign overgrowth of squamous epithelium . May have led to Labyrinthis which is a complication of Otitis Media.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Medical Surgical Nursing Practice Test Part 1Dokumen15 halamanMedical Surgical Nursing Practice Test Part 1cleznielBelum ada peringkat
- NCLEX Compilation 1Dokumen34 halamanNCLEX Compilation 1blazegomezBelum ada peringkat
- NEURODokumen19 halamanNEUROrex2005Belum ada peringkat
- NCLEX QuestionsDokumen5 halamanNCLEX Questionsijeoma00100% (2)
- 35 Nclex QuestionsDokumen6 halaman35 Nclex Questionsjohnnymyunghee0% (1)
- Everything Made EASY Mnemonic Devices Part 1Dokumen2 halamanEverything Made EASY Mnemonic Devices Part 1Raymark MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- Parasympathetic vs. Sympathetic Nervous System and Cranial Nerves QuizDokumen15 halamanParasympathetic vs. Sympathetic Nervous System and Cranial Nerves QuizQuantum XavierBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Nursing GastroDokumen3 halamanPediatric Nursing GastronieacatleyaBelum ada peringkat
- Maternal and Child Nursing 4Dokumen17 halamanMaternal and Child Nursing 4gellie100% (1)
- NCLEX Neurology Practice TestDokumen6 halamanNCLEX Neurology Practice Testojoj2206Belum ada peringkat
- This Study Resource WasDokumen3 halamanThis Study Resource WasSam CuevasBelum ada peringkat
- TPN for Major Burn InjuryDokumen31 halamanTPN for Major Burn InjuryBobet ReñaBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen41 halamanUntitledvioletdeocaresBelum ada peringkat
- Medical and Surgical NursingDokumen4 halamanMedical and Surgical NursingCrystal Ann Monsale TadiamonBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Nursing-Cardiovascular DisordersDokumen10 halamanPediatric Nursing-Cardiovascular Disordershasan ahmd100% (1)
- Medical Surgical ATI Proctored Exam 2019 Questions and Answers Verified 100Dokumen7 halamanMedical Surgical ATI Proctored Exam 2019 Questions and Answers Verified 100ianshirow834Belum ada peringkat
- Common Board QuestionsDokumen6 halamanCommon Board QuestionsRafael BasaBelum ada peringkat
- Nclex ReviewDokumen5 halamanNclex ReviewOncologynBelum ada peringkat
- Major Hormone Glands and Their FunctionsDokumen5 halamanMajor Hormone Glands and Their FunctionsSTEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System 2Dokumen7 halamanEndocrine System 2Lhaura Joy ArsenioBelum ada peringkat
- Nclex Exam Maternal and Child Health Nursing 2 30 Items PDF FreeDokumen8 halamanNclex Exam Maternal and Child Health Nursing 2 30 Items PDF FreeLianne BuensucesoBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of the Nervous System and Key ConceptsDokumen121 halamanOverview of the Nervous System and Key ConceptsRy AnneBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Surgical NursingDokumen21 halamanMedical Surgical Nursingcfournier1982Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 66 - ShockDokumen9 halamanChapter 66 - ShockCrysta Venice Tapoc100% (1)
- Nle Practice Test III DDokumen15 halamanNle Practice Test III DKira100% (27)
- EndoDokumen8 halamanEndoAqcoh Ce Erica ParzueloBelum ada peringkat
- Professional Adjustment, Legal Management, Ethics & Research in NursingDokumen14 halamanProfessional Adjustment, Legal Management, Ethics & Research in NursingMary Roan RonatoBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology QuestionsDokumen20 halamanPharmacology Questionsdelluismanuel100% (2)
- NLE - CGFNS - Nclex Review Materials 4Dokumen6 halamanNLE - CGFNS - Nclex Review Materials 4ChieChay DubBelum ada peringkat
- Nclex Practice Exam 01Dokumen7 halamanNclex Practice Exam 01puzzled_14100% (1)
- Nutrition: Recommendation: No More Than 30% of Calories Avoid Butter and Coconut OilDokumen48 halamanNutrition: Recommendation: No More Than 30% of Calories Avoid Butter and Coconut OilKira100% (3)
- Hema Q&aDokumen126 halamanHema Q&aHoney Lyn AlebioBelum ada peringkat
- Nle Tips For OrthopedicDokumen2 halamanNle Tips For OrthopedicCharie OcampoBelum ada peringkat
- DISEASE SIGNSDokumen7 halamanDISEASE SIGNSMary Roan RonatoBelum ada peringkat
- Flaccid Bladder Risks and TreatmentsDokumen29 halamanFlaccid Bladder Risks and TreatmentsphotosaurusrapBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalanceDokumen8 halamanFluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalanceJo Marchianne PigarBelum ada peringkat
- MedSurg Ch30-31Dokumen8 halamanMedSurg Ch30-31Vanessa Da Cruz100% (1)
- Ob Nursing BulletsDokumen22 halamanOb Nursing BulletsDick Morgan FerrerBelum ada peringkat
- Pyschiatric Nursing SummarizeDokumen39 halamanPyschiatric Nursing SummarizeKyssel Seyer100% (1)
- Med Surg Chap QuestionsDokumen9 halamanMed Surg Chap Questionslani0% (1)
- ATI NotesDokumen2 halamanATI NotesCharlotte Whobrey-Duvall100% (3)
- CorrectsDokumen46 halamanCorrectsnursing_hallBelum ada peringkat
- Ob Part 2Dokumen7 halamanOb Part 2gmik02Belum ada peringkat
- NLE & Nclex Mp3 Nursing Lectures DownloadDokumen1 halamanNLE & Nclex Mp3 Nursing Lectures DownloadChieChay DubBelum ada peringkat
- Assessing Clients with Endocrine and Metabolic DisordersDokumen4 halamanAssessing Clients with Endocrine and Metabolic DisordersFelimon BugtongBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Care and ComfortDokumen74 halamanBasic Care and ComfortNikko PabicoBelum ada peringkat
- Psychiatric Nursing Bullets 4Dokumen25 halamanPsychiatric Nursing Bullets 4winner gift flowersBelum ada peringkat
- Mental Health Nursing ConceptsDokumen7 halamanMental Health Nursing ConceptsJay Soriano0% (1)
- DO NOT Delegate What You Can EATDokumen1 halamanDO NOT Delegate What You Can EATMerlin JosephBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 55Dokumen8 halamanChapter 55DelindaEvansBelum ada peringkat
- CA EndocrineDokumen8 halamanCA EndocrineCharlie Cotoner FalgueraBelum ada peringkat
- MedSurg Chapter 44: Pituitary, Adrenal & Thyroid DisordersDokumen5 halamanMedSurg Chapter 44: Pituitary, Adrenal & Thyroid DisordersMichele ShepardBelum ada peringkat
- This Study Resource Was: Hesi Pharmacology Test Bank 2018 RN V2 14 Total QuestionsDokumen3 halamanThis Study Resource Was: Hesi Pharmacology Test Bank 2018 RN V2 14 Total QuestionsCrystal B Costa78Belum ada peringkat
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideDari EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideBelum ada peringkat
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideDari EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideBelum ada peringkat
- EYE DISORDERS: GLAUCOMA AND CATARACTSDokumen127 halamanEYE DISORDERS: GLAUCOMA AND CATARACTSjoan olanteBelum ada peringkat
- Two Major Forms of Glaucoma: Acute and ChronicDokumen5 halamanTwo Major Forms of Glaucoma: Acute and ChronicKath CuevasBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma Guide: Types, Symptoms, Risks & TreatmentDokumen3 halamanGlaucoma Guide: Types, Symptoms, Risks & TreatmentplethoraldorkBelum ada peringkat
- Tubes NclexDokumen3 halamanTubes NclexYoke W Khoo100% (1)
- Testing NclexDokumen5 halamanTesting NclexYoke W KhooBelum ada peringkat
- Nclex Thyroid DisordersDokumen5 halamanNclex Thyroid DisordersYoke W KhooBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatrics NclexDokumen1 halamanPediatrics NclexYoke W KhooBelum ada peringkat
- Testing - 2 NclexDokumen12 halamanTesting - 2 NclexYoke W KhooBelum ada peringkat
- Nclex Reflexes and Their IndicationDokumen1 halamanNclex Reflexes and Their IndicationYoke W KhooBelum ada peringkat
- Gi NclexDokumen14 halamanGi NclexYoke W Khoo100% (3)
- Microsoft PowerPoint - BHDDokumen35 halamanMicrosoft PowerPoint - BHDandarias kevinBelum ada peringkat
- Functional Electrical Stimulation and Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation AHM 1Dokumen34 halamanFunctional Electrical Stimulation and Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation AHM 1Wilson OoiBelum ada peringkat
- Degenerative ScoliosisDokumen8 halamanDegenerative ScoliosisAnonymous 2q4eg3hgEvBelum ada peringkat
- Geriatric Case ScenarioDokumen2 halamanGeriatric Case ScenarioSasi NarayanasamyBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines on Aesthetic Medical PracticeDokumen47 halamanGuidelines on Aesthetic Medical Practicezahisma890% (1)
- Block 1 Board Review - Lecture NotesDokumen127 halamanBlock 1 Board Review - Lecture NotesCece RereBelum ada peringkat
- Ganglion: Ganglion (Cyst) of The WristDokumen5 halamanGanglion: Ganglion (Cyst) of The WristNoorazimah AminuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Synopsis DR ABCDokumen8 halamanSynopsis DR ABCFiaz medicoBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis Topics in Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDokumen7 halamanThesis Topics in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgerymonroeandertonsaltlakecity100% (2)
- Chapter 35 Part 1Dokumen31 halamanChapter 35 Part 1Gordon JamesonBelum ada peringkat
- Code Blue - Ali HaedarDokumen48 halamanCode Blue - Ali HaedaremansoelaimanBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise For Spondylolisthesis PDFDokumen2 halamanExercise For Spondylolisthesis PDFGouriBelum ada peringkat
- 06 Inguinal Hernia SrsDokumen10 halaman06 Inguinal Hernia SrslowhillBelum ada peringkat
- Endoscopic Procedures in Colon and RectumDokumen164 halamanEndoscopic Procedures in Colon and RectumChargerBelum ada peringkat
- Running (continuous) sutures: Types, uses, advantages & disadvantagesDokumen3 halamanRunning (continuous) sutures: Types, uses, advantages & disadvantagesIo DobriBelum ada peringkat
- BLS Pretest AllDokumen8 halamanBLS Pretest AllTatianaGutuBelum ada peringkat
- Hirschsprung DiseaseDokumen13 halamanHirschsprung Diseaseganesh reddyBelum ada peringkat
- Mutilating Hand Injuries, Hand Clinics, Volume 19, Issue 1, Pages 1-210 (February 2003)Dokumen201 halamanMutilating Hand Injuries, Hand Clinics, Volume 19, Issue 1, Pages 1-210 (February 2003)Timofey Sukhinin100% (3)
- EAU Guideline 2021Dokumen20 halamanEAU Guideline 2021G WBelum ada peringkat
- InfertilityDokumen55 halamanInfertilityFedlu SirajBelum ada peringkat
- CDC/NHSN Surveillance Definitions For Specific Types of InfectionsDokumen30 halamanCDC/NHSN Surveillance Definitions For Specific Types of InfectionssofiaBelum ada peringkat
- Ultrasound Report The Black Box of Fetal StatusDokumen43 halamanUltrasound Report The Black Box of Fetal StatusKalpavriksha19740% (1)
- The Radiology Assistant - CT in TraumaDokumen18 halamanThe Radiology Assistant - CT in Traumaابو عبد الرحمنBelum ada peringkat
- Revised CPR Guidelines 1Dokumen56 halamanRevised CPR Guidelines 1little mushroomBelum ada peringkat
- World of Surgical Instruments Textbook Preview WebDokumen12 halamanWorld of Surgical Instruments Textbook Preview Webpryanka40% (5)
- Pretreatment Medications For Rapid Sequence Intubation in Adults For Emergency Medicine and Critical Care - UpToDateDokumen19 halamanPretreatment Medications For Rapid Sequence Intubation in Adults For Emergency Medicine and Critical Care - UpToDateignacia.conejerosBelum ada peringkat
- Adult Care of Children From Pediatric Urology - Part 2Dokumen7 halamanAdult Care of Children From Pediatric Urology - Part 2Jad DegheiliBelum ada peringkat
- NG Tube, Lavage and Gavage Procedure ChecklistDokumen6 halamanNG Tube, Lavage and Gavage Procedure ChecklistBitew Tefera ZewudieBelum ada peringkat
- CABGDokumen41 halamanCABGJasmin Jacob100% (2)
- Oculoplasty Surgeon in AhmedabadDokumen8 halamanOculoplasty Surgeon in AhmedabadhniramayBelum ada peringkat