Classification of Signals Part 1
Diunggah oleh
Ajay Kumar R0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
51 tayangan15 halamanfj
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inifj
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
51 tayangan15 halamanClassification of Signals Part 1
Diunggah oleh
Ajay Kumar Rfj
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 15
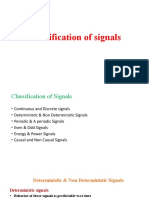
Classification of Signals
(Continuous and Discrete)
Continuous and discrete-time signals
Continuous and discrete-valued signals
Deterministic and random signals
Symmetric (Even) and Ant symmetric(odd) signals
Periodic signals and non-periodic (Aperiodic) signals
Causal, Noncausal and Anticausal signals
Right-handed and left-handed signals
Finite and infinite length signals
Energy and Power signals
Continuous and Discrete-Time signals
Continuoussignal
- It isdefinedfor all timet : x(t)
Discrete-timesignal
- It is defined only at discrete instants of time :
x[n]=x(nT)
Continuous and Discrete-Time Signals
Continuous-TimeSignals
Most signals in the real world are
continuous time, as the scale is
infinitesimallyfine.
Eg: voltage, velocity
Denote by x(t), where the time interval
maybebounded(finite) or infinite
Discrete-TimeSignals
Somereal worldandmany digital signals
arediscretetime, astheyaresampled
E.g. pixels, daily stock price (anything
that adigital computer processes)
Denote by x[n], where n is an integer
valuethat variesdiscretely
Sampled continuous signal
x[n] =x(nT) T issampleperiod
x(t)
t
x[n]
n
Continuous and Discrete valued signals
CV corresponds to a continuous y-axis
DV corresponds to a discrete y-axis
Digital signal
Deterministic signals, random signals
Deterministic signals
-There is no uncertainty with respect to its value at any time.
(ex) sin(3t)
Random signals
- There is uncertaintybefore its actual occurrence.
(ex) Noise of an amplifier
Even and odd signals
Even signals : x(-t)=x(t)
Odd signals : x(-t)=-x(t)
Even and odd signal decomposition
x
e
(t)=1/ 2(x(t)+x(-t))
x
o
(t)=1/ 2(x(t)-x(-t))
Even and Odd Parts of Functions
( )
( ) ( )
The of a function is
2
e
x t x t
x t
+
= even part
( )
( ) ( )
The of a function is
2
o
x t x t
x t
= odd part
Afunctionwhoseevenpart iszero, isoddandafunction
whoseoddpart iszero, iseven.
Various Combinations of even and
odd functions
Function type Sum Difference Product Quotient
Both even Even Even Even Even
Both odd Odd Odd Even Even
Even and odd Neither Neither Odd Odd
Combination of even and odd
function for DT Signals
Function type Sum Difference Product Quotient
Both even Even Even Even Even
Both odd Odd Odd Even Even
Even and odd Even or Odd Even or odd Odd Odd
Periodic signals, non-periodic signals
Periodic signals
- A function that satisfies the condition x(t)=x(t+T) for all t
T that satisfied the above equation is called fundamental
period of x(t).
- Fundamental frequency : f=1/ T
- Angular frequency : e=2t/ T
(radians/ sec)
Non-periodic signals
Anysignal x(t) for whichthereisnovalueof T tosatisfythecondition
of Equation(1) iscalledaperiodicor nonperiodicsignal.
Anon-periodicsignal isassumedtohaveaperiodT =
Exampleof nonperiodicsignal isanexponential signal
A Periodic signal with period To
x(t) x(t+T)
Causal and Anti-causal Signals
Causal signals: zerofor all negativetime
Anticausal signals: zerofor all positivetime
Noncausal signals : Non-zero values in both
positiveandnegativetime
causal
signal
anticausal
signal
noncausal
signal
Right-handed and left-handed Signals
Right-handed and left handed-signal : zero
between a given variable and positive or
negativeinfinity
Finite and infinite length
Finite-lengthsignal : nonzeroover afiniteinterval
t
min
<t<t
max
Infinite-length singal : nonzero over all real
numbers
Energy and Power over Infinite Time
For many signals, wereinterestedin examiningthepower
andenergyover aninfinitetimeinterval (-, ). Hence:
If thesums or integrals donot converge, theenergyof such
asignal isinfinite
Twoimportant (sub)classesof signals
1. Finitetotal energy(andthereforezeroaveragepower)
2. Finiteaveragepower (andthereforeinfiniteenergy)
} }
= = dt t x dt t x E
T
T
T
2 2
) ( ) ( lim
= =
= =
n
N
N n
N
n x n x E
2 2
] [ ] [ lim
}
=
T
T
T
dt t x
T
P
2
) (
2
1
lim
=
+
=
N
N n
N
n x
N
P
2
] [
1 2
1
lim
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- COM336 Lecture 1Dokumen65 halamanCOM336 Lecture 1Hamid AwanBelum ada peringkat
- Analisis Spektrum Sinyal Digital - Pertemuan 1Dokumen23 halamanAnalisis Spektrum Sinyal Digital - Pertemuan 1Adji NugrohoBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Contents: Signals and SystemsDokumen40 halamanLecture Contents: Signals and SystemsFahad KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Unit I - Classification of Signals and SystemsDokumen45 halamanUnit I - Classification of Signals and SystemsAswath selvaBelum ada peringkat
- Signal & Systems - EDUSATDokumen87 halamanSignal & Systems - EDUSATNaresh MundraBelum ada peringkat
- Principle of Communication EngineeringDokumen52 halamanPrinciple of Communication Engineeringسعيد ابوسريعBelum ada peringkat
- Lect1 SignalProcessingDokumen82 halamanLect1 SignalProcessingEng:Mostafa Morsy MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Wa0003Dokumen64 halamanWa0003dileep kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Ppts of InstruDokumen35 halamanPpts of Instrurao asadBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of Signals & SystemsDokumen82 halamanClassification of Signals & SystemsRaja Desingu94% (16)
- Classification of Signals and SystemsDokumen77 halamanClassification of Signals and Systemsrajalakshmi boopathiBelum ada peringkat
- ECE121 - Signals Spectra and ProcessingDokumen18 halamanECE121 - Signals Spectra and ProcessingJr OlivarezBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of Signals & Systems: PresentationDokumen36 halamanClassification of Signals & Systems: PresentationSneha NagarBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of Signals & SystemsDokumen82 halamanClassification of Signals & SystemsNanmaran RajendiranBelum ada peringkat
- S&S - Week 3Dokumen41 halamanS&S - Week 3machasong98Belum ada peringkat
- Signal & Systems - EDUSATDokumen87 halamanSignal & Systems - EDUSATomkarBelum ada peringkat
- Signal and Systems: Dr. Avinash Chandra Assistant Professor (Senior) SENSE, VIT VelloreDokumen30 halamanSignal and Systems: Dr. Avinash Chandra Assistant Professor (Senior) SENSE, VIT VelloreSathwik YadalamBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Signal and Syatem BeginnerDokumen87 halamanElectrical Signal and Syatem Beginnerজীবন আহমেদBelum ada peringkat
- 2-Classification of Signals and Systems-05!01!2024Dokumen67 halaman2-Classification of Signals and Systems-05!01!2024rupinsgmBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Continuous Time Signals and SystemsDokumen55 halamanIntroduction to Continuous Time Signals and SystemsSiddhant SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1Dokumen33 halamanLecture 1Farooq GhaziBelum ada peringkat
- Classification-of-Signals-Systems Unit1Dokumen59 halamanClassification-of-Signals-Systems Unit1Durgarao Nagayalanka0% (1)
- Unit 1Dokumen30 halamanUnit 1swapnil jainBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Signal Processing: Discussion #2 Discrete Time Signals & Systems Tarun Choubisa Dept. of ETC, KIIT UniversityDokumen39 halamanDigital Signal Processing: Discussion #2 Discrete Time Signals & Systems Tarun Choubisa Dept. of ETC, KIIT Universitymyself a student of btech 1st yr100% (1)
- Introduction to Signals & Systems: An OverviewDokumen87 halamanIntroduction to Signals & Systems: An OverviewDanial AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Transmission Signals 24.08.2010Dokumen18 halamanBasic Transmission Signals 24.08.2010astroalianBelum ada peringkat
- CommunicationDokumen18 halamanCommunicationSamah Abu SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of Signals & Systems: PresentationDokumen36 halamanClassification of Signals & Systems: PresentationRajeeBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of Signals & Systems: PresentationDokumen36 halamanClassification of Signals & Systems: PresentationRamya NBelum ada peringkat
- Signals and SystemsDokumen40 halamanSignals and SystemsAmeen PeBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction Signal ProcessingDokumen25 halamanIntroduction Signal Processinghafsakhan21Belum ada peringkat
- SIGNALS - Session 1Dokumen17 halamanSIGNALS - Session 1hakkem bBelum ada peringkat
- 1-Signal Analysis 01 PDFDokumen16 halaman1-Signal Analysis 01 PDFAmanya Luka OliangBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-1 Introduction To Signals and Systems: SignalDokumen24 halamanChapter-1 Introduction To Signals and Systems: SignalYaregal ChalachewBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 2 CH 2Dokumen37 halamanLec 2 CH 2Aimen AnwarBelum ada peringkat
- Industry 4.0 in Manufacturing: ME F426 (I SEM, 2020-2021) byDokumen17 halamanIndustry 4.0 in Manufacturing: ME F426 (I SEM, 2020-2021) byakash chBelum ada peringkat
- Section ADokumen70 halamanSection AAyaneBelum ada peringkat
- Signals and SystemsDokumen29 halamanSignals and Systemsabc75Belum ada peringkat
- SignalDokumen18 halamanSignalET201040 Mohin UddinBelum ada peringkat
- 5th Sem SS - 1 UnitDokumen10 halaman5th Sem SS - 1 Unitvyas_tthBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of SignalsDokumen36 halamanClassification of SignalsMayuBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-1 Introduction To Signals and Systems: SignalDokumen257 halamanChapter-1 Introduction To Signals and Systems: SignalYaregal ChalachewBelum ada peringkat
- Signals and Systems EE-315: Muhammad Asim Butt Asim - Butt@umt - Edu.pkDokumen28 halamanSignals and Systems EE-315: Muhammad Asim Butt Asim - Butt@umt - Edu.pkFAISAL RAHIMBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 1Dokumen31 halamanLec 1عبدالمنعم الشعراويBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture - 1Dokumen46 halamanLecture - 1sena.mokoninBelum ada peringkat
- Analog and Digital Signals, Time and Frequency Representation of SignalsDokumen31 halamanAnalog and Digital Signals, Time and Frequency Representation of SignalsVamsi ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Signals and Systems Lecture Note #1: Presentation By: I.Nelson Sl/Ece SSN College of EngineeringDokumen36 halamanSignals and Systems Lecture Note #1: Presentation By: I.Nelson Sl/Ece SSN College of Engineeringvasece4537577Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 UpdatedDokumen43 halamanLecture 1 UpdatedZamshed FormanBelum ada peringkat
- BEE2143 - Chap 1Dokumen72 halamanBEE2143 - Chap 1mohd danialBelum ada peringkat
- 1-dsp SBT PDFDokumen68 halaman1-dsp SBT PDFNeelabro KonarBelum ada peringkat
- ECE 334 A Assignment 1Dokumen7 halamanECE 334 A Assignment 1Tiffany Fate AnoosBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter OneDokumen22 halamanChapter OneMedhanyeBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Signals, Their Properties & Energy/PowerDokumen9 halamanTypes of Signals, Their Properties & Energy/PowerMas ShariBelum ada peringkat
- Unit1 1SS1Dokumen20 halamanUnit1 1SS1Ram MurthyBelum ada peringkat
- C & S Unit-1 Introduction To SignalsDokumen40 halamanC & S Unit-1 Introduction To SignalsGauravBelum ada peringkat
- Unit I (DSP)Dokumen24 halamanUnit I (DSP)kjairam80Belum ada peringkat
- Review of Signals and SystemsDokumen25 halamanReview of Signals and SystemsAdrian TanBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1Dokumen47 halamanLecture 1oswardBelum ada peringkat
- Signals and Linear Systems IntroductionDokumen17 halamanSignals and Linear Systems IntroductionShahriar TarvirBelum ada peringkat
- Noise in AM FMDokumen14 halamanNoise in AM FMHarsha100% (1)
- Dynamips I8 LogDokumen1 halamanDynamips I8 LogAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Networks Prof. S. Ghosh Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurDokumen41 halamanComputer Networks Prof. S. Ghosh Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture25-26 NoiseAMFMDokumen35 halamanLecture25-26 NoiseAMFMAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamips I5 LogDokumen2 halamanDynamips I5 LogAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- AsdDokumen46 halamanAsdAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- RFC 2018Dokumen12 halamanRFC 2018Ajay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- EIGRP Stub Routing: Feature OverviewDokumen12 halamanEIGRP Stub Routing: Feature OverviewTharakaBelum ada peringkat
- (Cisco) Frame Relay Illustrated GuideDokumen44 halaman(Cisco) Frame Relay Illustrated GuideAriel H. CochiaBelum ada peringkat
- AsdDokumen46 halamanAsdAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- AsdDokumen46 halamanAsdAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamips I6 LogDokumen1 halamanDynamips I6 LogAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- AsdDokumen46 halamanAsdAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- AsdDokumen46 halamanAsdAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- AsdDokumen46 halamanAsdAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamips I3 LogDokumen2 halamanDynamips I3 LogAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- 31 Steps Learn A New Language - Philip Vang - 2015Dokumen83 halaman31 Steps Learn A New Language - Philip Vang - 2015ajrojas1359Belum ada peringkat
- Dynamips I3 LogDokumen2 halamanDynamips I3 LogAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco Licensing Details in 40 CharactersDokumen4 halamanCisco Licensing Details in 40 CharactersAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- APT ScheduleDokumen315 halamanAPT ScheduleDrunkDracula6950% (2)
- Dynamips I7 LogDokumen1 halamanDynamips I7 LogAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamips I2 LogDokumen2 halamanDynamips I2 LogAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Fix MS SystemUser Bug: Java, Visual C++, .NET Framework, Adobe Flash & Silverlight ErrorsDokumen1 halamanFix MS SystemUser Bug: Java, Visual C++, .NET Framework, Adobe Flash & Silverlight ErrorsminoziziBelum ada peringkat
- HelpDokumen3 halamanHelpAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Solar Micro Usb LedDokumen1 halamanSolar Micro Usb LedAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Origins of The Reserve Bank of IndiaDokumen1 halamanOrigins of The Reserve Bank of IndiaAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Aec SyllabusDokumen2 halamanAec SyllabusAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- The Economics OF Development and PlanningDokumen24 halamanThe Economics OF Development and PlanningKamal Singh88% (8)
- Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design by NeamenDokumen1.307 halamanElectronic Circuit Analysis and Design by NeamenAjay Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- CV Iqbal Wahyu SaputraDokumen1 halamanCV Iqbal Wahyu SaputraIqbal WahyuBelum ada peringkat
- Public Relations Review: Juan Meng, Bruce K. BergerDokumen12 halamanPublic Relations Review: Juan Meng, Bruce K. BergerChera HoratiuBelum ada peringkat
- The Blow Cup ChallengeDokumen9 halamanThe Blow Cup Challengeapi-459062106Belum ada peringkat
- Mathematics Curriculum in MalaysiaDokumen38 halamanMathematics Curriculum in MalaysiaSK Lai100% (1)
- Earthworks Computations and MethodsDokumen24 halamanEarthworks Computations and MethodsBryan ResullarBelum ada peringkat
- Stokoe and Stokoe (2001) Plenary PaperDokumen10 halamanStokoe and Stokoe (2001) Plenary Paperjames_frankBelum ada peringkat
- 05 01 2024 SR S60 Elite, Target & LIIT BTs Jee Main GTMDokumen24 halaman05 01 2024 SR S60 Elite, Target & LIIT BTs Jee Main GTMsaridelakshmikanthBelum ada peringkat
- 9789533073248UWBTechnologiesDokumen454 halaman9789533073248UWBTechnologiesConstantin PişteaBelum ada peringkat
- Urriculum Itae Et TudiorumDokumen21 halamanUrriculum Itae Et TudiorumEnricoBelum ada peringkat
- MPhil PhD Research MethodsDokumen2 halamanMPhil PhD Research MethodsSaifullah KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- 1-15-15 Kinematics AP1 - Review SetDokumen8 halaman1-15-15 Kinematics AP1 - Review SetLudwig Van Beethoven100% (1)
- Rust Cheat SheetDokumen8 halamanRust Cheat Sheetnewgmail accountBelum ada peringkat
- Canal OutletsDokumen32 halamanCanal OutletsAhmed Hassan83% (6)
- SSR in DFIG SystemsDokumen49 halamanSSR in DFIG SystemsHossein_jujujuBelum ada peringkat
- Evolutionary Computation:: Genetic AlgorithmsDokumen49 halamanEvolutionary Computation:: Genetic AlgorithmsShobanraj LetchumananBelum ada peringkat
- UCC Computer Science student explores greedy algorithmsDokumen3 halamanUCC Computer Science student explores greedy algorithmsEmmanuel EshunBelum ada peringkat
- Irace Comex TutorialDokumen5 halamanIrace Comex TutorialOmarSerranoBelum ada peringkat
- Centrifugal ForceDokumen9 halamanCentrifugal ForcecataiceBelum ada peringkat
- DOMENE WHO - QoLDokumen21 halamanDOMENE WHO - QoLSahim KahrimanovicBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 - Probability SolutionsDokumen24 halamanChapter 8 - Probability SolutionsDumoraSimbolonBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Integral Equations by D.C. Sharma M.C. GoyalDokumen200 halaman4 Integral Equations by D.C. Sharma M.C. GoyalManas Ranjan MishraBelum ada peringkat
- CSE 304-Digital Signal Processing: Dr. Amir A. Khan Office: A-218, SEECS 9085-2162 Amir - Ali@seecs - Edu.pkDokumen22 halamanCSE 304-Digital Signal Processing: Dr. Amir A. Khan Office: A-218, SEECS 9085-2162 Amir - Ali@seecs - Edu.pkAlamgir Ahmad KhattakBelum ada peringkat
- Sensex 1Dokumen354 halamanSensex 1raghav4life8724Belum ada peringkat
- Design and Analysis of Tension MemberDokumen29 halamanDesign and Analysis of Tension MemberJhianne Dulpina RoqueBelum ada peringkat
- Phy1 11 - 12 Q1 0603 PF FDDokumen68 halamanPhy1 11 - 12 Q1 0603 PF FDhiroBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment / Tugasan - Mathematics For ManagementDokumen7 halamanAssignment / Tugasan - Mathematics For ManagementKetz NKBelum ada peringkat
- Application of Modified Euler's Method in Obtaining Numerical Solution of Swing EquationDokumen7 halamanApplication of Modified Euler's Method in Obtaining Numerical Solution of Swing EquationijsretBelum ada peringkat
- A RANS-based Analysis Ool For Ducted Propeller Systems in Open Water ConditionDokumen23 halamanA RANS-based Analysis Ool For Ducted Propeller Systems in Open Water ConditionLeonardo Duarte MilfontBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Predictive Magic Cards.Dokumen26 halamanDesign of Predictive Magic Cards.aries25th3Belum ada peringkat
- Best Dives West Hemisphere ExcerptDari EverandBest Dives West Hemisphere ExcerptPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Arizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksDari EverandArizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Naples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoDari EverandNaples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- South Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptDari EverandSouth Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptDari EverandThe Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- New York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksDari EverandNew York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksBelum ada peringkat
- Japanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensDari EverandJapanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensBelum ada peringkat