Victor Grignard
Diunggah oleh
Nad SngHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Victor Grignard
Diunggah oleh
Nad SngHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Victor Grignard
Full name Born Died Age of death Cause of death Gender Race or Ethnicity Nationality Military service Occupation Father Mistress
: Franois Auguste Victor Grignard : 6 May 1871, Cherbourg, France : 13 December 1935, Lyon, France : 63 : Infection : Male : White : France : French Army (1892-93, and again during WWI) : Chemist : Thophile Henri Grignard (marine carpenter) : Marie Hbert Grignard 1
Wife Son Son Award Field
: Augustine Marie Boulant (m. 1910, one son, one daughter) : Robert Paindestre (stepson) : Roger Grignard (chemist, b. 1911) : Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1992 (with Paul Sabatier) : organic chemistry : 41
Age at the time of award
Affiliation at the time of the award: Nancy University, Nancy, France Prize motivation : "for the discovery of the so-called Grignard reagent, which in recent years has greatly advanced the progress of organic chemistry" Other awards : Cahours Prize 1901, 1902; Berthelot Medal 1902; Jecker Prize 1905; Lavoisier Medal 1912; French Legion of Honor Chevalier (1912; French Legion of Honor Officer (1920); French Legion of Honor Commander (1933)
Education Background: University: cole Normale Spcial, Cluny, France (attended, 1889-91) University: BS Chemistry, University of Lyon (1894) University: PhD Chemistry, University of Lyon (1901) Scholar: Chemistry, University of Lyon (1901-05) Scholar: Chemistry, University of Besanon (1905-06)
Working experience: Teacher: Chemistry, University of Lyon (1906-08) Professor: Chemistry, University of Lyon (1908-09) Professor: Organic Chemistry, University of Nancy (1909-19) Professor: General Chemistry, University of Lyon (1919-35) Administrator: Director, cole de Chimie Industrielle de Lyons (1921-35) British Chemical Society Foreign Member French Academy of Sciences French Society of Industrial Chemistry Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences Foreign Member
BIOGRAPHY
Franois Auguste Victor Grignard which known as Victor Grignard is a French chemist that shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1992 with Paul Sabatier [1,2,4,5]. He was born on 6 May 1871 at Cherbourg, France [2, 4, 5]. His father's' Thophile Henri Grignard is a marine carpenter. Like other normal children, he attended the local primary school there. In 1889, Grignard got scholarship to attend Normale Special de Cluny, a school for modern teachers of secondary schools. However, the school closed in 1891 due to disputes between proponents o f classical and modern education [1]. After that, he was transferred to the Faculte des Sciences of the University of Lyons, where he studied science and mathematics. His initial failure prompted him to complete his military service (French Army) in 1892, and in 1893 he returned to Lyons to successfully receive the Licencie es Sciences Mathematiques in 1894 [1, 4].
In 1894, Victor Gridnard convinced to take the job in the Faculte des Sciences in Lyon even though chemistry is not his field of study. He is working under the developer Bouveault Aldehyde Synthesis, Professor Louis Bouveault [1]. After get promoted to prparateur, he began to get along and working closely with Philippe Barbier, of the Barbier reaction. Philippe Barbier are well known as father of organometallic chemistry for the synthesis of the first organomagnesium compound [1]. After obtained the degree Licenci-s-Sciences Physiques, he was promoted to become chef des travaux pratiques in 1898. In 1901, He was awarded the degree Docteur s Sciences de Lyons after submitted his first paper which jointly with Barbier, thesis on organic magnesium compounds Sur les Combinaisons organomagnsiennes mixtes [1]. He was awarded professeur-adjoint in 1908. After that, he transferred to Nancy University, Nancy, France because he cannot rise further at Lyon.
Within a year at the Universite de Nancy, he was promoted to professeur titulaire. In 1910, he was married to Augustine Marie Boulant[1]. Two years later, he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1912 (share with Paul Sabatier) for the discovery and develop Grignard reagent [1-4]. His prize motivation is "for the discovery of the so-called Grignard reagent, which in recent year has greatly advanced the progress of organic chemistry" [2].
Grignard was mobilized as corporal at the beginning of World War I in 1914. However, after that, Grignard was commissioned for study on dichloroethyl sulfide (mustard gas) for use as chemical weaponry in Nancy and Paris. Once War 1 ended, he joins the Universite de Lyon as Professor of General Chemistry [1]. In 1992 he was promoted as Directeur de lEcole de Chimie Industrielle de Lyons [1]. Grignard became the Dean of the Faculty of Sciences in 1929. Unfortunately, he got an infection that causing death at the age of 63 years old, on 13 December 1935 at Lyon, France [5]. During his life time, he also involved in different analysis areas, like condensation of aldehydes and ketones, ketone splitting of tertiary alcohols, chemical action and dehydrogenation underneath reduced pressure, and quantitative ozonolysis[1,5]. Grignard not only be remembered as successful professor and chemical researcher in Nancy and Lyon; where he tutored many of doctoral candidates but he also being honored by world as there 170 publications on his research are available all around the world.
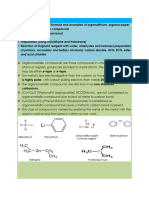
THE GRIGNARD REACTION Previous literature stated that the Grignard reaction is important in organic synthesis to prepare organic compounds from smaller precursor molecules [1, 5]. Grignard Reagent can be classified as extremely reactive and unstable chemical compounds. This reagent has being used to synthesize alcohols, carboxylic acids, hydrocarbons, and other compounds [3]. Grignard is most noted for devising a new method for generating carbon-carbon bonds using magnesium to couple ketones and alkyl halides. It occurs in two steps which is formation of the Grignard reagent and addition Grignard reagent to carbonyl. In the formation of the "Grignard reagent", which is an organomagnesium compound made by the reaction an organohalide, R-X (R = alkyl or aryl; and X is a halide, usually bromide or iodide) with magnesium metal. The Grignard reagent is usually described with the general chemical formula R-Mg-X, although its structure is more complex. Grignard reaction procedure is: R-X + Mg R-X.- + Mg.+ R-X. - R. + XX- + + Mg. + XMg. R. + XMg. RMgx
Figure 1 : Grignard reaction procedure (source: chemistry.tutorvista.com)
Aforementioned, the second step is addition of the carbonyl (ketone or aldehyde) to the solution that contains Grignard reagent. The carbon atom that is bonded to Mg transfers to the carbonyl carbon atom, and the oxygen of the carbonyl carbon becomes attached to the magnesium to give an alkoxide. The reaction is an example of a nucleophilic addition to a carbonyl. After the addition, the reaction mixture is treated with aqueous acid to give an alcohol, and the magnesium salts are subsequently discarded [3].
REFERENCES 1. "Victor Grignard - Biographical". Nobelprize.org. Nobel Media AB 2013. Web. 20 Nov 2013. http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/1912/grignard-bio.html 2. "Victor Grignard - Facts". Nobelprize.org. Nobel Media AB 2013. Web. 24 Nov 2013. http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/1912/grignard-facts.html 3. "Victor Grignard - Nobel Lecture: The Use of Organomagnesium Compunds in Preparative Organic Chemistry". Nobelprize.org. Nobel Media AB 2013. Web. 23 Nov 2013. http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/1912/grignard-lecture.html 4. Victor Grignard. Todayinsci. Today in Science History 1999-2013. WEB. 23 Nov 2013. http://todayinsci.com/5/5_06.htm#GrignardVictor 5. Victor Gridnard and Paul Sebatier. Humantouchofchemistry.com. NNDB tracking the entire world. WEB. 23 Nov 2013. http://humantouchofchemistry.com/victor-grignard-paulsabatier.htm
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Earth and Life Science DLLDokumen6 halamanEarth and Life Science DLLGsoon Sibulan100% (3)
- Urea Process (Technical Report)Dokumen42 halamanUrea Process (Technical Report)Heidi Adel100% (2)
- Raus IAS - Focus Special Edition - Geography, Environment - For Prelims 2017Dokumen101 halamanRaus IAS - Focus Special Edition - Geography, Environment - For Prelims 2017Rohit Sharma100% (1)
- Power Tube Biasing Operation Manual 15-01-08Dokumen2 halamanPower Tube Biasing Operation Manual 15-01-08MitchBelum ada peringkat
- Reviewer (Lec) OrgChemDokumen30 halamanReviewer (Lec) OrgChemChel Andrea Poblete100% (1)
- Haber ProcessDokumen10 halamanHaber ProcessTon5698Belum ada peringkat
- Regenerative Medicine Manual ISSCA 2020 EnglishDokumen21 halamanRegenerative Medicine Manual ISSCA 2020 EnglishDana MihutBelum ada peringkat
- Symbols For Signalling Circuit DiagramsDokumen27 halamanSymbols For Signalling Circuit DiagramsrobievBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 2: Electrolytic Cell-Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionDokumen8 halamanExperiment 2: Electrolytic Cell-Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionNad Sng90% (21)
- LIST Real Estate Contacts ListDokumen4 halamanLIST Real Estate Contacts ListChauhan Harshit100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry: An Introductory CourseDari EverandOrganic Chemistry: An Introductory CoursePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (3)
- The Chemistry of Nitrogen: Pergamon Texts in Inorganic ChemistryDari EverandThe Chemistry of Nitrogen: Pergamon Texts in Inorganic ChemistryPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- History of Some Special ExplosivesDokumen24 halamanHistory of Some Special ExplosivesShazil KhanBelum ada peringkat
- 4608 Eed 01Dokumen29 halaman4608 Eed 01NickBelum ada peringkat
- Greenhouse Gases and Global WarmingDokumen57 halamanGreenhouse Gases and Global WarmingUno CarilloBelum ada peringkat
- M Le Bras, C Wilkie, S Bourbigot-Fire Retardancy of Polymers New Applications of Mineral Fillers-Royal Society of Chemistry (2005)Dokumen433 halamanM Le Bras, C Wilkie, S Bourbigot-Fire Retardancy of Polymers New Applications of Mineral Fillers-Royal Society of Chemistry (2005)Michaux Gwénaëlle100% (3)
- Roster ChemistsDokumen26 halamanRoster ChemistsMichaela DelacruzBelum ada peringkat
- Inorganic Chemistry: Principles, Applications, and SustainabilityDokumen40 halamanInorganic Chemistry: Principles, Applications, and SustainabilityPhilipBelum ada peringkat
- Proceedings 2012Dokumen163 halamanProceedings 2012Miguel ToledoBelum ada peringkat
- Powerful liquid explosive nitroglycerinDokumen3 halamanPowerful liquid explosive nitroglycerinAfriyanti Rosmadiana100% (1)
- Mypchem Ch1answers PDFDokumen3 halamanMypchem Ch1answers PDFanilkumarmuntha868_5Belum ada peringkat
- Schlumberger Brothers BiographyeditDokumen2 halamanSchlumberger Brothers BiographyeditCloupers CloupersBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1Dokumen16 halamanModule 1Joan Dadivas AmancioBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Tokoh Organometallic GilmanDokumen7 halamanAssignment Tokoh Organometallic GilmanniniBelum ada peringkat
- Kaufman M 1968 PHD ThesisDokumen290 halamanKaufman M 1968 PHD ThesisZa KiBelum ada peringkat
- Moses Gomberg Discovery of Organic Free Radicals Historical ResourceDokumen8 halamanMoses Gomberg Discovery of Organic Free Radicals Historical ResourceradhikaBelum ada peringkat
- The History of NylonsDokumen7 halamanThe History of NylonsFalak NazBelum ada peringkat
- Joseph Black: Jöns Jakob BerzeliusDokumen2 halamanJoseph Black: Jöns Jakob BerzeliusMikaerika AlcantaraBelum ada peringkat
- Climate ChangeDokumen17 halamanClimate ChangeAnne MargaretteBelum ada peringkat
- Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming: Assignment#01Dokumen11 halamanGreenhouse Effect and Global Warming: Assignment#01Abeerataimur AbeerataimurBelum ada peringkat
- PPT12 Global Warming and Climate ChangeDokumen57 halamanPPT12 Global Warming and Climate ChangeJamaica DavidBelum ada peringkat
- Louis de Broglie's Wave Theory of ElectronsDokumen11 halamanLouis de Broglie's Wave Theory of ElectronsNikhil ChariBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Carbon FootprintDokumen46 halamanLecture Carbon FootprintNguễn NamBelum ada peringkat
- Ch03 - Lecture PPT-Part 1-Types of Chemical ReactionsDokumen19 halamanCh03 - Lecture PPT-Part 1-Types of Chemical ReactionsWilliam AndreasBelum ada peringkat
- Henry Louis Le ChatelierDokumen4 halamanHenry Louis Le ChatelierBlitzkrieg AudiomachineBelum ada peringkat
- Missy1235 OriginalDokumen20 halamanMissy1235 OriginalMisba KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Air Pollution SafetyDokumen27 halamanAir Pollution Safetysirajudeen IBelum ada peringkat
- Safety and security of dual-use chemicalsDokumen26 halamanSafety and security of dual-use chemicalsmyreen20Belum ada peringkat
- Notes and Answerkey ofDokumen190 halamanNotes and Answerkey ofBernát GulyásBelum ada peringkat
- Organic Chemistry PDFDokumen11 halamanOrganic Chemistry PDFAli AyanBelum ada peringkat
- Springer Biogeochemistry: This Content Downloaded From 132.236.27.217 On Sun, 04 Sep 2016 21:51:04 UTCDokumen28 halamanSpringer Biogeochemistry: This Content Downloaded From 132.236.27.217 On Sun, 04 Sep 2016 21:51:04 UTCBenjamin D. RubinBelum ada peringkat
- Biomass GasificationDokumen21 halamanBiomass GasificationMahesh ParitBelum ada peringkat
- Biomass Gasification AK RajvanshiDokumen21 halamanBiomass Gasification AK RajvanshiBharat AggarwalBelum ada peringkat
- History of Ziegler-Natta CatalystsDokumen28 halamanHistory of Ziegler-Natta CatalystsJohn MihelcicBelum ada peringkat
- Organic ChemistryDokumen7 halamanOrganic ChemistryRonBelum ada peringkat
- Semester 1 ChemistryprojectDokumen6 halamanSemester 1 Chemistryprojectapi-239328348Belum ada peringkat
- The Origin of Activated CarbonDokumen9 halamanThe Origin of Activated Carbonancientmoon1025Belum ada peringkat
- Justus Von LiebigDokumen7 halamanJustus Von LiebigNadia Novia WulandariBelum ada peringkat
- Grignard Reagents PDFDokumen12 halamanGrignard Reagents PDFAdedolapo Ademola Odunsi100% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S0959378021001655 MainDokumen10 halaman1 s2.0 S0959378021001655 MainNiyam ÆBelum ada peringkat
- Biografia de Hugo SchiffDokumen26 halamanBiografia de Hugo SchiffMartin LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Kinetics of Vanillin Production From Kraft Lignin OxidationDokumen9 halamanKinetics of Vanillin Production From Kraft Lignin OxidationKevin David Aguirre VallejoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Iv - Envt'l Issues MST 21Dokumen53 halamanChapter Iv - Envt'l Issues MST 21del143masBelum ada peringkat
- Climate Change: UNIT 4 Module 2 Solar Energy and The AtmosphereDokumen24 halamanClimate Change: UNIT 4 Module 2 Solar Energy and The AtmosphereCriselAlamagBelum ada peringkat
- EssayDokumen2 halamanEssayalex espinozaBelum ada peringkat
- On Environmental Chemistry For G-12Dokumen21 halamanOn Environmental Chemistry For G-12lenlucy13frBelum ada peringkat
- The Co2 Absorber Based On LiohDokumen3 halamanThe Co2 Absorber Based On LiohVipin GBelum ada peringkat
- SmI2 in Organic SynthesisDokumen220 halamanSmI2 in Organic Synthesisyshi8141Belum ada peringkat
- A World Map of Biodynamic Agriculture: John Paull, Benjamin HennigDokumen6 halamanA World Map of Biodynamic Agriculture: John Paull, Benjamin HennigLuxBelum ada peringkat
- CaseStudy PrisonBiogasProgrammeDokumen43 halamanCaseStudy PrisonBiogasProgrammePatrick BakkeBelum ada peringkat
- Patricia A Swain - BERNARD COURTOIS (1777-1838), FAMED FOR DISCOVERING IODINE (1811), AND HIS LIFE IN PARIS FROM 1798Dokumen9 halamanPatricia A Swain - BERNARD COURTOIS (1777-1838), FAMED FOR DISCOVERING IODINE (1811), AND HIS LIFE IN PARIS FROM 1798Amanda ReznorBelum ada peringkat
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDokumen11 halamanThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedGod is every whereBelum ada peringkat
- History of RefrigerantsDokumen50 halamanHistory of RefrigerantsMahesh ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Dmitri Mendeleev in 1897Dokumen5 halamanDmitri Mendeleev in 1897marthafitriBelum ada peringkat
- A.D. Chemistry Organometallic CompoundsDokumen11 halamanA.D. Chemistry Organometallic Compoundsombiraji122Belum ada peringkat
- Organometallic Compounds: Guest Lecturer: Prof. Jonathan L. SesslerDokumen40 halamanOrganometallic Compounds: Guest Lecturer: Prof. Jonathan L. Sesslerhera hmBelum ada peringkat
- Adsorption of MB Onto XMCM PDFDokumen63 halamanAdsorption of MB Onto XMCM PDFNad SngBelum ada peringkat
- Textile Industry ManagementDokumen12 halamanTextile Industry ManagementNad SngBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 4: Determination of Avogadro's Number Using ElectrogravimetryDokumen7 halamanExperiment 4: Determination of Avogadro's Number Using ElectrogravimetryNad Sng91% (11)
- Adsorption of MB Onto XMCM PDFDokumen61 halamanAdsorption of MB Onto XMCM PDFNad SngBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment CSC 134Dokumen9 halamanAssignment CSC 134Nad SngBelum ada peringkat
- District: Surkhet: PopulationDokumen13 halamanDistrict: Surkhet: PopulationkarunBelum ada peringkat
- 1999 - Seismic Soil Structure Interaction in Buildings - I Analytical Aspects PDFDokumen13 halaman1999 - Seismic Soil Structure Interaction in Buildings - I Analytical Aspects PDFCesar PugsioBelum ada peringkat
- Personality Types and Character TraitsDokumen5 halamanPersonality Types and Character TraitspensleepeBelum ada peringkat
- CLIC Catalogue PDFDokumen28 halamanCLIC Catalogue PDFsangram patilBelum ada peringkat
- Qand ADokumen5 halamanQand AJoshua PascasioBelum ada peringkat
- Elements of Plane and Spherical Trigonometry With Numerous Practical Problems - Horatio N. RobinsonDokumen228 halamanElements of Plane and Spherical Trigonometry With Numerous Practical Problems - Horatio N. RobinsonjorgeBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Ideal Models of Engine CyclesDokumen23 halaman4 Ideal Models of Engine CyclesSyedBelum ada peringkat
- IITG MA101 Endsem Question PaperDokumen12 halamanIITG MA101 Endsem Question PaperNarravula Harshavardhan100% (2)
- The Creators College of Science & Commerce: 1 TermDokumen2 halamanThe Creators College of Science & Commerce: 1 TermJhangir Awan33% (3)
- Kingspan Spectrum™: Premium Organic Coating SystemDokumen4 halamanKingspan Spectrum™: Premium Organic Coating SystemNikolaBelum ada peringkat
- Ethics Module 2 - NotesDokumen1 halamanEthics Module 2 - Notesanon_137579236Belum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Financial Statements Project: GUL AHMAD Textile MillsDokumen32 halamanAnalysis of Financial Statements Project: GUL AHMAD Textile MillsHanzala AsifBelum ada peringkat
- Cars Ger Eu PCDokumen157 halamanCars Ger Eu PCsergeyBelum ada peringkat
- Ebook Drugs and The Neuroscience of Behavior An Introduction To Psychopharmacology 2Nd Edition Prus Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokumen62 halamanEbook Drugs and The Neuroscience of Behavior An Introduction To Psychopharmacology 2Nd Edition Prus Test Bank Full Chapter PDFeffigiesbuffoonmwve9100% (10)
- Applying Value Engineering to Improve Quality and Reduce Costs of Ready-Mixed ConcreteDokumen15 halamanApplying Value Engineering to Improve Quality and Reduce Costs of Ready-Mixed ConcreteayyishBelum ada peringkat
- Downstream Processing and Bioseparation - Recovery and Purification of Biological Products PDFDokumen313 halamanDownstream Processing and Bioseparation - Recovery and Purification of Biological Products PDFgonbio67% (3)
- A Feature Selection Based On The Farmland Fertility Algorithm For Improved Intrusion Detection SystemsDokumen27 halamanA Feature Selection Based On The Farmland Fertility Algorithm For Improved Intrusion Detection SystemsRashed ShakirBelum ada peringkat
- Business PlanDokumen63 halamanBusiness PlanKristine BalanayBelum ada peringkat
- CSC-1321 Gateway User Guide: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDokumen48 halamanCSC-1321 Gateway User Guide: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineKislan MislaBelum ada peringkat
- Retired Car Jacker Screen PlayDokumen4 halamanRetired Car Jacker Screen Playapi-633948182Belum ada peringkat
- Synopsis - AVR Based Realtime Online Scada With Smart Electrical Grid Automation Using Ethernet 2016Dokumen19 halamanSynopsis - AVR Based Realtime Online Scada With Smart Electrical Grid Automation Using Ethernet 2016AmAnDeepSinghBelum ada peringkat
- Vincent Hoa's English 101 PortfolioDokumen24 halamanVincent Hoa's English 101 PortfoliovincentBelum ada peringkat
- Mfz-Odv065r15j DS 1-0-0 PDFDokumen1 halamanMfz-Odv065r15j DS 1-0-0 PDFelxsoonBelum ada peringkat
- White Paper Without Track ChangesDokumen7 halamanWhite Paper Without Track Changesapi-609064761Belum ada peringkat