1.3 Test
Diunggah oleh
danielphilip68Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1.3 Test
Diunggah oleh
danielphilip68Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Name: ..
80%
70%
AS Level Chemistry
60%
2007 - 2008
50%
40%
Below
Year 12
1.3
Assessed Homework
Bonding
55
10.3 Chemical Bond
1.
(a)
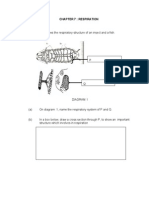
An ammonium ion, made by the reaction between ammonia molecule and a
hydrogen ion, can be represented as shown in the diagram below.
+
H
H
(i)
H
H
Name the type of bond represented in the diagram N-H
.
(ii)
Name the type of bond represented in the diagram by NH
(iii)
In terms of electrons, explain why an arrow is used to represent this N H
bond
(iv)
In terms of electron pairs, explain why the bond angles in the NH 4+ ion are all
109o28
(7)
(b)
Define the term electronegativity
(2)
(c)
A bond between nitrogen and hydrogen can be represented as N - H
(i)
In this representation, what is the meaning of the symbol ?
10.3 Chemical Bond
(ii)
From this bond representation, what can be deduced about the electronegativity of
hydrogen relative to that of nitrogen?
(2)
(Total 11 marks)
10.3 Chemical Bond
2.
(a)
Both HF and HCl are molecules having a polar covalent bond. Their boiling points
are 293 K and 188 K respectively.
(i)
State which property of the atoms involved causes a bond to be polar.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(ii)
Explain, in terms of the intermolecular forces present in each compound,
why HF has a higher boiling point than HCl.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(4)
(b)
When aluminium chloride reacts with chloride ions, as shown by the equation
below, a co-ordinate bond is formed.
AlCl3 + Cl
AlCl4
Explain how this co-ordinate bond is formed.
..................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
(2)
(c)
+
Draw the shape of the PCl5 molecule and of the PCl4 ion. State the value(s) of
the bond angles.
PCl5
+
PCl4
Bond angle(s) ...................................... Bond angle(s)
..........................................
(4)
(Total 10 marks)
10.3 Chemical Bond
3.
Lithium hydride, LiH, is an ionic compound containing the hydride ion, H
The reaction between LiH and aluminium chloride, AlCl3, produces the ionic compound
LiAlH4
(a)
Balance the equation below which represents the reaction between LiH and AlCl3
LiH +
AlCl3
LiAlH4 +
LiCl
(1)
(b)
Give the electronic configuration of the hydride ion, H
......................
(1)
(c)
Predict the shape of the AlH 4 ion. Explain why it has this shape.
Shape ..........................................................................................................
Explanation .................................................................................................
......................
......................
(3)
(d)
A bond can be represented by H Al
Name this type of bond and explain how it is formed.
Type of bond ................................................................................................
Explanation ..
......................
(3)
(Total 8 marks)
10.3 Chemical Bond
4.
The table below shows some values of melting points and some heat energies needed for
melting.
Substance
I2
NaCl
HF
HCl
HI
Melting point/K
387
1074
190
158
222
Heat energy for melting /kJ mol1
7.9
28.9
3.9
2.0
2.9
(a)
Name three types of intermolecular forces
Force 1 ..
Force 2 ..
Force 3 ..
(3)
(b)
(i)
Describe the bonding in a crystal of iodine
..
(ii)
Name the crystal type which describes an iodine crystal
.
(iii)
Explain why heat energy is required to melt an iodine crystal.
(4)
(c)
In terms of intermolecular forces involved, suggest why
(i)
hydrogen fluoride requires more heat energy for melting than does of
hydrogen chloride
10.3 Chemical Bond
..
(ii)
Hydrogen iodide requires more heat energy for melting than does hydrogen
chloride.
..
(5)
(d)
(i)
Explain why the heat energy required to melt sodium chloride is large
(ii)
The heat energy need to vaporise one mole of sodium chloride (171 KJ mol1
) is much greater than the heat energy required to melt one mole of sodium
chloride. Explain why this is so.
..
(3)
(e)
In terms of structure and bonding, suggest why graphite has a very high melting and
boiling point
(2)
(Total 17 marks)
10.3 Chemical Bond
5.
The diagram below represents a section of a crystal of silicon dioxide.
Si
O
Si
Si
Si
O
(a)
O
O
Name an element which has a structure similar to this.
.
(b)
(1)
Name the type of bonding between silicon and oxygen in this crystal
.
(1)
(c)
Name the type of structure illustrated by this diagram
.
(1)
(d)
Describe the motion of the atoms in this crystalline solid
.
(2)
(e)
In terms of structure and bonding, describe what happens to the atoms in this
crystal when it melts
..
(f)
Explain why this crystal is a non conductor of electricity in the solid state and why
graphite is a good conductor.
10.3 Chemical Bond
(4)
(Total 9 marks)
TEST 2
Answer all questions
Total 50 marks
Name:
SECTION A TOTAL ../35
SECTION B TOTAL /15
TOTAL ./50
= ..%
Grade __________
10.3 Chemical Bond
SECTION A
1.
(a)
What is a covalent bond?
.................................................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
Draw dot-and cross diagrams (outer shells only) to show the bonding in carbon
disulphide (CS2) and hydrogen sulphide (H2S).
Bonding in CS2
Bonding in H2S
(2)
(b)
Showing the outer electrons only, draw a dot-and-cross diagram to indicate the
bonding in calcium oxide.
(2)
(c)
(i)
Give the type of bonding present in BeCl2
(ii)
..................................................................................................................
Give the type of bonding present in BaCl2
..................................................................................................................
(iii)
Explain why the type of bonding is different in these two compounds.
..................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 8 marks)
10
10.3 Chemical Bond
2.
(a)
Draw diagrams to show the shapes of the following molecules and in each case
show the value of the bond angle on the diagram.
BeCl2
BF3
CCl4
SF6
(8)
(b)
Explain why the shape of NF3 is not the same as the shape of BF3.
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 11 marks)
11
10.3 Chemical Bond
3.
The boiling temperatures, Tb, of some Group IV and Group V hydrides are given below
(a)
Compound
CH4
SiH4
NH3
PH3
Tb/K
112
161
240
185
The polarity of a carbon-hydrogen bond can be shown as C H
(i)
What does the symbol + above the hydrogen atom signify?
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
(ii)
Explain briefly, in terms of its shape, why a CH4 molecule has no overall
polarity.
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
(3)
(b)
Name the type of intermolecular forces which exist between CH4 molecules in
liquid methane.
.................................................................................................................................
.
(1)
(c)
Explain why the boiling temperature of PH3 is greater than that of CH4.
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
(3)
(d)
Explain why the boiling temperature of NH3 is greater than that of PH3
.................................................................................................................................
12
10.3 Chemical Bond
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
(2)
(e)
Suggest why the strength of the CH bond in CH4 is greater than that of the SiH
bond in SiH4. State the relationship, if any, between the strength of the covalent
bond in CH4 and the boiling temperature of CH4
Reason for stronger C-H bond:
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
Relationship between covalent bond strength and boiling temperature:
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 11 marks)
13
10.3 Chemical Bond
4.
Draw sketches to predict the shape of a CIF' ion and the shape of a ClF5
molecule. In each case indicate, on the sketch, the bond angle value(s).
ClF +2
CIF5
(5)
(Total 5 marks)
14
10.3 Chemical Bond
SECTION B
5.
(a)
Define the term electronegativity and explain why the electronegativity values of
the Group II elements BeBa decrease down the group.
(4)
(b)
Name the strongest type of intermolecular force between hydrogen fluoride
molecules and draw a diagram to illustrate how two molecules of HF are attracted
to each other.
In your diagram show all lone pairs of electrons and any partial charges. Explain
the origin of these charges.
Suggest why this strong intermolecular force is not present between HI
molecules.
(7)
(c)
Crystals of sodium chloride and of diamond both have giant structures. Their
melting points are 1074 K and 3827 K, respectively. State the type of structure
present in each case and explain why the melting point of diamond is so high.
(4)
(Total 15 marks)
15
10.3 Chemical Bond
16
10.3 Chemical Bond
17
10.3 Chemical Bond
18
10.3 Chemical Bond
19
10.3 Chemical Bond
20
10.3 Chemical Bond
21
10.3 Chemical Bond
22
10.3 Chemical Bond
23
10.3 Chemical Bond
24
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Bonding HomeworkDokumen8 halamanBonding HomeworkAndrei Florea100% (1)
- Revision For First Term 9GCE 2010 11Dokumen30 halamanRevision For First Term 9GCE 2010 11Anonymous 8VJhV1eI2yBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry 5070 2023 Gce Question Paper 2Dokumen8 halamanChemistry 5070 2023 Gce Question Paper 2andrew silungweBelum ada peringkat
- Example PTE Structured QuestionsDokumen5 halamanExample PTE Structured Questions301 Dhia JaharahBelum ada peringkat
- 6 ElectrochemistryDokumen20 halaman6 ElectrochemistryahlonggBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDokumen7 halamanChapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneNoraliza Mohd AliBelum ada peringkat
- g10 Review WorkbookDokumen16 halamang10 Review WorkbookAnh Quân NghiêmBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen14 halamanChapter 5Ishraqi IlyasBelum ada peringkat
- Shapes of Simple Molecules - Ions 5 QPDokumen8 halamanShapes of Simple Molecules - Ions 5 QPSiddhant DuggalBelum ada peringkat
- 6 ElectrochemistryDokumen20 halaman6 ElectrochemistryhanifzainolBelum ada peringkat
- AS Progress Check - BondingDokumen10 halamanAS Progress Check - BondingMatthew James PopeBelum ada peringkat
- Reactions of Alkane Alkene AlcoholDokumen3 halamanReactions of Alkane Alkene AlcoholAnita Bong Yung LiBelum ada peringkat
- Sda 3 Form 4Dokumen13 halamanSda 3 Form 4Crystal MachipisaBelum ada peringkat
- Form 4: Atom Proton Number Nucleon NumberDokumen8 halamanForm 4: Atom Proton Number Nucleon NumberAzie Nurul AkhtarBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Test 2Dokumen2 halamanChemistry Test 2Daniel Ngenokesho WandyaBelum ada peringkat
- Form 3 Chapter 1 QuestionsDokumen11 halamanForm 3 Chapter 1 QuestionsCheah Foo Kit50% (2)
- Chem 11Dokumen7 halamanChem 11Raheem Abdul ManyambaBelum ada peringkat
- Activity Sheet-02 (Atomic Structure)Dokumen3 halamanActivity Sheet-02 (Atomic Structure)Nkemzi NzetengenleBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet IGCSEDokumen6 halamanWorksheet IGCSEsiennaBelum ada peringkat
- SCLP Samaj School Year 10 Chemistry Revision WorksheetDokumen11 halamanSCLP Samaj School Year 10 Chemistry Revision WorksheetHarshil PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Revision ExerciseDokumen7 halamanRevision ExerciseNana BBelum ada peringkat
- Chem Unit 5 Organic QuestionsDokumen77 halamanChem Unit 5 Organic Questionsareyouthere92Belum ada peringkat
- January 2022Dokumen12 halamanJanuary 2022Issei SenpaiBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz 2 Chapter 3 The Mole Concept, Chemical Formulae and EquationsDokumen3 halamanQuiz 2 Chapter 3 The Mole Concept, Chemical Formulae and EquationsIVAN TIONG WEI JUN MoeBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 9 Term 1 Chemistry RevisionDokumen7 halamanGrade 9 Term 1 Chemistry Revisionsiddloves.snowBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment of Electrolysis 2023 BookDokumen8 halamanAssignment of Electrolysis 2023 Bookaxmedbadali561Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 F4Dokumen5 halamanChapter 7 F4riyashreeBelum ada peringkat
- Single Award End of Feb 2023Dokumen8 halamanSingle Award End of Feb 2023Lone G. MokgalagadiBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Kimia Jul12 PDFDokumen49 halamanSPM Kimia Jul12 PDFSyazwani RadziBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Chemistry Paper 2Dokumen19 halamanSPM Chemistry Paper 2AnneLeongBelum ada peringkat
- Panduan & Teknik Menjawab Kimia Yang Berkesan: Program Perfect Score SPM Sekolah Menengah Negeri MelakaDokumen12 halamanPanduan & Teknik Menjawab Kimia Yang Berkesan: Program Perfect Score SPM Sekolah Menengah Negeri MelakaChew Boon WeiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6: Sources of Energy 1. The Object Shown in Table Below Possess Certain Forms of Energy. (A) Draw Lines To Show The Correct Match Between The Object That Forms Types of EnergyDokumen11 halamanChapter 6: Sources of Energy 1. The Object Shown in Table Below Possess Certain Forms of Energy. (A) Draw Lines To Show The Correct Match Between The Object That Forms Types of EnergyNg Lay HoonBelum ada peringkat
- Projek Skor Kimia 2014 Siri 3Dokumen9 halamanProjek Skor Kimia 2014 Siri 3Zul BaidiBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Form 4 Quiz AnswerDokumen8 halamanChemistry Form 4 Quiz Answerkhangsiean89Belum ada peringkat
- Test On Chemical BondsDokumen3 halamanTest On Chemical Bondsjoaco volpeBelum ada peringkat
- X Chemistry Holiday HomeworkDokumen2 halamanX Chemistry Holiday HomeworkhsrA amrahSBelum ada peringkat
- F324 All QuestionsDokumen95 halamanF324 All QuestionsIntesar NurBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryDokumen7 halaman01 Atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryMalak Sellat100% (1)
- 13.6 Assessed HomeworkDokumen8 halaman13.6 Assessed Homeworkarch0wnzBelum ada peringkat
- 5th Form Exam ET 2014Dokumen20 halaman5th Form Exam ET 2014NIRVAN RAMESHBelum ada peringkat
- Answer All Questions in This SectionDokumen6 halamanAnswer All Questions in This SectionAri AdiantariBelum ada peringkat
- 1st Term Chemistry Paper - 42Dokumen12 halaman1st Term Chemistry Paper - 42Krish PatelBelum ada peringkat
- British International College: Year 11 Half Term Assessment ChemistryDokumen9 halamanBritish International College: Year 11 Half Term Assessment ChemistryHarry SonBelum ada peringkat
- Mock 3 O Level Paper 2 Source1Dokumen13 halamanMock 3 O Level Paper 2 Source1Dewan Olin ChotepadaeBelum ada peringkat
- Newdocument1 6Dokumen16 halamanNewdocument1 6Magd OsamaBelum ada peringkat
- FORM 1 2023 END T3 CHEMISTRY QN - TEACHER - CO - .KE - SET - ADokumen9 halamanFORM 1 2023 END T3 CHEMISTRY QN - TEACHER - CO - .KE - SET - AYussuf HirowBelum ada peringkat
- CHEM PAPER 1 FORM 3 T3 2023 Kcse RevDokumen9 halamanCHEM PAPER 1 FORM 3 T3 2023 Kcse ReveastnetdigitalBelum ada peringkat
- End of Unit Test: Biology: PhotosynthesisDokumen6 halamanEnd of Unit Test: Biology: PhotosynthesisLovy Le ErBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Exam Revision 11TH April 2024Dokumen17 halamanChemistry Exam Revision 11TH April 2024gabrielsuva6Belum ada peringkat
- The Particulate Nature of Matter 3 QPDokumen10 halamanThe Particulate Nature of Matter 3 QPSajia EhsaniBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Extra Excercise Paper 2Dokumen16 halaman11 Extra Excercise Paper 2Norazla MustafaBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 5-Modul Bimbingan SPMDokumen11 halamanCHAPTER 5-Modul Bimbingan SPMNovah GurulooBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1Dokumen27 halamanChemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1ZekZanaBelum ada peringkat
- Making Molar Solutions: From LiquidsDokumen11 halamanMaking Molar Solutions: From Liquidsdanielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson 2 Igcse Chemistry Carbon CycleDokumen35 halamanLesson 2 Igcse Chemistry Carbon Cycledanielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- GCSE Exam QuestionsDokumen155 halamanGCSE Exam Questionsdanielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Rate of Reaction Part 1Dokumen19 halamanRate of Reaction Part 1danielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Igcse Topic 1 Lesson 1 Water Cycle IgcseDokumen25 halamanIgcse Topic 1 Lesson 1 Water Cycle Igcsedanielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Titration Practice QuestionsDokumen3 halamanIGCSE Titration Practice Questionsdanielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Rates & Energy NotesDokumen11 halamanRates & Energy Notesdanielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Igcse Structure Question 12Dokumen3 halamanIgcse Structure Question 12danielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Igcse Structure Question 13Dokumen2 halamanIgcse Structure Question 13danielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Redox ReactionsDokumen8 halamanRedox Reactionsdanielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Chemical Equilibria AS Level ChemistryDokumen4 halamanChemical Equilibria AS Level Chemistrydanielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Igcse Structure Question 11Dokumen2 halamanIgcse Structure Question 11danielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Good IGCSE Chemistry CIE Paper 6 Set 1Dokumen15 halamanGood IGCSE Chemistry CIE Paper 6 Set 1danielphilip680% (1)
- Igcse Structure Question 5Dokumen2 halamanIgcse Structure Question 5danielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Igcse Structure Question 9Dokumen2 halamanIgcse Structure Question 9danielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Igcse Structure Question 10Dokumen2 halamanIgcse Structure Question 10danielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Igcse Structure Question 8Dokumen2 halamanIgcse Structure Question 8danielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Igcse Structure Question 4: (A) Complete The Following TableDokumen2 halamanIgcse Structure Question 4: (A) Complete The Following Tabledanielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Igcse Structure Question 7Dokumen2 halamanIgcse Structure Question 7danielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Igcse Structure Question 3Dokumen2 halamanIgcse Structure Question 3danielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Good Igcse Cie Question 4Dokumen4 halamanGood Igcse Cie Question 4danielphilip68Belum ada peringkat
- Alternative To Practical Questions IGCSEset 1Dokumen15 halamanAlternative To Practical Questions IGCSEset 1danielphilip68100% (1)
- Alternative To Practical Questions IGCSEset 1Dokumen15 halamanAlternative To Practical Questions IGCSEset 1danielphilip68100% (1)
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 3 Atoms and MoleculesDokumen7 halamanCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 3 Atoms and Moleculespavan kasaBelum ada peringkat
- Poly Vinyl ChlorideDokumen2 halamanPoly Vinyl ChlorideGłfghh GhklBelum ada peringkat
- Notes - Thermodynamics of Polymer Solution and Solubility ParameterDokumen6 halamanNotes - Thermodynamics of Polymer Solution and Solubility Parameter79Jay ShethBelum ada peringkat
- A Review On Water Used in Pharma Industry: European Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical ResearchDokumen11 halamanA Review On Water Used in Pharma Industry: European Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical ResearchDinesh babuBelum ada peringkat
- Cascade Aerator: How It WorksDokumen29 halamanCascade Aerator: How It WorksMahaveer ChaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Acid BaseDokumen63 halamanAcid BaseFrian LiaBelum ada peringkat
- Acrylate and Polybutadiene Coages As Reactive PlasticizersDokumen11 halamanAcrylate and Polybutadiene Coages As Reactive PlasticizerstinyumchiBelum ada peringkat
- Food Chemistry Testing SUGAR, STARCH ETCDokumen5 halamanFood Chemistry Testing SUGAR, STARCH ETCrangerblue75% (12)
- Ferrite in Weld Metal PDFDokumen1 halamanFerrite in Weld Metal PDFhassan debianeBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 - Chemistry - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDokumen16 halamanUnit 3 - Chemistry - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inN S PatidarBelum ada peringkat
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis To Cosmetics: Katherine A. Biebl, BS, Erin M. Warshaw, MD, MSTDokumen18 halamanAllergic Contact Dermatitis To Cosmetics: Katherine A. Biebl, BS, Erin M. Warshaw, MD, MSTMARIA PATERNINABelum ada peringkat
- FINAL SMAW-12-Quarter-3-module 1 PDFDokumen22 halamanFINAL SMAW-12-Quarter-3-module 1 PDFRandy Sacatani100% (1)
- Inconel 690Dokumen8 halamanInconel 690Ronak shahBelum ada peringkat
- Endangered ElementsDokumen1 halamanEndangered ElementsAditya KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Specification For Low-Alloy Steel Electrodes and Rods For Gas Shielded Arc WeldingDokumen48 halamanSpecification For Low-Alloy Steel Electrodes and Rods For Gas Shielded Arc WeldingAnonymous SLI4aG100% (1)
- NC Block NaamsDokumen46 halamanNC Block NaamseldibujanteBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry Laboratory ManualDokumen27 halamanBiochemistry Laboratory ManualroyalBelum ada peringkat
- BiochemistryDokumen20 halamanBiochemistryRitesh SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Thermocouple CharacteristicsDokumen1 halamanThermocouple CharacteristicsRoberto_PrrBelum ada peringkat
- Acidchem Bulletin 300-6-0Dokumen1 halamanAcidchem Bulletin 300-6-0kanBelum ada peringkat
- Cat NGEC 50 - 50Dokumen2 halamanCat NGEC 50 - 50shamsalihu2729Belum ada peringkat
- E6 Isolation of GlycogenDokumen19 halamanE6 Isolation of GlycogenGlenn Vincent Tumimbang100% (1)
- Modern Pharmaceutics: Presented by M Pharm Pharmaceutics Department, Nargund College of PharmacyDokumen57 halamanModern Pharmaceutics: Presented by M Pharm Pharmaceutics Department, Nargund College of PharmacyBERNI ABEL CONDORI FLORESBelum ada peringkat
- Fluids and LubricantsDokumen2 halamanFluids and LubricantsHeywood JablowmeBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding The Revisions To USP Monograph : Residual SolventsDokumen4 halamanUnderstanding The Revisions To USP Monograph : Residual SolventsPhuc DVBelum ada peringkat
- BackStop - Sma09047Dokumen18 halamanBackStop - Sma09047Diego PalaciosBelum ada peringkat
- Coal PetrologyDokumen29 halamanCoal PetrologyIlham El-sirazhyBelum ada peringkat
- Manuf Lec Finals PDFDokumen35 halamanManuf Lec Finals PDFRaizane Sky PalecBelum ada peringkat
- 8 M Guanidine Hydrochloride SolutionDokumen2 halaman8 M Guanidine Hydrochloride SolutionWater ShurikenBelum ada peringkat
- Lipids Part 3Dokumen9 halamanLipids Part 3Anonymous 596wAK78eCBelum ada peringkat
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDari EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingDari EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (10)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDari EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Well Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsDari EverandWell Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodDari EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (20)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsDari EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (14)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolDari EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideDari EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Oxygen: The molecule that made the worldDari EverandOxygen: The molecule that made the worldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (108)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeDari EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (90)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeDari EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeBelum ada peringkat
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsDari EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (146)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsDari EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsBelum ada peringkat
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionDari EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- The Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugDari EverandThe Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsDari EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (10)
- Fundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionDari EverandFundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)