SAP SD: Essentials of Sales and Distribution Module
Diunggah oleh
soorya6969Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
SAP SD: Essentials of Sales and Distribution Module
Diunggah oleh
soorya6969Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
SAP: systems, applications and products in data processing.
client server technology highly customizable multi lingual (international) SAP SD (Sales and Distribution) is one the largest functional Module in SAP. It handles all the processes from an Order to delivery. The main operations this module handles are Customer Sales Orders processing, pricing, picking, packing, shipping, billing and risk management etc. Consultants gives professional advice and offers business improvement, transformation and organizational services to small and medium sized businesses, corporate and local authorities. Here is a list of roles and responsibilities of functional consultant during his assignment to different types of SAP Projects. The functional consultant has to understand the modules they are implementing and the set up and configuration options available, the key skill is being able to map the requirements of the customer to the capabilities of the ERP system. A mistake often made is to try and configure or customize the ERP system to match exactly an existing business process, rather than look to improve the processes."A functional consultant is expected to generate knowledge about the current business process, design current business flows, study current business processes and its complication - in all we can say that this is getting through with the current business setup. Flow diagrams and DFDs are prepared, all this forms the part of the AS IS document.""Everything configured has to be documented according to their categories in the form of predefined templates; these then have to be approved by the team leads or whoever the consultant is reporting to.""Mapping and GAP analysis is done for each module.""Before starting configuring future business processes in SAP, the DFDs/ERDs are prepared; this documentation is called TO BE, which can be also said as the result of mapping and gap analysis." "Sometimes Functional consultants are also expected to prepare test scripts for testing the configured scenarios. Testing may also include Unit testing, System Integration Testing, Performance Testing, User Acceptance Testing, Regression Testing or any client specific software testing."A configuration document showing all the setting done by the consultant is also comes under the area of role & responsibilities of consultant."End user manual and user training is also expected from Functional Consultants."There will also be interaction with other modules consultants. Updating project status to Project Manager & other concerned persons. Interaction with core team members, end users & other team members (consultants)A Functional consultant has to be a good communicator he has to communicate with Customer ERP core team, implementing team, Technical consultant and
his project leader. Written communication skill is to be demonstrated by a functional consultant to e-mail to different groups, documentation about the erp, reports generation. Verbal communication is to understand the requirement, interact with customer, to explain and convince the customer. SAP system comprises of a number of fully integrated modules, which covers virtually every aspect of the business. SAP R/3 conceptual areas: 1. Application area: initiate and execute SAP transactions. (Functional) 2. Basis area: the technical administration of the system (authorizations/ IDs/ etc) 3. Development area: a developers work bench (technical) SAP R/3 components: APPLICATION: master data, Transaction data ABAP PROGRAMES Configuration organization structure Key data elements Functionality configuration
Some SD module functionalities: inquiry processing, sales order processing, delivery processing, billing. Client: User: Every SAP user has a name. Users of SAP system are client specific, which means that having a user identification on one client will only allow access to that particular client. client is a numeric field This number defines a whole business entity.
TOOL BARS:
SESSIONS: An SAP session is a window in which the user may perform a particular task. A user may have up to six sessions open at a time. A sales org is responsible for: distribution of goods and services Negotiating sales conditions. Product liability and rights of recourse. A sales org is uniquely assigned to a company code. Masters datas are separately maintained for a sales organization. All items in the sales and distribution document belong to a sales org.
Distribution channel: means through which products and services reach t6he customer. A distribution channel: Defines responsibilities. Helps in achieve flexible pricing. Differentiate sales statistics
A division: A division is used to group products and services. A division represents a product line.
Sales area: a sales is area is a combination of Sales organization Distribution channel Division
Each sales and distribution document is assigned exactly to one sales area. A sales area can belong to only one company code.
Sales org Distribution channel
division sales area
Plant and storage location: A plant is a location where stock is maintained. Plant and storage locations are used by all logistics area of R/3 system. A plant is uniquely assigned to a company code.
Shipping point: Shipping point is the highest level of organizational unit in shipping. Each outbound delivery is processed by one shipping point. Shipping points are assigned to a plant. More than one shipping point can be assigned to a plant.
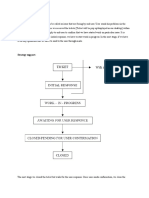
Sales and distribution in SD begins with establishment of customer relationship and ends with invoicing for the delivery of goods or service provide to the customer. A standard sales transaction has the following flow: Inquiry Quotation Order Delivery Billing The customer order management cycle begins with pre sales activities.
A standard order in SAP contains: Customer and material info Pricing conditions Delivery dates and quantities. Shipping info Billing info
Inventory sourcing in SAP is taken care by Availability check
Shipping in SAP supports: Outbound delivery creation Picking Packing Post goods issue
Billing in SAP supports: Creating invoices for products and services Creating credit and debit memo Cancel previously posted billing documents Automatically transferring billing documents to accounting.
When a billing document is created for sales order we Credit the sales revenue account Debit the customer receivables account
Sales document A sales document is grouped into three structures Header Item Schedule line
Outbound delivery: A delivery document is grouped into 2 structures Header Item
Several orders can be grouped into same outbound delivery if they have same Shipping point Delivery date Ship to address
Picking: A transfer order is created for an outbound delivery A transfer order is created for a warehouse number.
Post goods issue: When PGI done in the system, Billing: We can group deliveries into single billing document if the deliveries have same Billing date Payer Destination country Update the quantity in inventory management and delivery requirements in materials planning Generates additional documents for accounting Adds the delivery to the billing due list Updates status in sales document.
The effects of billing are Debit on the customer receivables account credit on sales revenue account is created Sales information system Sales statistics is updated.
Master data in SAP: SAP SD has got the following main masters Customer master Material master Condition master Output master Customer material information master
Plant determination in sales and distribution: To determine the plant in an order the system checks the master in the following order a) Customer material info, record of the sold to party b) Customer master record of the ship to part. c) Material master record of the material Shipping point determination: The following rule is used in determining shipping point in a sales order: Plant+ shipping condition (sold to party) + loading group shipping point
Maintained in material master general: plant data Route determination Route determined using the following rule in sales and distribution (SAP)
Departure zone of shipping point + Shipping condition (sold to party) + Transportation group (material master) + Transportation zone (ship to party)
ROUTE Delivery scheduling: Deliver scheduling is, scheduling delivery for an order and it carries the following important dates Material availability date Transportation planning date Loading date Goods issue date Delivery date
Availability Check in SAP: Availability check is carried out at item level for a plant. Availability check is done on the material availability date If material availability date is in the past the forward scheduling is done, if not backward scheduling is done.
Item category in a sales document mainly controls the following: Relevance for billing of an item Billing block pricing relevance business data relevance item schedule line allowed item relevant for delivery returns determine cost credit active incompletion procedure structure scope value contract material contract release control
Schedule line category mainly controls: delivery block movement type item relevant for delivery Request/assembly Availability
Product allocation
Copy Control: Copy control is normally set for Header Item Schedule line levels
To control copying procedure we have Data transfer routines Copying requirements switches
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Smith Generator BlueprintsDokumen36 halamanThe Smith Generator BlueprintsZoran AleksicBelum ada peringkat
- U2 All That You Can't Leave BehindDokumen82 halamanU2 All That You Can't Leave BehindFranck UrsiniBelum ada peringkat
- 2010 HD Part Cat. LBBDokumen466 halaman2010 HD Part Cat. LBBBuddy ButlerBelum ada peringkat
- Deloitte Managed Analytics (DMA) Application CatalogDokumen33 halamanDeloitte Managed Analytics (DMA) Application CatalogDeloitte Analytics100% (3)
- All Determinations Sap SDDokumen1 halamanAll Determinations Sap SDsoorya6969100% (1)
- O2C Cycle PresentationDokumen82 halamanO2C Cycle PresentationRBelum ada peringkat
- Cap Gemini Sap SD Interview QnsDokumen6 halamanCap Gemini Sap SD Interview Qnssoorya6969100% (3)
- SAP SD Interview Questions and AnswersDokumen23 halamanSAP SD Interview Questions and Answerskanhaiya_priyadarshi100% (1)
- Sap SD Interview QuestionsDokumen0 halamanSap SD Interview QuestionsSA130974Belum ada peringkat
- SAP Order To Cash Business ProcessDokumen75 halamanSAP Order To Cash Business Processrk_solomon100% (2)
- SAP PR Release Strategy Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyDari EverandSAP PR Release Strategy Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- IELTS Speaking Q&ADokumen17 halamanIELTS Speaking Q&ABDApp Star100% (1)
- MM Scope Document by Mansoor Ali SeelroDokumen10 halamanMM Scope Document by Mansoor Ali SeelroAL-HAMD GROUP100% (5)
- SD ScenariosDokumen150 halamanSD Scenariossoorya696988% (8)
- Business Blueprint Best PracticeaDokumen6 halamanBusiness Blueprint Best PracticeadbedadaBelum ada peringkat
- SAP FICO Basic SettingsDokumen43 halamanSAP FICO Basic SettingsAPBelum ada peringkat
- Role of A MySAP Functional ConsultantDokumen7 halamanRole of A MySAP Functional Consultantdhirajsatyam98982285Belum ada peringkat
- Logistics Management System Complete DocumentationDokumen99 halamanLogistics Management System Complete DocumentationDrapeeto33% (9)
- Basic Rules in SAP SD ModuleDokumen14 halamanBasic Rules in SAP SD Modulesoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- Sales and Distribution (SD)Dokumen12 halamanSales and Distribution (SD)talha2kkBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing Product TourDokumen40 halamanManufacturing Product Toureresource_1234Belum ada peringkat
- Shipping Point Determination in SAP: Standard Output Types in SDDokumen2 halamanShipping Point Determination in SAP: Standard Output Types in SDsoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- Fit-Gap Analysis - OverviewDokumen8 halamanFit-Gap Analysis - Overviewsoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- Short SAP SD Questions 1Dokumen36 halamanShort SAP SD Questions 1srilekha02Belum ada peringkat
- Basic Rules in SD ConfigurationDokumen14 halamanBasic Rules in SD ConfigurationDeepak Sangramsingh100% (1)
- SAP Sales & Distribution in ActionDokumen5 halamanSAP Sales & Distribution in Actionboss100% (1)
- Business Blueprint RequirementsDokumen6 halamanBusiness Blueprint Requirementsmehedi_orchidBelum ada peringkat
- Sap TablesDokumen29 halamanSap Tableslucaslu100% (14)
- SAP DocumentationDokumen23 halamanSAP DocumentationRamanjiReddy AlavalaBelum ada peringkat
- SAP ECC FI Transaction Codes: Unofficial Certification and Review GuideDari EverandSAP ECC FI Transaction Codes: Unofficial Certification and Review GuidePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Dell Compellent Sc4020 Deploy GuideDokumen184 halamanDell Compellent Sc4020 Deploy Guidetar_py100% (1)
- SAP Implementation DocumentDokumen8 halamanSAP Implementation Documentdeepankar senguptaBelum ada peringkat
- Uniform-Section Disk Spring AnalysisDokumen10 halamanUniform-Section Disk Spring Analysischristos032Belum ada peringkat
- Introducing SAP R/3 Sales and Distribution ModuleDokumen240 halamanIntroducing SAP R/3 Sales and Distribution ModulebjblackBelum ada peringkat
- SD0001 Overview of Sales & Distribution ModuleDokumen70 halamanSD0001 Overview of Sales & Distribution ModuleSmiti SinghBelum ada peringkat
- SD PresentationDokumen43 halamanSD Presentationesameer7837Belum ada peringkat
- Objective: SAP (SD) ConsultantDokumen5 halamanObjective: SAP (SD) ConsultantBiswajit SahooBelum ada peringkat
- Sap SD TopicsDokumen6 halamanSap SD Topicssoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- SAAAAAPDokumen2 halamanSAAAAAPCharity VenusBelum ada peringkat
- Audi Q5: First Generation (Typ 8R 2008-2017)Dokumen19 halamanAudi Q5: First Generation (Typ 8R 2008-2017)roberto100% (1)
- MD04 Problems With Sales OrdersDokumen2 halamanMD04 Problems With Sales Orderssoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- The Official Supply Chain Dictionary: 8000 Researched Definitions for Industry Best-Practice GloballyDari EverandThe Official Supply Chain Dictionary: 8000 Researched Definitions for Industry Best-Practice GloballyPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (4)
- Flexible Regression and Smoothing - Using GAMLSS in RDokumen572 halamanFlexible Regression and Smoothing - Using GAMLSS in RDavid50% (2)
- Standard Sales Cycle: Inquiry Quotation Order Delivery BillingDokumen3 halamanStandard Sales Cycle: Inquiry Quotation Order Delivery Billingsoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- Standard Sales Cycle: Inquiry Quotation Order Delivery BillingDokumen3 halamanStandard Sales Cycle: Inquiry Quotation Order Delivery Billingsoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- Sap Questions1Dokumen13 halamanSap Questions1happy1558Belum ada peringkat
- Enterprise Structure: AvinashDokumen37 halamanEnterprise Structure: AvinashmohitBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Rules in SD Configuration - ERP Operations - SCN WikiDokumen7 halamanBasic Rules in SD Configuration - ERP Operations - SCN Wikisalmanak18Belum ada peringkat
- Configuring SAP: Enterprise Wide Information SystemsDokumen43 halamanConfiguring SAP: Enterprise Wide Information Systemsash14arsBelum ada peringkat
- Group 1 Enumeration: Multiple ChoiceDokumen18 halamanGroup 1 Enumeration: Multiple ChoiceRanin, Manilac Melissa SBelum ada peringkat
- SAP Americas: Leading Provider of Enterprise Software SolutionsDokumen247 halamanSAP Americas: Leading Provider of Enterprise Software SolutionsernestomacipBelum ada peringkat
- Concept of ATP in Standard Sales OrdersDokumen28 halamanConcept of ATP in Standard Sales OrdersSandip SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Configuring SAP: Enterprise Wide Information SystemsDokumen43 halamanConfiguring SAP: Enterprise Wide Information Systemsyashkr2010Belum ada peringkat
- SAP SD Process FlowDokumen8 halamanSAP SD Process FlowSobuj SapBelum ada peringkat
- ERP Module Overview and Implementation MethodologyDokumen19 halamanERP Module Overview and Implementation MethodologySoumyajit PathakBelum ada peringkat
- Sales Order Process in 40 CharactersDokumen28 halamanSales Order Process in 40 CharactersVeena PindiBelum ada peringkat
- PepsiDokumen9 halamanPepsifaizaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Week: 5 Chapter 6: Technology Concepts: Tutorial: Bap 71 Ais Discussion Questions & ProblemDokumen5 halamanLecture Week: 5 Chapter 6: Technology Concepts: Tutorial: Bap 71 Ais Discussion Questions & ProblemOdria ArshianaBelum ada peringkat
- LO Extraction - Part 1 - SD Application Short OverviewDokumen14 halamanLO Extraction - Part 1 - SD Application Short OverviewVijay ChandraBelum ada peringkat
- KT Review PresentationDokumen23 halamanKT Review PresentationfonakBelum ada peringkat
- Sap SD Sap ErpDokumen2 halamanSap SD Sap ErpAnjan KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation By, J.Pracitha S.Radhika V.Sivaranjani B.VasupradhaDokumen80 halamanPresentation By, J.Pracitha S.Radhika V.Sivaranjani B.VasupradhavrekhavasuBelum ada peringkat
- SAP SD Interview Questions AllDokumen7 halamanSAP SD Interview Questions Allashok SapsdBelum ada peringkat
- MGT 1272 Management Information System Mid-Term NotesDokumen10 halamanMGT 1272 Management Information System Mid-Term NotesYvonne ChenBelum ada peringkat
- SAP & BlockchainDokumen9 halamanSAP & Blockchainanshumankumar10Belum ada peringkat
- E BillingDokumen10 halamanE BillingGokul KrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- Q1: SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) Is Commercial Software That WillDokumen8 halamanQ1: SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) Is Commercial Software That Willusmanehsan03Belum ada peringkat
- SAP Business Objects Administrative Report - BlueprintDokumen24 halamanSAP Business Objects Administrative Report - BlueprintVo Dinh HuyBelum ada peringkat
- SAP SD Sample ResumesDokumen4 halamanSAP SD Sample ResumesNuthan ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Interview Ques Ans - Sap SD CG 2023Dokumen8 halamanInterview Ques Ans - Sap SD CG 2023DZ CreativesBelum ada peringkat
- SAP SD Business Blueprint for Pharmaceutical Sales ProcessesDokumen16 halamanSAP SD Business Blueprint for Pharmaceutical Sales ProcessesVenkata SatyasubrahmanyamBelum ada peringkat
- Integration of SD and HRDokumen7 halamanIntegration of SD and HRchandutatiBelum ada peringkat
- SAP SD Interview QuestionsDokumen10 halamanSAP SD Interview QuestionsPrasad BudhwaniBelum ada peringkat
- SD Interview Questions and Answers: sap sd interview questions with answersDokumen20 halamanSD Interview Questions and Answers: sap sd interview questions with answersLokesh DoraBelum ada peringkat
- ConfigDokumen6 halamanConfigsoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- Item Categories: Rush Order (SO) : The Customer Picks Up The Goods or You Deliver The Goods On The SameDokumen1 halamanItem Categories: Rush Order (SO) : The Customer Picks Up The Goods or You Deliver The Goods On The Samesoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- Responsibilities and RolesDokumen6 halamanResponsibilities and Rolessoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- Qasd 121120124425 Phpapp02Dokumen5 halamanQasd 121120124425 Phpapp02soorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- SD TermsDokumen2 halamanSD Termssoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- Functions and Activities Fall UnderDokumen2 halamanFunctions and Activities Fall Undersoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- Sap SD PPT-1Dokumen47 halamanSap SD PPT-1vijaykumarBelum ada peringkat
- Sap SD TerminologyDokumen7 halamanSap SD Terminologysoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- Terminology & BasicsDokumen3 halamanTerminology & Basicssoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- Sap BasicDokumen5 halamanSap Basicsoorya6969Belum ada peringkat
- Ielts Practice Tests: ListeningDokumen19 halamanIelts Practice Tests: ListeningKadek Santiari DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Link Ratio MethodDokumen18 halamanLink Ratio MethodLuis ChioBelum ada peringkat
- Chromate Free CoatingsDokumen16 halamanChromate Free CoatingsbaanaadiBelum ada peringkat
- Physioex 9.0 Exercise 1 Act 1Dokumen5 halamanPhysioex 9.0 Exercise 1 Act 1Adela LhuzBelum ada peringkat
- List of Reactive Chemicals - Guardian Environmental TechnologiesDokumen69 halamanList of Reactive Chemicals - Guardian Environmental TechnologiesGuardian Environmental TechnologiesBelum ada peringkat
- Beauty ProductDokumen12 halamanBeauty ProductSrishti SoniBelum ada peringkat
- Shouldice Hospital Ltd.Dokumen5 halamanShouldice Hospital Ltd.Martín Gómez CortésBelum ada peringkat
- Hi-Line Sportsmen Banquet Is February 23rd: A Chip Off The Ol' Puck!Dokumen8 halamanHi-Line Sportsmen Banquet Is February 23rd: A Chip Off The Ol' Puck!BS Central, Inc. "The Buzz"Belum ada peringkat
- Excess AirDokumen10 halamanExcess AirjkaunoBelum ada peringkat
- SOP-for RecallDokumen3 halamanSOP-for RecallNilove PervezBelum ada peringkat
- AtlasConcorde NashDokumen35 halamanAtlasConcorde NashMadalinaBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar Course Report ON Food SafetyDokumen25 halamanSeminar Course Report ON Food SafetyYanBelum ada peringkat
- Process Financial Transactions and Extract Interim Reports - 025735Dokumen37 halamanProcess Financial Transactions and Extract Interim Reports - 025735l2557206Belum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1 Discussion Document - Batch 03Dokumen4 halamanTutorial 1 Discussion Document - Batch 03Anindya CostaBelum ada peringkat
- Indian Standard: Pla Ing and Design of Drainage IN Irrigation Projects - GuidelinesDokumen7 halamanIndian Standard: Pla Ing and Design of Drainage IN Irrigation Projects - GuidelinesGolak PattanaikBelum ada peringkat
- Kalley Ltdn40k221twam Chassis msd6308 SM PDFDokumen49 halamanKalley Ltdn40k221twam Chassis msd6308 SM PDFjulio cesar calveteBelum ada peringkat
- Guia de Usuario GPS Spectra SP80 PDFDokumen118 halamanGuia de Usuario GPS Spectra SP80 PDFAlbrichs BennettBelum ada peringkat
- AD Chemicals - Freeze-Flash PointDokumen4 halamanAD Chemicals - Freeze-Flash Pointyb3yonnayBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Features of The Microcredit Regulatory Authority Act, 2006Dokumen10 halamanBasic Features of The Microcredit Regulatory Authority Act, 2006Asif Hasan DhimanBelum ada peringkat
- Busbar sizing recommendations for Masterpact circuit breakersDokumen1 halamanBusbar sizing recommendations for Masterpact circuit breakersVikram SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Differential Pulse Code ModulationDokumen12 halamanDifferential Pulse Code ModulationNarasimhareddy MmkBelum ada peringkat
- Srimanta Sankaradeva Universityof Health SciencesDokumen3 halamanSrimanta Sankaradeva Universityof Health SciencesTemple RunBelum ada peringkat